Bio Chapter 1 Test
1/92
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
mass number
the sum of the protons and neutrons
isotope
atoms that contain more neutrons than protons
-to determine the ages of rocks and fossils
-treat cancer
-kill bacteria that causes food to spoil
-covalent
-Ionic
Electronegativity
an atom’s ability to attract electrons
What affects electronegativity?
atomic weight and it’s distance from the nucleus
If the difference in electronegativity is >1.67 then…
the bond is ionic
If the difference in electronegativity is <1.67 then…
the bond is covalent
Hydrogen bonds
hydrogen bonded to a highly electronegative element
Cohesion
attraction between elements of the same substance
Surface tension
attraction between molecules of a liquid on the surface that act as a sheet
Adhesion
water attached to something else
capillary action
when surface tension pulls water up through narrow tubes(ex: plant stems)
Solvent
Dissolving agent
Solute
substance being dissolved
Solute+Solvent
Solution
H+
Hydrogen ion
OH-
Hydroxide ion
What does pH measure?
the number of Hydrogen ions
pH <7
acidic(more Hydrogen than Hydroxide)
pH >7
basic/alkaline(more Hydroxide than Hydrogen)
buffer
a weak acid or base that controls your body’s pH(homeostasis)
Organic Chem
study of all compounds w/ Carbon bonds
How many electrons does Carbon want?
4
Carbon chains
almost unbreakable links between carbon atoms
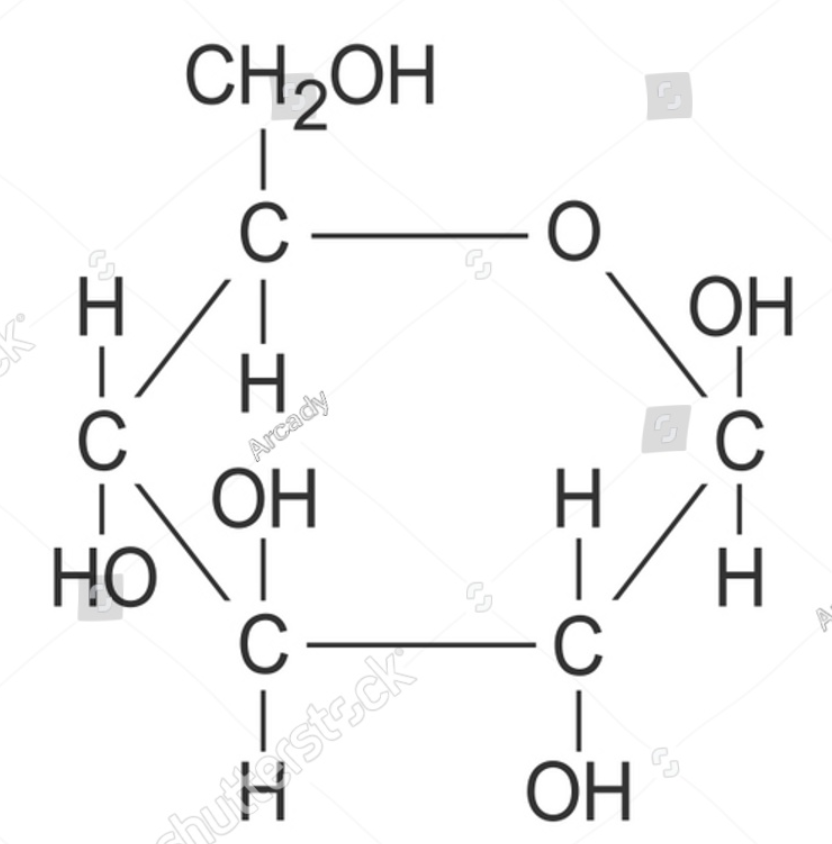
Be able to draw glucose
Macromolecule
a super large molecule
Monomers
the smallest unit in macromolecules; make up polymers
How are macromolecules formed?
condensation and dehydration reactions
What are the four types of macromolecules?
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic acids
What are carbs made of?
Monosaccharides(a type of monomer)
How are carbs used?
as an energy source
-ose means…
monosaccharides(sugar)
3+ monosaccharides is…
polysaccharide
Excess sugar in animals
Glycogen
Excess sugar in plants
starch
Do lipids have monomers?
No
What are the types of lipids?
Fats
Steroids
Waxes
Oils
Phospholipids
What is a lipid’s main function?
Store energy
Form cell membranes
Protect against H2O loss
Hydroxyl
OH (Not OH-)
Fats
made of glycerol and fatty acids
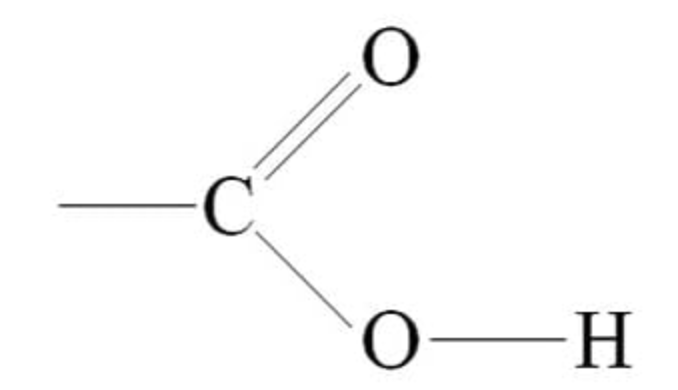
Be able to draw a functional Carboxyl group
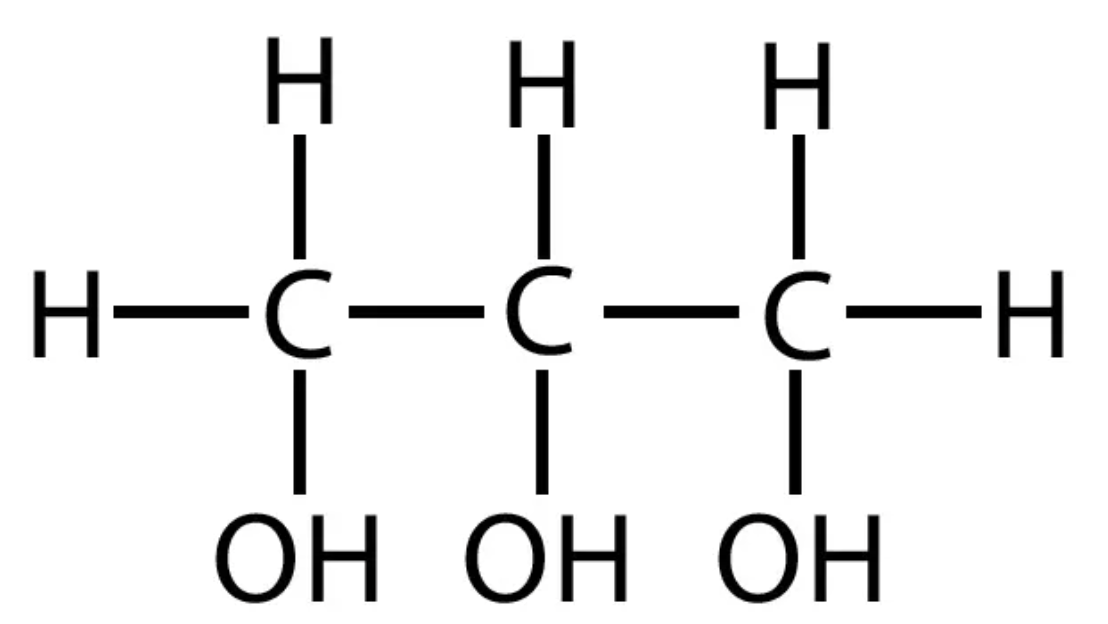
Be able to draw Glycerol
Saturated fats
All C bonded to a H and/or a functional group
Unsaturated fat
C linked with double bonds
Unsaturated fat does what to a molecule?
Makes a kink
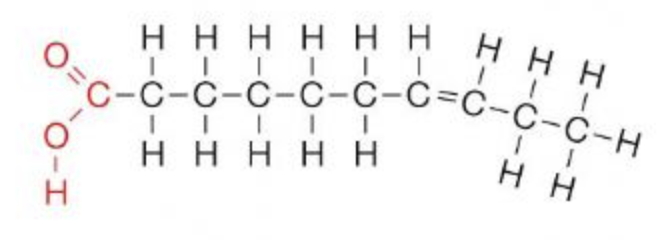
Where can you find unsaturated fats?
Plant and fish oils(liquid)
Nucleic acid
DNA and RNA
Be able to draw a nucleotide
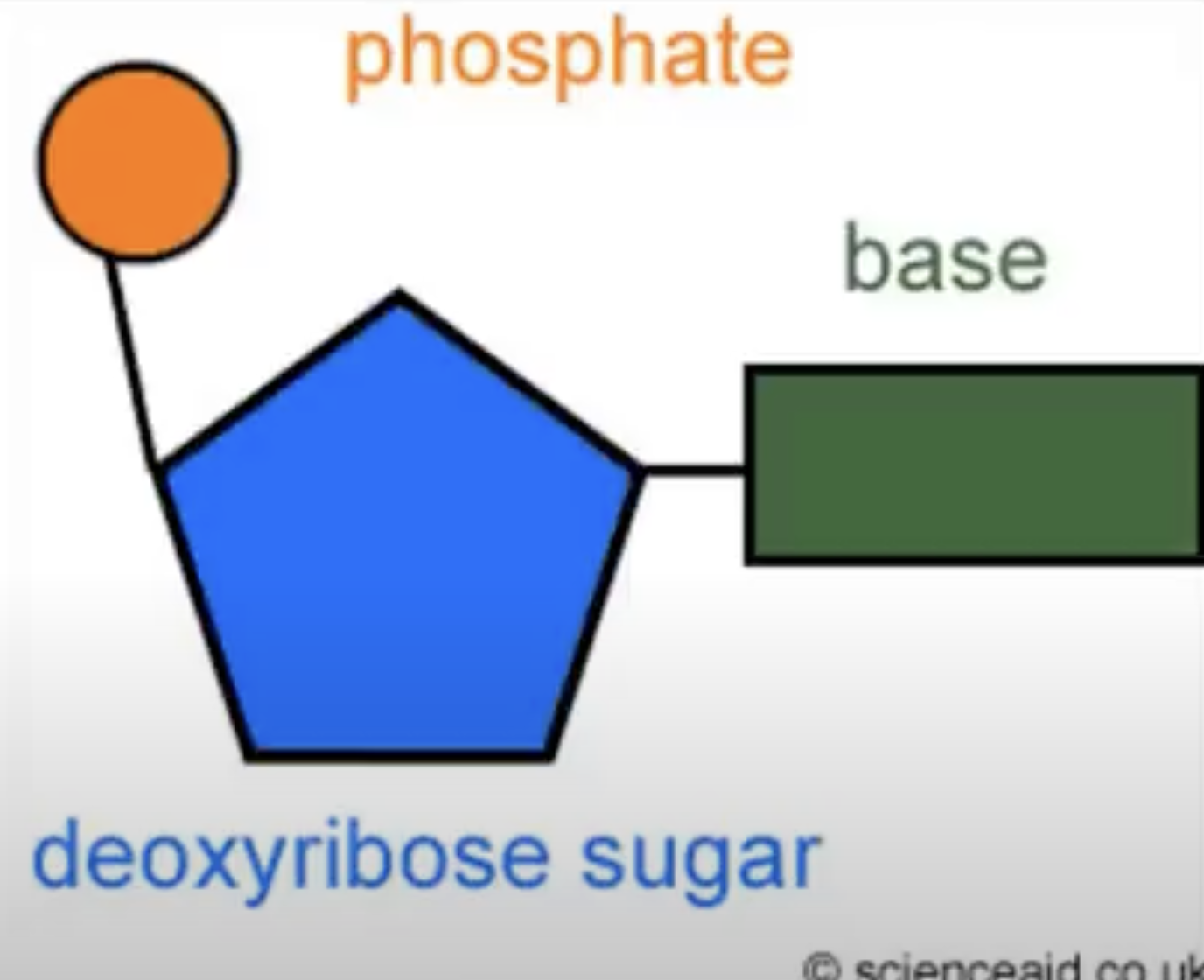
What are the two types of nucleic acids?
DNA(2 strands)
RNA(1 strand)
Proteins are…
polymers made of amino acids
Amino acids make up what?
Protiens
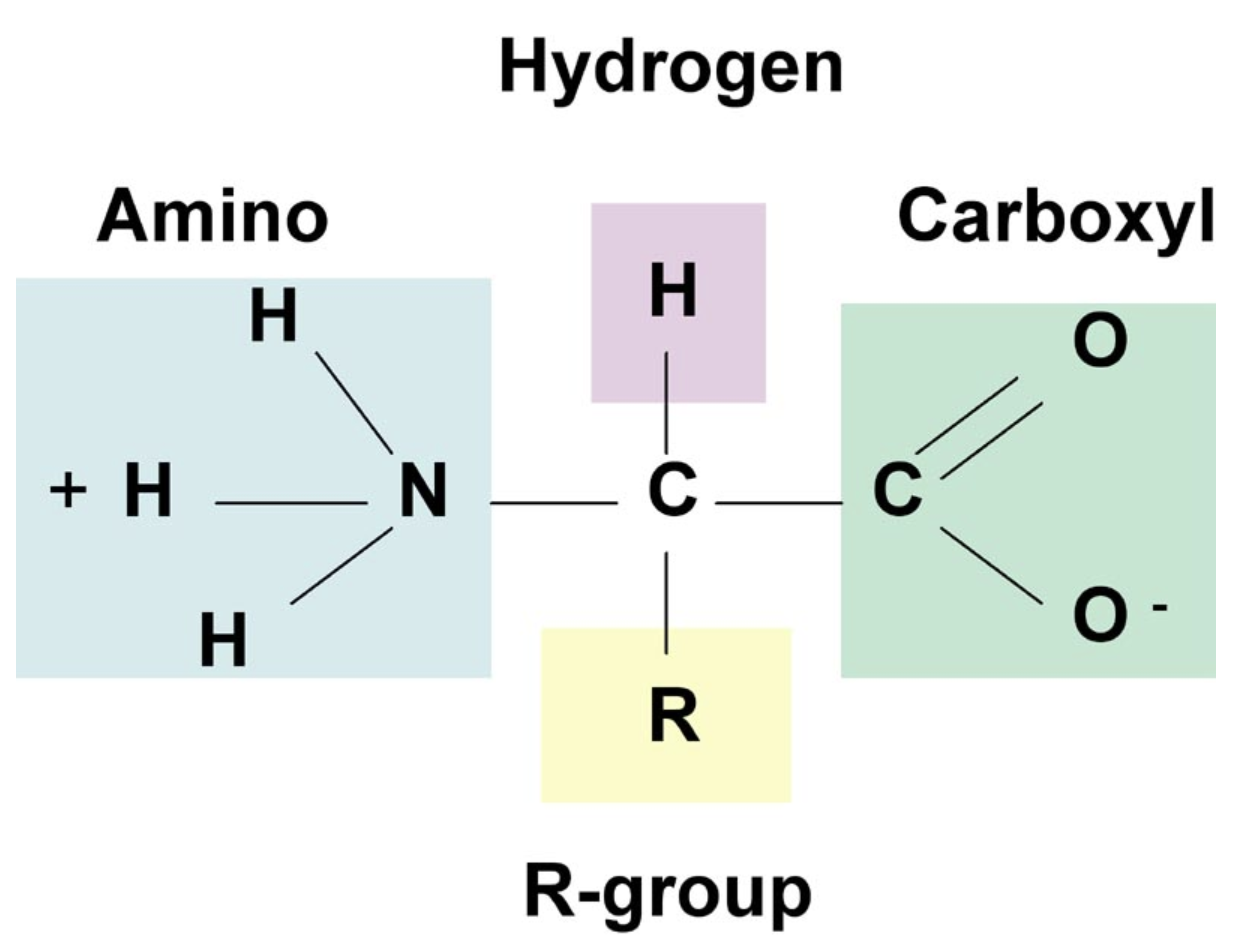
R-group
What makes each amnio acid different
What is the function of proteins?
Transport, structural support, movement(muscles), cellular communication, and defend against foreign substances
Plants and animals need to do what to stay alive?
carry out chemical reactions
Chemical reaction
a process during which chemical bonds are broken or created
reactant
starting materials
reactants become…
products
Reactions that are too slow need what?
a catalyst
Catalyst
speeds up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy
activation energy
the energy needed to start a reaction
Enzyme
a protein and catalyst
Enzymes work with different types of chemical reaction(T/F)
False
substrate
the reactant an enzyme works on
What 2 things are bonded until converted into products?
Enzymes and substrates
What affects an enzyme?
pH, salinity, and temp(makes proteins unravel)
Be able to draw an amino acid
Be able to draw a nucleotide