MACRO - Protectionism
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
Protectionism
Government impose trade barriers on international trade (USA) to limit imports & protect domestic production.
Reasons for protectionism
Protect domestic producers
Improve BOP
Earn government revenue
Protect infant (sectors that have just started) & sunset (sectors that have matured) industries
Prevent goods w/ negative externalities being imported (cigarettes)
Strategy to retaliate - When a country impose barriers on another’s products, they retaliate through protectionism
Prevent dumping
Arguments against protectionism
Limits consumer choice
Higher prices - import inflation
May result in domestic monopoly —> less foreign competition - less firms in market - market power increases - domestic monopolies
Retaliation - if a country restricts imports - other countries act like spoiled rich kids and become petty
Protectionism policies
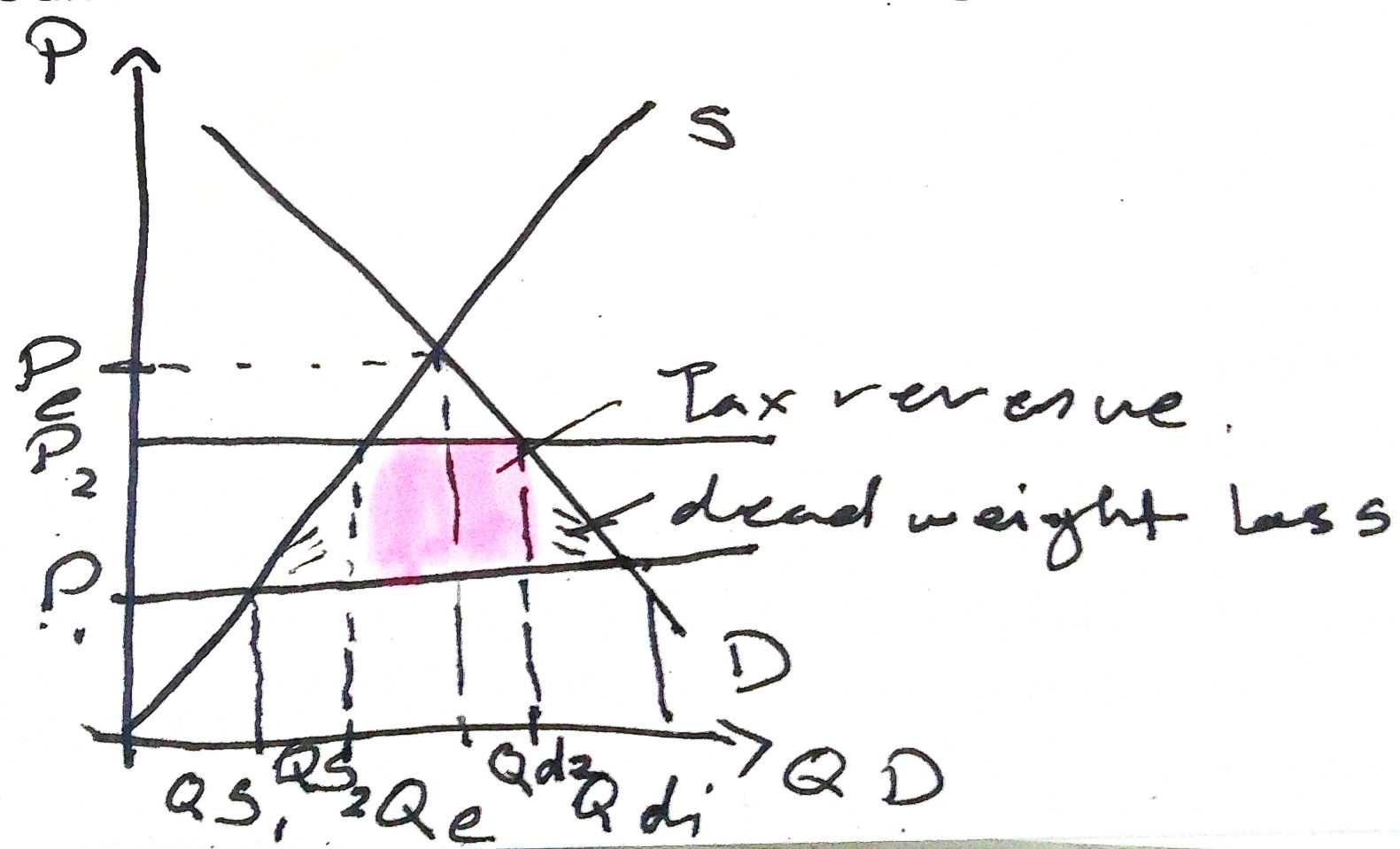
Tariffs - Tax on imports
Makes goods relatively expensive
However, if demand is inelastic people will still buy at higher prices (essential goods - petrol) - import inflation
Quotas - Physical limit on imports
Consumers would therefore, purchase locally
However, effectiveness depends on size of quota & governments assurance illegal purchases don’t happen.
Subsidies to local firms
Admin barriers - Rules & regulations set of importing goods to make it harder for foreign goods to enter the country
Voluntary export restrictions - Importing country requests exporting country to limit their export to said country
Devaluation of currency - imports more expensive - less demand - less imports
Sanctions (penalties/restrictions placed on a country) & embargos (complete ban on trade with a particular country)