ppharm lab
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
Solubility
What is defined as the concentration of solute in a saturated solution at a certain temperature?
Solubility
What is the spontaneous interaction of two or more substances to form a homogeneous molecular dispersion called?
Nature of solute and solvent
What factor affecting solubility follows the rule “like dissolves like”?
Nature of solute and solvent
polar solutes dissolve in polar solvents and nonpolar
solutes dissolve in nonpolar solvents; “like dissolves like”
polar solvents
Nature of solute and solvent- polar solutes dissolve in _ and nonpolar solutes dissolve in nonpolar solvents; “like dissolves like”
nonpolar solvents
Nature of solute and solvent- polar solutes dissolve in polar solvents and nonpolar solutes dissolve in _; “like dissolves like”
Temperature
higher temperature = greater solubility (solids); solubility of gases decreases with higher temperature
higher
Temperature- _ temperature = greater solubility (solids); solubility of gases decreases with higher temperature
greater
Temperature- higher temperature = _ solubility (solids); solubility of gases decreases with higher temperature
higher
Temperature- higher temperature = greater solubility (solids); solubility of gases decreases with _ temperature
Temperature
What factor affecting solubility states that higher temperature increases solubility of solids but decreases solubility of gases?
Particle size of solute
finer the solute = greater the surface area= more rapid the
dissolving process
finer
Particle size of solute- _ the solute = greater the surface area= more rapid the dissolving process
greater
Particle size of solute- finer the solute = _the surface area= more rapid the dissolving process
rapid
Particle size of solute- finer the solute = greater the surface area= more _ the dissolving process
Particle size of solute
What factor affecting solubility states that finer solute particles dissolve faster due to greater surface area?
Physical agitation
greater the agitation= more unsaturated= more faster the formation
of the solution
greater
Physical agitation- _ the agitation= more unsaturated= more faster the formation of the solution
unsaturated
Physical agitation- greater the agitation= more _= more faster the formation of the solution
faster
Physical agitation- greater the agitation= more unsaturated= more _ the formation of the solution
pH of solvent
ionized drugs dissolve better; unionized forms are less soluble
ionized
pH of solvent- _ drugs dissolve better; unionized forms are less soluble
unionized
pH of solvent- ionized drugs dissolve better; _ forms are less soluble
Pressure
Higher pressure increases the solubility of gases in liquids
Physical agitation
What factor affecting solubility involves stirring or shaking to speed up the dissolving process?
pH of solvent
What factor affecting solubility involves ionization, where ionized drugs dissolve better than unionized forms?
Pressure
What factor affecting solubility is described by Henry’s law, where higher pressure increases gas solubility in liquids?
Co-solvents
What factor affecting solubility involves using substances like ethanol or propylene glycol to enhance solubility?
Complexing agents
What factor affecting solubility involves agents like cyclodextrins or chelators that form complexes to improve solubility?
Polymorphism/Crystalline forms
What factor affecting solubility states that amorphous forms are more soluble than crystalline forms?
Common ion effect
What factor affecting solubility states that the presence of a common ion reduces the solubility of a salt?
Henry’s law
the
solubility of a gas is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas above the liquid
Co-solvents
Substances like ethanol or propylene glycol enhance solubility
Complexing agents
Cyclodextrins or chelators improve solubility by forming complexes
Polymorphism/ Crystalline forms
Amorphous forms are more soluble than
crystalline ones
Common ion effect
The presence of a common ion suppresses the solubility of the
salt
Osmosis
What is the diffusion or movement of solvent molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from a region of higher solvent concentration to a region of lower solvent concentration?
Osmotic pressure
What is the pressure responsible for osmosis and its prevention?
TONICITY
is a measure of the osmotic pressure of two solutions
separated by a semi-permeable membrane.
higher solvent concentration
to a region of lower solvent concentration
movement of conc in osmosis
ISOTONIC SOLUTION
Solution that has the same osmotic
pressure as the body fluid or 0.9% NaCl
HYPOTONIC SOLUTION (0.5%)
Solution that has lower osmotic pressure
than the body fluid or 0.9% NaCl
HYPERTONIC SOLUTION (1.0%)
Solution that has a higher osmotic pressure
than the body fluid or 0.9% NaCl
isotonic soln
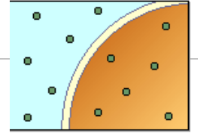
hypotonic soln
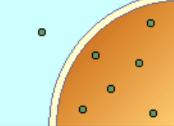
hypertonic soln
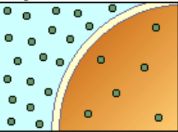
hypotonic soln
Causes swelling and
bursting of RBC
isotonic soln
No changes in RBC size
hypertonic soln
Causes crenation and
shrinkage of RBC
hypotonic soln
isotonic soln
hypertonic soln
Blood, eye, nasal tract, and other body fluids
With what body fluids or areas are isotonic solutions commonly used?
No swelling, no contraction, no discomfort
What happens to tissues when they come in contact with isotonic solutions?
Class 1
Addition of NaCl
Class 2
Addition of Water
Class I- Addition of NaCl
A. Sodium Chloride Equivalent
B. Cryoscopic Method
C. Freezing Point Depression
Class II- Addition of Water
A. Sprout’s Method
B. White Vincent Method
The number of particles of solute in solution
What does the osmotic pressure of an electrolyte depend on in relation to solute particles?
i
What is the symbol for the dissociation factor used in calculating osmotic pressure?
By dividing the total number of particles (undissociated molecules + ions) in a solution by the number of particles before dissociation
How is the dissociation factor (i) calculated?
Sodium chloride equivalent (E)
What is defined as the weight of sodium chloride that will produce the same osmotic effect as 1g of a drug?
Water movement in and out of the cell is the same, and RBCs remain unchanged
What happens to red blood cells in an isotonic solution?
RBCs swell and burst
What happens to red blood cells in an iso-osmotic solution?
Viscosity (n) “ eta”
◦Internal friction or resistance of fluid to flow
resistance
Viscosity (n) “ eta” - Increase viscosity = increase _
Viscosity (n) “ eta”
◦Increase viscosity = increase resistance
viscosity
Viscosity (n) “ eta” - Increase _ = increase resistance
Resistance to flow increases.
What happens to flow when viscosity increases?
dyn·s/cm², poise, or g/(cm·s)
What are the units of viscosity?
Viscosity (n) “ eta” units
Units: dynes x sec/ cm2
, poise, g/ cm x sec
n
shear stress/ rate of shear
n= shear stress/ rate of shear
What is the formula for viscosity?
Shear Stress (t) “tau”
It is a measure of the force of friction from a fluid acting on a body in the path of that fluid.
Shear rate
It is the rate of change of velocity at which one layer of fluid
passes over an adjacent layer
rate if shear
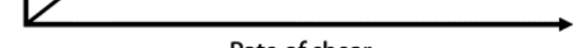
shear stress
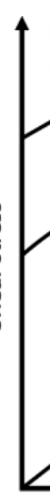
viscosity
factor affecting _ determination:
temperature = increasing temp - decreasing viscosity (inverse)
temperature
factor affecting viscosity determination:
_ = increasing temp - decreasing viscosity (inverse)
increasing
factor affecting viscosity determination:
temperature = _ temp - decreasing viscosity (inverse)
decreasing
factor affecting viscosity determination:
temperature = increasing temp - _ viscosity (inverse)
inverse
factor affecting viscosity determination:
temperature = increasing temp - decreasing viscosity (_)
Rheology
a branch of physics that deals with the deformation & flow
of matter
Newtonian flow
Non-Newtonian flow
Classification of Material according to type of flow: 2
Newtonian flow
Follows the Newtonian law of direct proportionality between shearing stress & rate of shear
Newtonian flow
Characterized by a constant viscosity regardless of the shear stress applied
Newtonian flow
castor oil
Newtonian flow
chloroform
Newtonian flow
ethanol
Newtonian flow
water
Newtonian flow
olive oil
Non-Newtonian flow
characterized by the change in viscosity
with increasing rate of shear
Plastic flow or Bingham body
Pseudoplastic flow
Dilatant flow
Classification of Non-Newtonian material 3
Plastic flow or Bingham body
Yield value/ yield stress must be applied to cause them flow
Plastic flow or Bingham body
Behavior: plasticity
Plastic flow or Bingham body
Characteristics: flocculated particles in concentration by suspension
Plastic flow or Bingham body
cerates
Plastic flow or Bingham body
cataplasm
Plastic flow or Bingham body
cream
Plastic flow or Bingham body
ointment