PAS 407 - (Exam 2) Anteromedial Thigh
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
quadriceps femoris mm.
sartorius m.
iliopsoas m.
pectineus m.
which muscles make up the anterior compartment of the leg?
femoral n.
femoral/profunda femora a.
neurovascular supply of the muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg
anterior inferior iliac spine
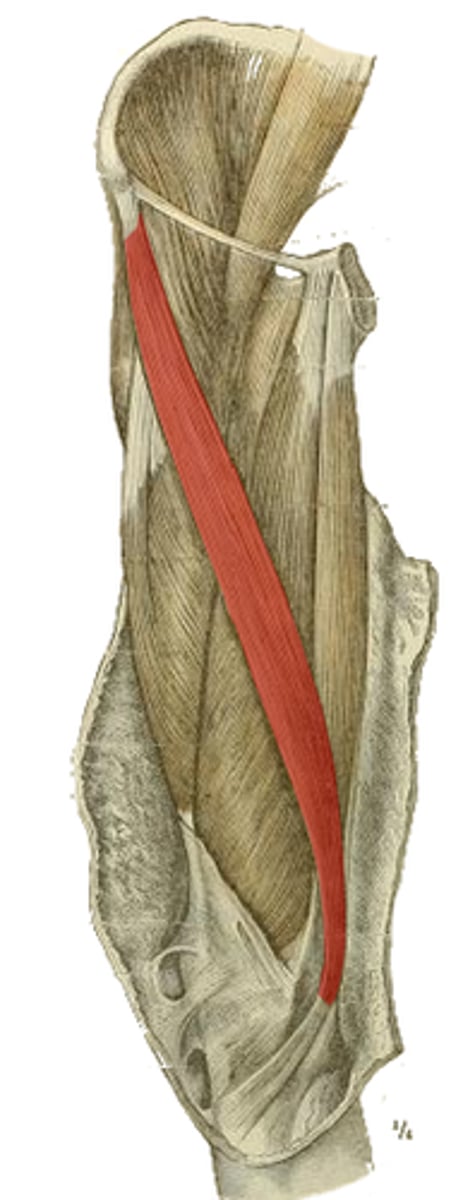
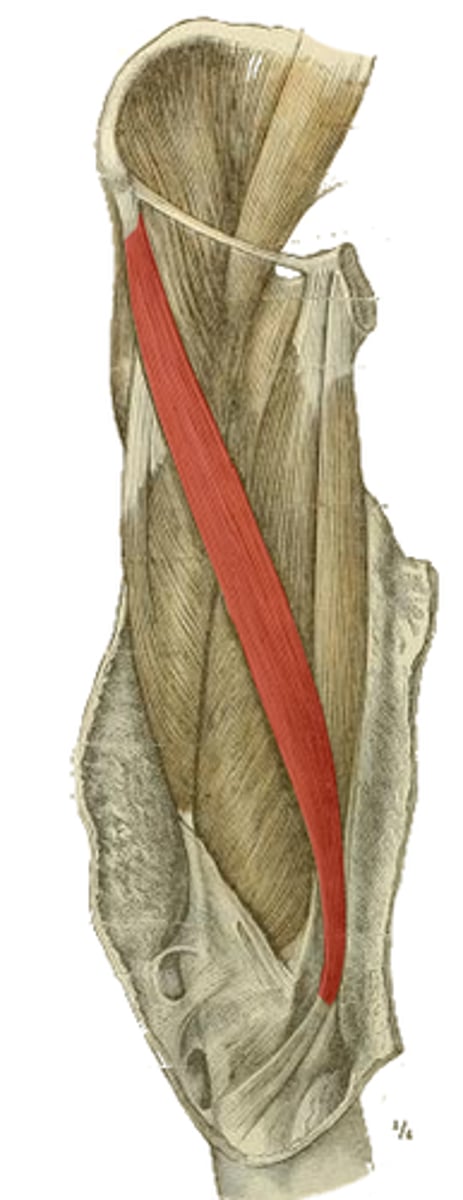
origin of the highlighted structure
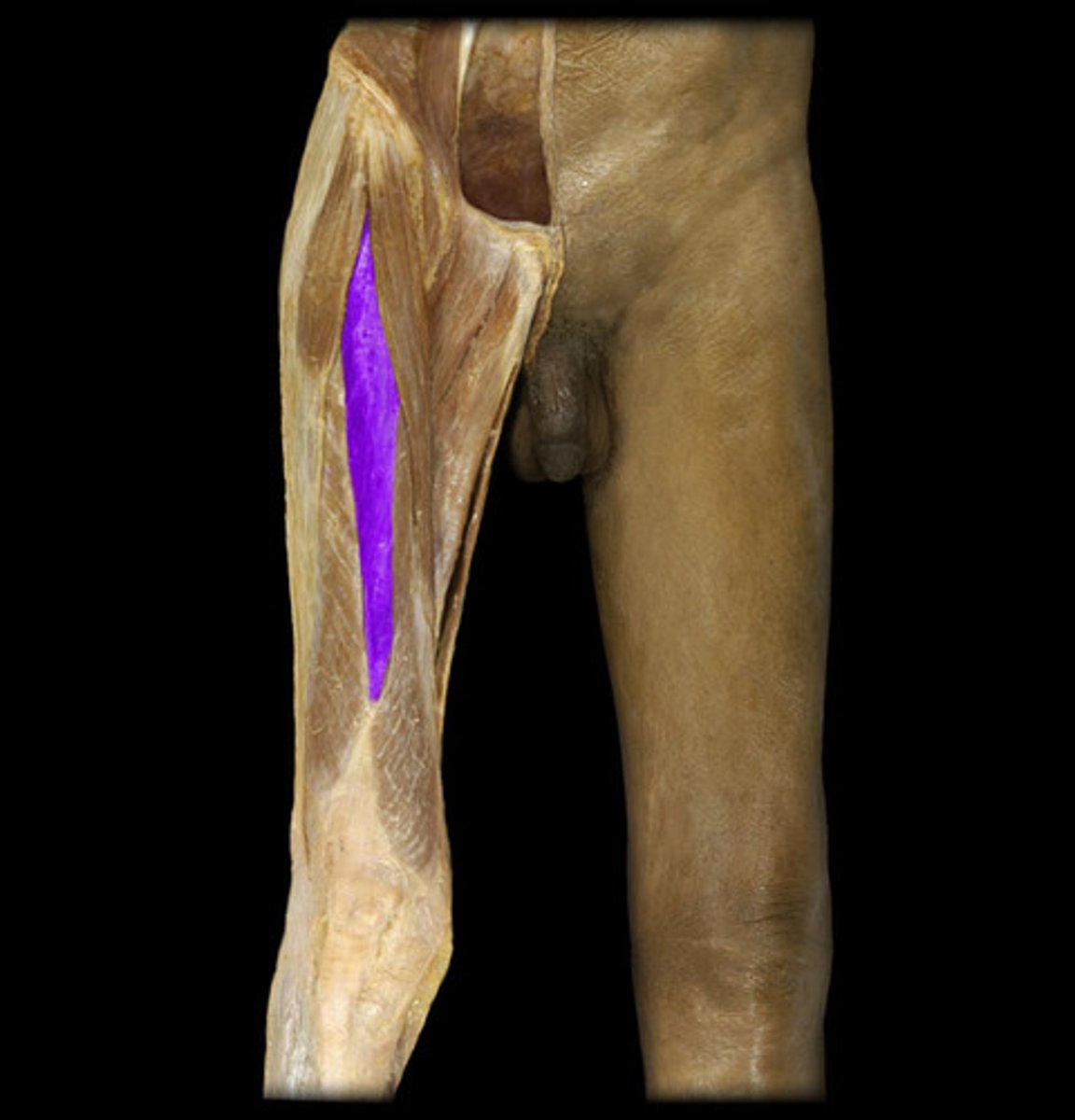
tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament
insertion of the highlighted structure
hip flexion, knee extension
action of the highlighted structure
tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament by way of the quadriceps tendon
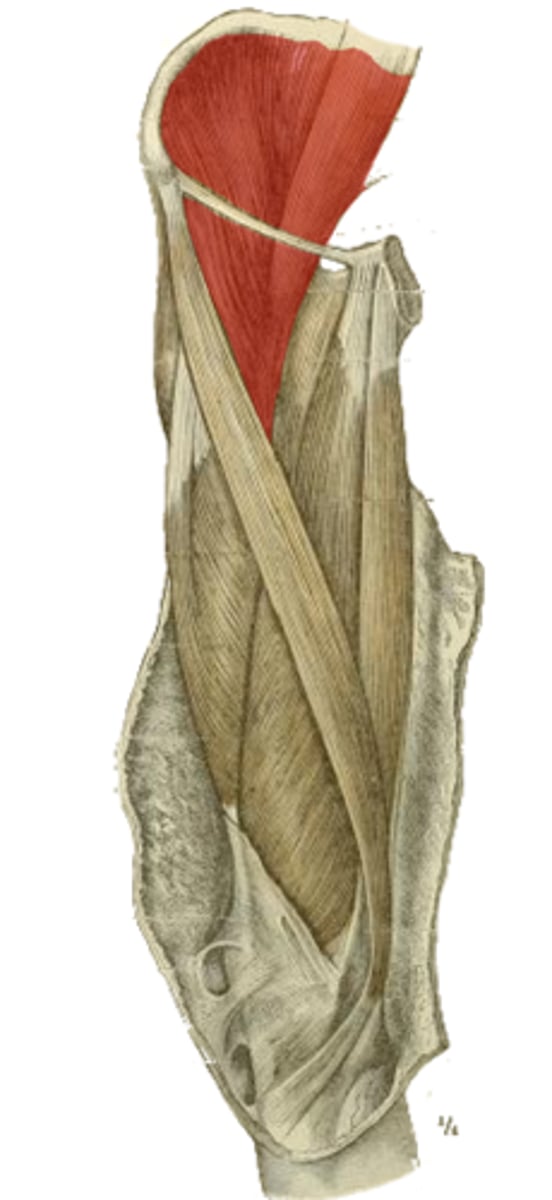
insertion of the vastus mm.
anterior surface of femur
deep to rectus femoris m.
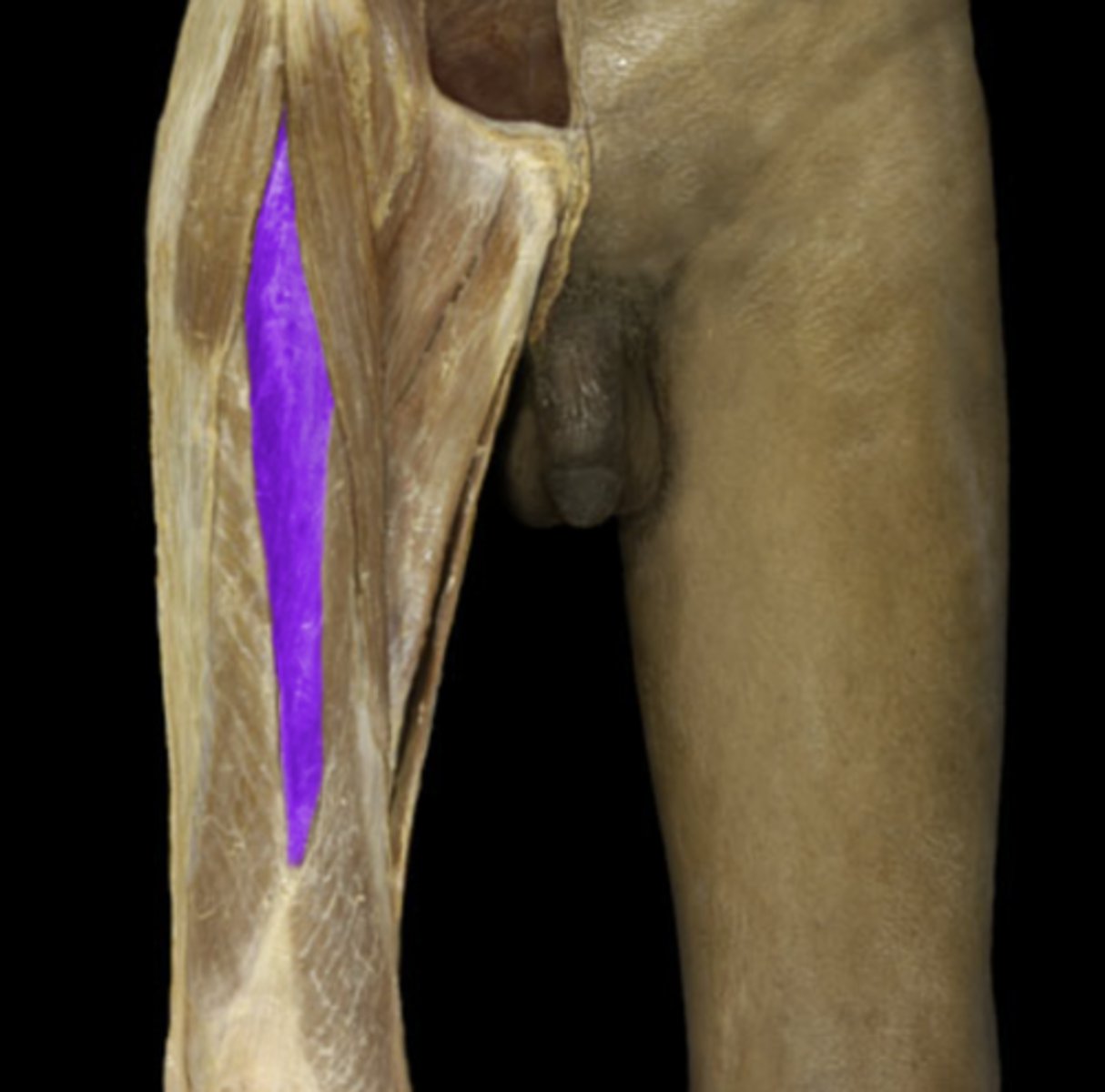
origin of the highlighted structure
counter the lateral pull of the quadriceps femoris m. of the patella
what may the role of the vastus medialis obliquus be?
vastus lateralis (lateral lip)
vastus medialis (medial lip)
which mm. originate off the linea aspera
gluteal tuberosity
lateral lip of linea aspera
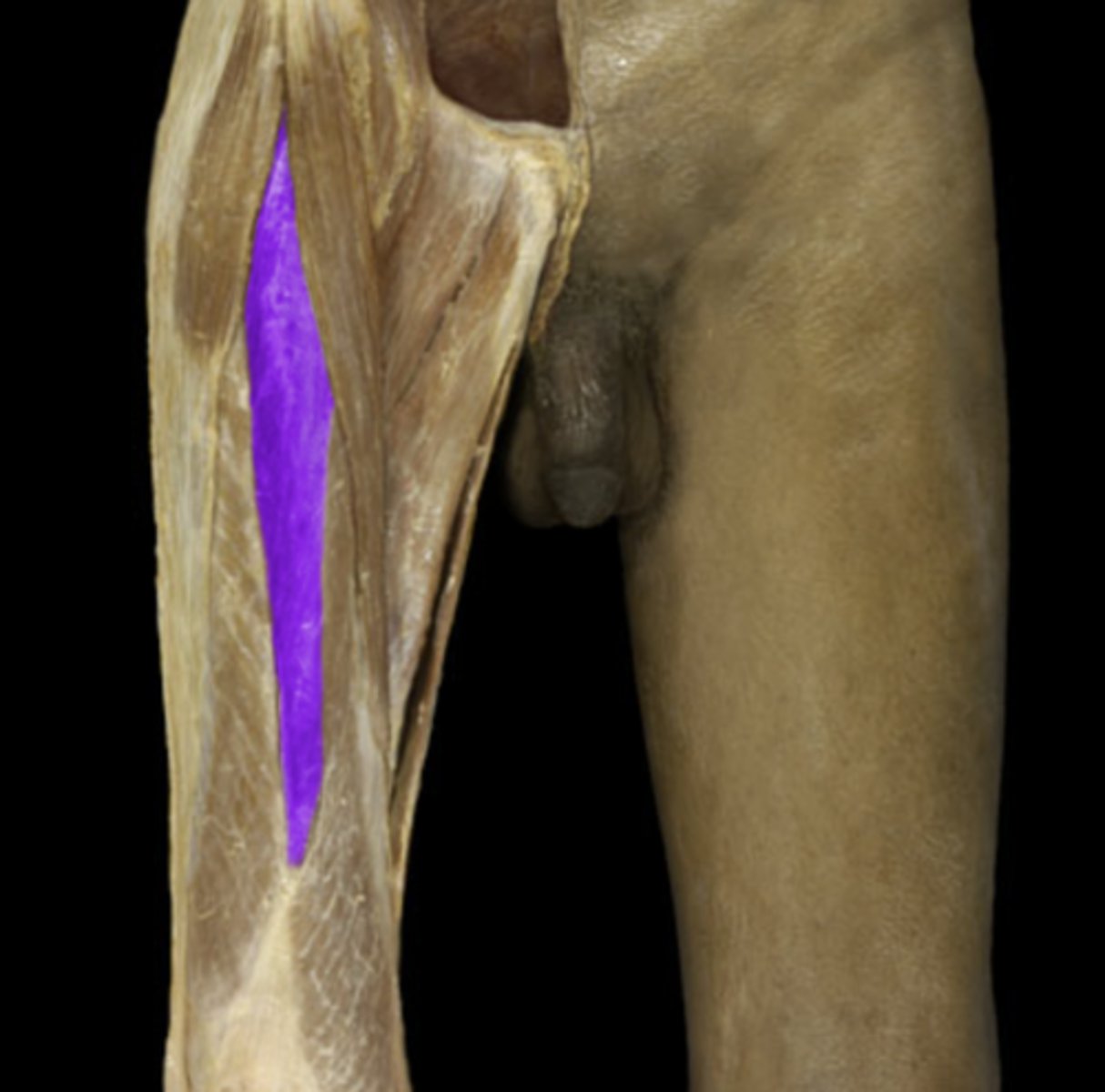
origin of the highlighted structure
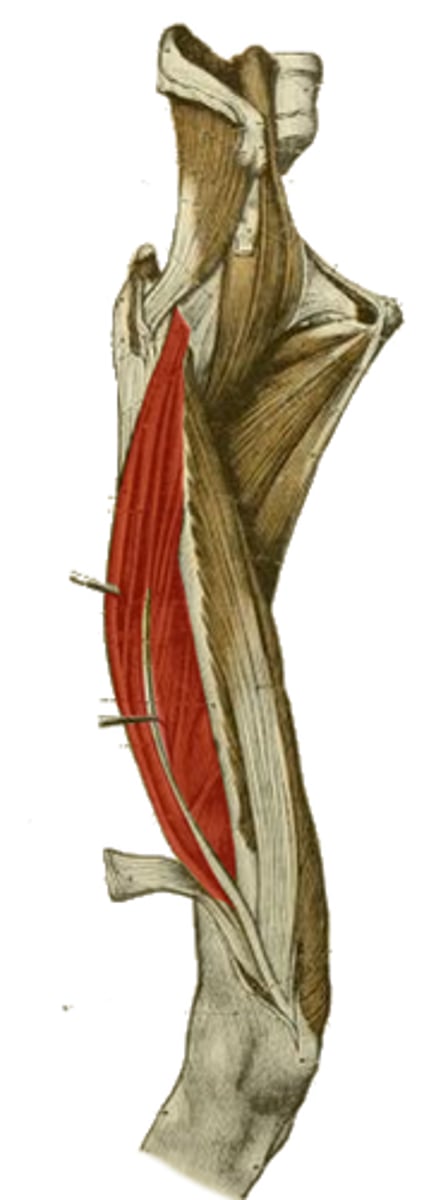
knee extension
action of vastus mm.
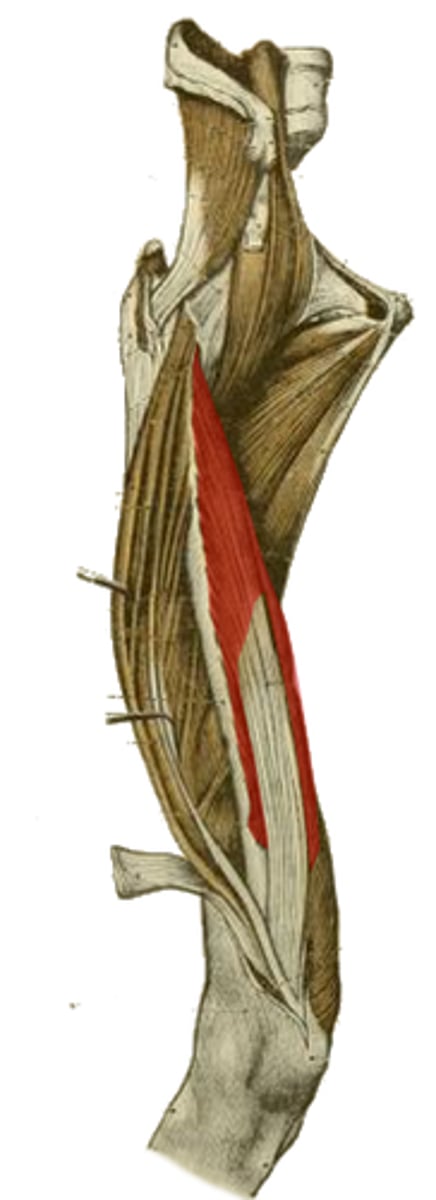
Sartorius m.
longest continuous muscle in the body
anterior superior iliac spine
origin of the highlighted structure
hip flexion
hip abduction
hip lateral rotation
knee flexion
action of the highlighted structure
sartorius m.
gracilis m.
semitendinosus m.
which muscles make up the pes anserine tendon group?
psoas major and minor mm. (lumbar vertebrae)
iliacus m. (anterior surface of ilium)
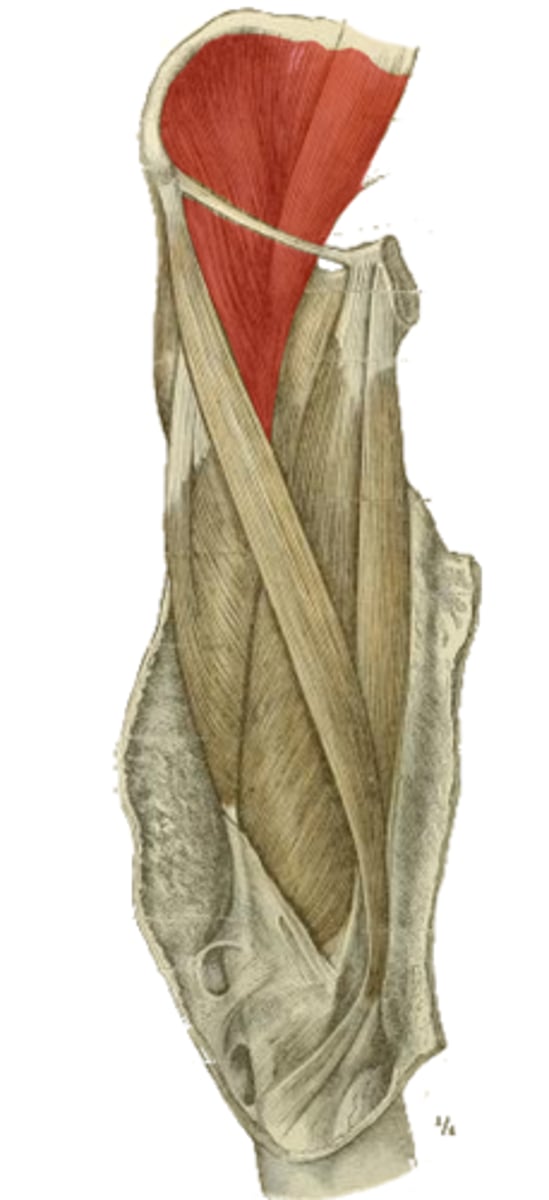
Which muscles is the highlighted structure made up of?
What are their origins?
common tendon to lesser trochanter
insertion of the highlighted structure
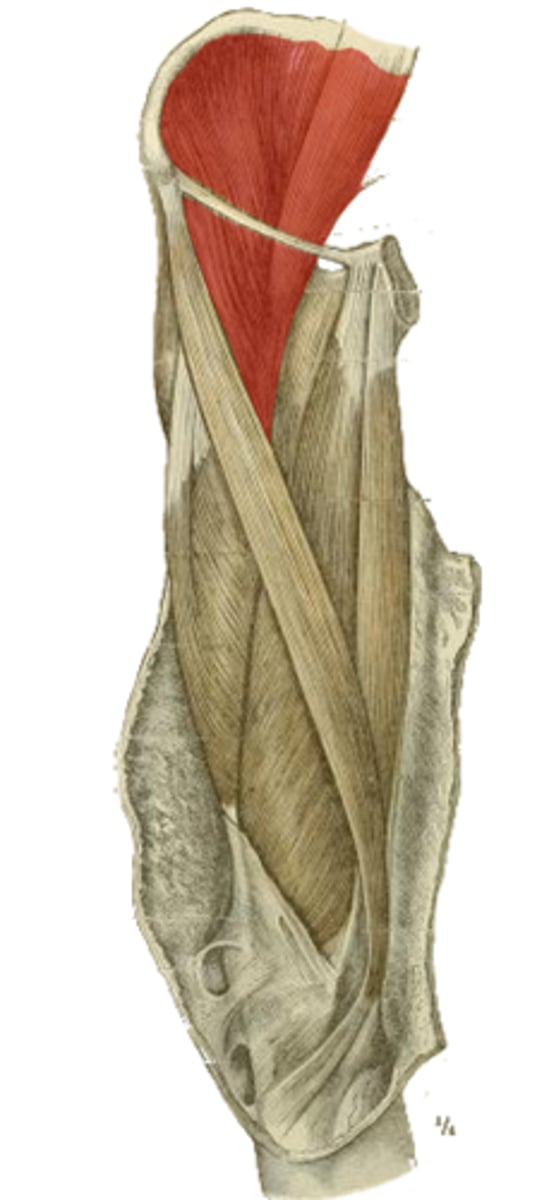
principle hip flexor
action of the highlighted structure
superior pubic ramus
origin of the highlighted structure
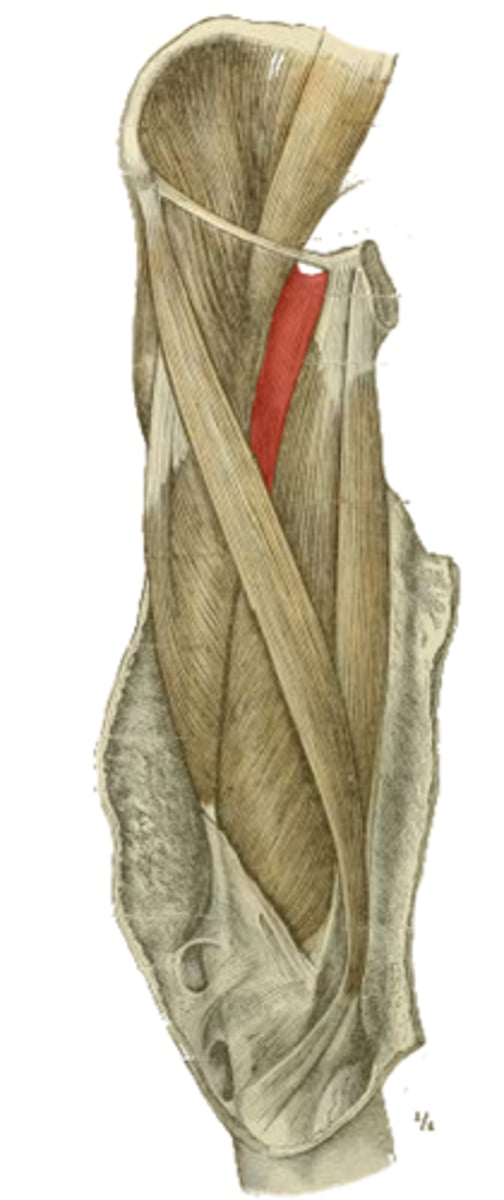
pectineal line of femur distal to lesser trochanter
insertion of the highlighted structure
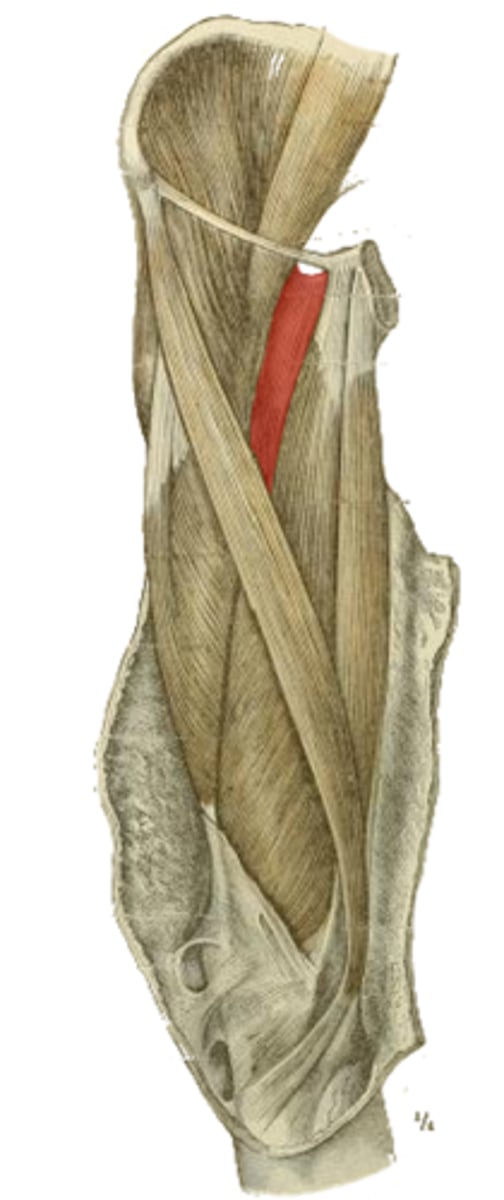
hip flexion
adduction
medial rotation
action of the highlighted structure
femoral n.
obturator n.
innervation of the highlighted structure
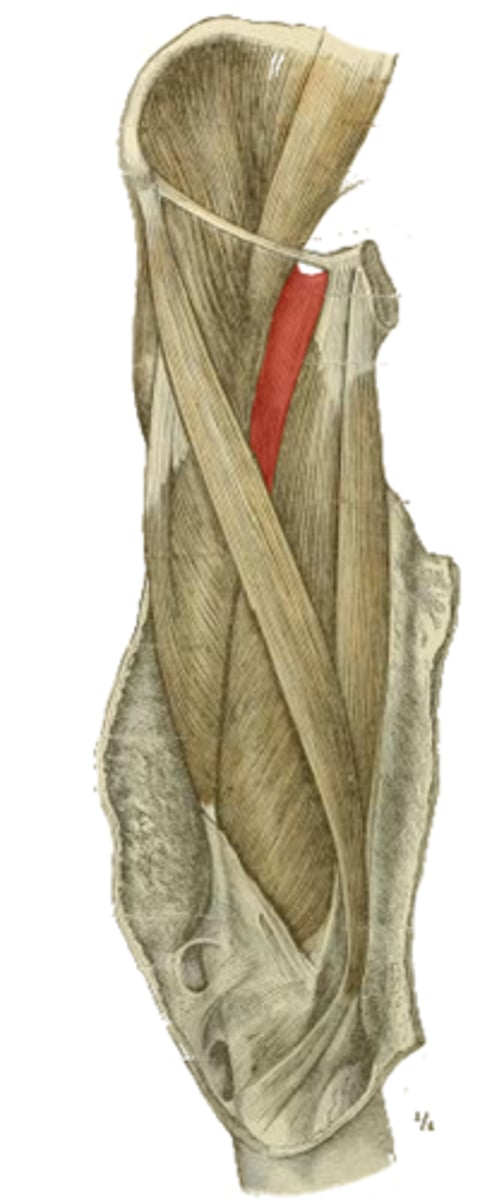
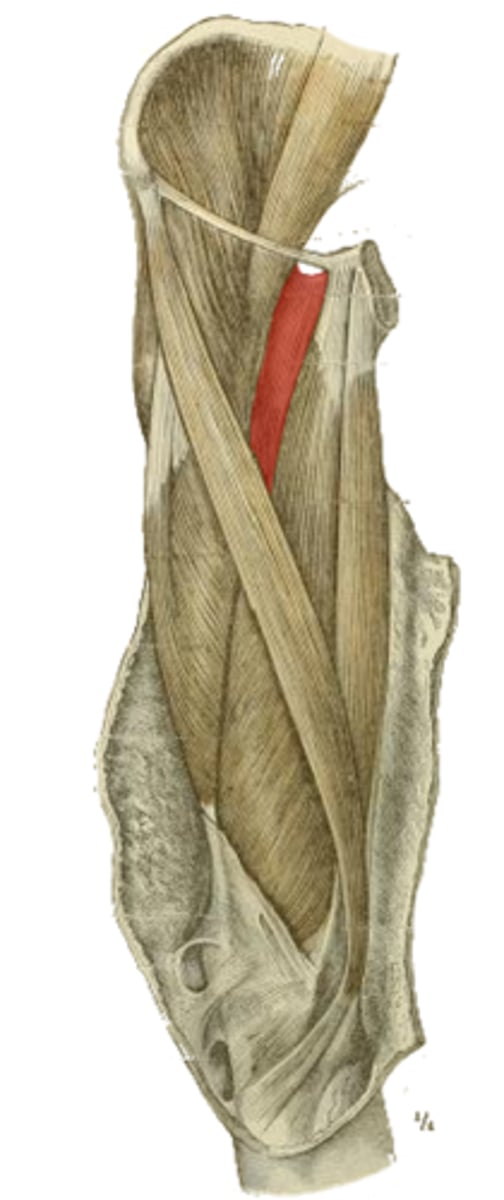
obturator externus m.
adductor longus m.
adductor brevis m
adductor magnus m.
gracilis m.
which muscles make up the medial compartment of the leg?
obturator n.
profunda femora a.
neurovascular supply of the muscles of the medial compartment of the leg
hip adduction
action of the mm. of the medial compartment of the leg
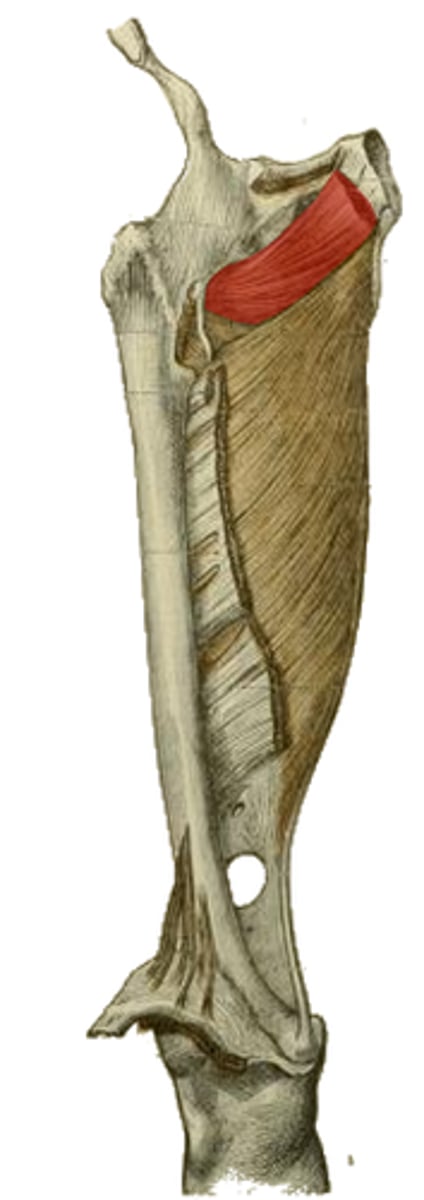
obturator membrane
origin of the highlighted structure
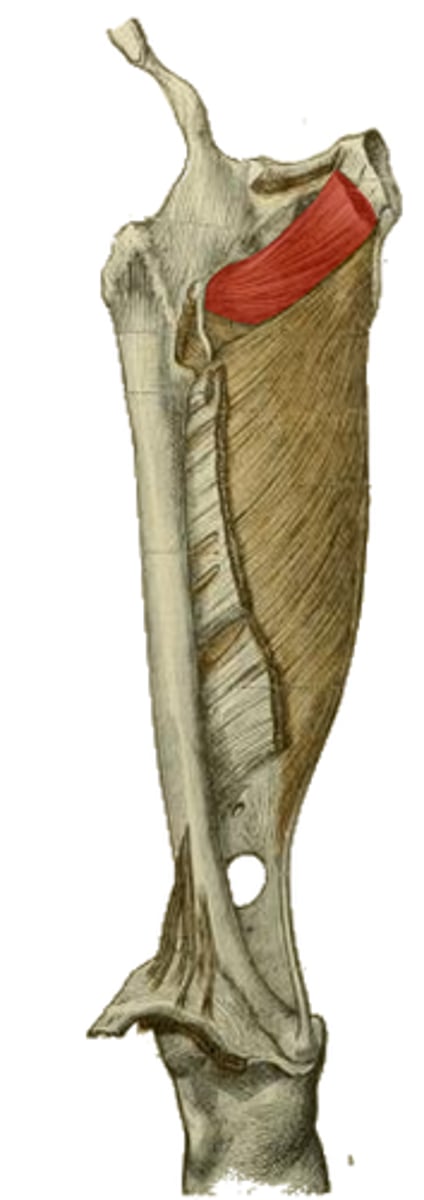
trochanteric fossa medial to greater trochanter
insertion of the highlighted structure
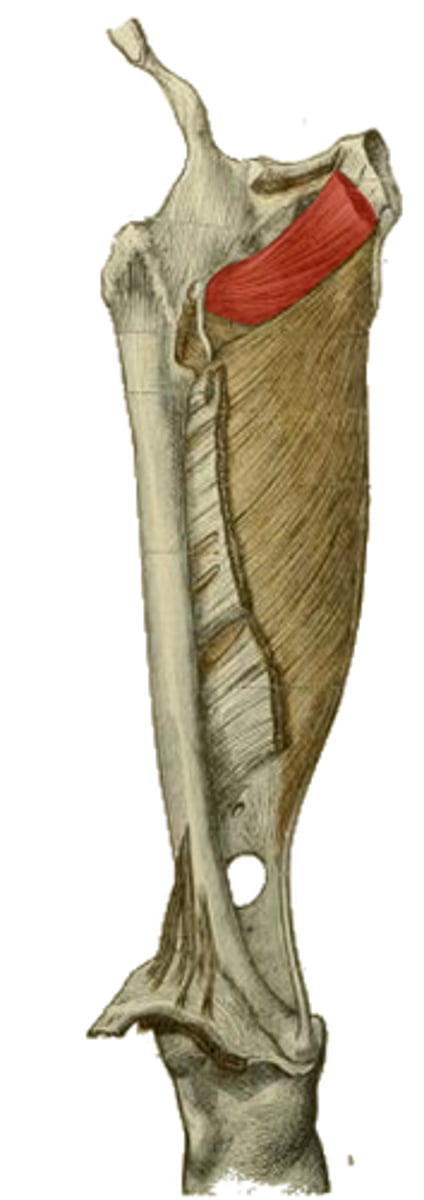
lateral rotation
hip stabilization
actions of the highlighted structure
adductor longus m. (close to pubic symphysis)
adductor brevis m. (inferior to adductor longus m.)
gracilis m. (inferior to adductor brevis m.)
Which mm. originate off the pubic bone? Where?
adductor longus m. (middle third)
adductor brevis (proximal portion)
adductor portion of adductor magnus m. (full length)
Which muscles insert at the linea aspera?
Which part?
hip adduction
obturator n.
profunda femora a.
action and innervation of the adductor portion of the highlighted structure
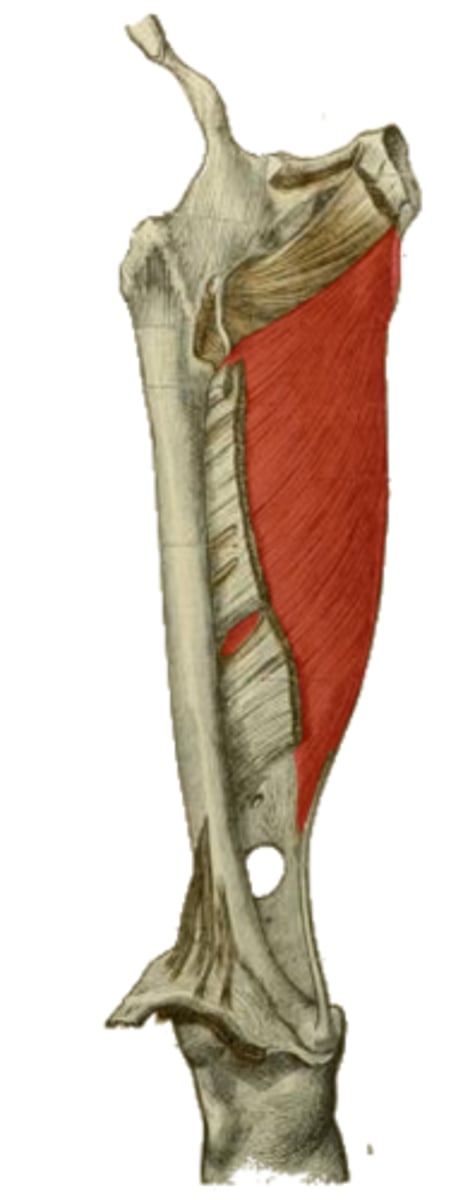
hip adduction
branches of sciatic n.
profunda femoris a.
action and neurovascular supply of the hamstring portion of the highlighted structure
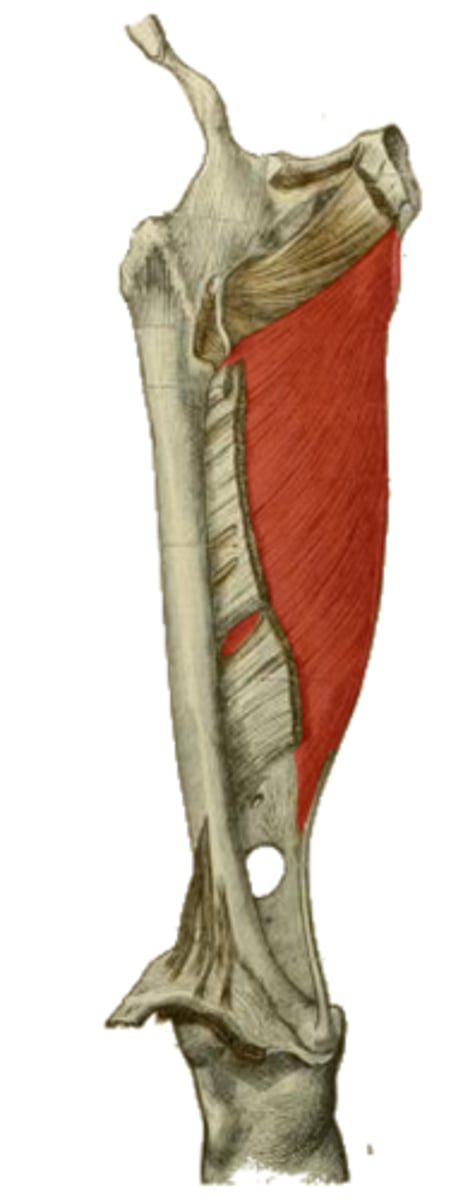
inferior rami of ischium/pubic bones anterior to hamstring origin
origin of the highlighted structure
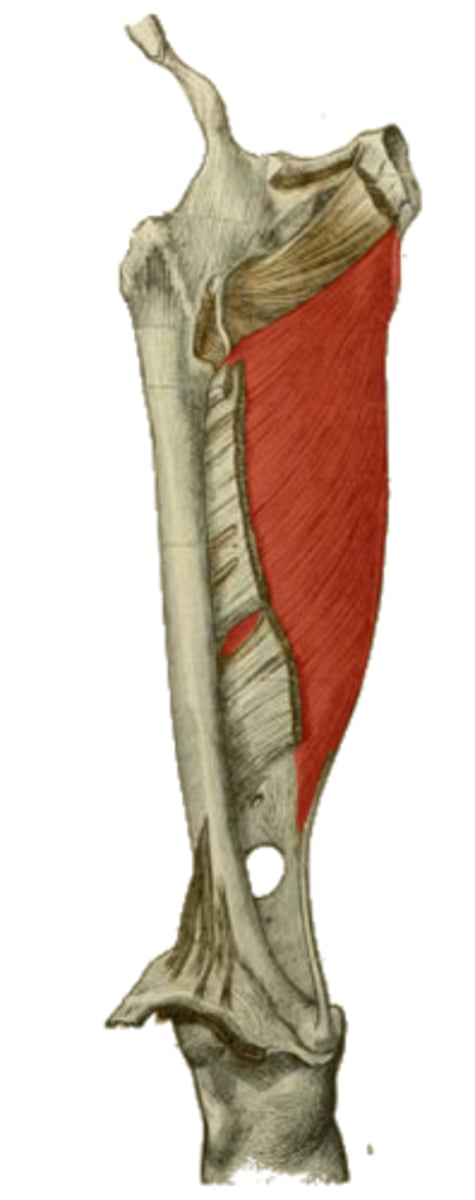
adductor tubercle of femur
insertion of the hamstring portion of the highlighted structure
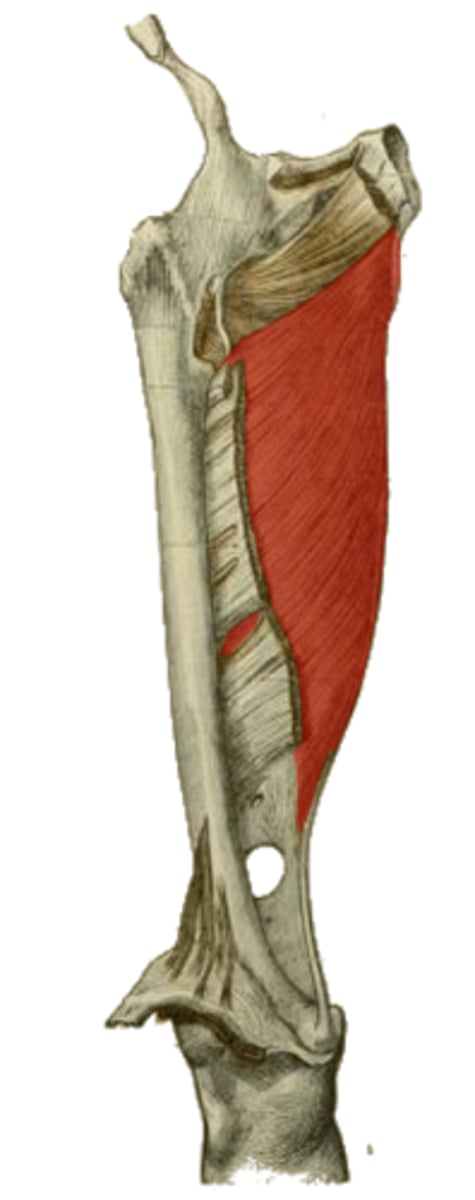
Arch between adductor and hamstring parts of adductor magnus m. at attachment to femur
Allows passage of vessels between anterior and posterior compartments of leg
Where is the adductor hiatus?
What does it do?
adduction of hip
assists with knee flexion
action of the highlighted structure

knee stability and postural support especially when raising contralateral leg
function of iliotibial tract
superior - ingluinal canal
medial - adductor longus m.
lateral - sartorius m.
apex - where sartorius crosses adductor longus m.
floor - pectineus m., iliopsoas m.
covered by - fascia lata, cruciform fascia over saphenous opening
what makes up the borders of the femoral triangle?
transit of neurovascular structures to and from lower limb embedded in femoral sheath
permits gliding of vascular structures during hip flexion/extension
significance of femoral triangle
(NAVEL)

anterolateral - vastus medialis
posterior - adductor longus m., adductor magnus m.
covered by - sartorius m.
borders of adductor (subsartorial) canal
allows passage of femoral vessels to adductor hiatus, saphenous nerve, motor branch to VMO
significance of adductor (subsartorial) canal
obturator a. and n.
which structures pass through the obturator canal?
femoral triangle
the external iliac a. becomes the femoral a. once it passes which structure?
superficial epigastric a.
superficial circumflex inguinal a.
what branches first come off of the femoral a.?
between the anterior and medial compartments of the leg
where does the profunda femora a. reside?
lateral and medial femoral circumflex aa.
Intertrochanteric mass of bone and proximal femoral head
Which arteries come off of the profunda femora a.?
What structures do they supply?
3-4 perforating branches (posterior compartment)
Which arteries come off of the profunda femora a. distally?
What area does it supply?
ascending branch (region surrounding hip)
transverse branch (proximal head of femur)
descending branch (lateral part of anterior compartment)
which arteries come off of the lateral femoral circumflex a.?
Which structures does it supply?