Lectures 34 & 35 (Protozoan Parasites of Veterinary Importance)
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Made by Harley Chase and Kylee Wood
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
All vertebrate hosts
Who are Protozoan Parasites parasitic in?
Trophozoite
What is the living, motile form of Protozoan Parasites?
Cyst/Oocyst
What is the environmental transmission form of Protozoan Parasites?
True
T or F: Protozoan Parasites are parasitic in all host tissues/systems.
Solid tissues directly or after liquefying them
What do Protozoan Parasites feed on?
Through the body wall and block absorptive a capacity of the host GI (Giardia)
Protozoan Parasites compete with the host for ingested food - how do they absorb nutrients?
By growing in them
--- Coccidia, Malaria
How do Protozoan Parasites destroy host cells?
Give an example
Their ability to enter host tissues, feed or reproduce
How does the production of various toxic substances aid Protozoan Parasites in?
- Allergic
- Inflammatory
- Hyperplasia
- Thrombocytopenia
Protozoan Parasites cause various host reactions such as what?
Other diseases and parasites
What do Protozoan Parasites reduce host resistance to?
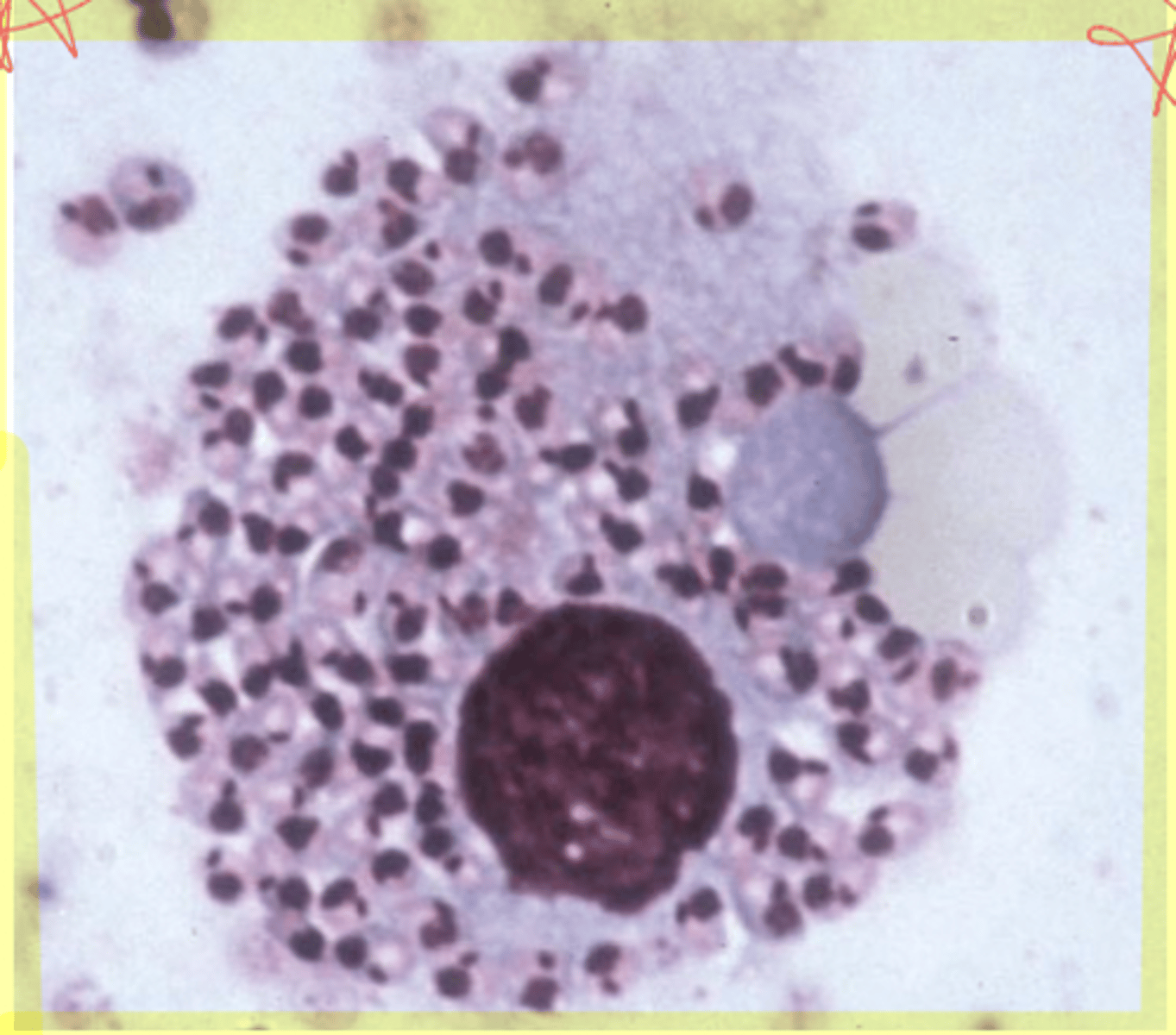
Giardia sp.
What is seen in the following image?
> Waterborne outbreaks
> Daycare centers, Occupational risk (Vets/Techs), Outdoor Recreation
What are Giardia sp. primarily associated with?
Where?
Direct Lifecycle
What type of lifecycle do Giardia sp. have?
Via fecal-oral contamination and ingestion of immediately infective cysts
How does host infection/re-infection with Giardia sp. occur?
Dogs and cats
Who do symptomatic infections with Giardia sp. occur in?
> Watery diarrhea in acute phase (~ 5 days post-infection)
> Voluminous, malodorous stools w/ mushy consistency
> Gas, flatulence
> Cysts appear in stools 7-14 days post-infection
What clinical signs might be seen with Giardia sp. infection?
> Prevalence in Children in daycare and their parents
--- 2% vs 29% age matched prevalence
> Daycare workers, Backpackers, People who drink from shallow wells, vet personnel, international travelers
Who's at risk for infection with Giardia sp.? (Human Pop.)
> Animals in shelters, boarding kennels, etc.
> Multi animal situations facilitate spread from infected asymptomatic animals to susceptible hosts
Who's at risk for infection with Giardia sp.? (Companion Animals)
ZnSO4 flotation
What can be used to diagnose Giardia infections in companion animals?
> Supportive care (especially in young animals)
--- Restore electrolyte balances
What can be used to manage and treat Giardia infections in companion animals?
Neurotoxicity
What does prolonged use of Metronidazole cause when treating Giardia infections?
> Bathe pet
> To remove immediately infective cysts
What should be done at the beginning and end of treatment protocol for Giardia infections?
Why?
Giardia sp.
A 3 month old beagle mix presents with 2 wk history of intermittent diarrhea and foul smelling, mushy stools. A ZnSO4 fecal flotation reveals many cyst-like structures measuring 12 x 8 um, nuclei and other features are apparent in some. What is your diagnosis?
Tritrichomonas blagburni
What is a flagellate protozoan parasite found in the large intestine of cats?
> Lymphoplasmacytic/neutrophilic colitiis
> Crypt abscess
> Increased mucous production
> Generalized erosion of colonic mucosa
What might be caused by Tritrichomonas blagburni?
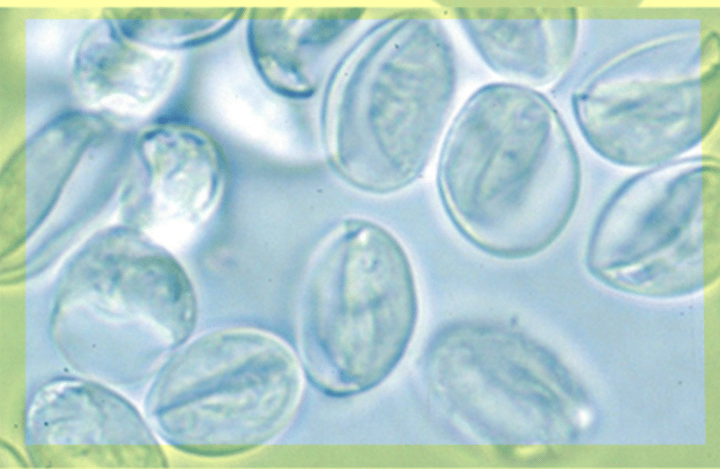
Tritrichomonas blagburni
What is seen in the following image?
Tritrichomonas foetus
What is a flagellate protozoan parasite found in the reproductive tract of cattle?
True
T or F: Tritrichomonas foetus is morphologically indistinguishable from T. blagburni.
> Infertility
> Spontaneous abortion in 1st trimester
> Generalized repro tract infection
Tritrichomonas foetus is the causative agent of bovine genital trichomoniasis - what does this lead to?
African Sleeping Sickness & Chagas Disease
Blood and Tissue Flagellates are broadly classified as the Trypanosomes - family members are well known as the causative agent of what?
> Trypomastigote
> Arthropod IH
What are the flagellate trophozoite stage circulating in blood/lymph known as that are infective for the vertebrate host?
Where are other stages developmental in?
During blood meal
How are Arthropod IH infected with Trypanosomes?
Divide and Multiply
What do Epimastigotes of Trypanosomes do in the IH?
Trypomastigotes
What do Trypanosomes develop into within the IH?
False - Multiplication does occur
T or F: Trypanomastigotes are transferred to Human/Animal host but multiplication does not occur in the human/animal host/
- T. brucei
- T. gambiense
What parasites are associated with African Trypanosomiasis?
> In blood
> Lymph nodes, intracellular spaces
Where do parasites associated with African Trypanosomiasis live?
Where do they invade?
> Anemia
> Depressed erythropoiesis
> Hyperplasia bone marrow and spleen
> Erythrophagocytosis b/c trypanosome antigens attach to RBCs
African Trypanosomiasis generally produces what from immune-mediated processes and mechanisms?
What else is associated with this?
Trypanosoma cruzi
What is the causative agent of "Chaga's Disease" or American Trypanosomiasis?
Domestic and Sylvan Lifecycle
What type of lifecycle does Trypanosoma cruzi have?
Triatomin/Reduviid bugs
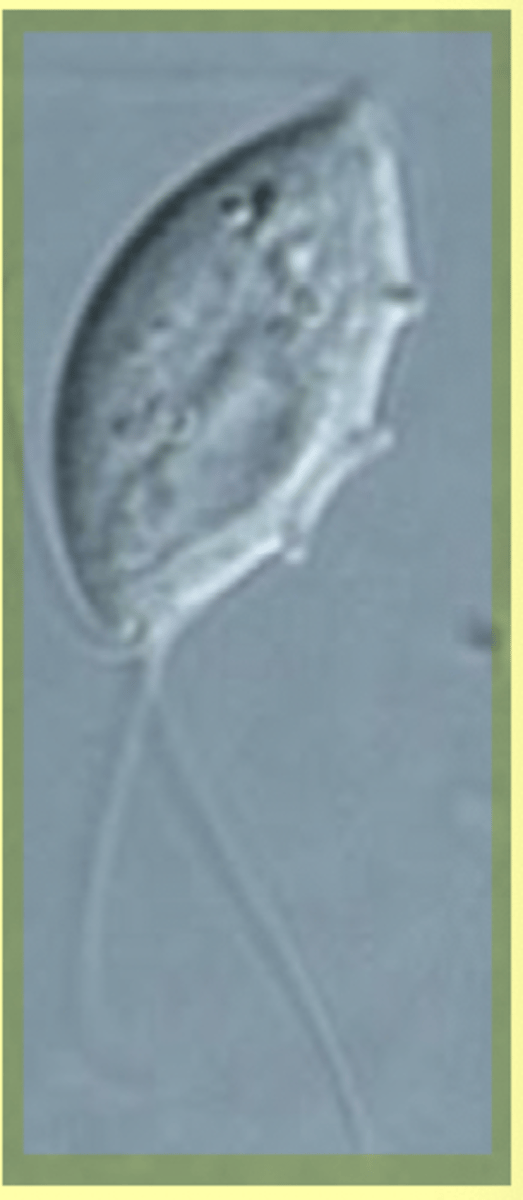
Who is the obligate IH for Trypanosoma cruzi?
Trypanosoma cruzi IH - Kissing bug
What is seen in the following image?
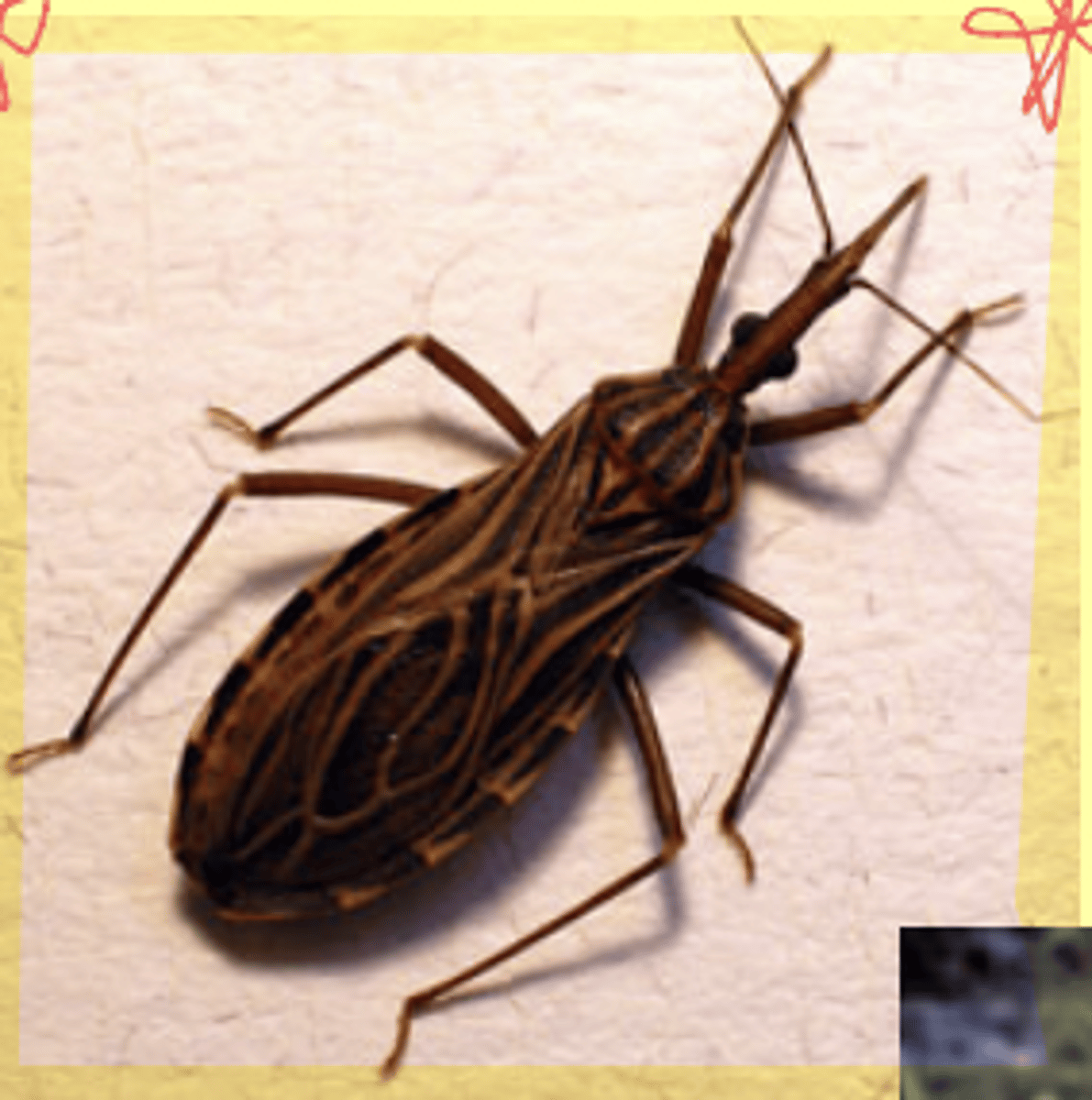

Trypanosoma cruzi
What is seen in the following image?
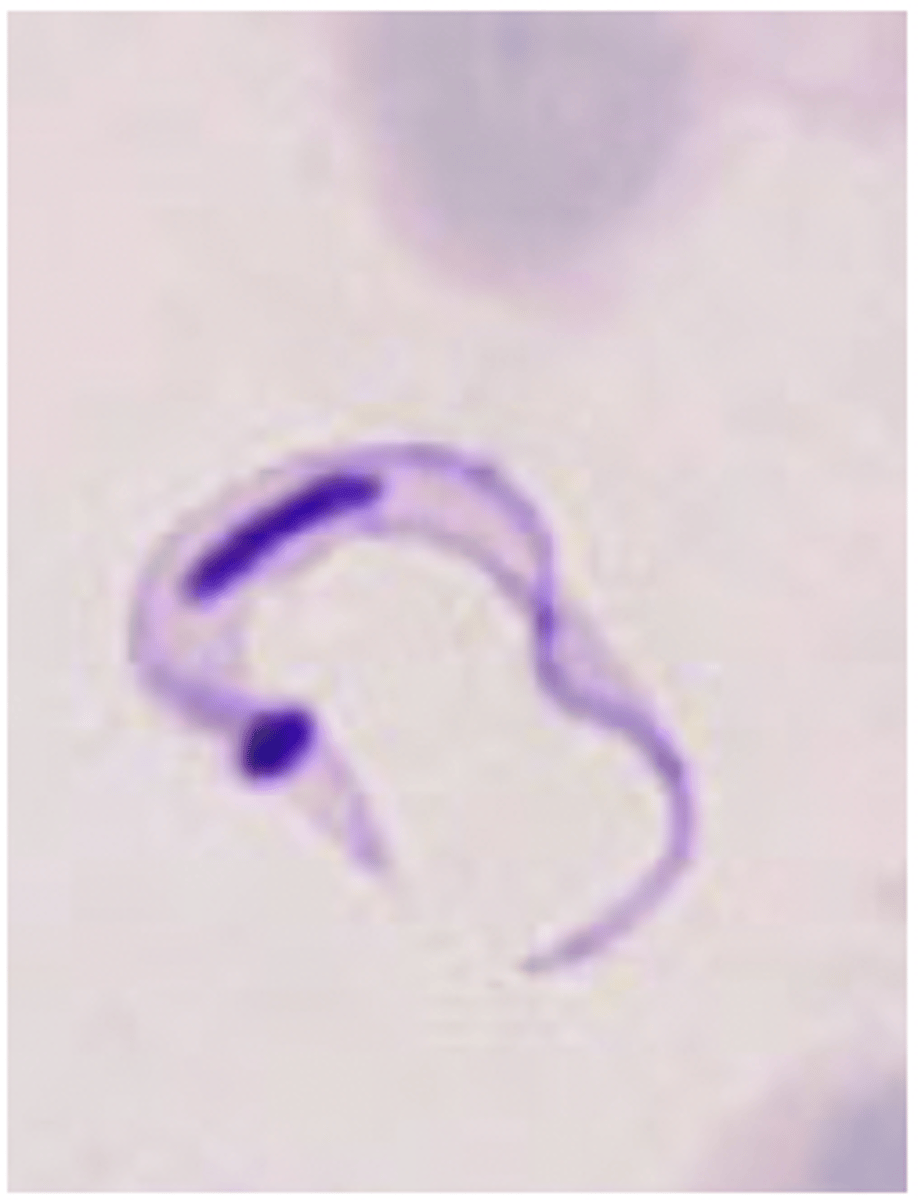
> Active defecation by IH
> Ingestion of IH
How does vector borne transmission of Trypanosoma cruzi occur?
> Blood transfusion
> Organ/tissue transplantation
> Congenital
> Lab exposure
> Fecal contamination of food items
How does non vector borne transmission of Trypanosoma cruzi occur?
> Host associations
> Transmission, oral, congenital, etc.
What is involved with genotypic variation of Trypanosoma cruzi?
Amastigote stage organisms
Trypomastigotes proliferate asexually in histocytes as what?
- Lymphadenopathy
- Myocarditis
- Pale MM
- Tachycardia
- Splenomegaly
What is associated with acute T. cruzi disease in dogs?
> the lymphatics
> proliferate
T. cruzi is spread via what?
They enter tissues and continue to what?
Trypanosoma cruzi
What is seen in the following image?
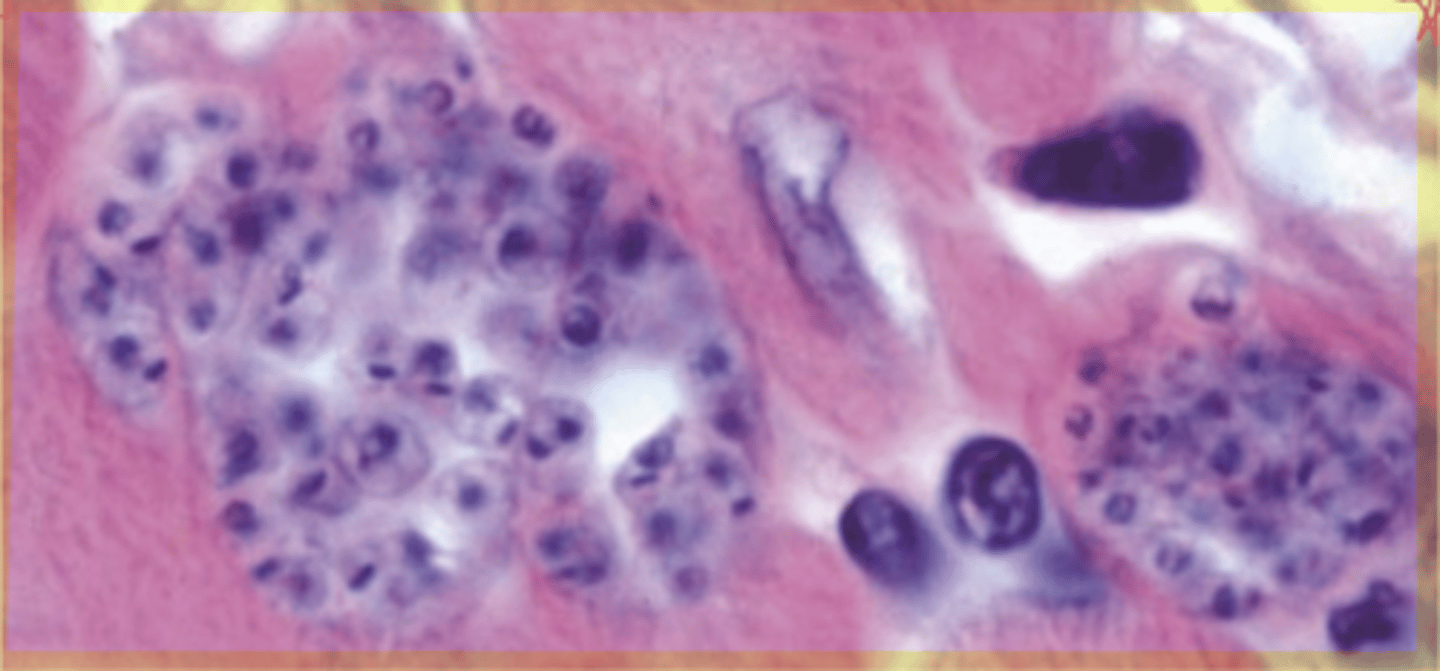
Trypanosoma cruzi
A 4 year old mixed breed hound was presented w/ lethargy, pale mm, tachycardia and ascites. Numerous "nests" of protozoa-like organisms were evident on post-mortem histopathologic examination of heart muscle. What is your diagnosis?
Obligate IH for T. cruzi
Many dorso-ventrally flattened bugs were found in the bedding of the dog's house during the field investigation. What role, if any, did these bugs play in the disease picture of this dog?
Leishmania sp.
What is seen in the following image?