Phonatory System Anatomy- Intrinsic Laryngeal Muscles
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What roles do intrinsic muscles play?
Change: VF postion (abducted vs adducted vocal folds), glottis size (increased or decrease space between vocal folds) and vf legnth (short vs long) and tension
What are the tensor muscles
Thyroarytenoids
--> a. internal thyroarytenoids
-->b. external thyroartenoids
What muscle changes vocal fold length?
cricothyroids
what is the abductor muscle
posterior cricoarytenoid
what are the adductor muscles
lateral cricoarytenoid
Interarytenoids: transverse arytenoid and oblique arytenoid
what muscle provides airway protection
aryepiglottic
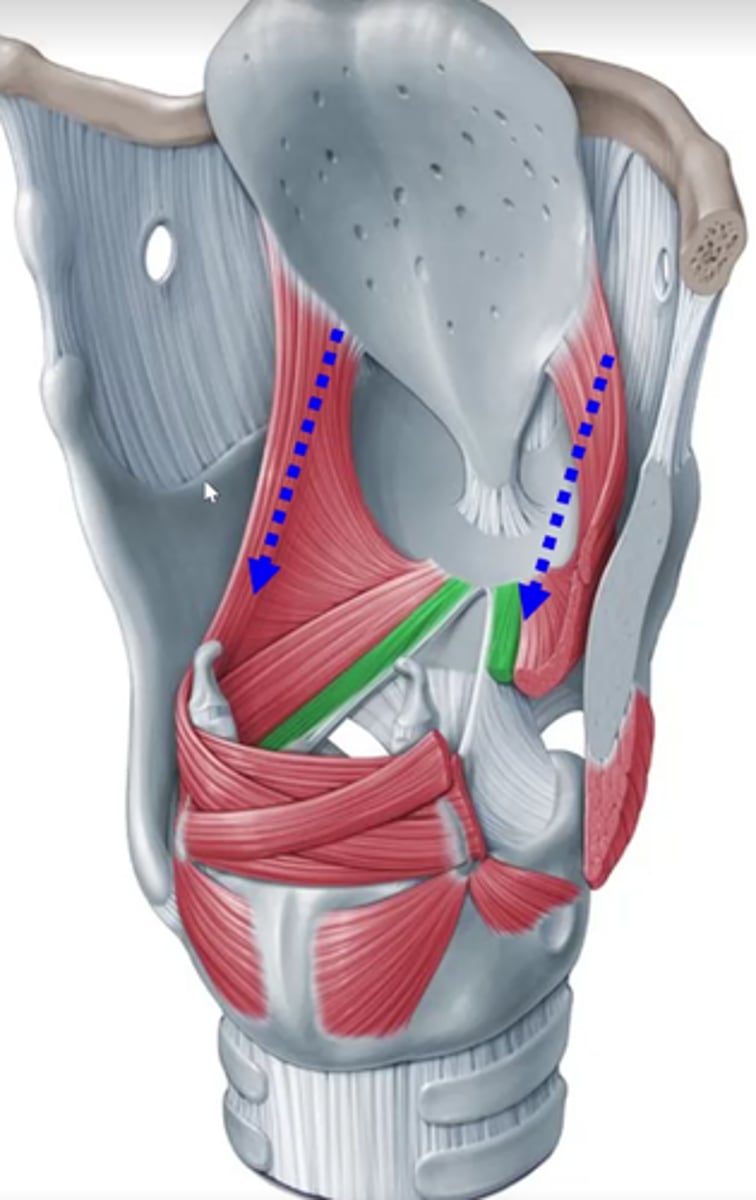
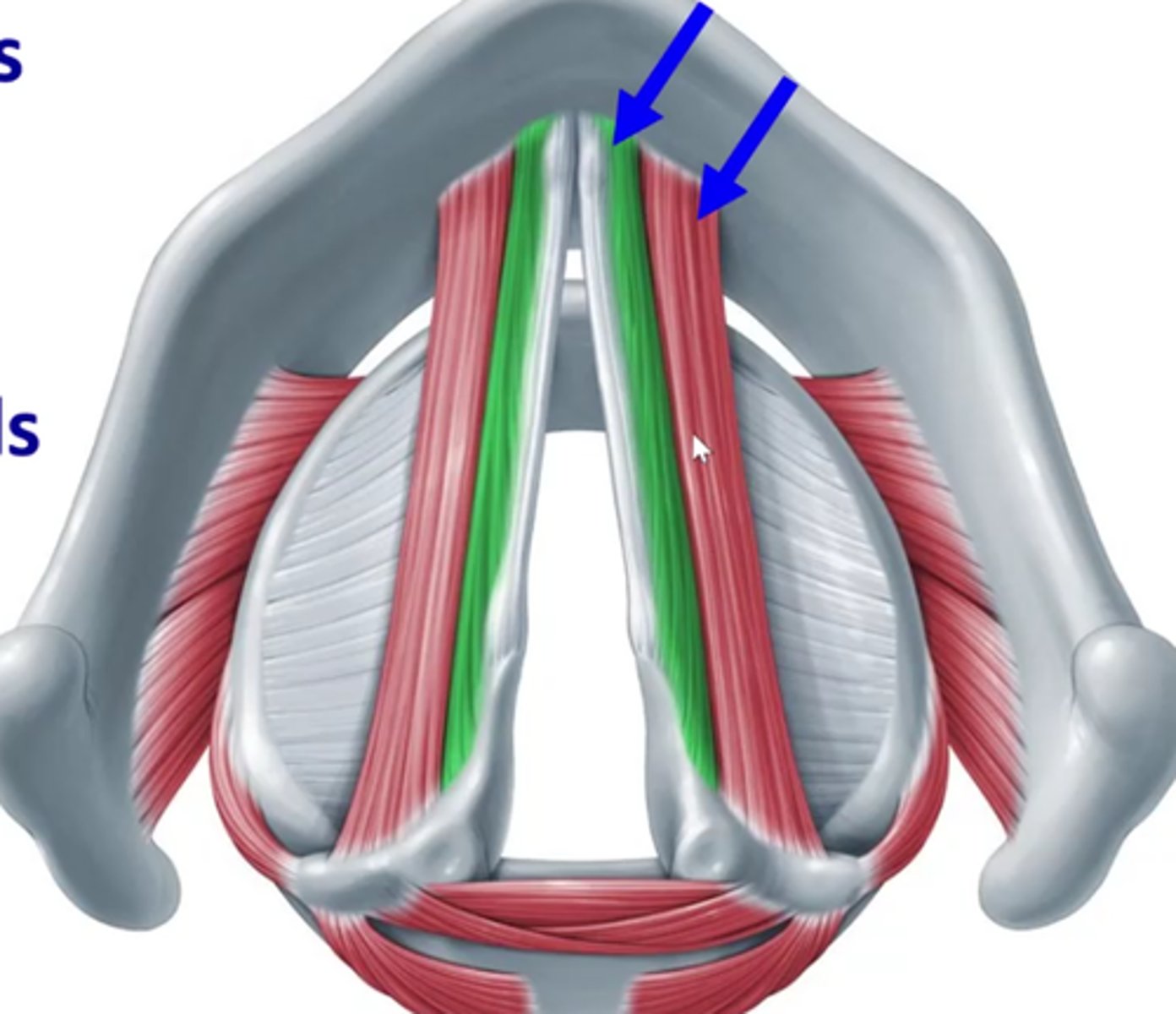
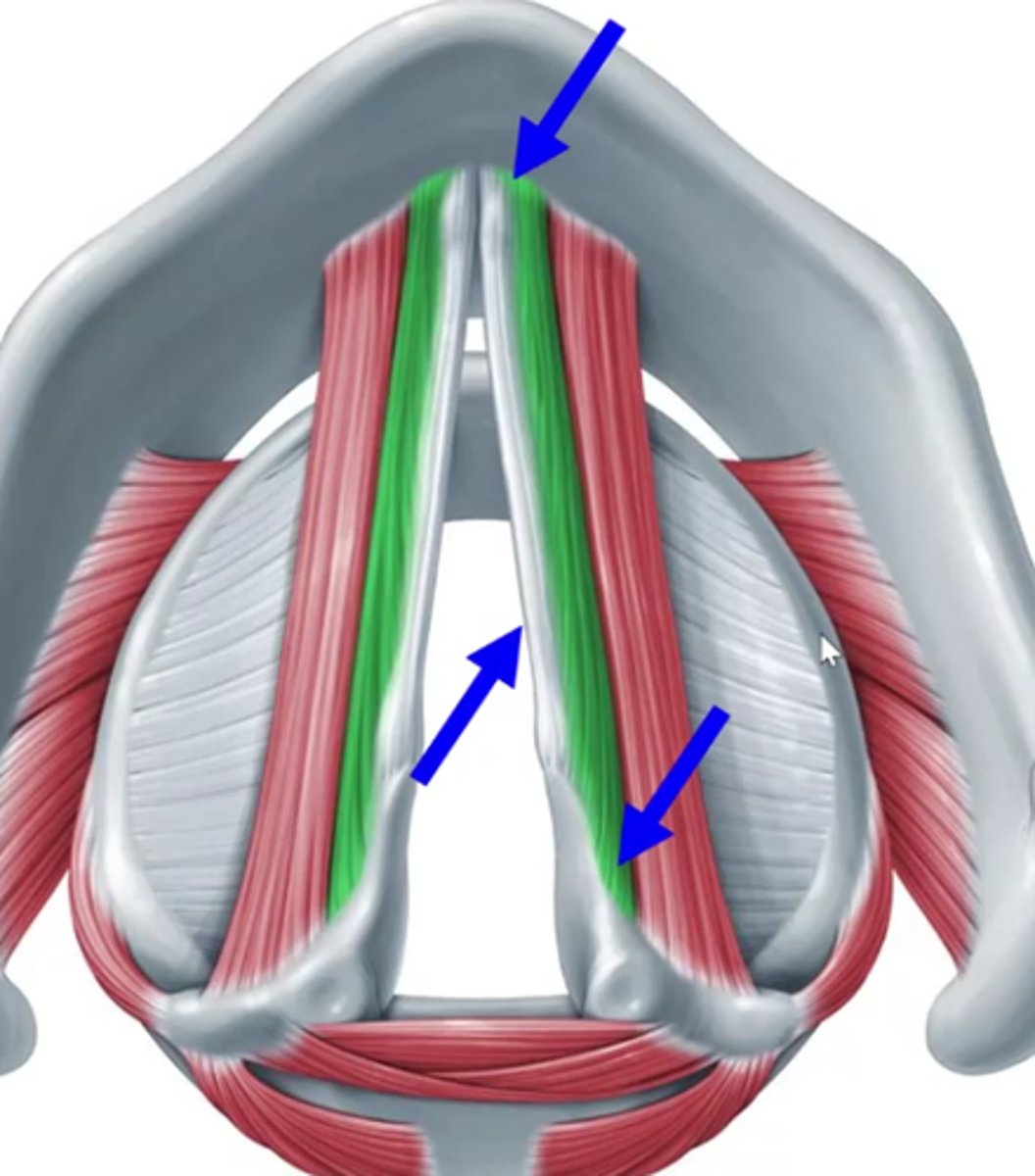
internal thryoarytenoid (green)
closer to midline- deeper
- also vocalis
- also thyrovocalis
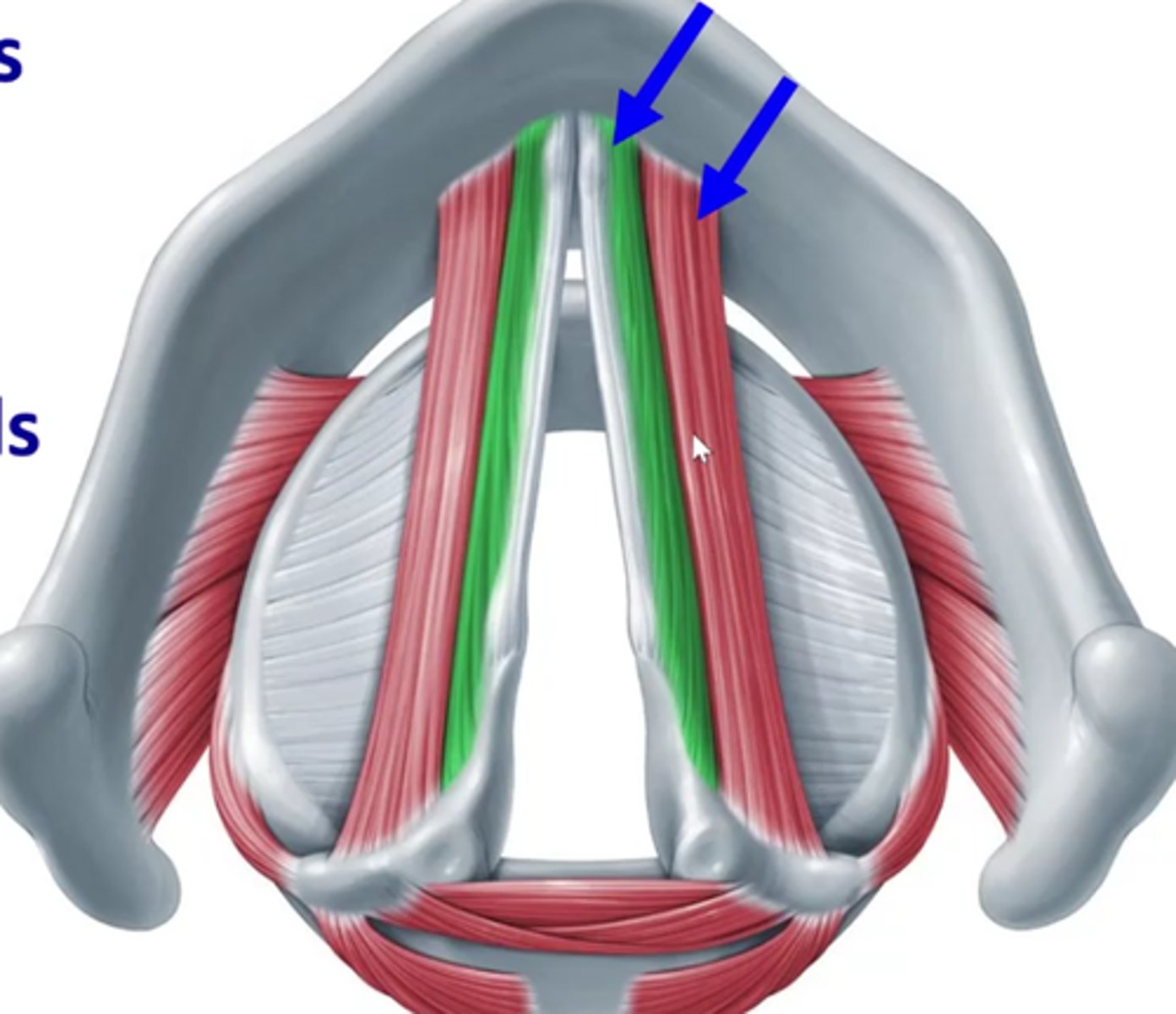
External thyroarytenoids (red)
Also thyromuscularis
Anterior view of thryoarytenoids- relative to where the vocal folds and other cartilages would be located
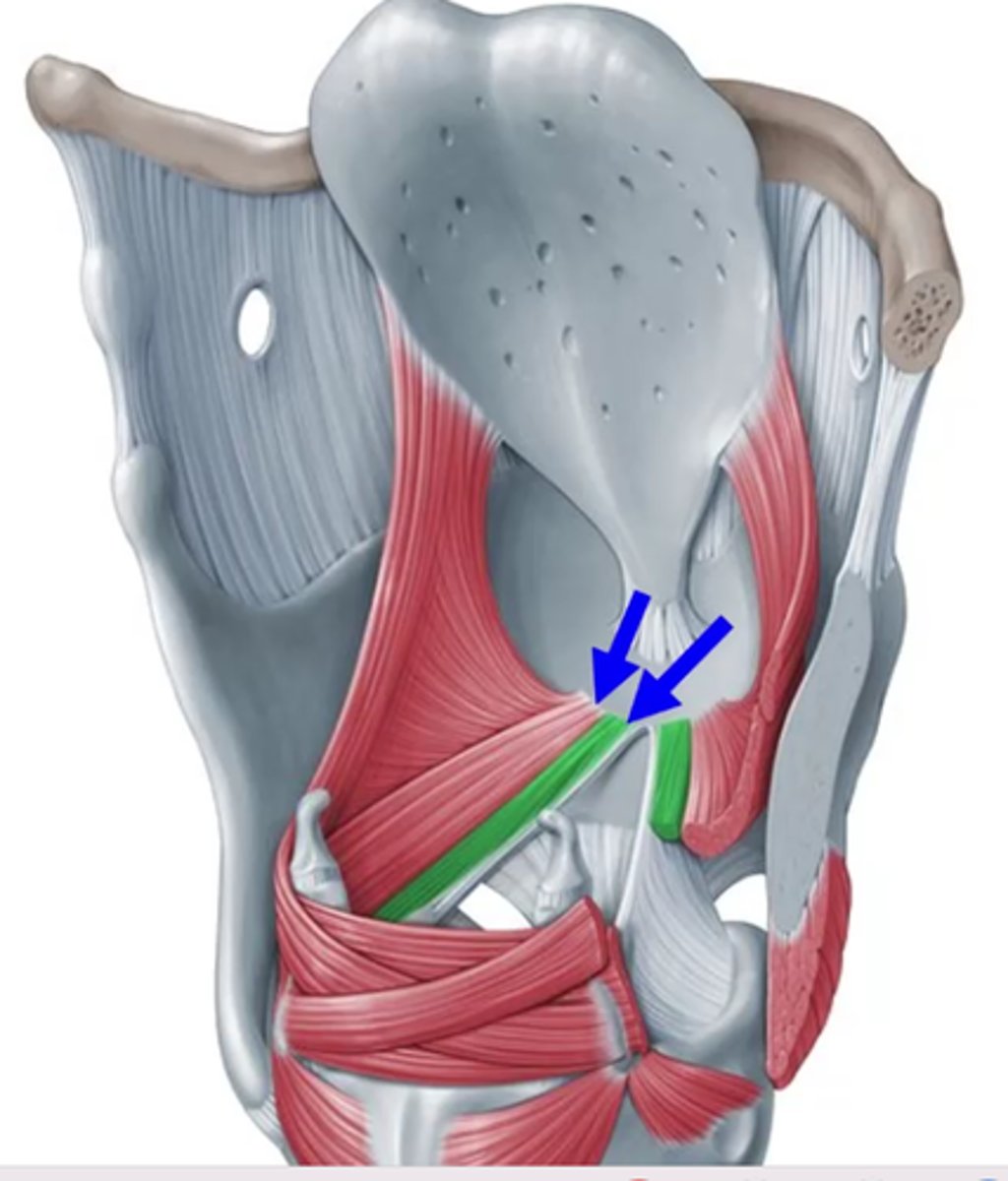
Internal thyroarytenoids attachments
thyroid (top), vocal process of arytenoid (white lining) vocal ligament (bottom)
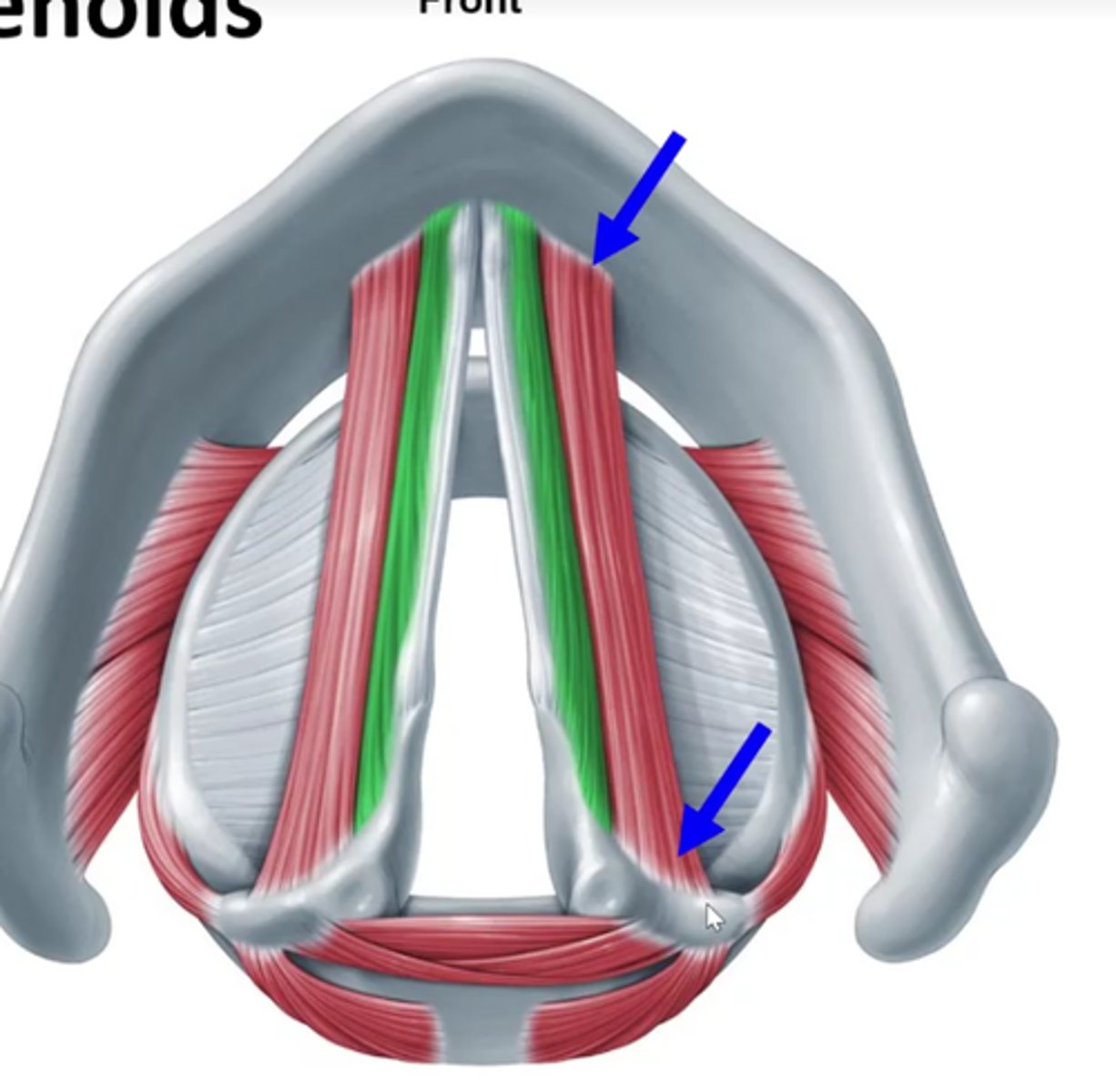
External thyroarytenoids (lateral border)
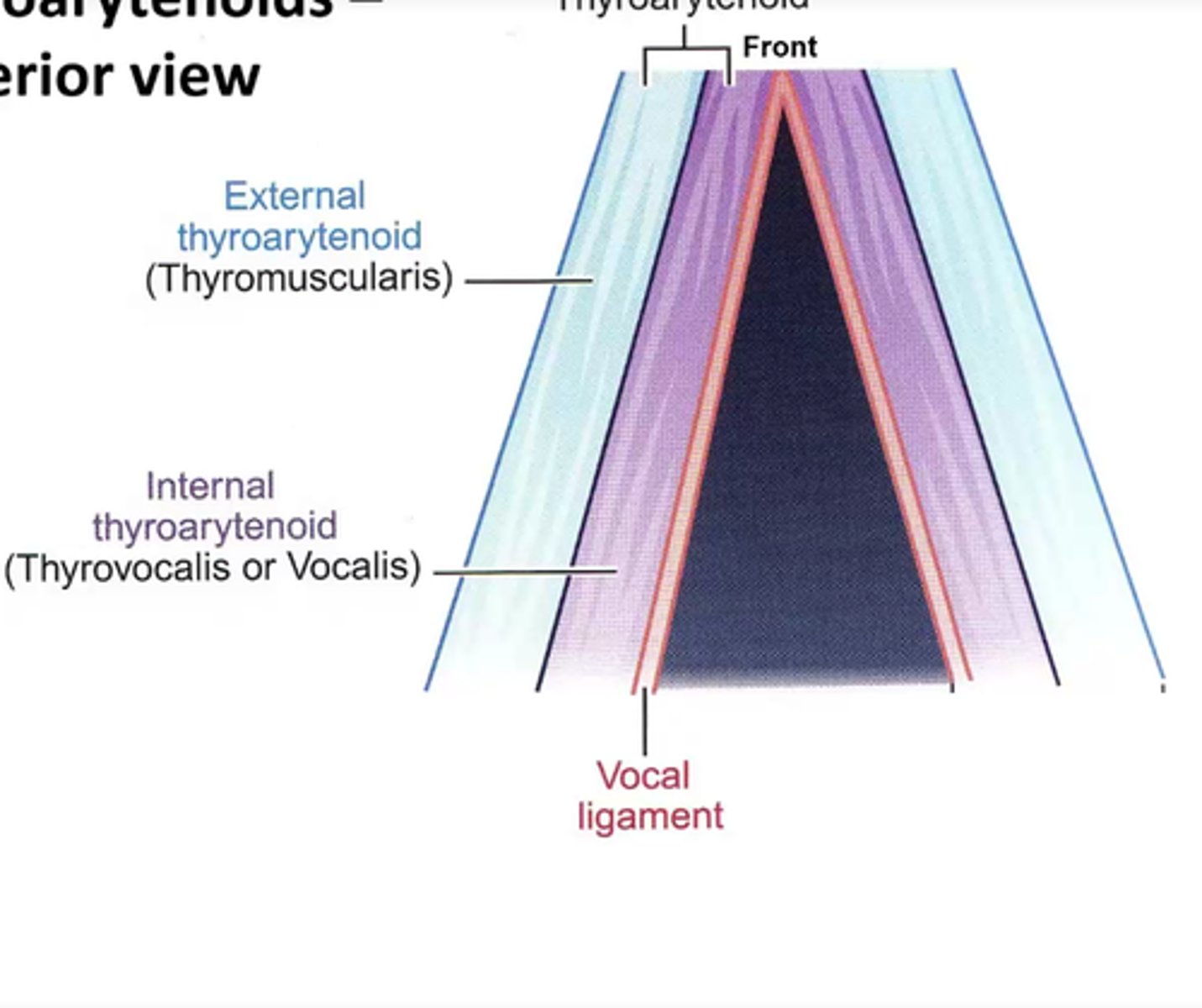
Thyroarytenoids- superior view with attachments removed
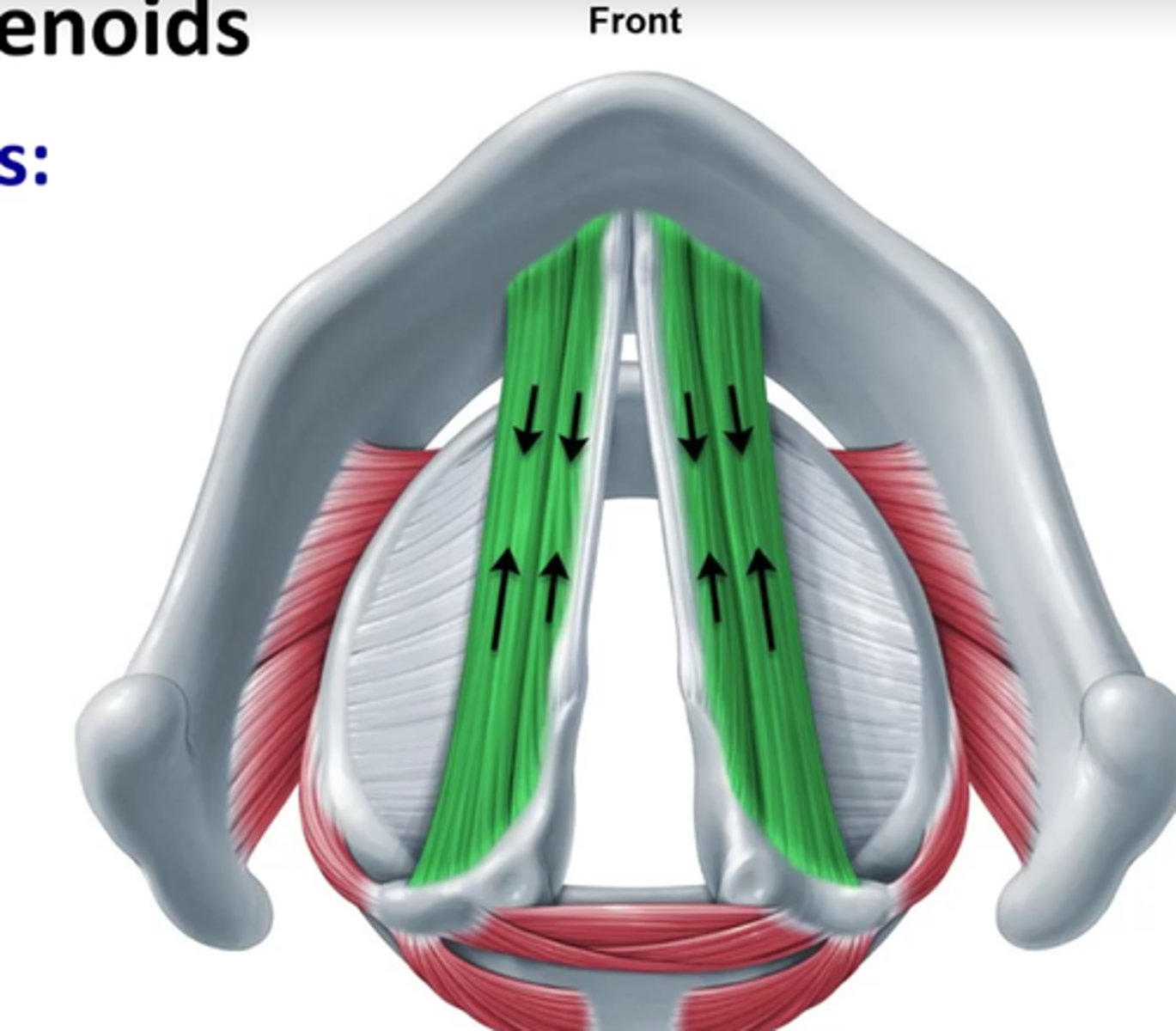
The thyroarytenoids muscles comprise _____ of vfs
bulk esp. the internal thyroarytenoid
Both thyroarytenoids have the same functions what are they? (both parts in green)
tense vfs
relax vfs
shorten vfs
What are the two parts of the cricothyroids?
Pars Recta (top- runs more straight and down)
Pars oblique (bottom-runs at an angle)
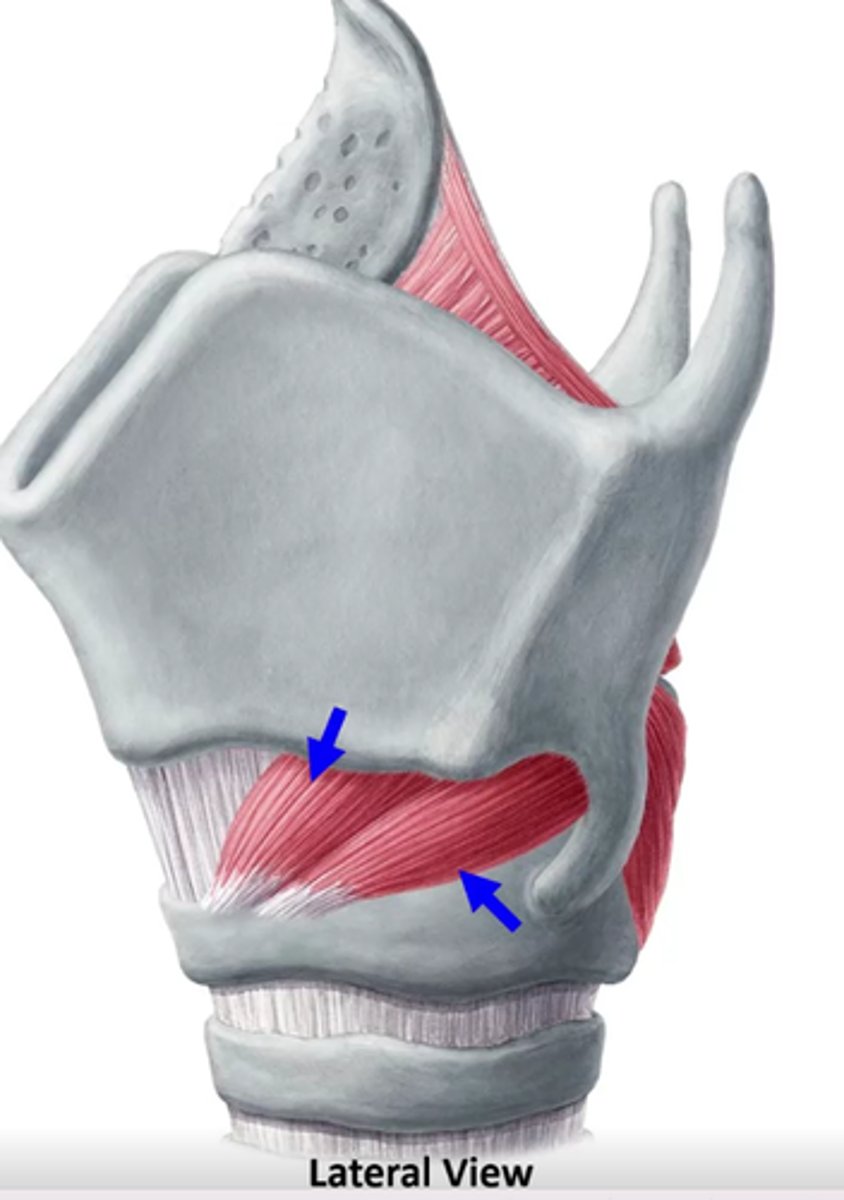
cricothyroids attachments
Cricoids (anterolateral border)- bottom arrow
thyroid- top arrow

cricothyroids function (both have the same function)
lengthen vfs
what is the result of the cricothyroids lengthening the vfs
thin and stiffen vfs
How do the cricothyroids thin and stiffen vfs
- when contracts = tips thyroid cartilage forward and cricoid tilts back which will in turn tilt arytenoids back
- when cricothyroids contract, distance between thyroid & crioid... and thus arytenoids (that sit on superior posterior border of the cricoid) increase. See 10:54 of ELC video
result of vfs lengthened, thinned and stiffened
higher pitch
a little analogy to understand cricothyroid effect on vfs- Biceps
Lengthen muscle --> appears thinner and stiffer
shorten muscle--> appears thicker and floppy
posterior cricoarytenoid
abducts vocal folds
posterior cricoarytenoid located
cricoid (posterior side)
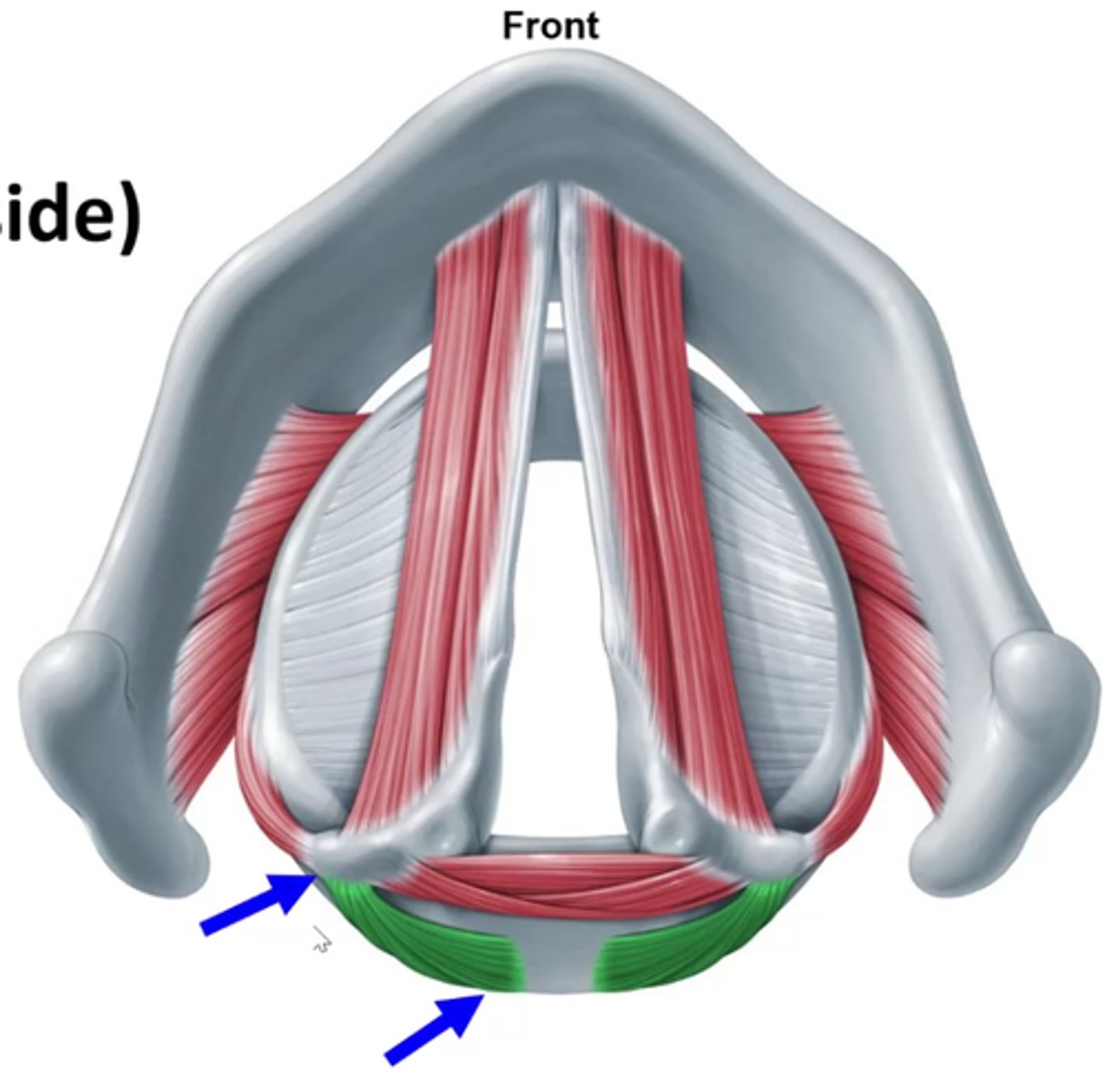
posterior cricoarytenoid attachments
cricoid (posterior side) - left arrow
muscular process of arytenoid (right arrow)
muscular process of arytenoid: Why is it called muscular process?
A lot of muscular converge on that process of the arytenoid
posterior cricoarytenoid functions: function 1
- abduct vfs (from contracting)
- used during speech for: voiceless sounds: /p/, /s/, /ch/
why do we want the vfs to abduct during voiceless sounds?
so the exhaled airstream wont cause the vfs to vibrate
posterior cricoarytenoid functions: function 2 (watch 20:49 of video for visuals)
- abduct vfs
- used for inhalation, esp deep one bc we want to get greater volume and air in (remember during inhalation muscles contract)
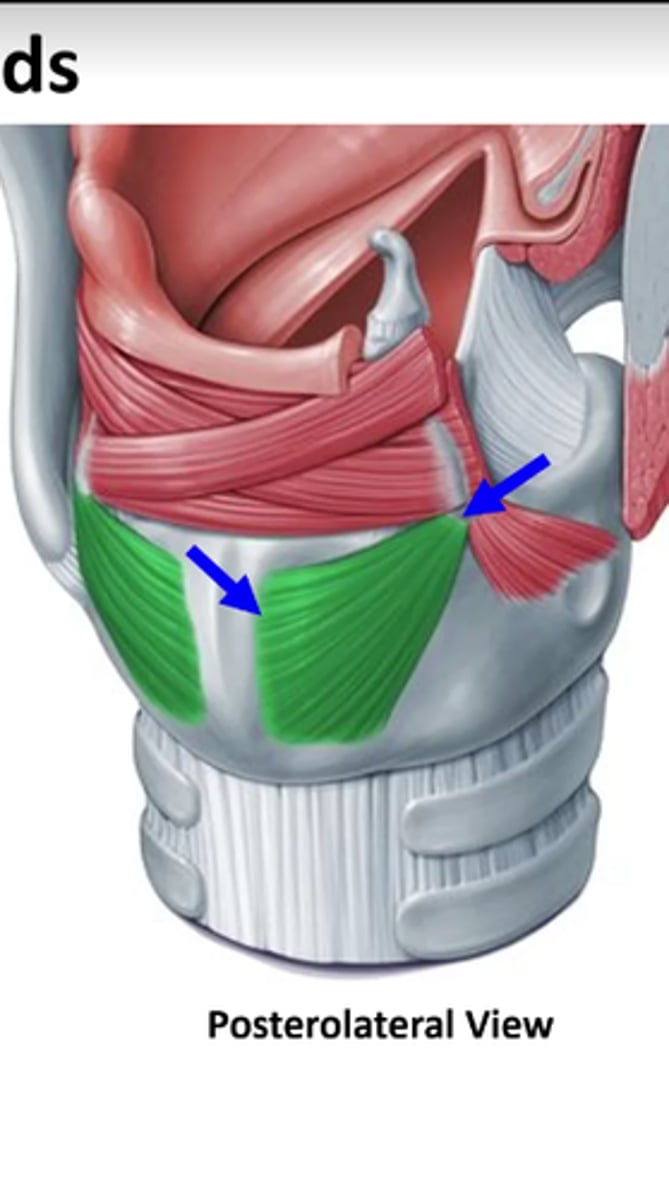
where is the lateral cricoarytenoid located? (in green)
lateral border of cricoid
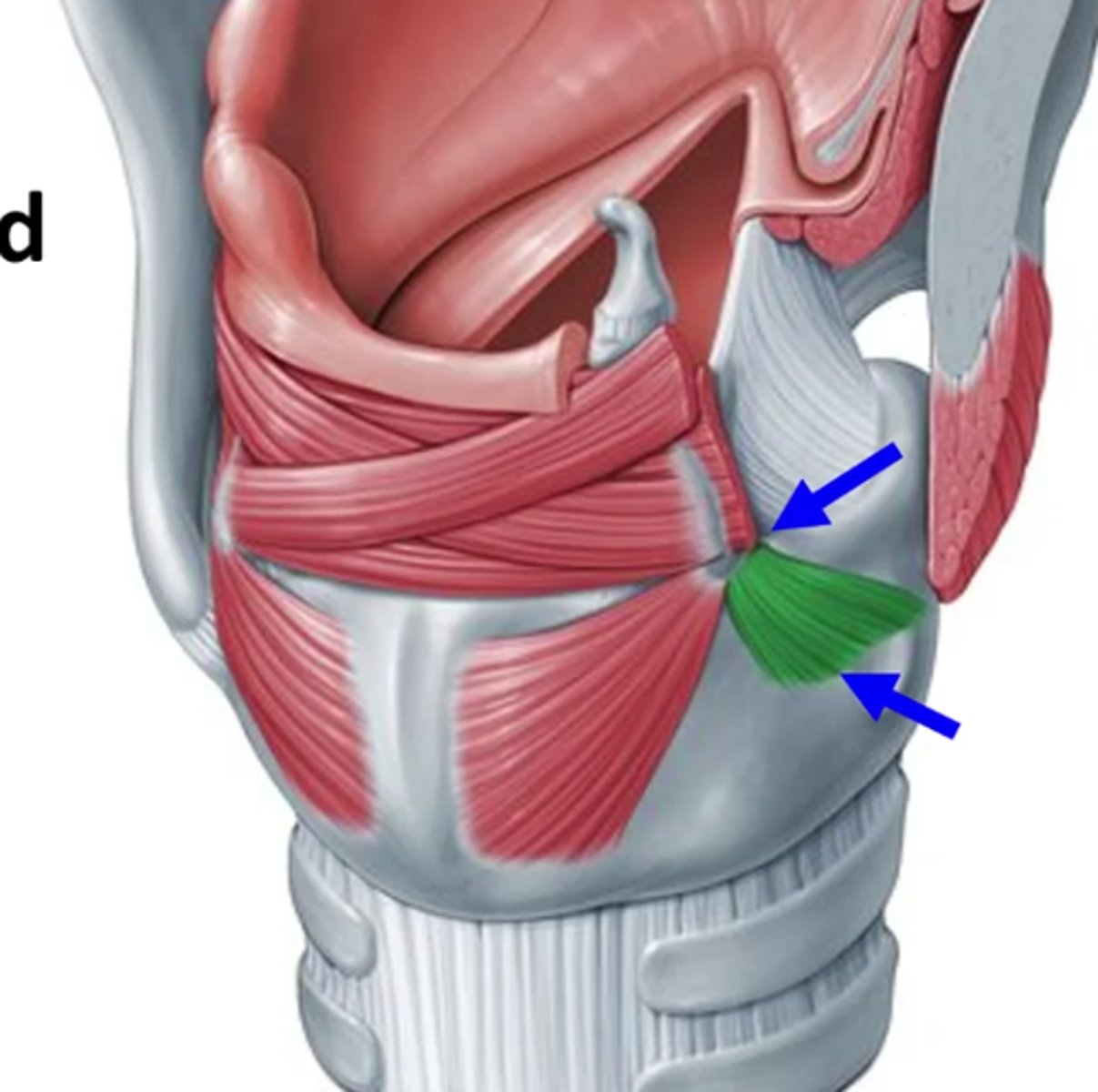
lateral cricoarytenoid attachments
lateral border of crcoid (top arrow)
muscular process of arytenoid (bottom arrow)
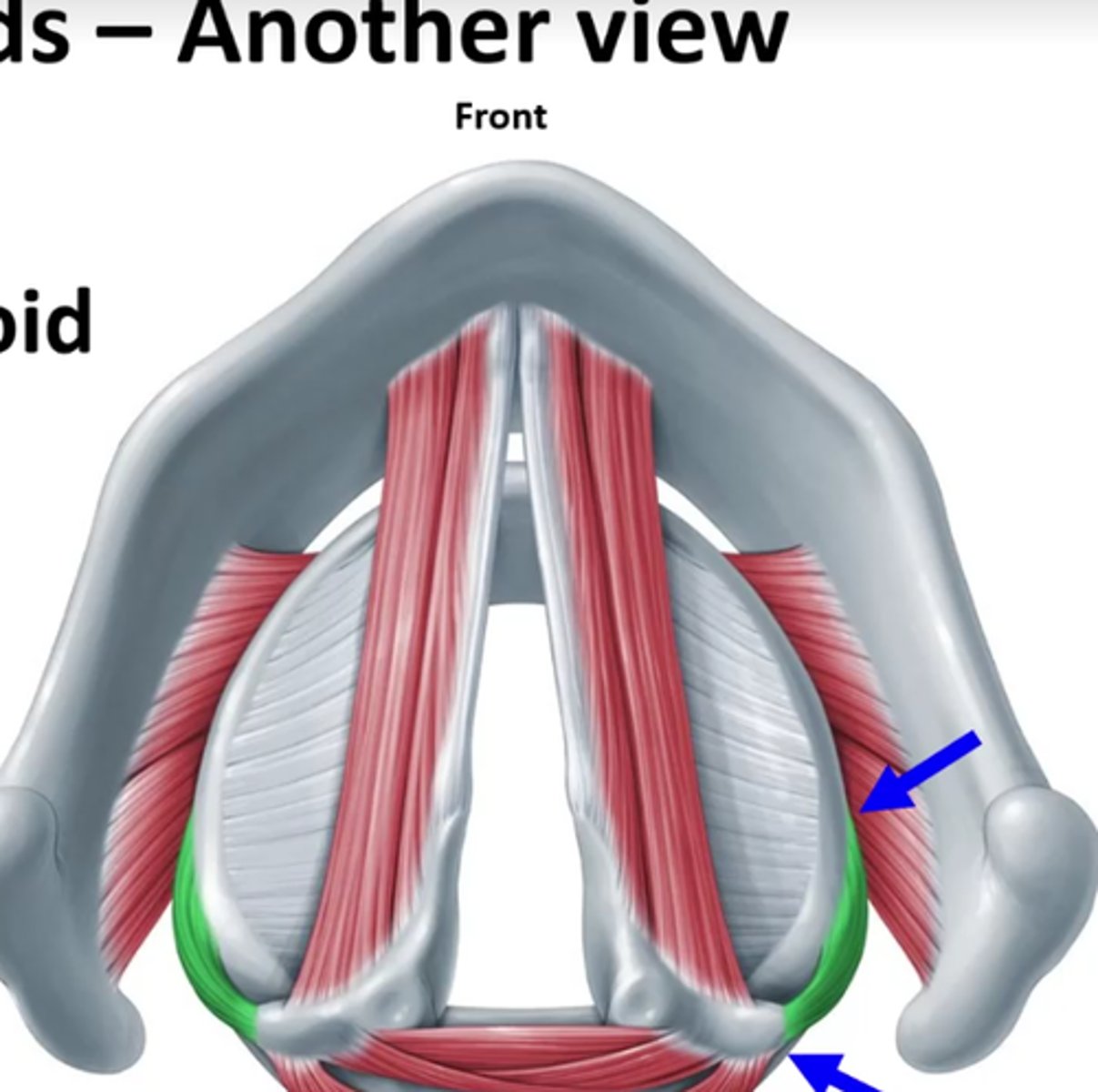
lateral cricoarytenoid function
adduct vfs (when it contracts)
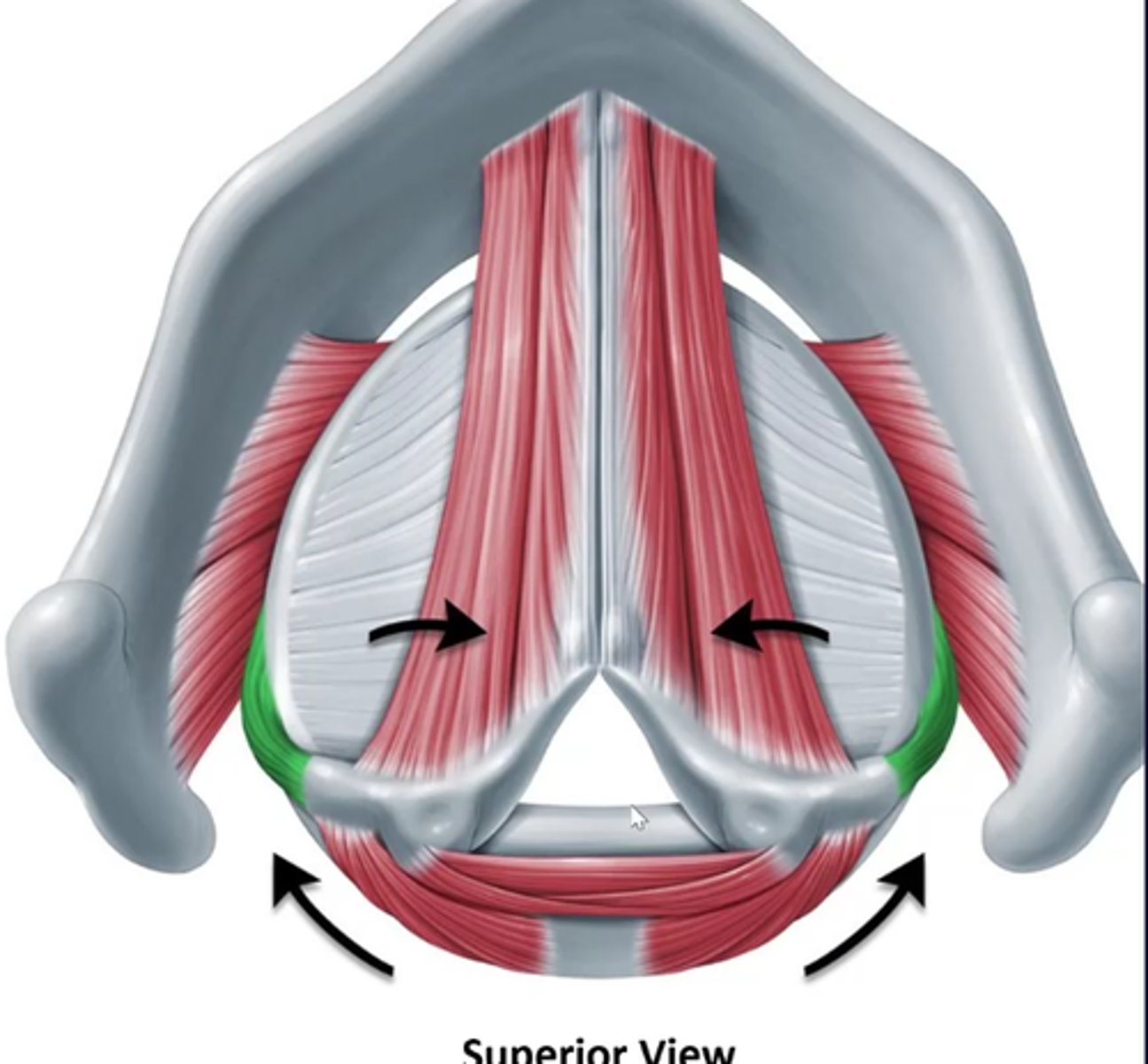
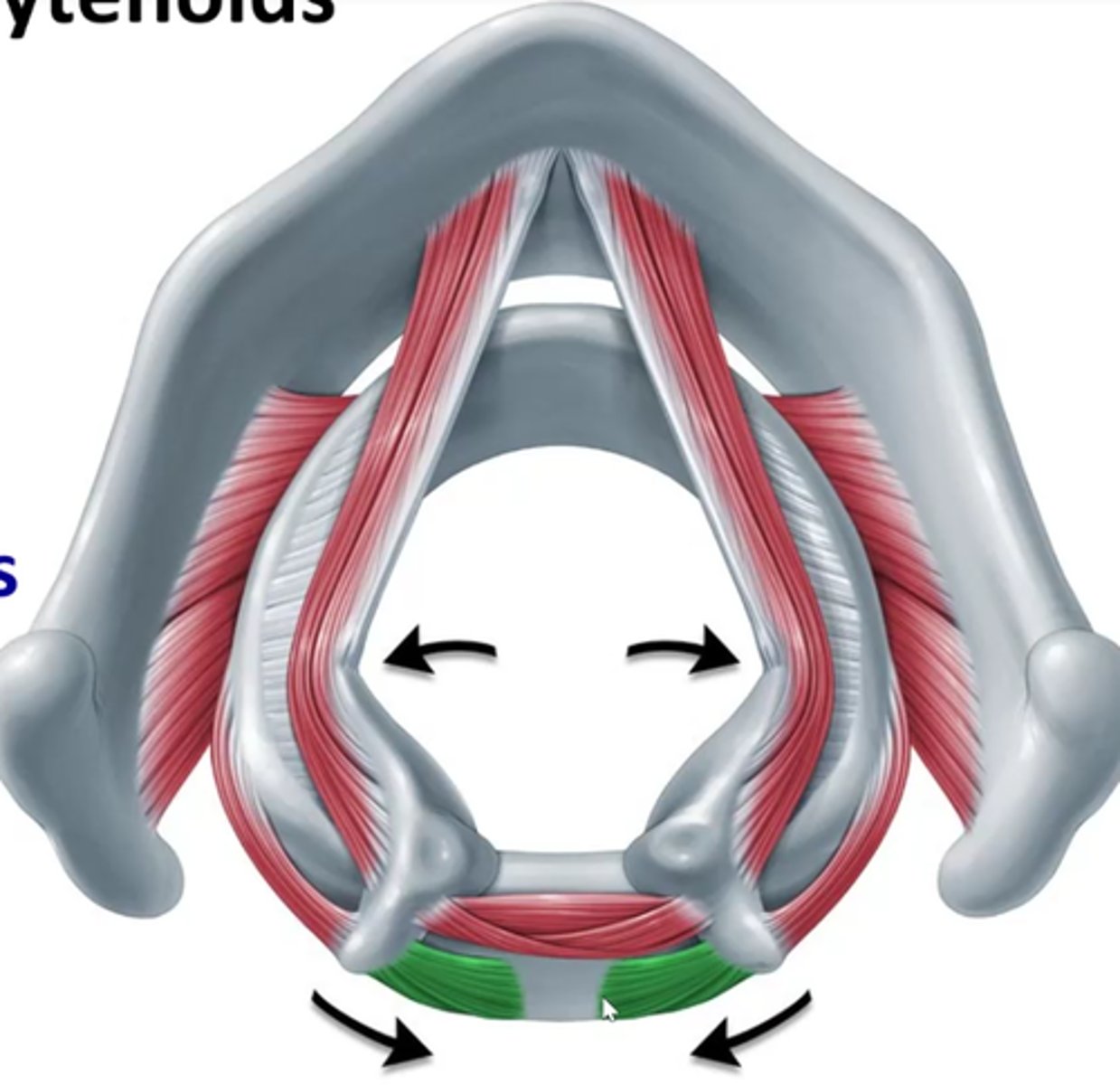
Interarytenoids (transverse and oblique)
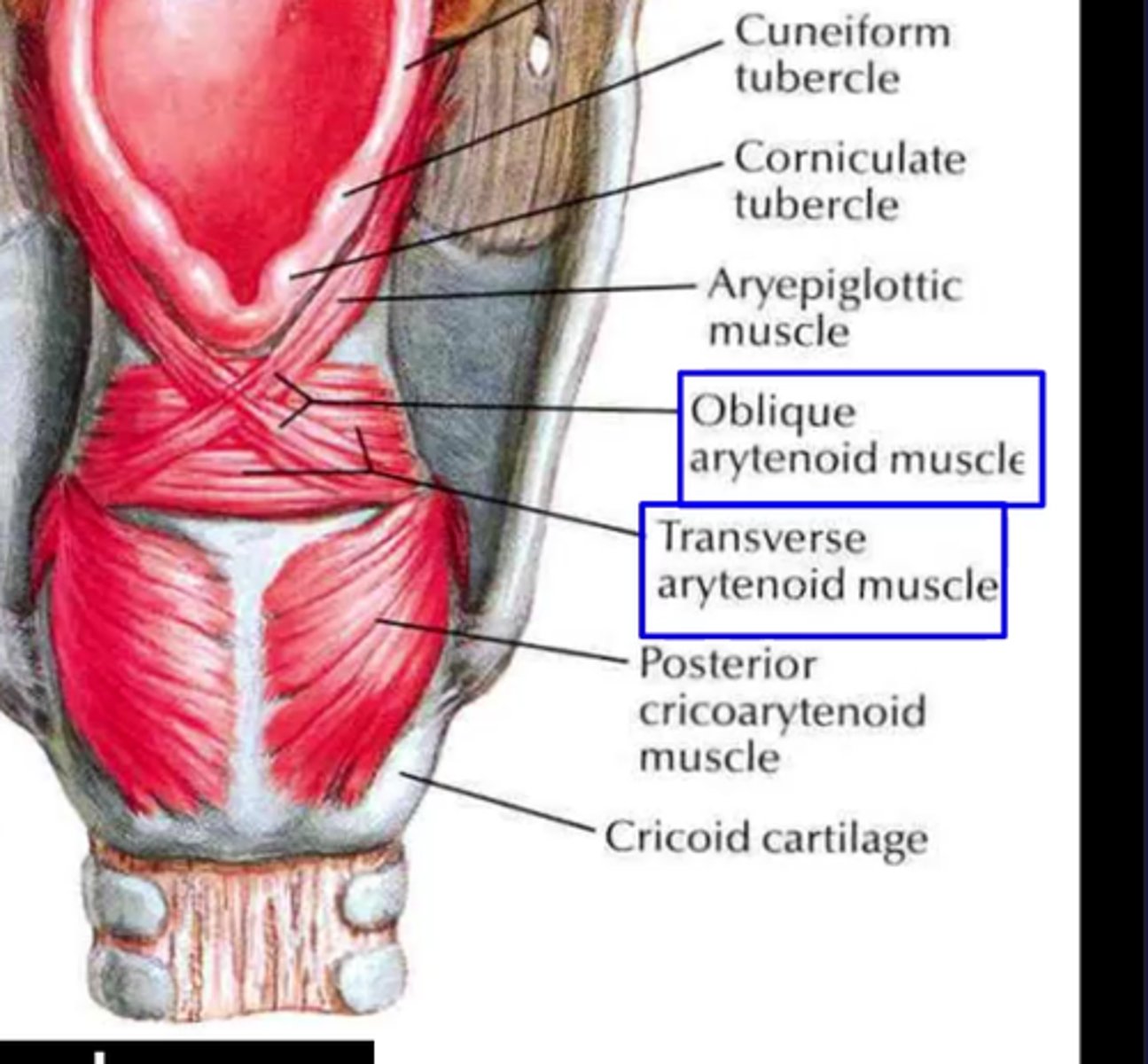
oblique arytenoids attachments
muscular process of one arytenoid (left arrow) to apex of other arytenoid(right arrow)
--- criss-cross pattern.
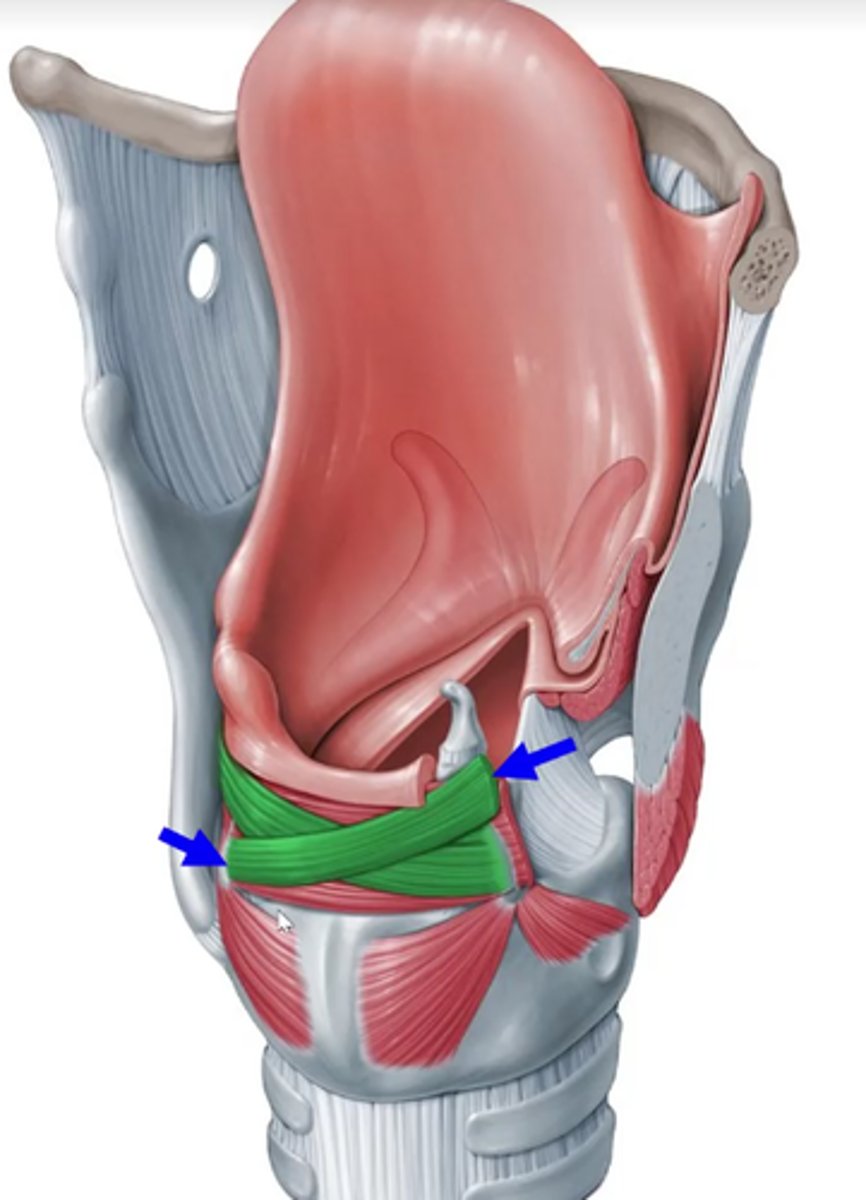
How is the transverse arytenoid unique?- deep to oblique arytenoid
- unpaired muscle
transverse arytenoid attachments
lateral border of one arytenoid
lateral border of other arytenoid
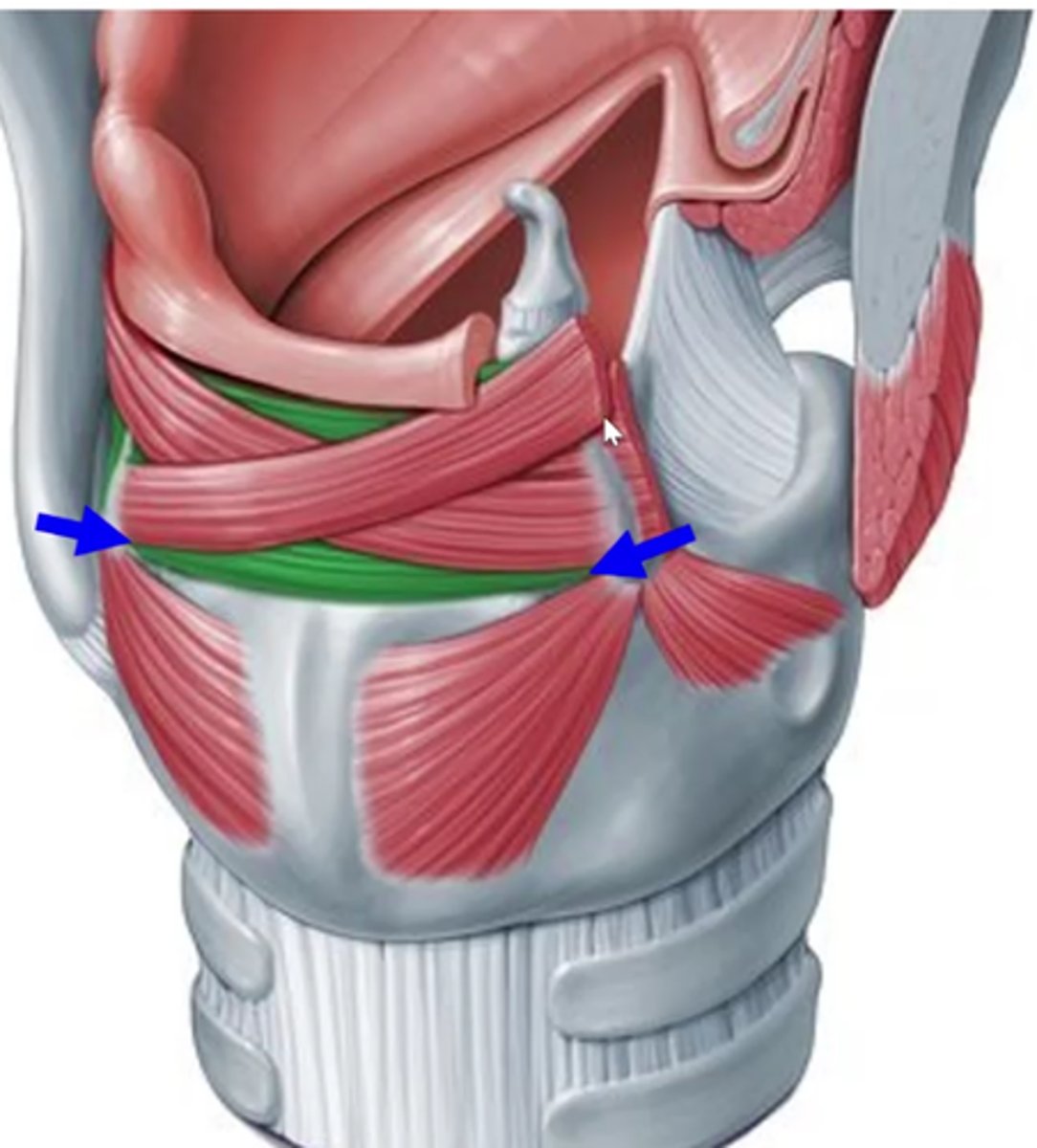
interarytenoid functions together
adduct vfs- pull apart two vocal processes of each arytenoid together as well- effectively closing off the entire glottis
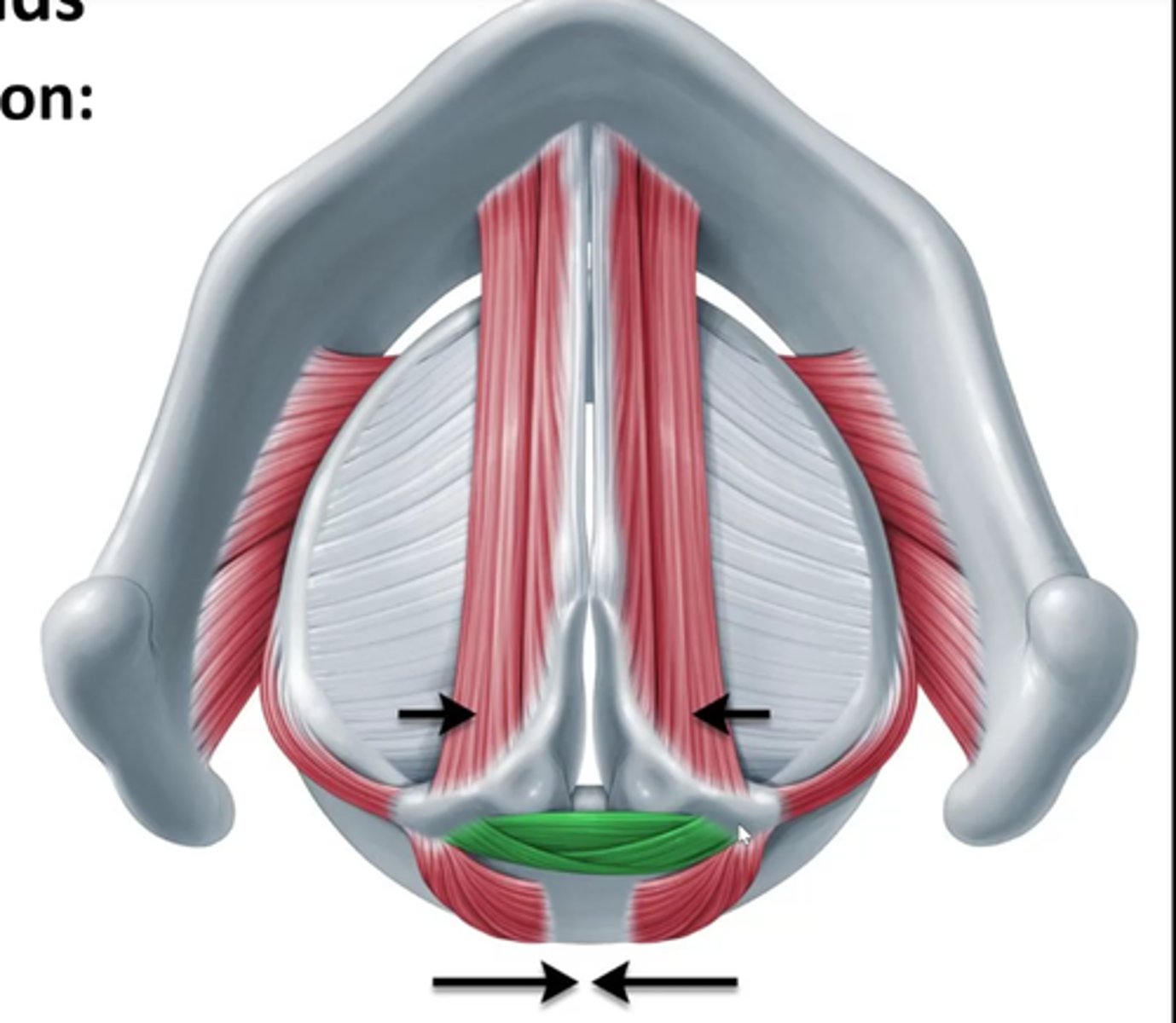
aryepiglottic muscle
deflects epiglottis over airway opening to help protect the airway during swallowing
aryepiglottic muscle location
lateral walls of supraglottal cavity (supraglottal cavity is the space above the glottis)
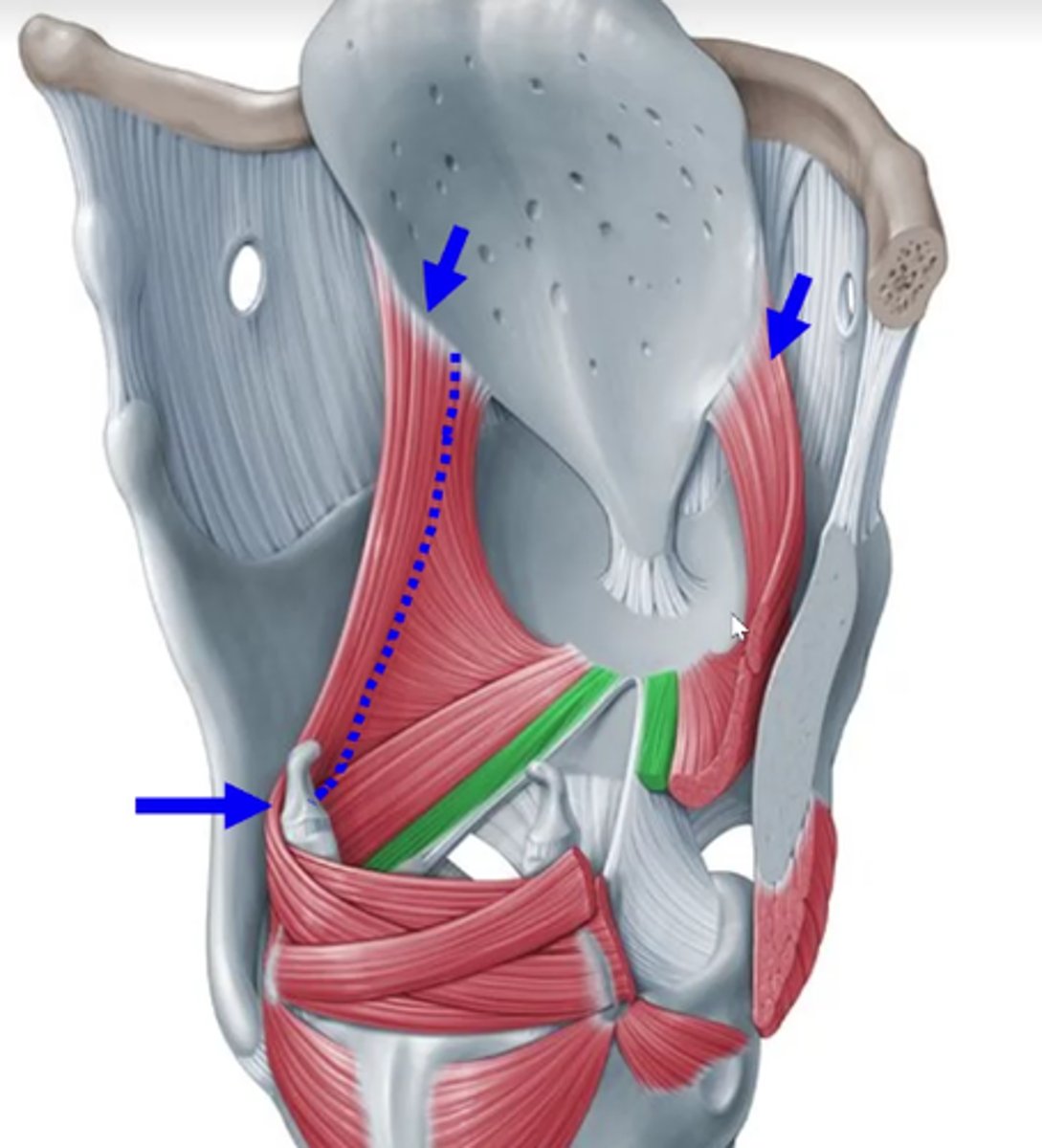
aryepiglottic muscle function
pull epiglottis down
cover/protect airway (over the top of the trachea)