2. Supply Side Policies
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
State some issues with the supply side of the economy.
- Productivity gap
- Ageing infrastructure
- Inequality
- Skill shortages
- Low investment
What are supply side policies?
Policies designed to increase the productive capacity of the economy, shifting LRAS to the right
Name the two types of supply side policy.
- Market-led policies
- State/ government interventions
What is the purpose of market led supply-side policies?
To boost LRAS by reducing the role of the government from the market to boost efficiency and competition.
Give some examples of market led supply-side policies.
- Cutting government spending
- Lowering business and income tax
- Improving flexibility of labour market
- Privatisation of state assets
- Opening economy to overseas trade
What is the purpose of government led supply-side policies?
For the government to actively intervene and have a larger role in the economy.
Give some examples of government led supply-side policies.
- State investment in public services and infrastructure
- Commitment to minimum wage/ living wage
- Progressive tax
- Active regional policy to inject demand into underperforming areas
- Selective import controls
- Management of exchange rate
State 5 disadvantages of supply-side policies.
1. Time lags
2. No guarantee of success
3. May lead to inequality of income and wealth
4. Sustainability issues
5. Expensive
What is production?
The vale of output of goods and services.
How may production be measured?
GDP or an index of production in specific industries
What is productivity and how is it measures?
A measure of the efficiency of factors or production using output per person employed or per person hour.
What is the key objective of supply side policies?
To increase productivity.
Why does an increase in production not automatically mean an increase in productivity?
As it depends on how many factors of production have been utilised to supply extra output.
What factors may negatively impact productivity?
- Lack of investment
- Financial crisis
- Underemployment
- Skill gaps
- Low government spending
What are the 6 main causes of a productivity gap within the UK?
- Low rates of capital investment
- Banking crisis
- Slowing innovation
- Skill shortages in key industries
- Low levels of market competition
- Low aggregate demand and lots of spare capacity.
Draw a long run aggregate supply diagram.
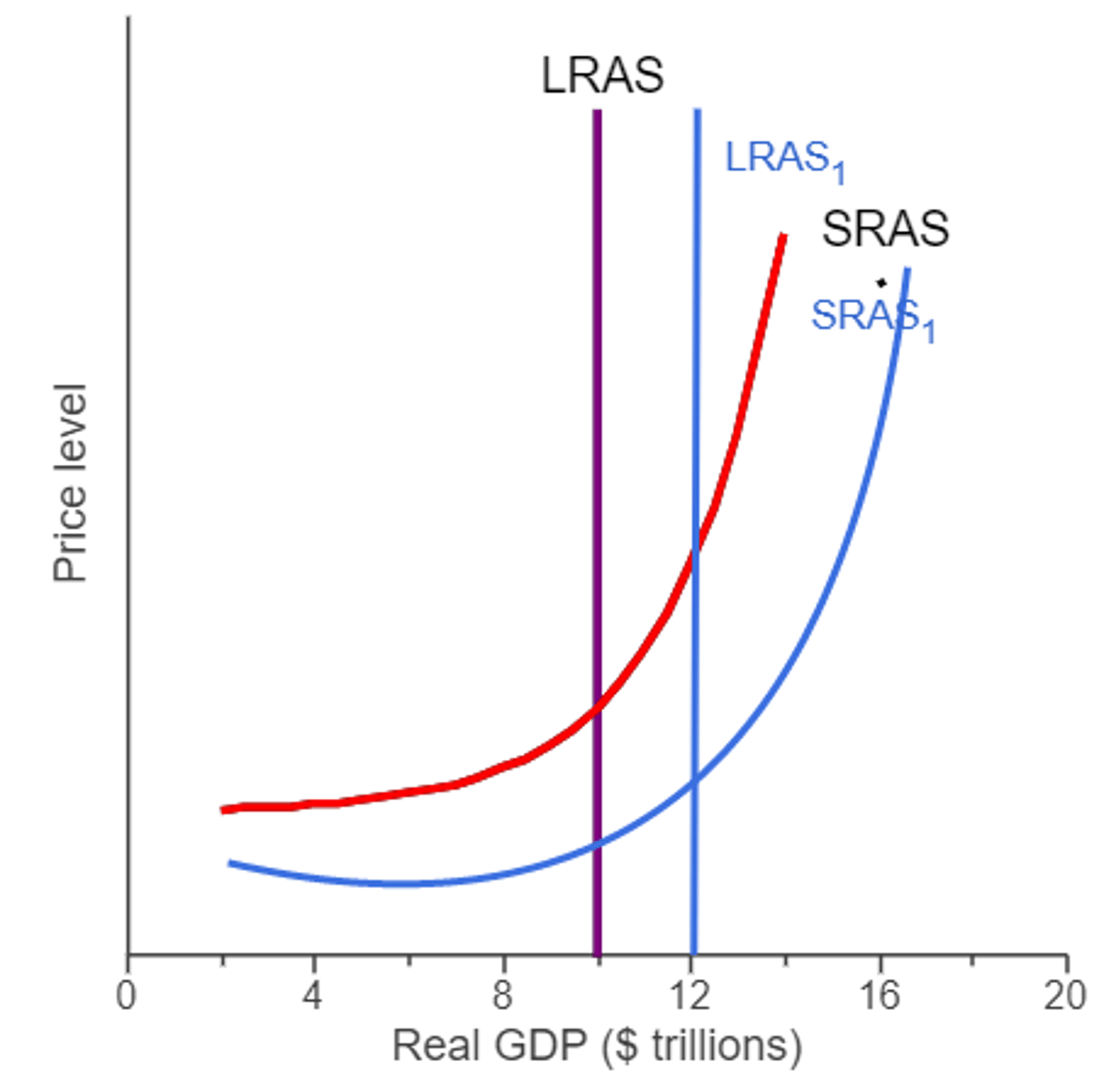
State 5 economic advantages of higher productivity.
1. Lower unit costs
2. Improved competitiveness
3. Higher profits
4. Higher wages
5. Economic growth.