Chem 103 Chapter 2 Matter and Energy
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
the universe is compromised of
matter and energy.
Matter exists at all scales – from galaxies to atoms
Vera Rubin (1928–2016)
First to find evidence of dark matter.
Revolutionized the field of
cosmology.
Won 1993 National Medal of
The universe is comprised of
What is Matter?
Anything that occupies
space and has mass.
• All matter is made up of
atoms.
• Atoms may bond together
to form molecules.
perspective of atoms
they are incredbly small. Imagine this:
• Take a little pebble.
• If every atom in that pebble were the size of the pebble itself...
• That “pebble” would end up bigger than Mount Everest!
Modeling Atoms and Molecules
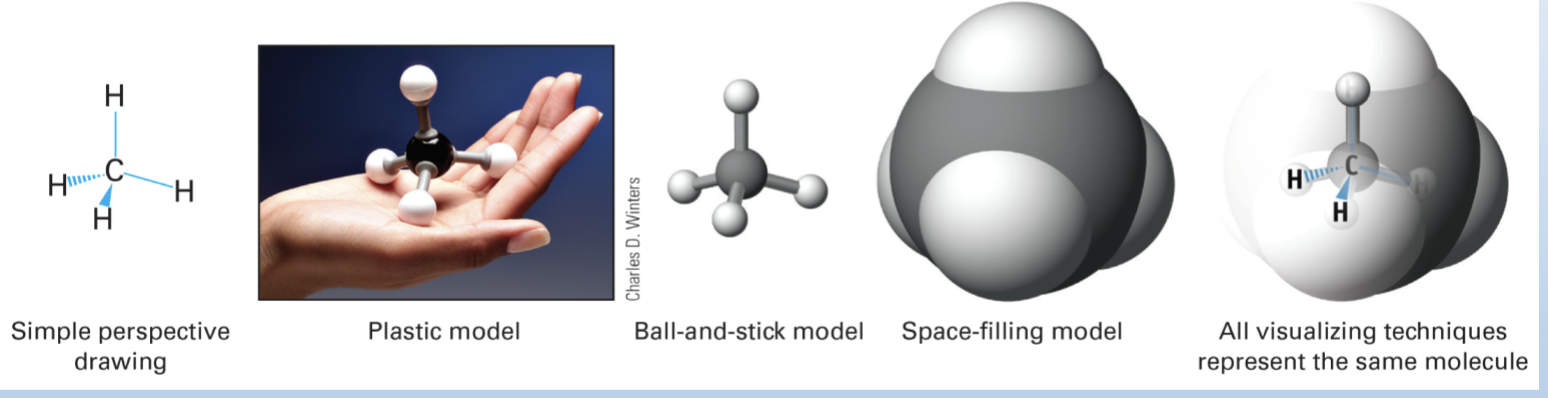
Three diff types of matter
liquid, solid, gas
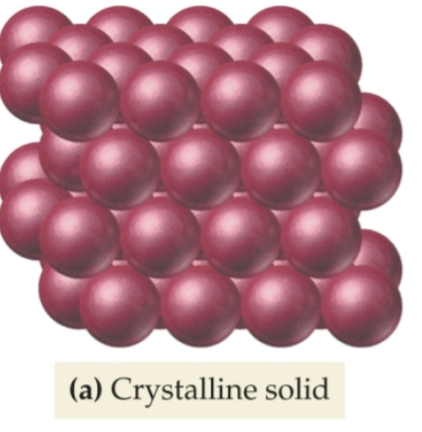
one out of the two types of solids
Crystalline:
• Atoms/molecules arranged in neat,
repeating patterns
• Examples: snowflakes, salt, diamonds
second type of solid
Amorphous solid:
• Atoms/molecules are jumbled; no long-
range order
• Examples: glass, rubber, plastic

Matter can go under physical change. What is physical change?
the appearance changes, but the molecule remains the same
ex: Ice → water → steam
• all still H₂O
• Ripping paper in half
• both halves are still paper.
ex: The substance stays the same chemical, but its form changes.
• Example: melting ice, dissolving sugar, grinding coffee
matter: physical properties
Physical properties are observed by watching physical changes.
ex: Things you can observe or measure without changing what the substance is.
• Example: color, odor, size, conductivity, electric charge, boiling point, melting point.
matter: chem change (reaction)
The matter changes
into new molecules or splits into atoms.
• Water zapped with electricity →
splits into H₂ + O₂ gas.
• Copper left outside → reacts with air
→ turns green (copper oxide)
Atoms rearrange to create a new substance.
• Example: rusting iron, burning coal.
• ᾟA color change often indicates a chemical change.
matter: chem properties
can only be
determined through chemical changes.
The ability (or inability) for a chemical to undergo a chemical change.
• Example: ability to rust, burn/combust, decompose into new substances
Matter: Pure Substances
• Only one type of molecule.
• Pure water, oil, ethanol etc.
cannot be seperated into other substance by physical means
ex: phys means, filtration, evaporation, and distillation
if its a chem formula (H20l NACL, Co2) is a pure substance
Mixture
• Two or more pure
substances mixed together.
• Salt water, mud, tea, air etc.
consists of two or more pure substances that can be seperated by physical means.
for ex: salt in salt water can be seperated from the water by allowing the water to evaporate
words such as (saltwater, soda, trail mix) mixture
Most substances are
mixtures
Mixture: composed of two or
more types of molecules.
• Air contains primarily nitrogen
and oxygen.
• Seawater contains primarily
salt and water
Types of Mixtures—homogenous mixtures:
The same throughout. LOOKS UNIFORM
• Dissolved mixtures are called solutions.
• Examples
• Salt water
• Air
soda (water, sugar, co2, flavor, wine)
steel (iron + carbon)
solutions are homogenous mixtures. liquid solutions are trasnparent then cloudy
Types of Mixtures—-heterogeneous mixtures
Different parts, or phases, are visible.
• Examples
• Oil and water
• Pizza
salad
sand + water
cereal in milk
does not have a uniform appearance at macroscopic level
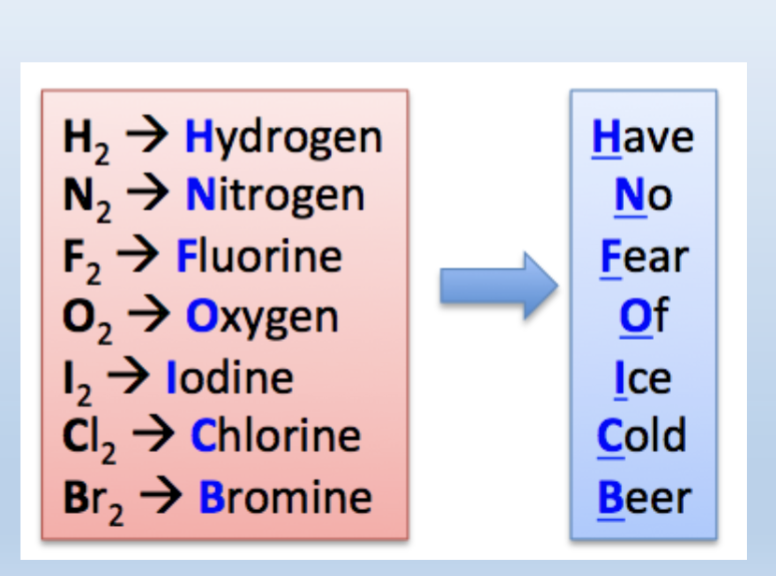
Diatomic Elements
major elements in the human body
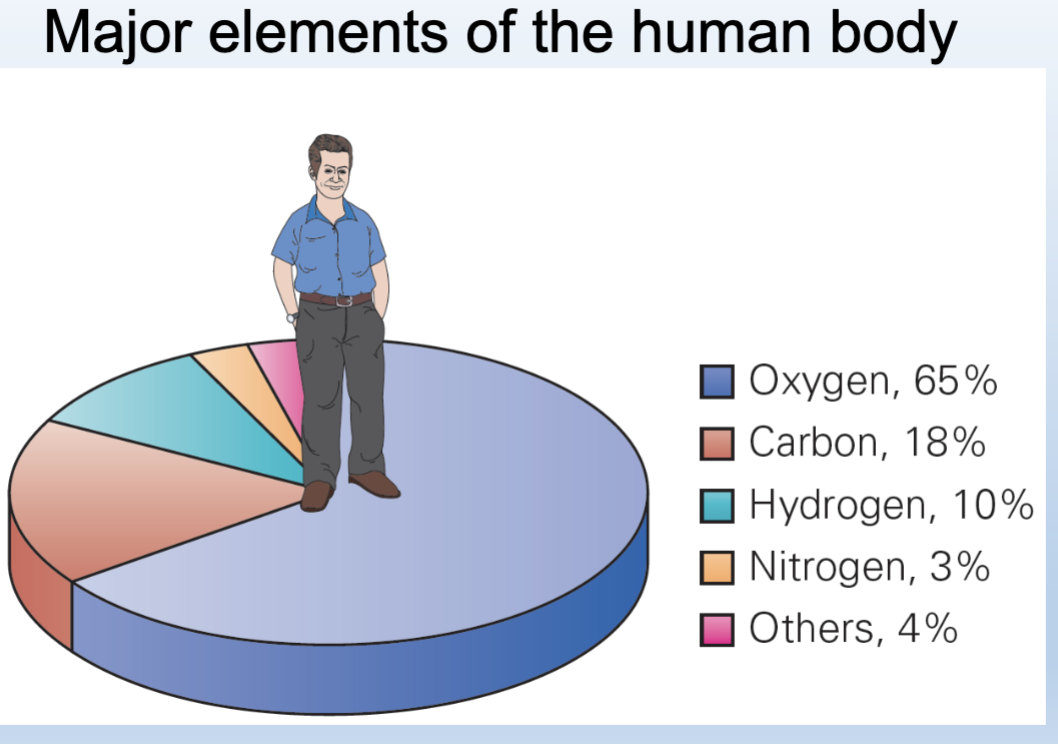
compounds
combination of elements. two or more elements. can be seperated.
Pure substance that can be decomposed
into two or more other new substances.
• Elements combine to form
compounds.
• Atoms in a compound are always
bonded in a set ratio
• Ex: water is always 2 H + 1 O (H2O)
• Compounds have different properties
than the elements they come from.
• Sodium (Na) = explosive metal ᾟ
• Chlorine (Cl2) = poisonous gas ᾟᾟ
• NaCl → table salt = safe & tasty ᾟ
elements
one singular thing that cannot be seperated into smaller things
particles (atoms) are the same elements
filtration
seperation of liquids and solids
Use a barrier (filter paper/strainer) to
trap solids but let liquids flow through
Distillation
Seperation of Solutions
Evaporate one a component of the mixture
without evaporating the other components.
• Boil it, catch the gas, cool back to liquid
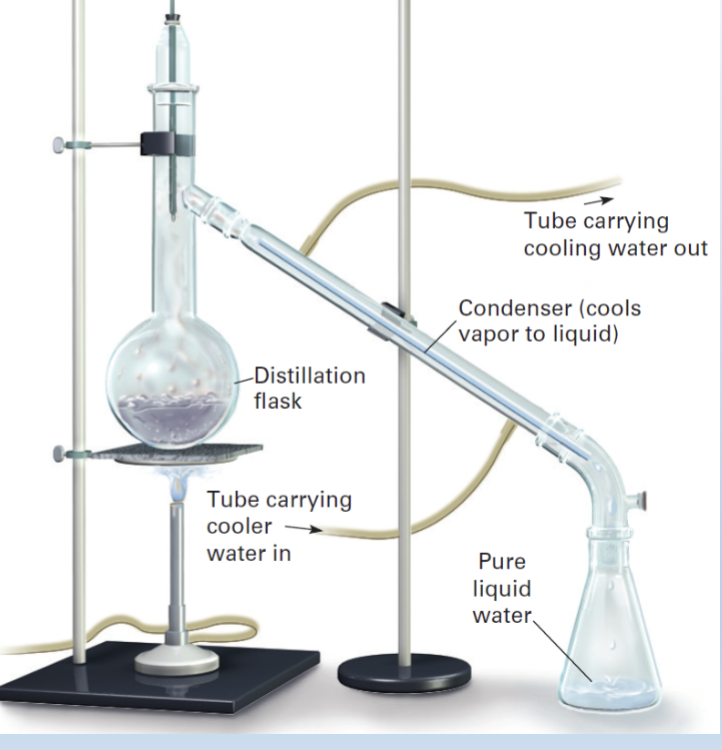
distilled water
Water purified by distillation
Mixtures can be separated
physically (filtering, distilling)
Compounds can ONLY be broken apart by
a chemical reaction
Decomposition of Water
Water (H₂O)
1. Zap it with electricity ᾟ
2. Splits into hydrogen + oxygen
gases.
This is a chemical change.
• The water molecules are now
hydrogen and oxygen molecules.
Chemical Equation
• Representation of a chemical change
• Reactants: Original substances
• Products: New substances formed
Carbon + Oxygen gas —→Carbon dioxide gas
Reactants Product
Chemical reactions
use or produce energy
chem reaction: potential energy
Energy stored in chemical bonds between atoms of a substance.
chem reactions: kinetic energy
Energy associated with movement.
• Temperature is a measure of the kinetic energy in atoms/molecules
energy in chem change: exothermic reaction
Releases energy into the environment
Butane reacts with oxygen
→ Chemical bonds break
→ stored energy is released (heat + light)
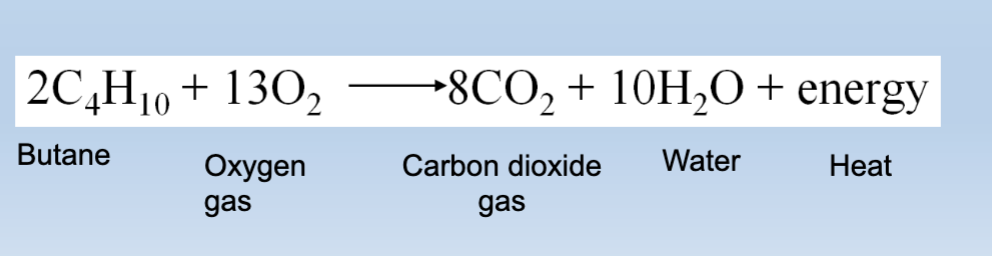
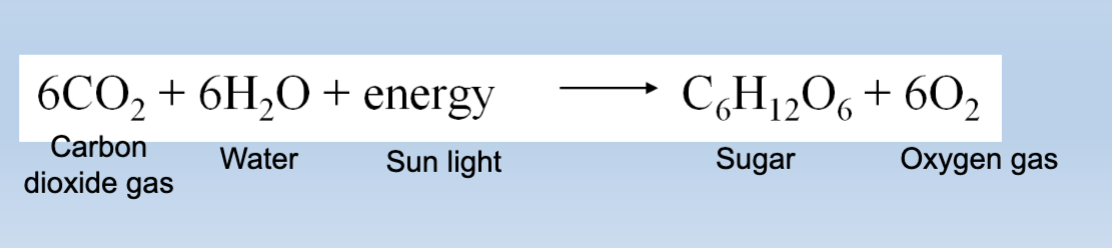
energy in chem change: endothermic reactions
Absorbs energy from the environment.
Photosynthesis
→ plants absorb energy (sunlight ☀)
→ new molecules are built (bonds are created)
The Laws of Conservation
Both matter and energy are always conserved
Law of Conservation of Mass
The total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products
Law of Conservation of Energy
The total energy of the reactants is equal to the total energy of the products.
• Potential energy (stored in bonds) may change to kinetic (heat) or vice versa
Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy
The total amount of mass and energy in the universe does not change.
to seperate sugar out of tea
evaporate water
seperate oil and water
by boiling water, evaporate