Physio+Lecture+2+-+Cell+Interactions+with+Environment (copy)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Based on what you know, explain the extracellular environment and how cells communicate with it
the extracellular environment refers to everything outside the cells. cells get nourishment from the ECE and release waste into it that’s how they communicate with it. Cells also communicate with each other by secreting chemical regulators into the ECE.
what is the most abundant solvent
Water
how does transport occur in the body
it occurs btw intracellular and extracellular compartment across plasma membrane
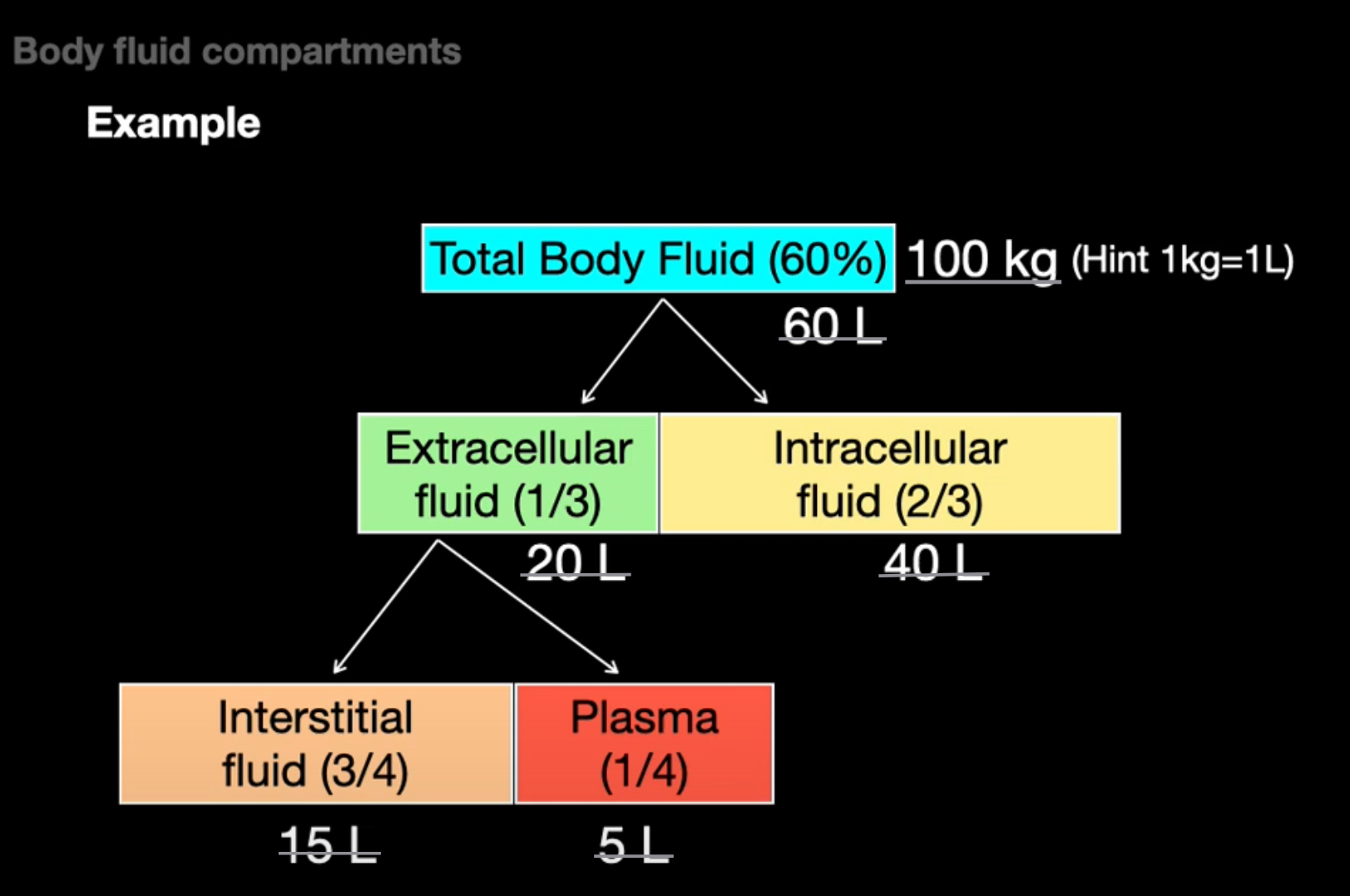
how is water compartmentalized in the body
in the body the water is separated into 2 compartment; the intracellular and extracellular fluid.
select the right % of intracellular fluid in the body
A) 10%
B) 70%
C) 65%
D) 67%
D
select the right % of extracellular fluid in the body
A) 30%
B) 33%
C) 25%
D) 10%
B
what is an adult total body of water
the TBW makes up 60% of an adult body weight
what is the the plasma membrane
it is a selectively permeable membrane that allows certain substances to move in and out of the cell by crossing it (membrane is dynamic)
Why is the plasma membrane permeable to small, uncharged polar molecules even though the interior of the membrane is hydrophobic?
because those uncharged polar molecules can move thru the gaps of the bilayer when it moves
Is the plasma membrane permeable to nucleic acids, proteins and structural molecules
generally no because they are large polar charged and hydrophilic molecules
how do large molecules like protein go thru the plasma membrane
large molecules like protein can thru with the help of carrier proteins
list the 2 ways movement across the plasma membrane can be categorized
movement can be categorized by energy, (what our class used) or by whether carrier proteins are required
explain what passive transport is and list its subsets
passive transport is spontaneous, requires no energy (downhill movement) its subsets are: simple diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion (carrier or channel mediated)
as you probably know when it comes to simple diffusion, the larger the surface area the faster the rate of diffusion. Give an example of something that can increase the surface area and where can we find them
Microvilli are an example of something that can increase membrane surface area we can see them in the digestive system
Most water molecules that cross the plasma membrane do so by
A) diffusion through the plasma membrane.
B) diffusion through ion channels.
C) diffusion through aquaporins.
D) active transport by ion channels.
E) active transport by aquaporins.
C
what is the optimal distance for simple diffusion
A) 25µm
B) 440µm
C) 90µm
D) 100µm
D
what’s the name of solute that cannot pass the plasma membrane which permits osmosis
A) glial cells
B) amino acids
C) osmotically active
D) osmotically inactive
C
what is active transport and what are its subsets
active transport is the movement of ions against (uphill) their concentration gradient (needs ATP). Its subsets are: primary active transport and secondary active transport
which ion is affected by the contraction of muscle in our body
A) Calcium
B) potassium
C) oxygen
D)Sodium
A
Which of the following statements correctly distinguishes between primary active transport and secondary active transport?
A) Primary active transport uses ATP directly, while secondary active transport uses the energy from electrochemical gradients (often created by primary active transport) to move ions.
B) Primary active transport moves molecules against their concentration gradient, while secondary active transport only moves molecules along their concentration gradient.
C) Primary active transport involves protein pumps, while secondary active transport uses only channel proteins.
D) Primary active transport is faster than secondary active transport.
A
what are the subsets of bulk transport
its subsets are: endocytosis and exocytosis