ap bio unit 5 college board mcq
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
A model of crossing over during gamete formation is shown in Figure 1.Based on Figure 1, which of the following questions could best be addressed?
A.Does synapsis of homologous chromosomes in the parent cell contribute to an increase in genetic diversity in the daughter cells?
B.Do sister chromatids separate and form diploid daughter cells?
C.Do chromatids from nonhomologous chromosomes rearrange to produce identical daughter cells?
D.Does synapsis of nonhomologous chromosomes produce
A.Does synapsis of homologous chromosomes in the parent cell contribute to an increase in genetic diversity in the daughter cells?
Huntington’s disease has been traced to the number of CAG repeats in the HTT gene, which is located on chromosome 4. The phenotypic influence of individual alleles with different numbers of repeats is shown in Table 1.
Which of the following is most likely the immediate cause of the first appearance of Huntington’s disease in a person?
Responses
A.A point mutation occurs in the HTT gene.
B.The first appearance of the CAG repeat occurs in the HTT gene.
C.An allele with more than 39 CAG repeats was inherited by the affected person.
D.The person inherited two alleles that each contained 20 CAG repeats.
C.An allele with more than 39 CAG repeats was inherited by the affected person.
In anaphase I of meiosis, cohesion between the centromeres of sister chromatids is maintained while homologous chromosomes migrate to opposite poles of the cell along the meiotic spindle as represented in Figure 1.A compound that prevents the separation of the homologous chromosomes in anaphase I is being studied. Which of the following questions can be best answered during this study?
Responses
A.Will the cells produced at the end of meiosis still be genetically identical to each other in the presence of this compound?
B.Will the long-term development of the individual be affected by this meiotic error?
C.When do the centrosomes start to move apart during meiosis I as compared to meiosis II?
D.Is there a pattern to the movement of homologous chromosomes in the presence of this compound?
D. Is there a pattern to the movement of homologous chromosomes in the presence of this compound?
When a mustard plant seedling is transferred to an environment with higher levels of carbon dioxide, the new leaves have a lower stomata-to-surface-area ratio than do the seedling's original leaves.
Which of the following best explains how the leaves from the same plant can have different stomatal densities when exposed to an elevated carbon dioxide level?
Responses
A.Increased photosynthesis leads to larger leaves that need more stomata for photosynthesis, leading to an increase in stomatal density.
B.Leaf growth is promoted through increased photosynthesis, but the genetically regulated rate of stomatal production is not altered, leading to a decrease in stomatal density.
C.Leaf growth is inhibited by decreased photosynthesis, and the genetically regulated rate of stomatal production remains the same, leading to an increase in stomatal density.
D.Leaf growth is inhibited by decreased photosynthesis, and the genet
B.Leaf growth is promoted through increased photosynthesis, but the genetically regulated rate of stomatal production is not altered, leading to a decrease in stomatal density.
Rubber rabbitbrush plants display heritable variation in plant height and insect-induced gall formation.The researchers calculated a chi-square value of 29.25. If there are three degrees of freedom and the significance level is p=0.05, which of the following statements best completes the chi-square test?
A.The critical value is 0.05, and the null hypothesis cannot be rejected because the calculated chi-square value is greater than the critical value.
B.The critical value is 0.05, and the null hypothesis can be rejected because the calculated chi-square value is greater than the critical value.
C.The critical value is 7.82, and the null hypothesis cannot be rejected because the calculated chi-square value is greater than the critical value.
D.The critical value is 7.82, and the null hypothesis can be rejected because the calculated chi-square value is greater than the critical value.
D.The critical value is 7.82, and the null hypothesis can be rejected because the calculated chi-square value is greater than the critical value.
Students carry out a genetics experiment to investigate the inheritance pattern of the white-eye trait in fruit flies. In the experiment, the students cross a red-eyed female with a white-eyed male to produce an F1 generation. The students observe that all the flies in the F1 generation have red eyes. The students then allow the F1 flies to mate and produce an F2 generation. The students will use the F2 data to perform a chi-square goodness-of-fit test based on a null hypothesis of autosomal recessive inheritance. The observed and expected values for the chi-square goodness-of-fit test are shown in Table 1.
The students plan to use a significance level of p=0.01. Which of the following is the most appropriate critical value for the students to use in their chi-square goodness-of-fit test?
Responses
A.7.82
B.11.34
C.13.28
D.326.7
B.11.34
A model showing the cells in anaphase I and anaphase II of meiosis during a nondisjunction event is shown in Figure 1.Which of the following best predicts the effect of the chromosomal segregation error shown in Figure 1?
Responses
A.All of the resulting gametes will have an extra chromosome.
B.All of the resulting gametes will be missing a chromosome.
C.Half of the resulting gametes will have an extra chromosome and the other half will be missing a chromosome.
D.Half of the resulting gametes will have the correct number of chromosomes, and the other half will have an incorrect number of chromosomes.
D.Half of the resulting gametes will have the correct number of chromosomes, and the other half will have an incorrect number of chromosomes.
Sex chromosomes determine the phenotype of sex in humans. Embryos containing XX chromosomes develop into females, and embryos containing XY chromosomes develop into males. The sex chromosomes separate during meiosis, going to different gamete cells.
A woman is heterozygous for the X-linked recessive trait of hemophilia A. Her sex chromosomes can be designated as XHXh. During meiosis the chromosomes separate as shown in Figure 1.If the woman and a man with normal clotting function have children, what is the probability of their children exhibiting hemophilia A?
Responses
A.50 percent for daughters, 0 percent for sons
B.50 percent for sons, 0 percent for daughters
C.50 percent for all children
D.0 percent for all children
B.50 percent for sons, 0 percent for daughters
Two fruit fly mutations are ebony body (e) and sepia eyes (s). Four different students performed dihybrid crosses with flies that were heterozygous with a mutant allele and a wild-type allele for both genes (EeSs×EeSs). The results are shown in Table 1.The mean number of fruit flies per student that are homozygous recessive for both genes is closest to which of the following?
A.89.75
B.29.0
C.22.75
D.18.5
B.29.0
Four trials measuring recombination frequency between gene R and gene L were conducted, and the results are shown in Table 1.The mean map distance between gene R and gene L is closest to which of the following?
Responses
A.0.28 map units
B.28 map units
C.0.14 map units
D.14 map units
B.28 map units
Researchers hypothesized that red eye color in Japanese koi, a type of fish, is due to a mutation. To study the inheritance of red eye color in koi, the researchers conducted breeding experiments over several generations. The results are summarized in Figure 1.Based on the data in Figure 1, which of the following is the best prediction of the mode of inheritance of red eyes in Japanese koi?
Responses
A.The allele for red eyes is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
B.The allele for red eyes is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern.
C.The allele for red eyes is inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern.
D.The allele for red eyes is inherited in an X-linked dominant pattern.
A.The allele for red eyes is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
Which of the following best explains a distinction between metaphase I and metaphase II?
Responses
A.The nuclear membrane breaks down during metaphase I but not during metaphase II.
B.Chromosomes align at the equator of the cell during metaphase II but not during metaphase I.
C.The meiotic spindle is needed during metaphase I but not during metaphase II.
D.Homologous pairs of chromosomes are aligned during metaphase I, but individual chromosomes are aligned during metaphase II.
D.Homologous pairs of chromosomes are aligned during metaphase I, but individual chromosomes are aligned during metaphase II.
Researchers performed a dihybrid cross with coffee bean plants to investigate whether the inheritance of two traits (height and stem circumference) follows Mendel’s law of independent assortment. The data for the F2 generation are presented in Table 1.Which of the following is closest to the calculated chi-square (χ2) value for the data presented in Table 1?
Responses
A.8.35
B.72.01
C.98.00
D.2,546.00
B.72.01
Himalayan rabbits are a breed of rabbits with highly variable fur color. If genetically similar rabbits are raised in environments that have different temperature conditions, the rabbits can have different color patterns.
Which of the following statements best explains how the fur color can be different in Himalayan rabbits raised under different temperature conditions?
A.The genotype does not contribute to coat color in Himalayan rabbits.
B.The phenotype determines the genotype of coat color in Himalayan rabbits.
C.Different environments cause specific mutations in the genes controlling pigment production.
D.The environment determines how the genotype is expressed.
D.The environment determines how the genotype is expressed.
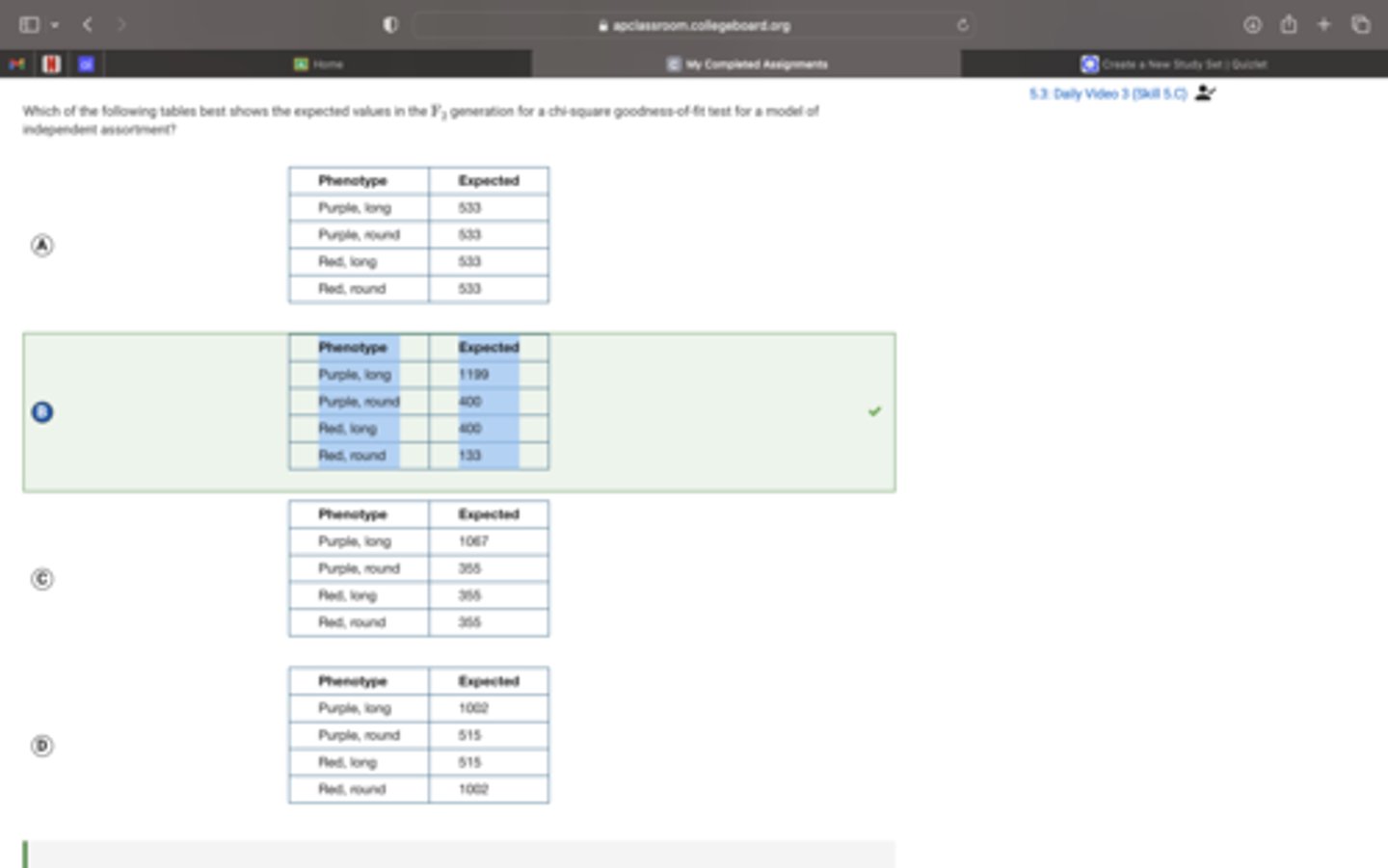
In pea plants, purple flower color is dominant to red flower color and long pollen grains are dominant to round pollen grains. Researchers crossed two pure-breeding lines of the pea plants to investigate whether the genes controlling flower color and pollen shape segregate independently. The procedure for the genetics experiment is summarized in Figure 1.
Which of the following tables best shows the expected values in the F2 generation for a chi-square goodness-of-fit test for a model of independent assortment?
For sexually reproducing diploid parent cells, which of the following statements best explains the production of haploid cells that occurs in meiosis but not in mitosis?
Responses
A.Separation of chromatids occurs once, and there is one round of cell division in meiosis.
B.Separation of chromatids occurs twice, and there are two rounds of cell division in mitosis.
C.Separation of chromatids occurs once, and there are two rounds of cell division in meiosis.
D.Separation of chromatids occurs twice, and there is one round of cell division in mitosis.
C.Separation of chromatids occurs once, and there are two rounds of cell division in meiosis.
In corn plants, purple kernel color is dominant to yellow kernel color, and smooth kernels are dominant to wrinkled kernels. Researchers carried out a genetics experiment to investigate whether the genes controlling kernel color and kernel texture segregate independently. Using a significance level of p=0.05, which of the following statements best completes a chi-square goodness-of-fit test for a model of independent assortment?
Responses
A.The calculated chi-square value is 0.66, and the critical value is 0.05. The null hypothesis can be rejected.
B.The calculated chi-square value is 0.66, and the critical value is 3.84. The null hypothesis cannot be rejected.
C.The calculated chi-square value is 3.91, and the critical value is 5.99. The null hypothesis can be rejected.
D.The calculated chi-square value is 3.91, and the critical value is 7.82. The null hypothesis cannot be rejected.
D.The calculated chi-square value is 3.91, and the critical value is 7.82. The null hypothesis cannot be rejected.
The tadpoles of Mexican spadefoot toads are known to exhibit phenotypic plasticity depending on food availability. Tadpole mouthparts can vary significantly, prompting researchers to categorize them as either omnivore-morph or carnivore-morph. Carnivore-morph tadpoles are larger and have mouthparts that are better suited for predation. Remarkably, carnivore-morph tadpoles can change into omnivore-morph tadpoles when the food supply changes.
Which of the following best describes an advantage of the phenotypic plasticity displayed by the tadpoles?
Responses
A.It allows the tadpoles to change their genome in response to environmental pressures.
B.It enables the tadpoles to develop into a distinct species of toads.
C.It gives the tadpoles increased versatility with respect to diet.
D.It allows the tadpoles to delay metamorphosis
C.It gives the tadpoles increased versatility with respect to diet.
Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate and is observed in each of the three domains. The hexokinase family of enzymes is required during glycolysis to phosphorylate six-carbon sugars. Researchers designed a general hexokinase inhibitor that is effective in the neurons of rats.
Which of the following best predicts the effect of adding this inhibitor to a culture of plant cells?
Responses
A.Plant cells will be unaffected by the inhibitor as they do not perform glycolysis.
B.Plant cells will be unable to perform glycolysis due to the inhibitor and will die.
C.Plant cells will be unable to perform photosynthesis due to the inhibitor and will die.
D.Plant cells will still be able to perform glycolysis since plant hexokinase is not structurally similar to animal hexokinase.
B.Plant cells will be unable to perform glycolysis due to the inhibitor and will die.
R. C. Punnett conducted experiments on the inheritance of traits in the sweet pea, Lathyrus odoratus. Which of the following best explains how the sweet pea plants in the parental generation produce F1 offspring with 14 chromosomes?
Responses
A.Meiosis I and II lead to the formation of cells with 14 chromosomes. When two cells combine during fertilization, extra chromosomes are randomly broken down, leading to offspring with 14 chromosomes.
B.Meiosis I and II lead to the formation of cells with 14 chromosomes. When two cells combine during fertilization, extra chromosomes with recessive traits are broken down, leading to offspring with 14 chromosomes.
C.Meiosis I and II lead to the formation of cells with 7 chromosomes. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes separate. During meiosis II, sister chromatids separate. Two cells combine during fertilization to produce offspring with 14 chromosomes.
C.Meiosis I and II lead to the formation of cells with 7 chromosomes. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes separate. During meiosis II, sister chromatids separate. Two cells combine during fertilization to produce offspring with 14 chromosomes.
Which of the following questions would be most useful to researchers trying to determine the role of meiosis in the F2 phenotypic frequencies?
Responses
A.What is the molecular mechanism underlying the dominance of erect petals and long pollen?
B.Which phenotypes give pea plants the highest level of fitness: erect or hooded petals and long or round pollen?
C.How do the phases of meiosis differ between sweet pea plants and other organisms?
D.What is the recombination frequency between the genes for petal shape and pollen shape?
D.What is the recombination frequency between the genes for petal shape and pollen shape?
How many degrees of freedom should be used when looking up the critical value for a chi-square analysis of the ratios of phenotypes observed among the F2 offspring versus the expected phenotypic ratio assuming independent assortment?
Responses
A.2
B.3
C.4
D.5
B.3
A true-breeding variety of wheat that produces deep-red-colored grain was crossed with a true-breeding variety that produces a white-colored grain.
Which of the follow indicates the mean number per cross of F2 plants producing medium-red grain and correctly explains the distribution of the phenotypes?
Responses
A.The mean number of medium-red phenotypes per cross is 20.8. The distribution of phenotypes suggests that grain color is under environmental control.
B.The mean number of medium-red phenotypes per cross is 20.8. The distribution of phenotypes suggests that multiple genes are involved in grain color determination.
C.The mean number of medium-red phenotypes per cross is 104. The distribution of phenotypes suggests that grain color is under environmental control.
D.The mean number of medium-red phenotypes per cross is 104. The distribution of phenotypes suggests that multiple genes
B.The mean number of medium-red phenotypes per cross is 20.8. The distribution of phenotypes suggests that multiple genes are involved in grain color determination.
Several members of a family are found to involuntarily sneeze when exposed to bright lights, such as sunlight. Following analysis of the condition in the family, a doctor predicts that the symptoms have an underlying genetic basis. A pedigree of the family is shown in Figure 1.
For this condition, which of the following modes of inheritance is most consistent with the observations?
A.Autosomal dominant
B.Autosomal recessive
C.X-linked dominant
D.X-link recessive
A.Autosomal dominant
Scientists have found that DNA methylation suppresses crossing-over in the fungus Ascobolus immersus. Which of the following questions is most appropriately raised by this specific observation?
Responses
A.Is the level of genetic variation in the gametes related to the amount of DNA methylation observed?
B.Without crossing-over, will gametes be viable and be able to produce zygotes?
C.Does DNA methylation result in shorter chromosomes?
D.Is this species of fungus a diploid organism?
A.Is the level of genetic variation in the gametes related to the amount of DNA methylation observed?
During prophase I replicated homologous chromosomes pair up and undergo synapsis. What testable question is generated regarding synapsis and genetic variability by Figure 1 ?
Responses
A.Is the distance between two gene loci related to crossover rate?
B.Does crossing over occur more often in some chromosomes than in others?
C.Is crossing over inhibited by methylation?
D.Is crossing over promoted by methylation?
A.Is the distance between two gene loci related to crossover rate?
Which of the following questions about genetic diversity could most appropriately be answered by analysis of the model in Figure 1 ?
Responses
A.Does crossing-over generate more genetic diversity than the fusion of gametes does?
B.Does DNA methylation prevent independent assortment during metaphase II?
C.How does the independent assortment of the two sets of homologous chromosomes increase genetic diversity?
D.Do daughter cells that are not genetically identical to parent cells produce viable zygotes?
C.How does the independent assortment of the two sets of homologous chromosomes increase genetic diversity?
Which of the following statements correctly describes the chromosomes in each daughter cell at the end of meiosis I?
A.Each daughter cell contains 12 chromatids. Each chromatid is one of two from a single chromosome with the other one of the pair found in the other daughter cell.
B.Each daughter cell contains 12 chromosomes, each composed of two chromatids. Since the chromosomes were randomly divided, one daughter cell may contain both of a pair of homologous chromosomes, while the other cell contains both of another pair of homologous chromosomes.
C.Each daughter cell contains 12 chromosomes, each composed of two chromatids. Each chromosome is one of a pair of homologous chromosomes from the parent cell, with the other homologue found in the other daughter cell.
D.Each daughter cell contains 24 separate chromatids. Since every two chromatids were originally joined..
C.Each daughter cell contains 12 chromosomes, each composed of two chromatids. Each chromosome is one of a pair of homologous chromosomes from the parent cell, with the other homologue found in the other daughter cell.
Both mitosis and meiosis begin with a parent cell that is diploid. Which of the following best describes how mitosis and meiosis result in daughter cells with different numbers of chromosomes?
Responses
A.In mitosis, the chromosomes consist of a single chromatid, which is passed to two haploid daughter cells. In meiosis, the chromosomes consist of two chromatids during the first round of division and one chromatid during the second round of division, resulting in two haploid daughter cells.
B.In mitosis, synapsis of homologous chromosomes results in four haploid daughter cells after one division...
C.Mitosis produces one identical daughter cell after one round of division. Meiosis has two rounds of division and...
D.Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells after one round of division. Meiosis produces four haploid daughter cells after two rounds of division.
D.Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells after one round of division. Meiosis produces four haploid daughter cells after two rounds of division.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a diploid yeast species that can reproduce either sexually or asexually. An experiment was performed to induce mitotically dividing S. cerevisiae cells in G2 to undergo meiosis. Which of the following best describes the steps these cells will follow to form gametes?
Responses
A.The first division will result in crossing over between homologous chromosomes, and the second division will reduce the original number of chromosomes by half in the daughter cells.
B.The first division will reduce the number of chromosomes by half for each daughter cell..
C.The first division will move single chromatids to each daughter cell, and the second division will double the number of chromosomes..
D.The first division will reduce the number of chromosomes by half for each daughter cell, and the second division will move single chromatids to each daughter cell.
D.The first division will reduce the number of chromosomes by half for each daughter cell, and the second division will move single chromatids to each daughter cell.