Ocr A level biology paper 2
1/438
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
439 Terms
Homozygous
When an organism carries two copies of the same alleles.
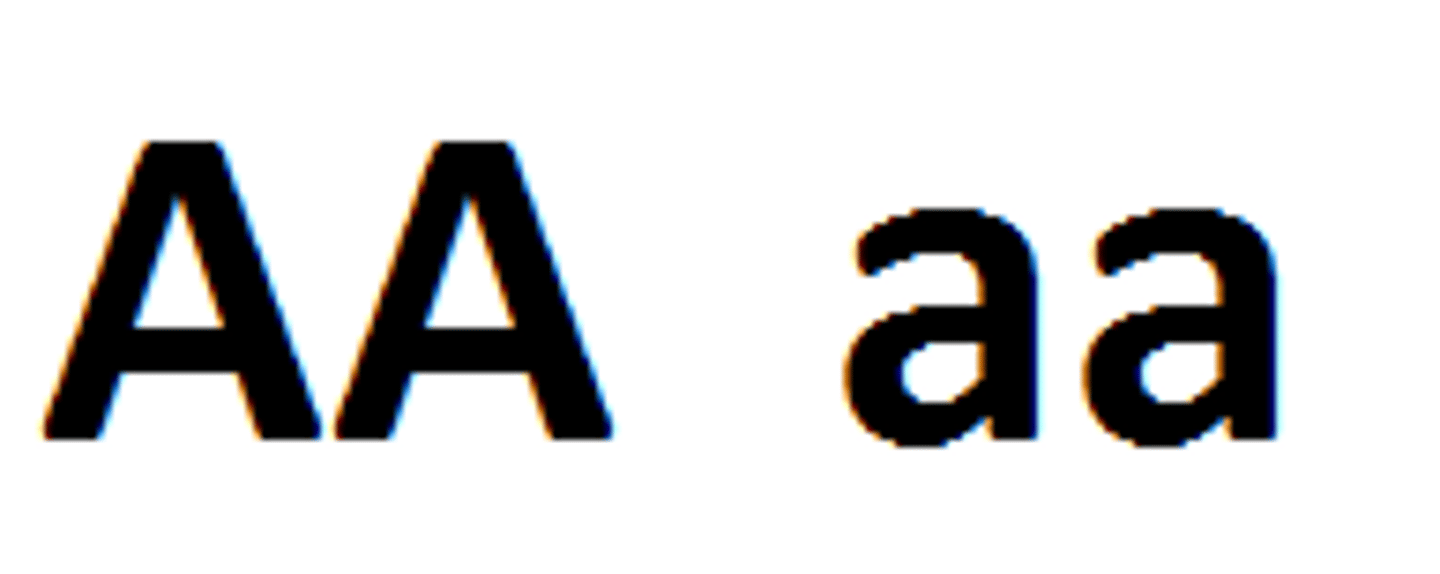
Heterozygous
When an organism has two different alleles of the same gene.
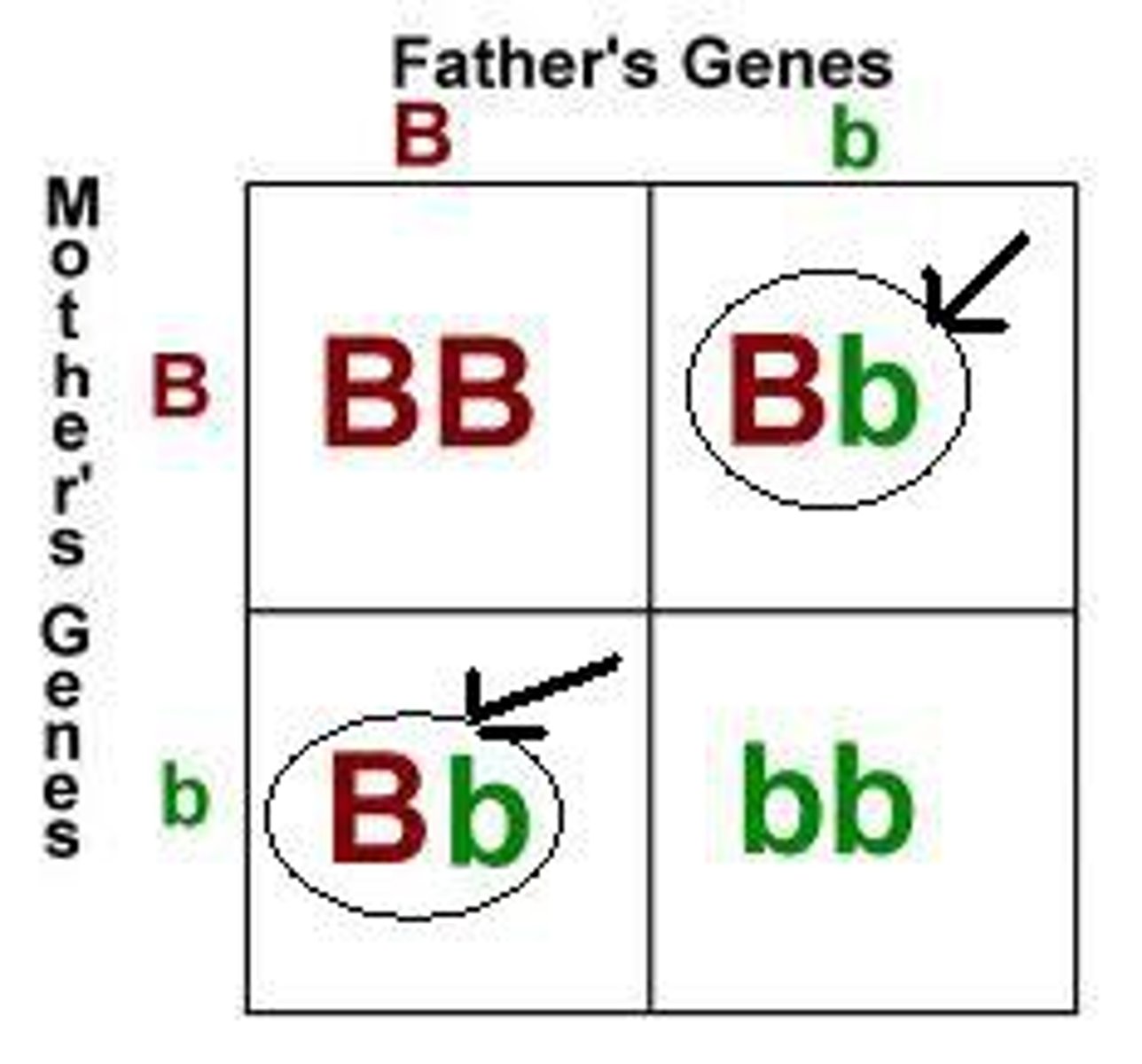
Genotype
Description of an organism's alleles.
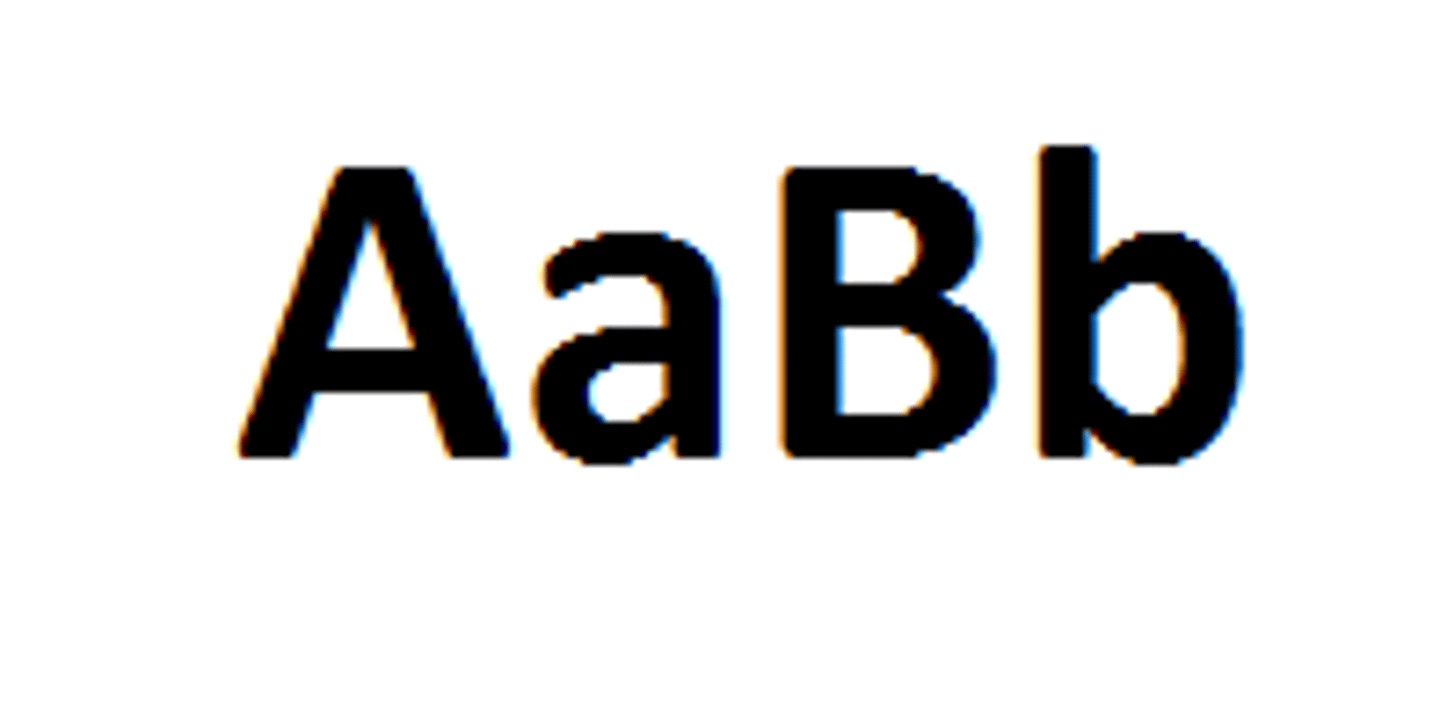
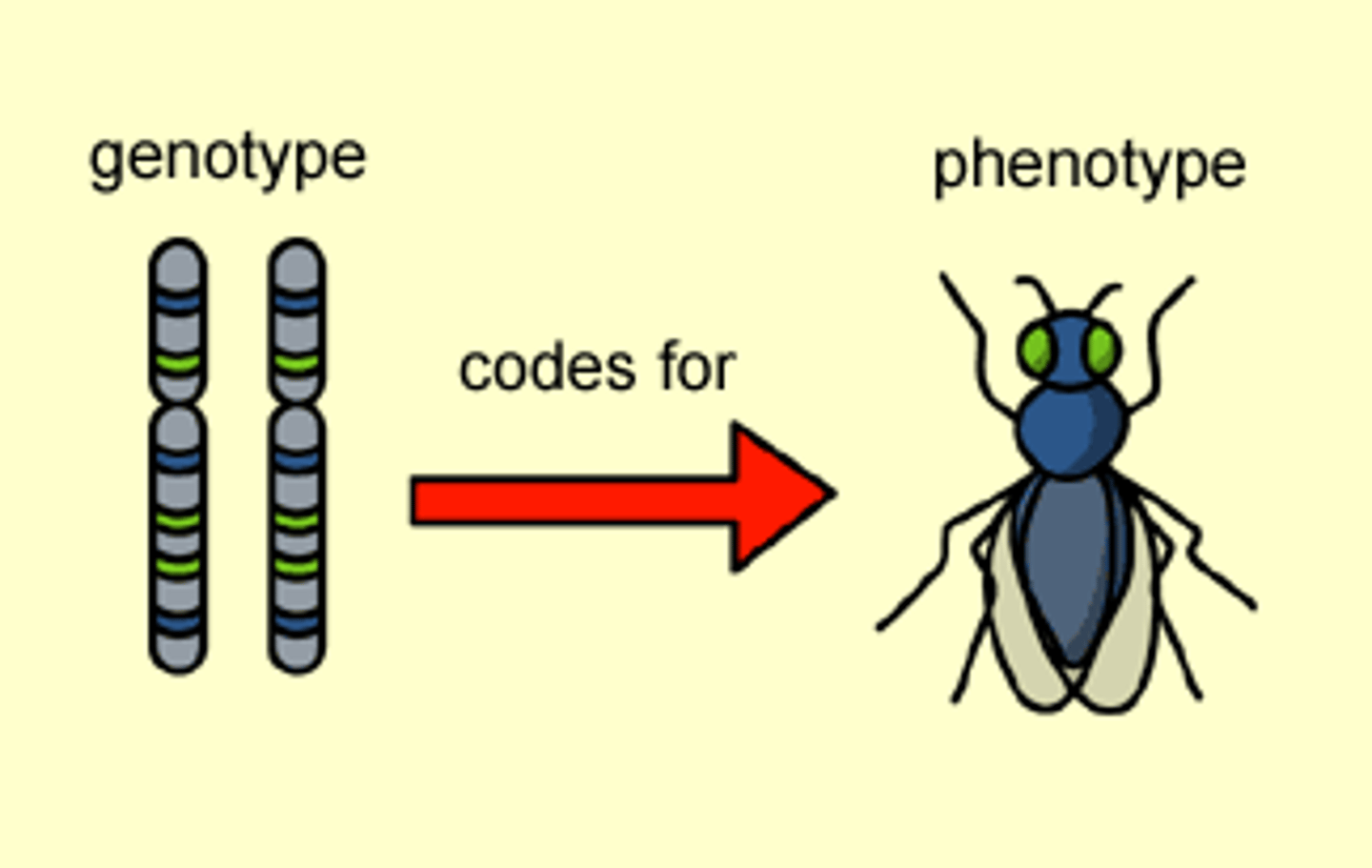
Phenotype
Characteristics of an organism as a result of the expression of its genotype and the environment.
Gene
Section of a chromosome that codes for a polypeptide.
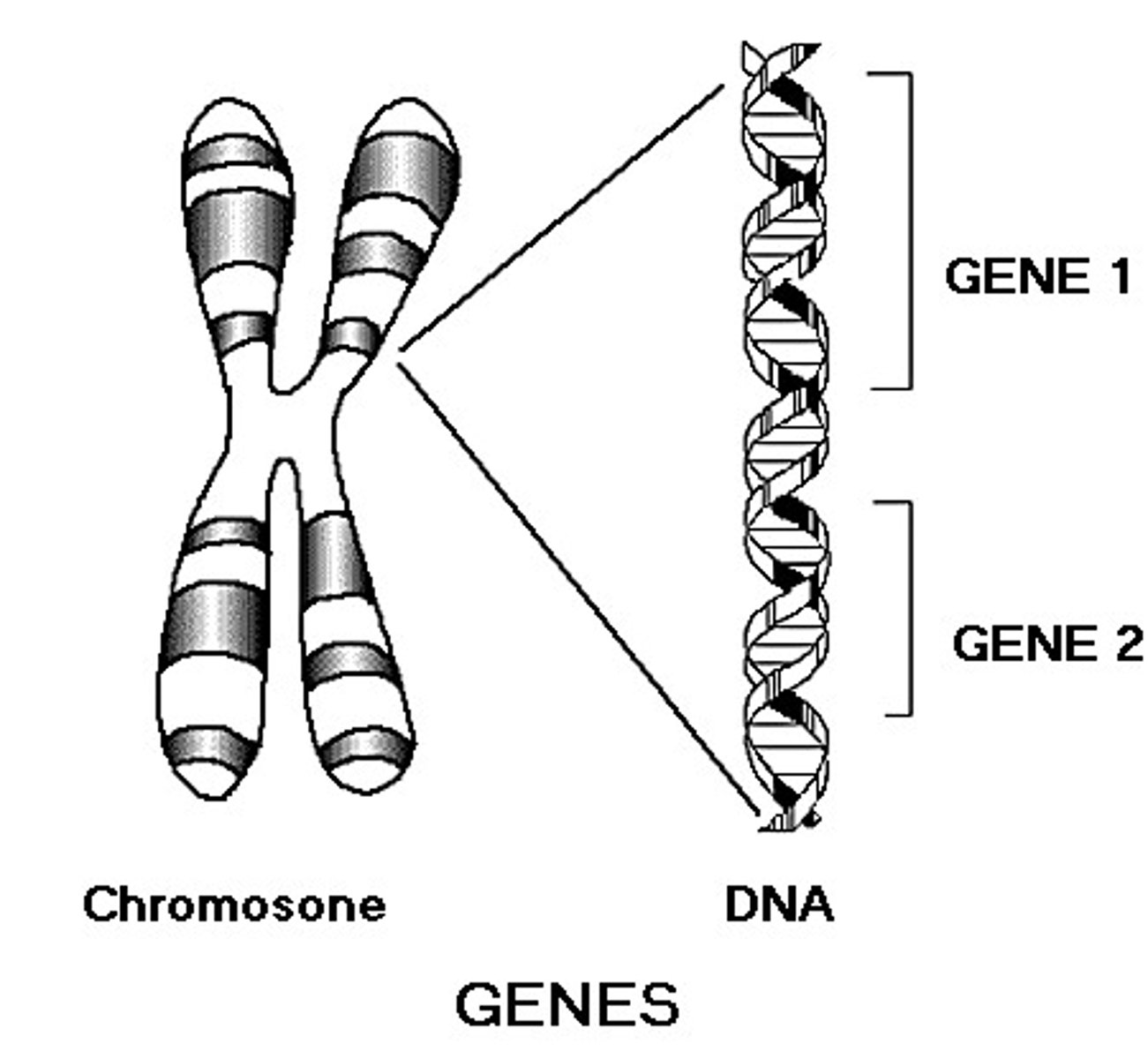
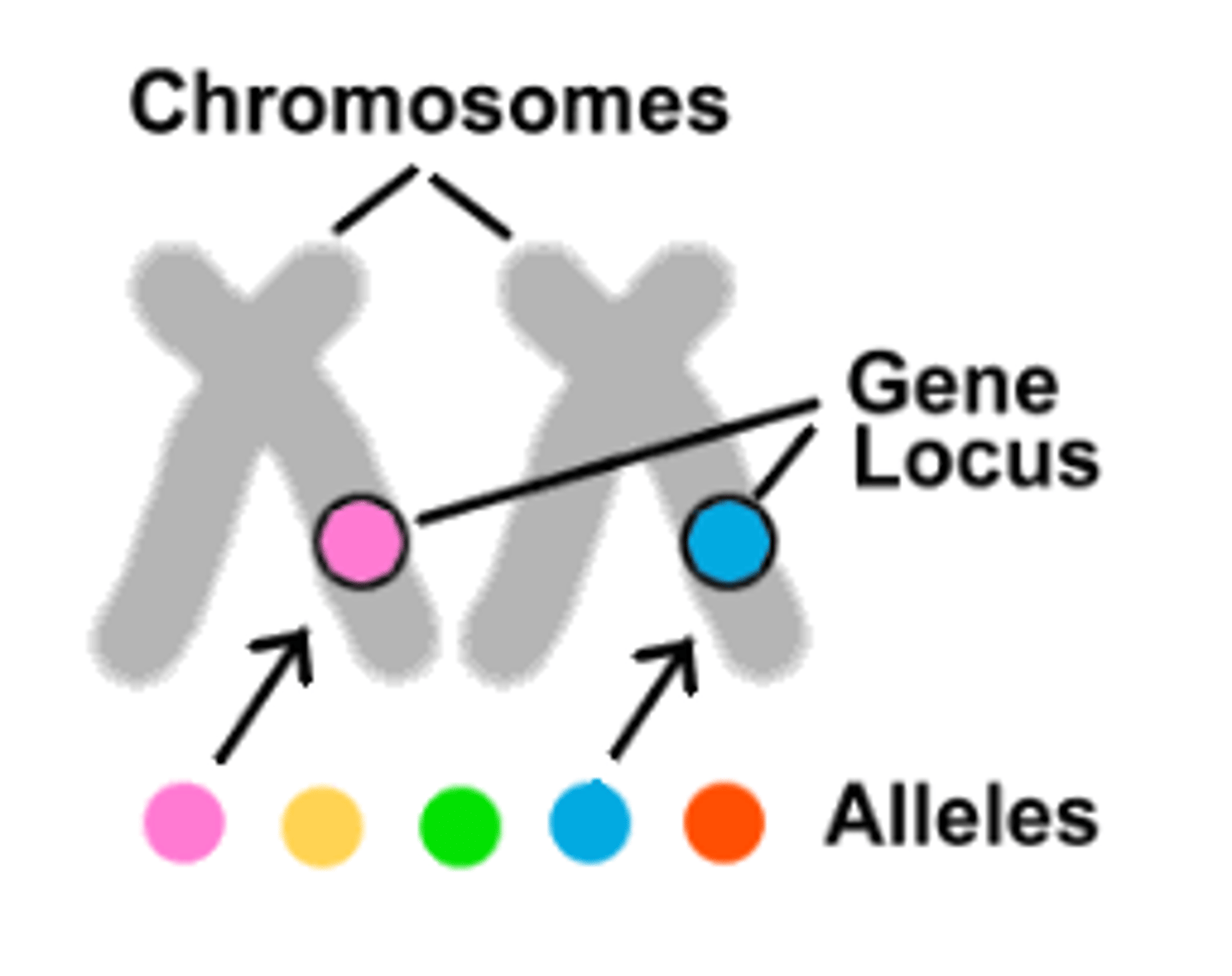
Allele
Alternative version of the same gene.
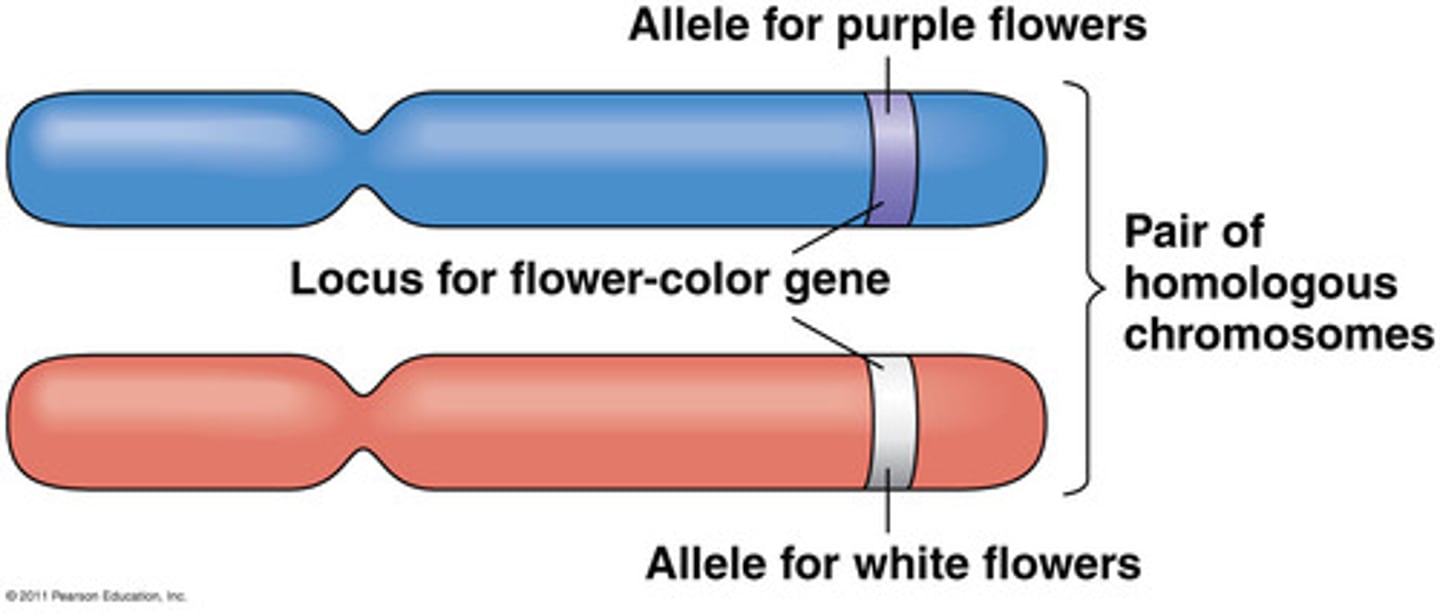
Gene locus
Location of a gene on a chromosome.
Dominant allele
Allele that is always expressed in the phenotype.

Recessive allele
Allele that is only expressed in the phenotype when there are two of them i.e. in a homozygote.
Codominant allele
Both alleles are expressed in the phenotype.
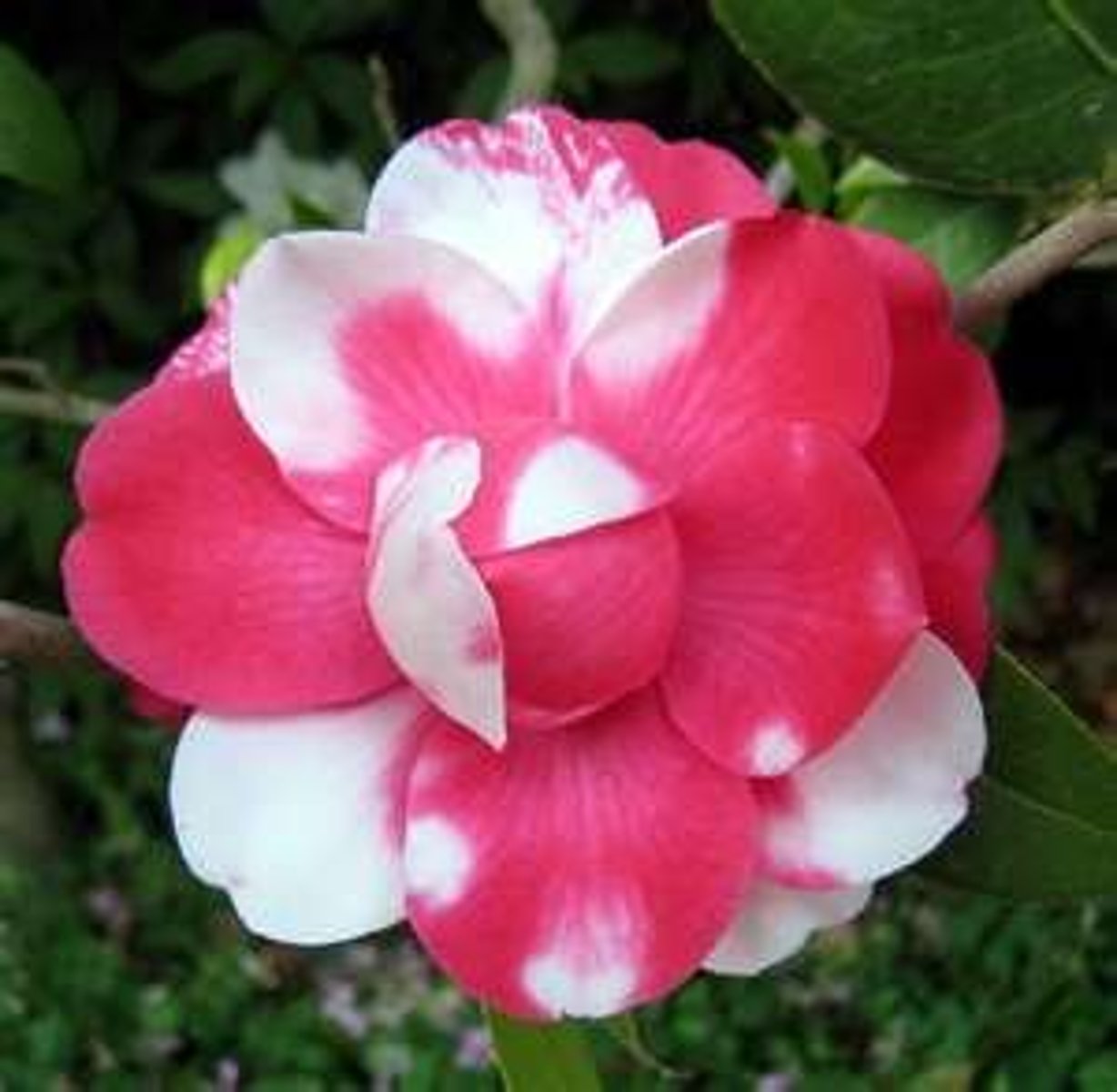

Multiple alleles
More than 2 alleles for a particular gene.
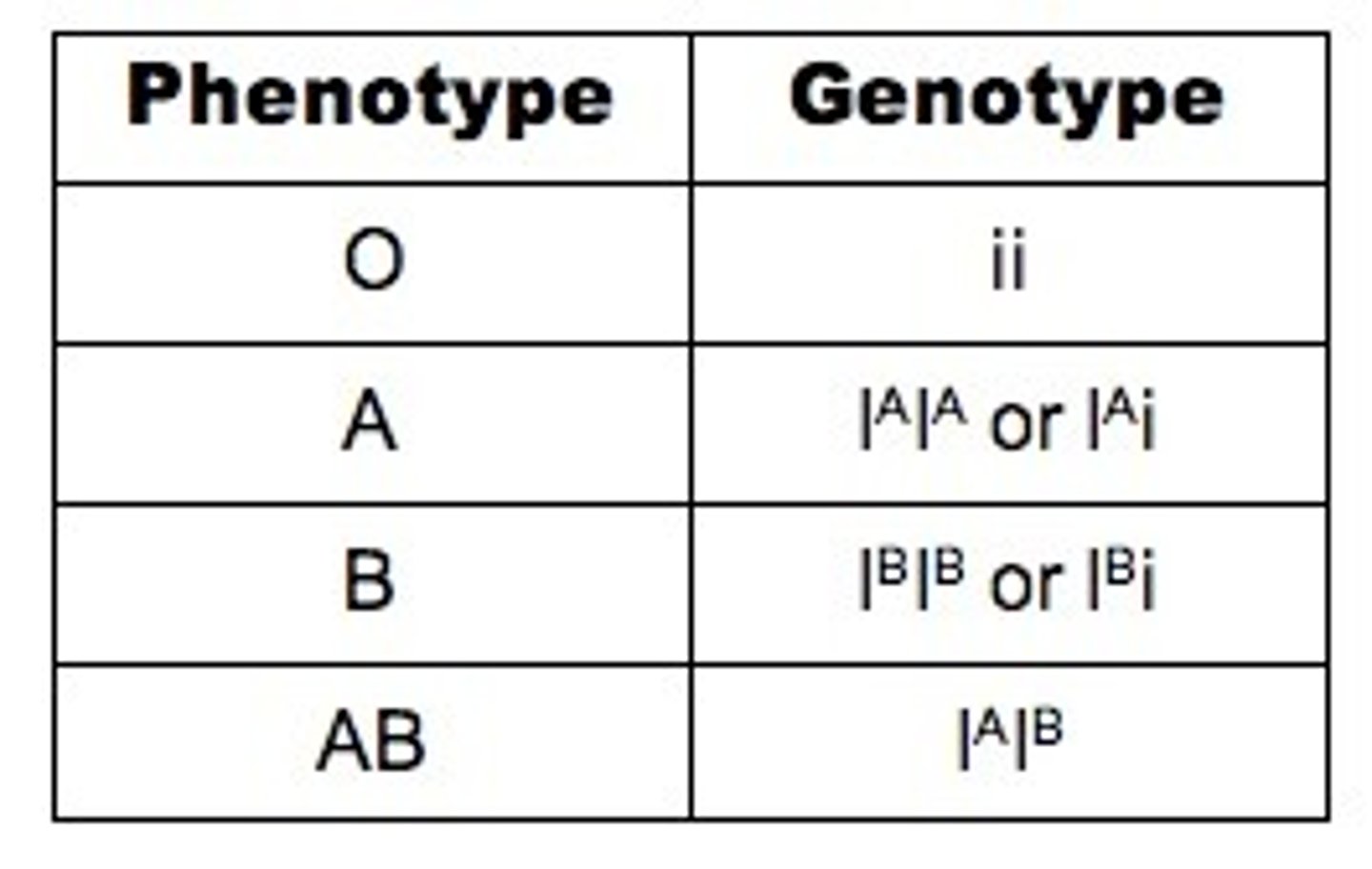
Sex linkage
Characteristic or trait controlled by a gene found on the sex chromosomes.
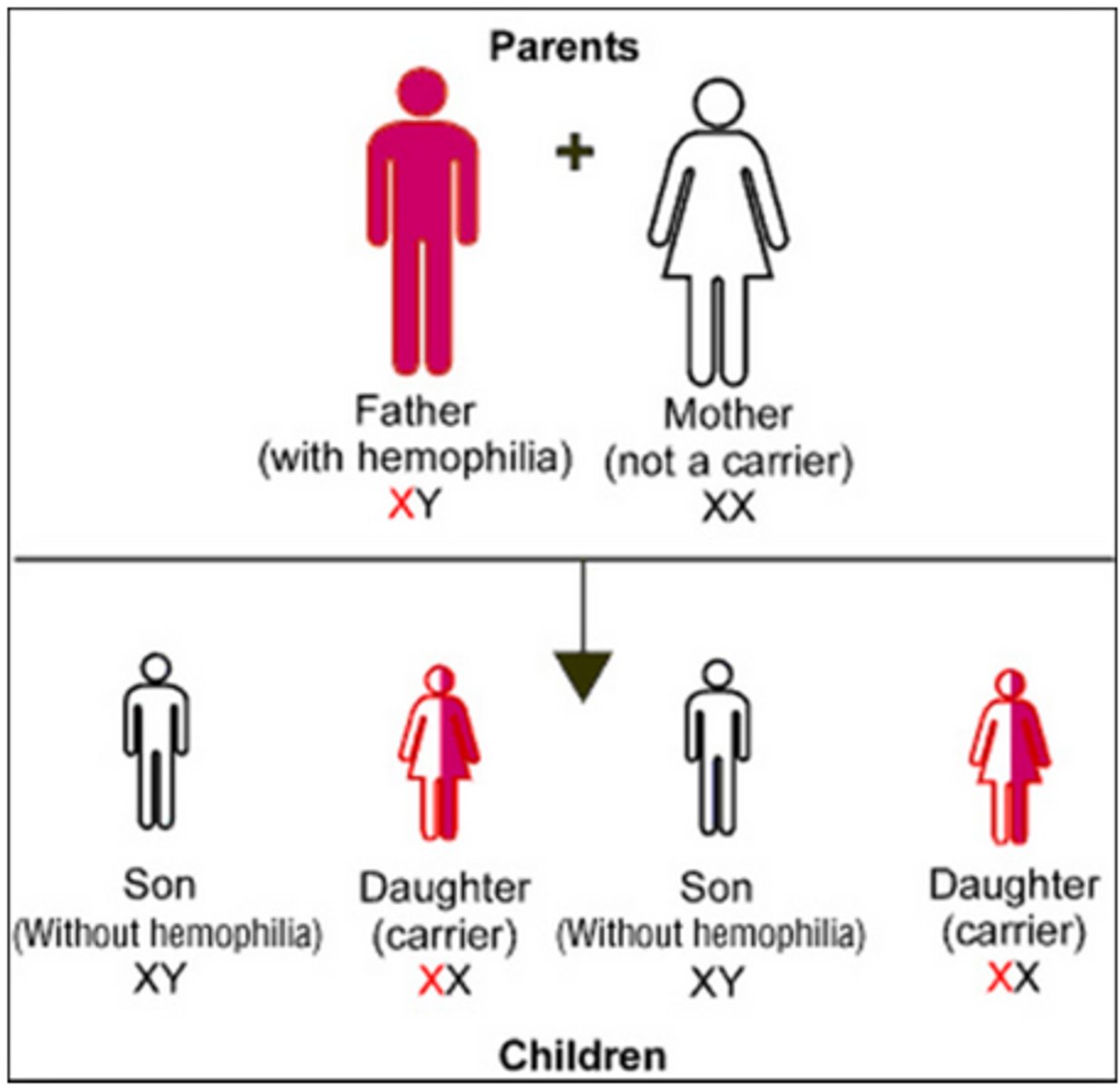
Homologous chromosomes
Pair of chromosomes that carry genes for the same characteristics, at the same gene loci.
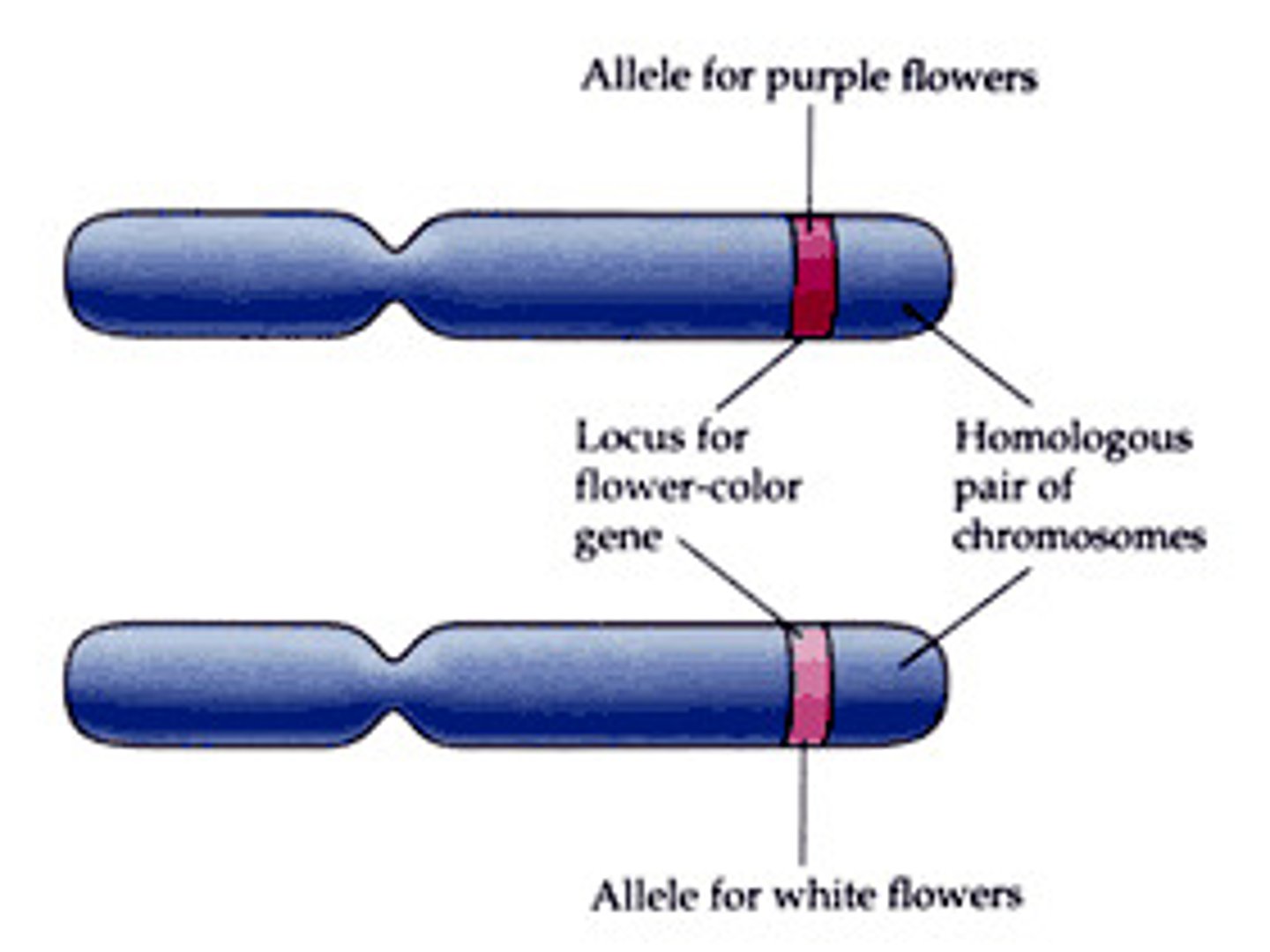
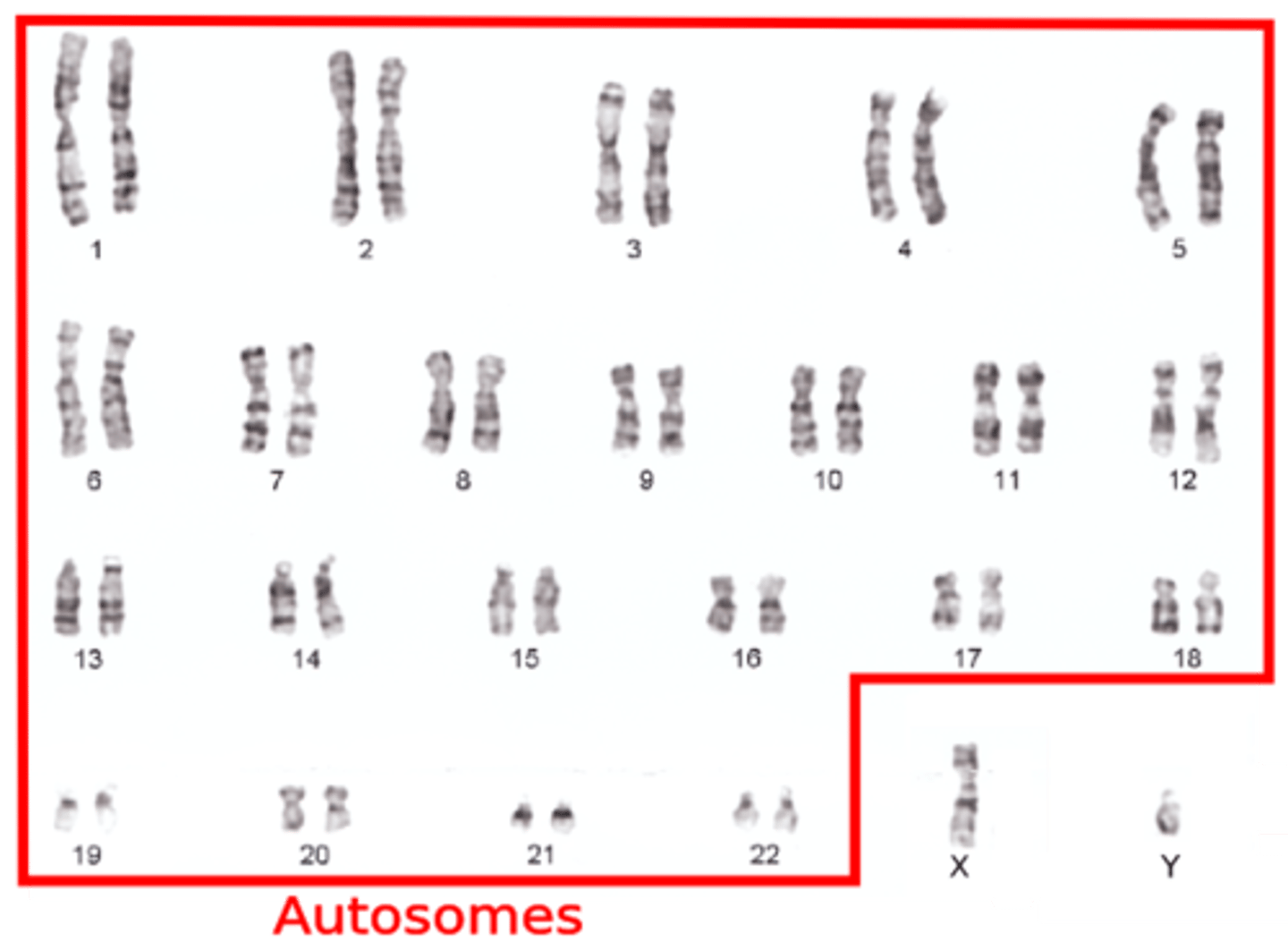
Autosome
Any chromosome that is NOT a sex chromosome.
Autosomal linkage
Genes coding for different characteristics, found on the same non-sex chromosome, are said to be linked.
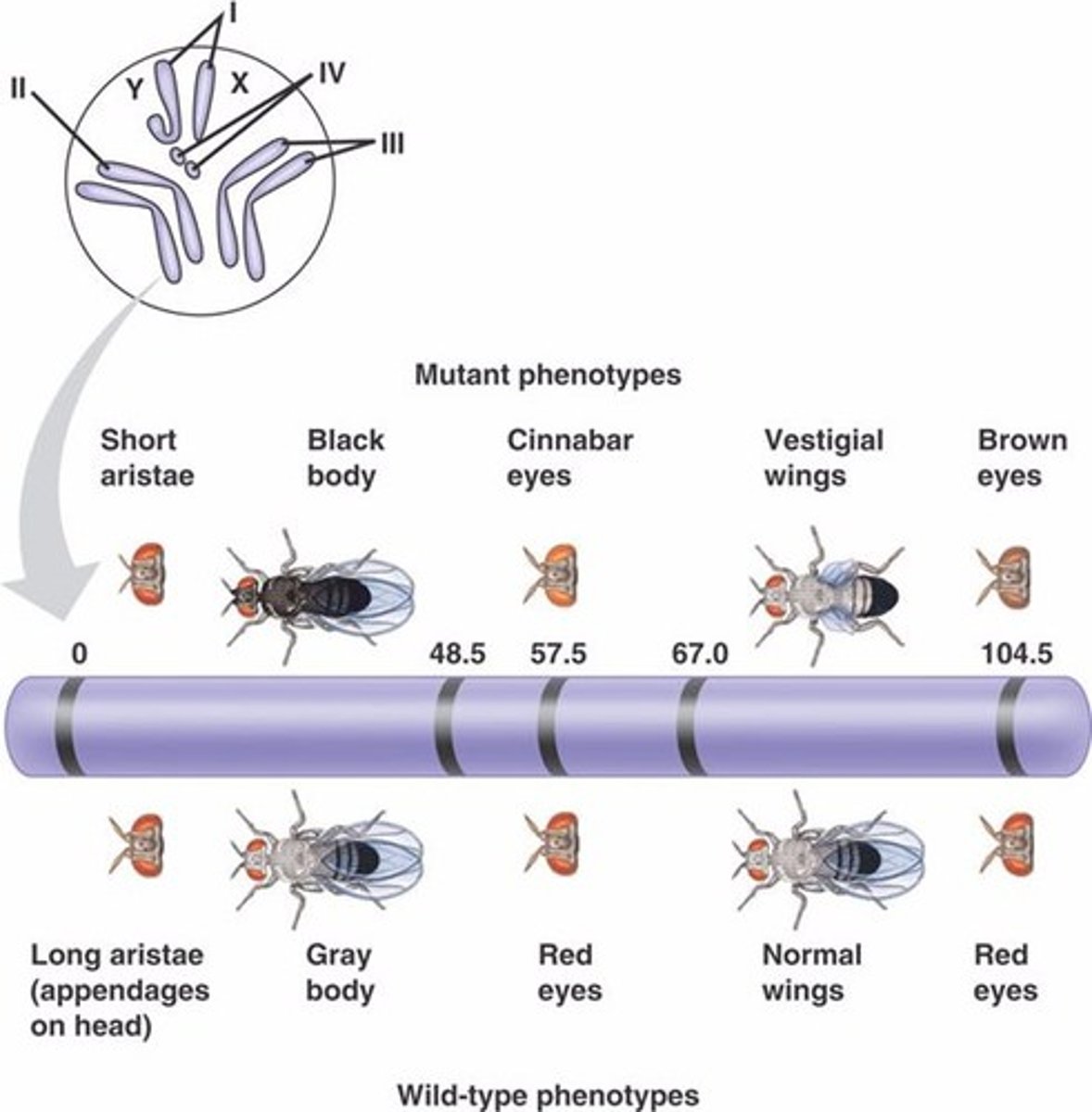
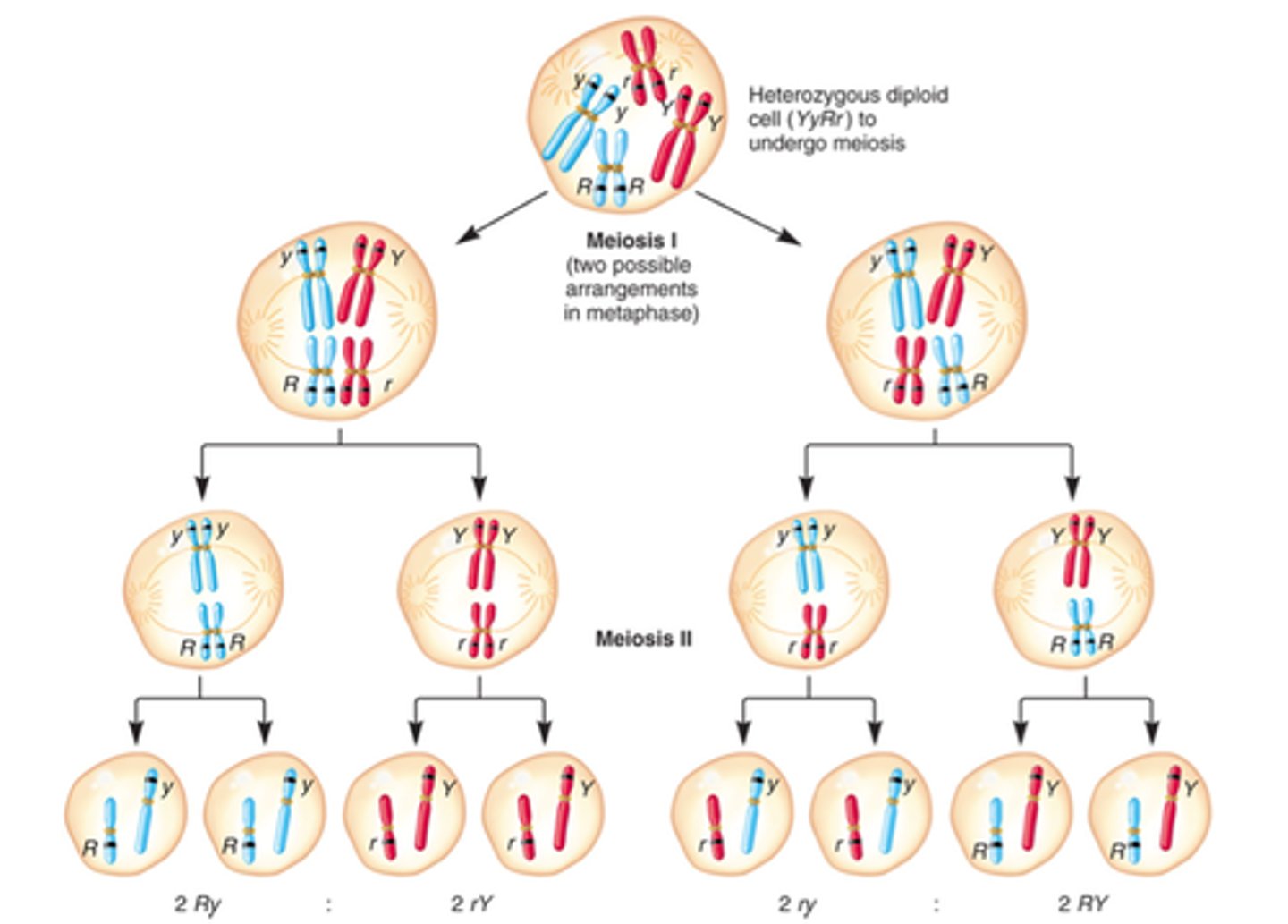
Independent assortment
During metaphase I of meiosis, the arrangement of one pair of homologous chromosomes on the equator of the spindle is independent of the arrangement of any other pair of chromosomes. A key event that produces GENETIC VARIATION in gametes.
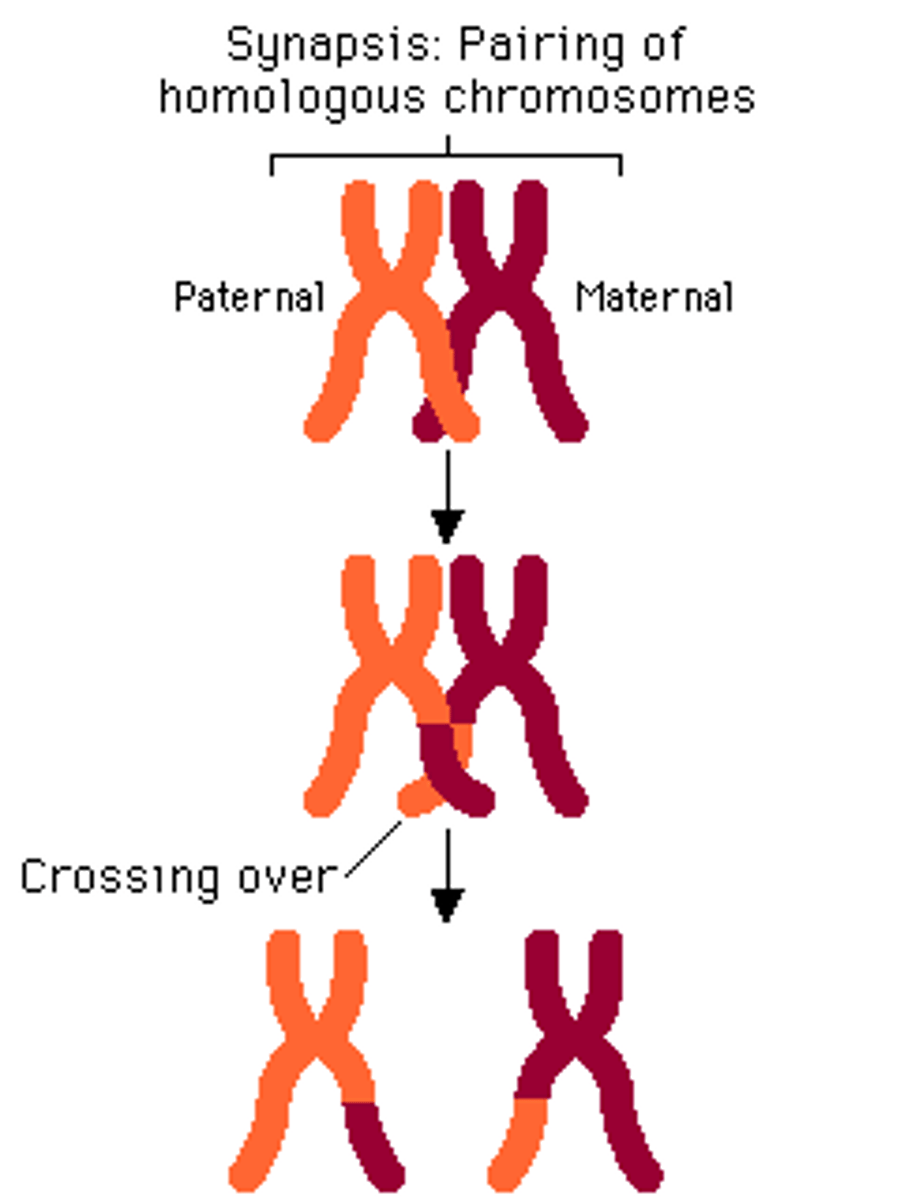
Crossing over
Where chromatids twist around each other and exchange genetic material. Happens during prophase I of meiosis which increases the amount of GENETIC VARIATION in gametes by producing new combination of alleles.
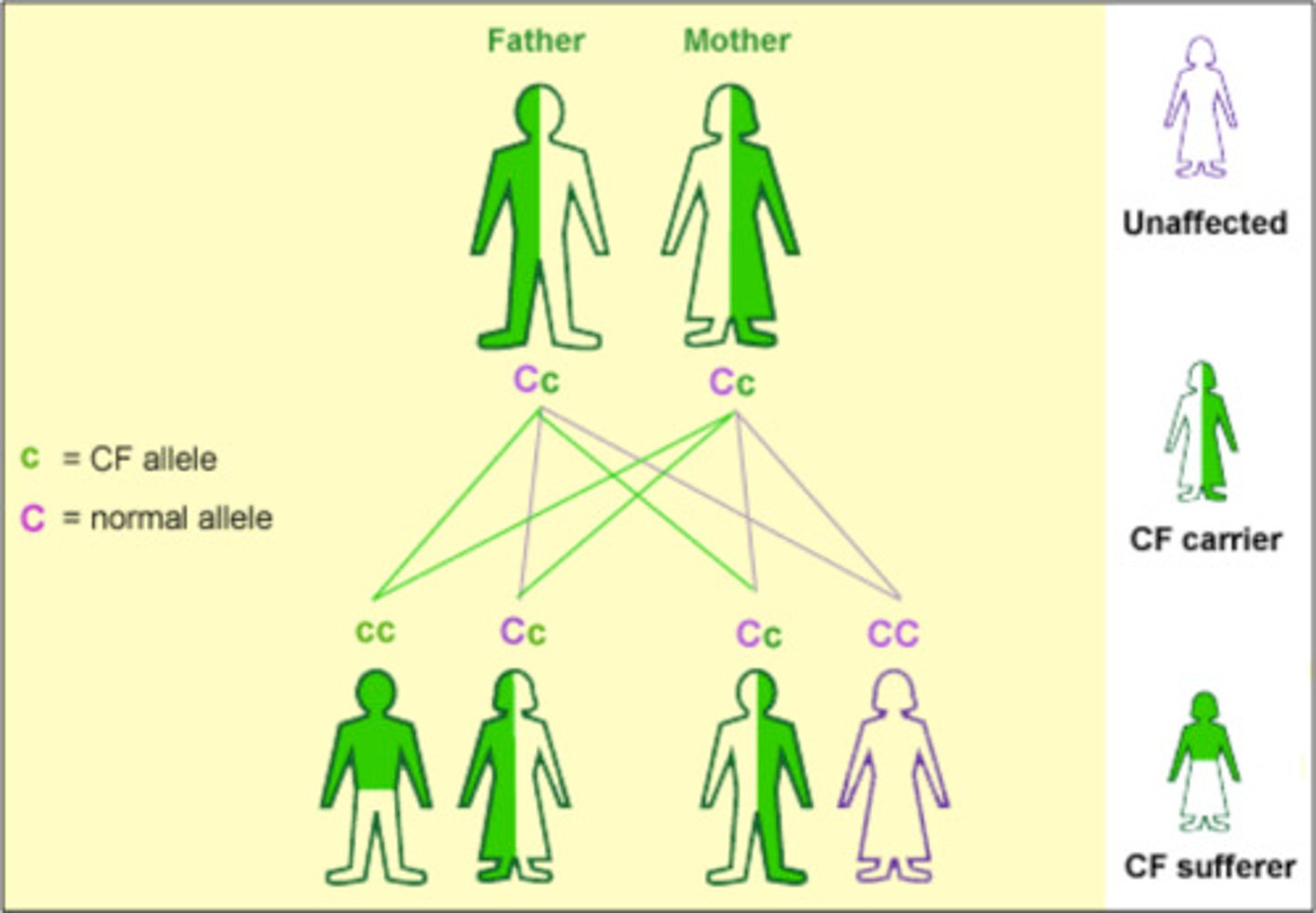
Carrier
Individual who has an allele, often for a disease, which is not expressed in the phenotype i.e. they are heterozygous.
True breeding
Individuals that are true breeding are homozygous for a particular characteristic or trait.
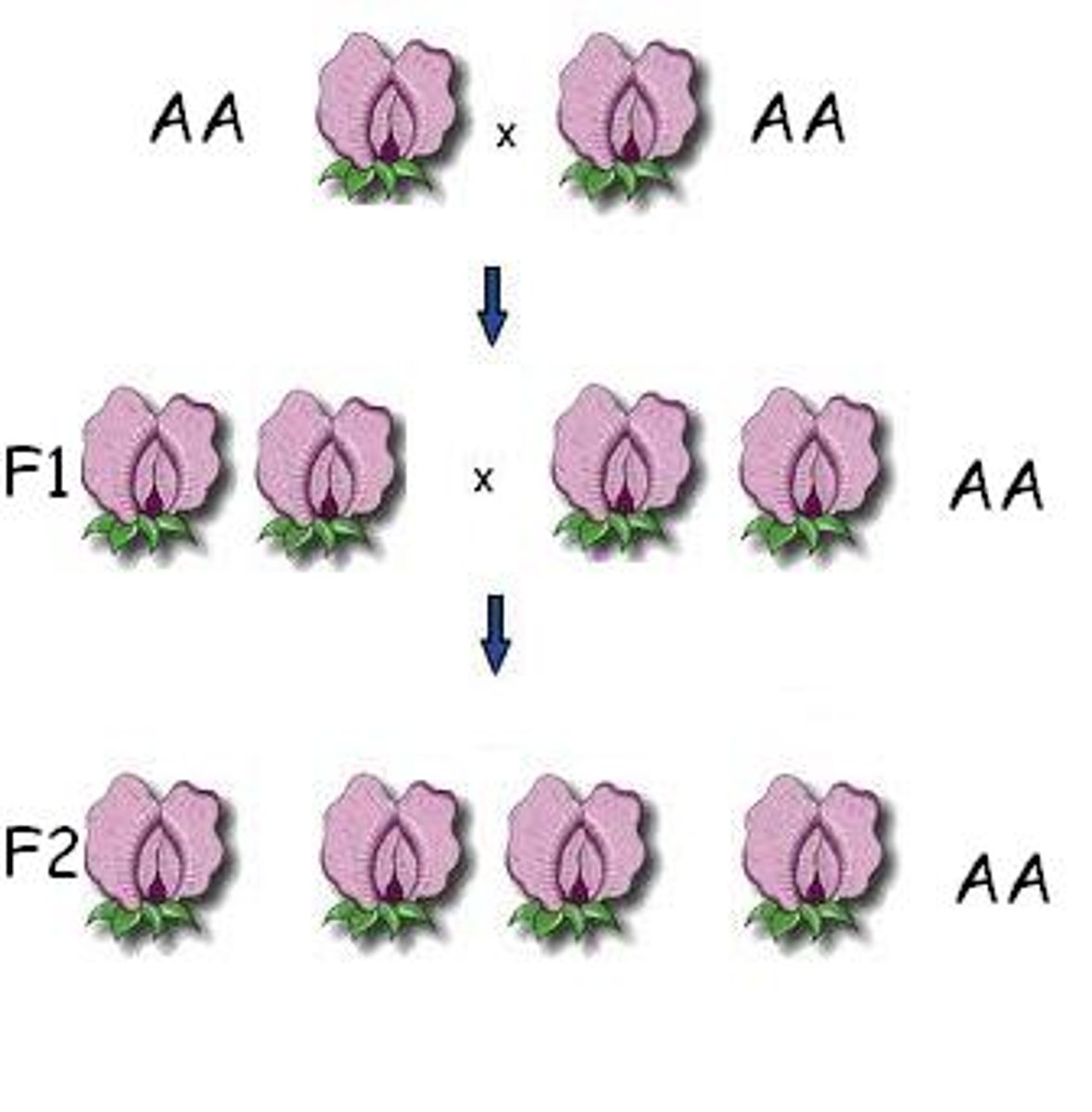
Epistasis
A type of gene interaction, where the allele of one gene masks the effect of the allele of a different gene.
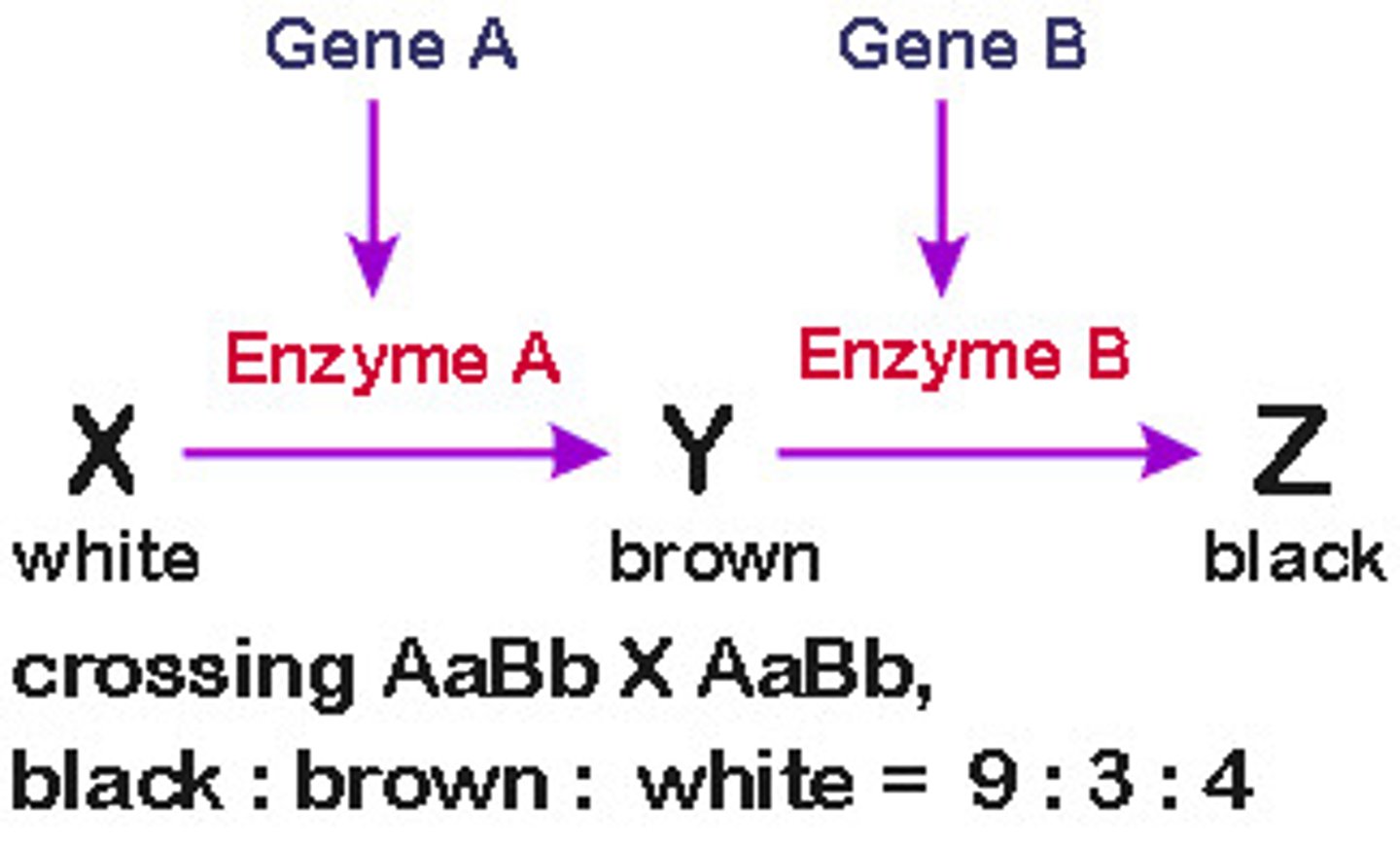
Hemizygous
Having a single copy of a gene instead of the normal two. For example, if there is heterozygous inheritance of the sex chromosomes, XY.
Variation
The range of differences in characteristics between organisms

Phencopy
When environmental conditions alter the phenotype to resemble the effects of genotypic change
Discontinuous variation
Variation where there are 2 or more distinct categories with no intermediates. Determined by a small number of genes with little or no environmental influence.
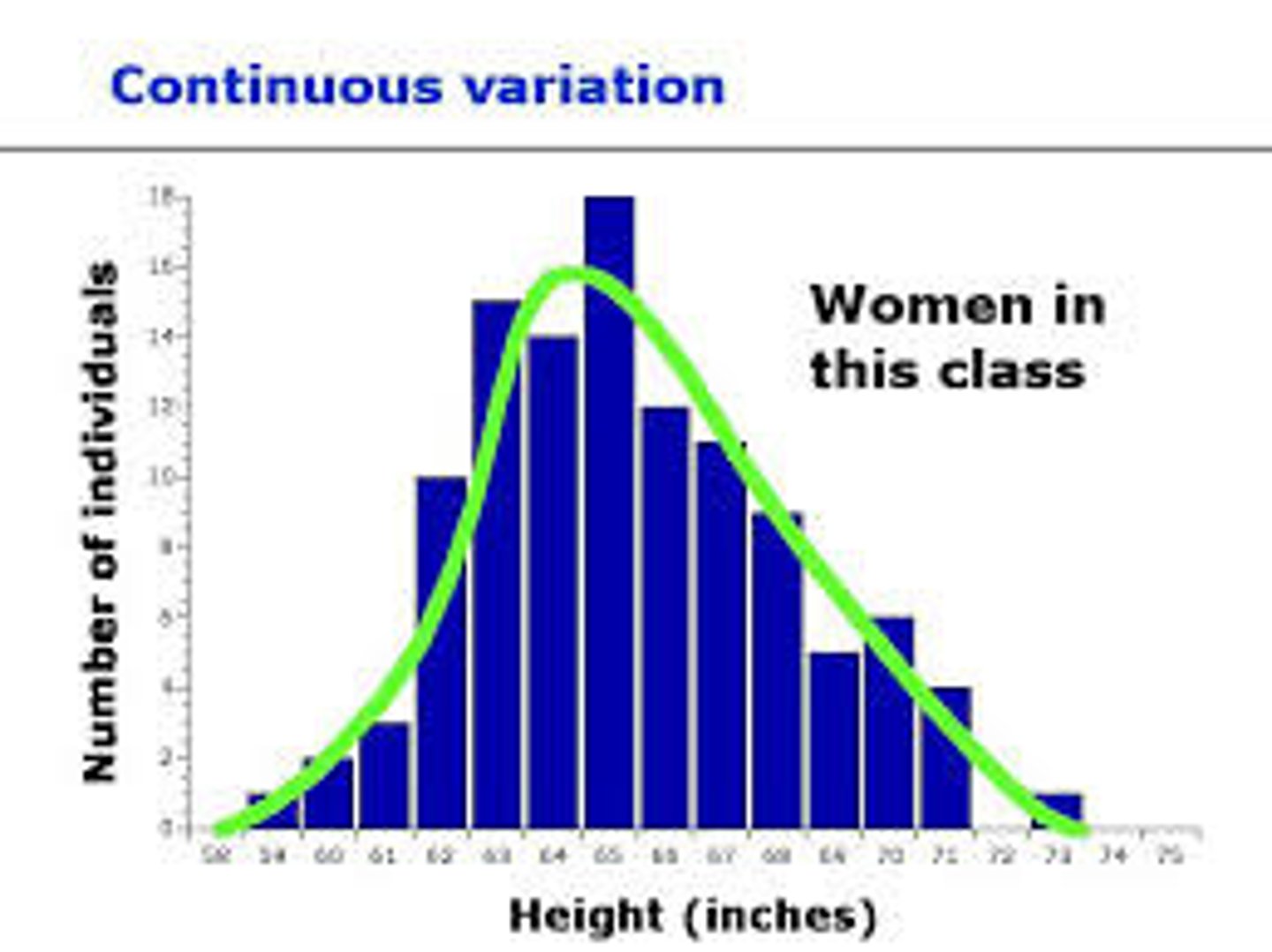
Continuous variation
Variation where there are two extremes and all possible intermediate forms. Determined by many genes (polygenic) and influenced by the environment.
Etiolation
When plants grow abnormally long and spindly because they are not getting enough light.
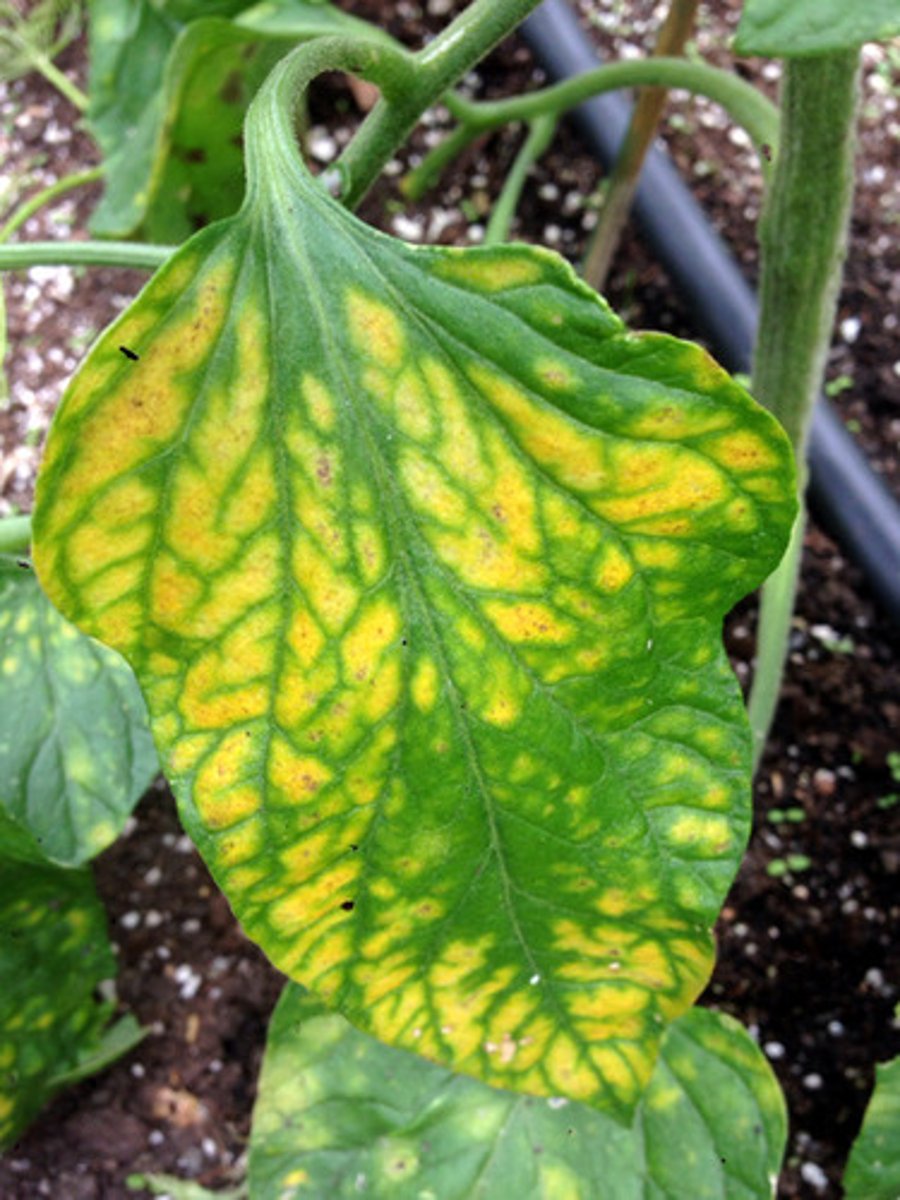
Chlorosis
When plants don't produce enough chlorophyll and turn yellow eg due to lack of magnesium in the soil.

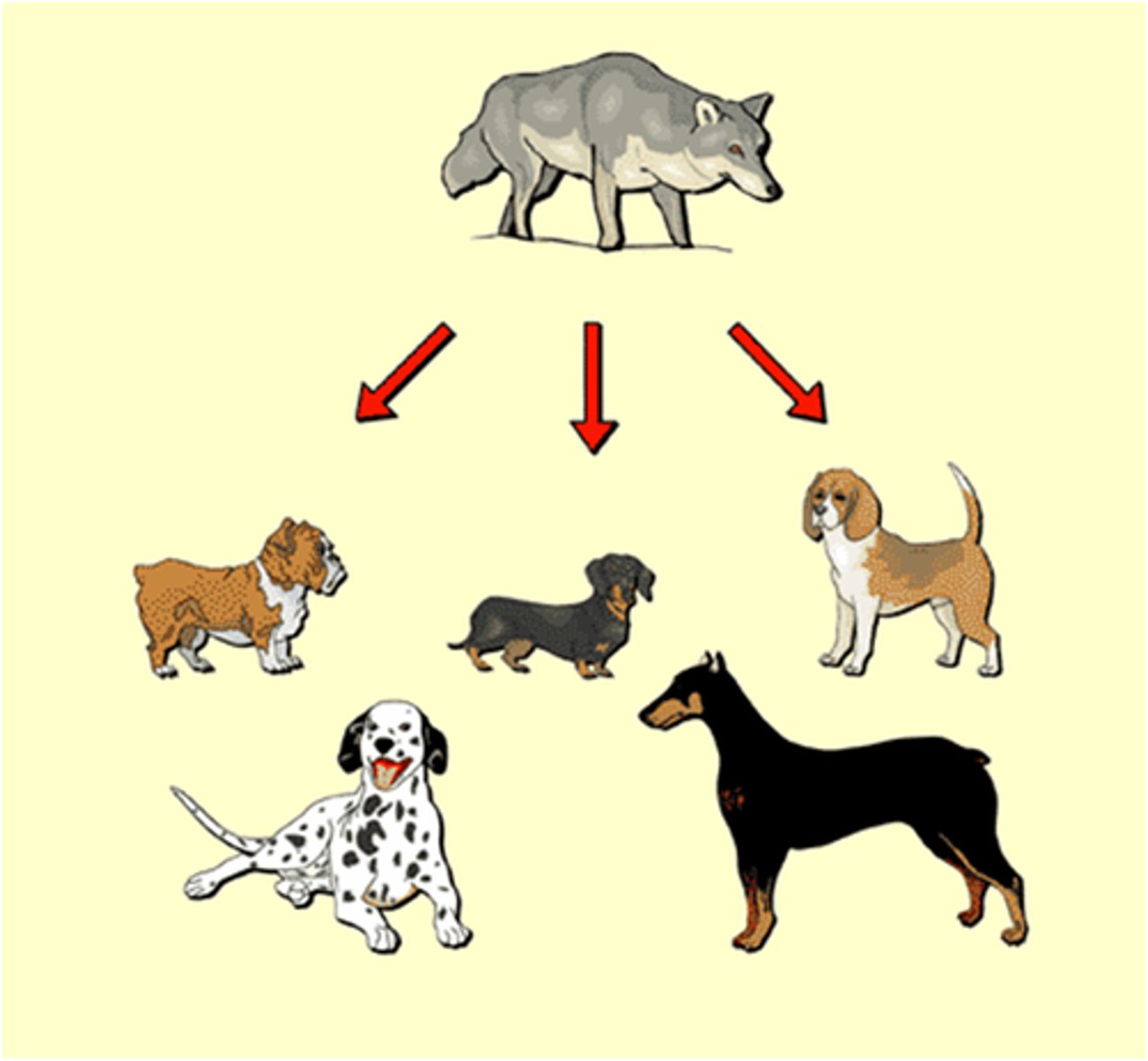
Artificial selection
When humans select which individuals in a population to breed together in order to get desirable traits.
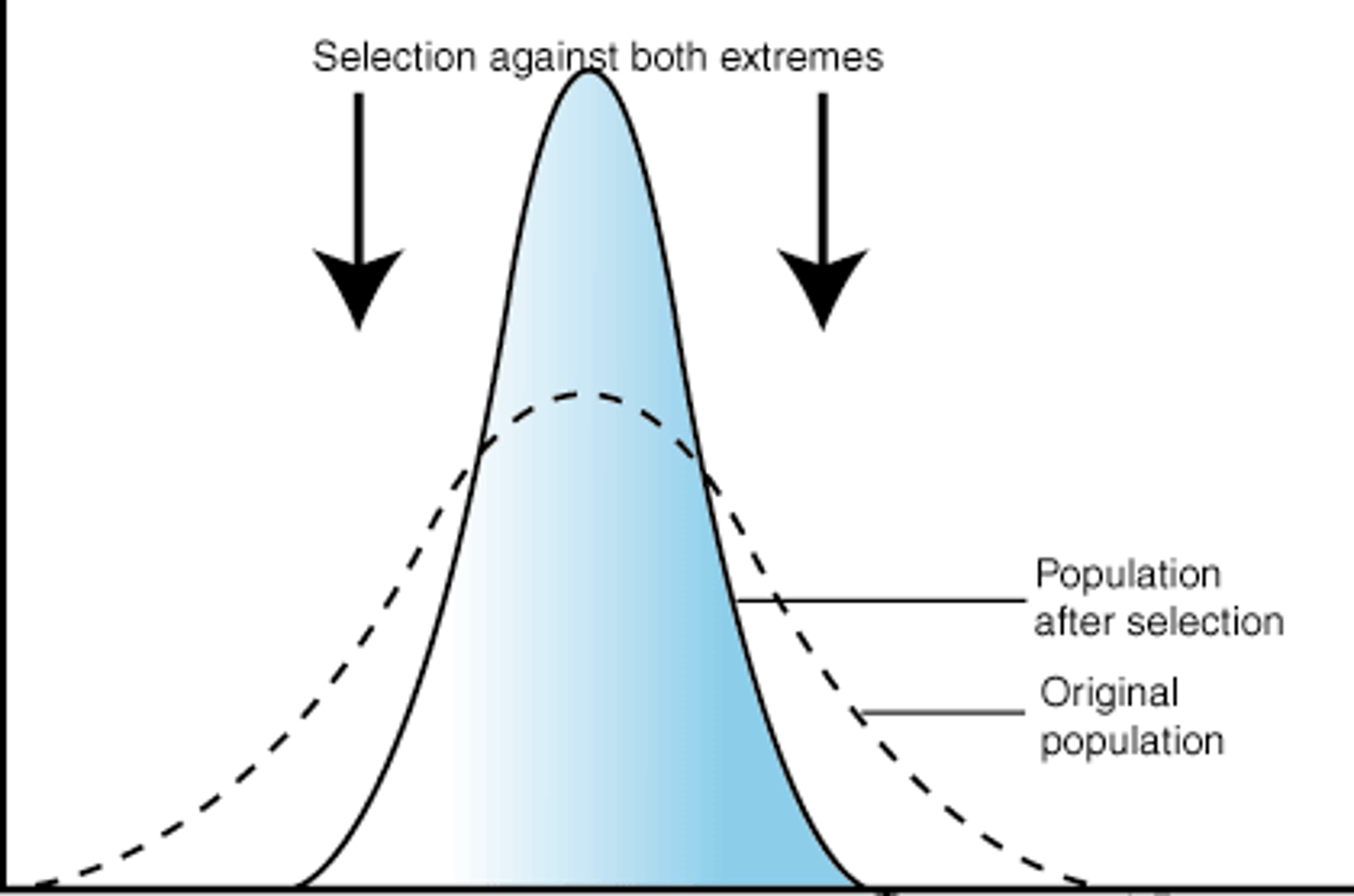
Stabilising selection pressure
Factor that reduces the range of phenotypes by selecting against individuals with the extreme phenotype.
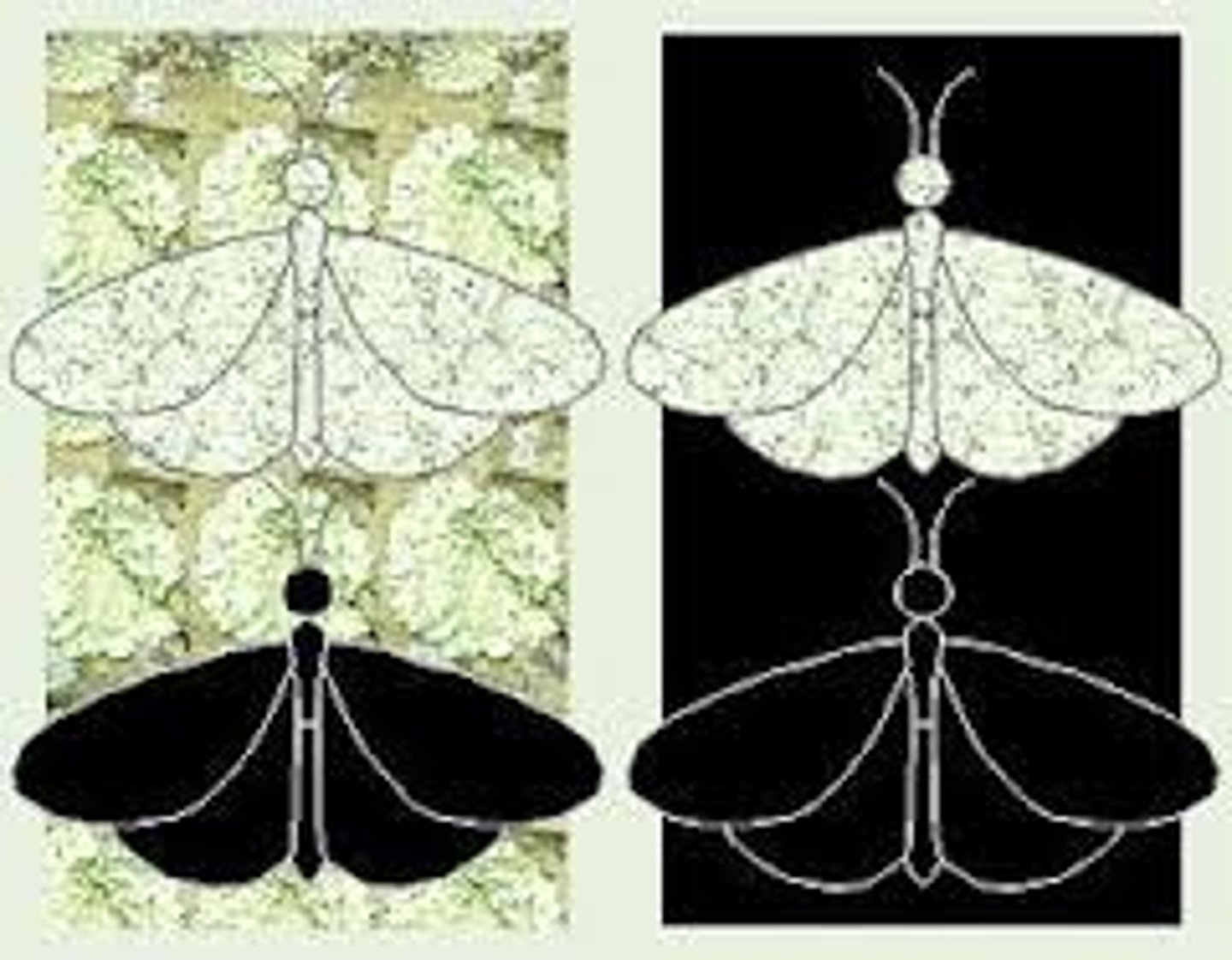
Selection pressure
A factor that gives a greater chance of surviving to some members of the population than others e.g. moth camouflage
Stabilising selection
Types of selection that operates against the extremes of the range of phenotypes so the population remains the same over time.
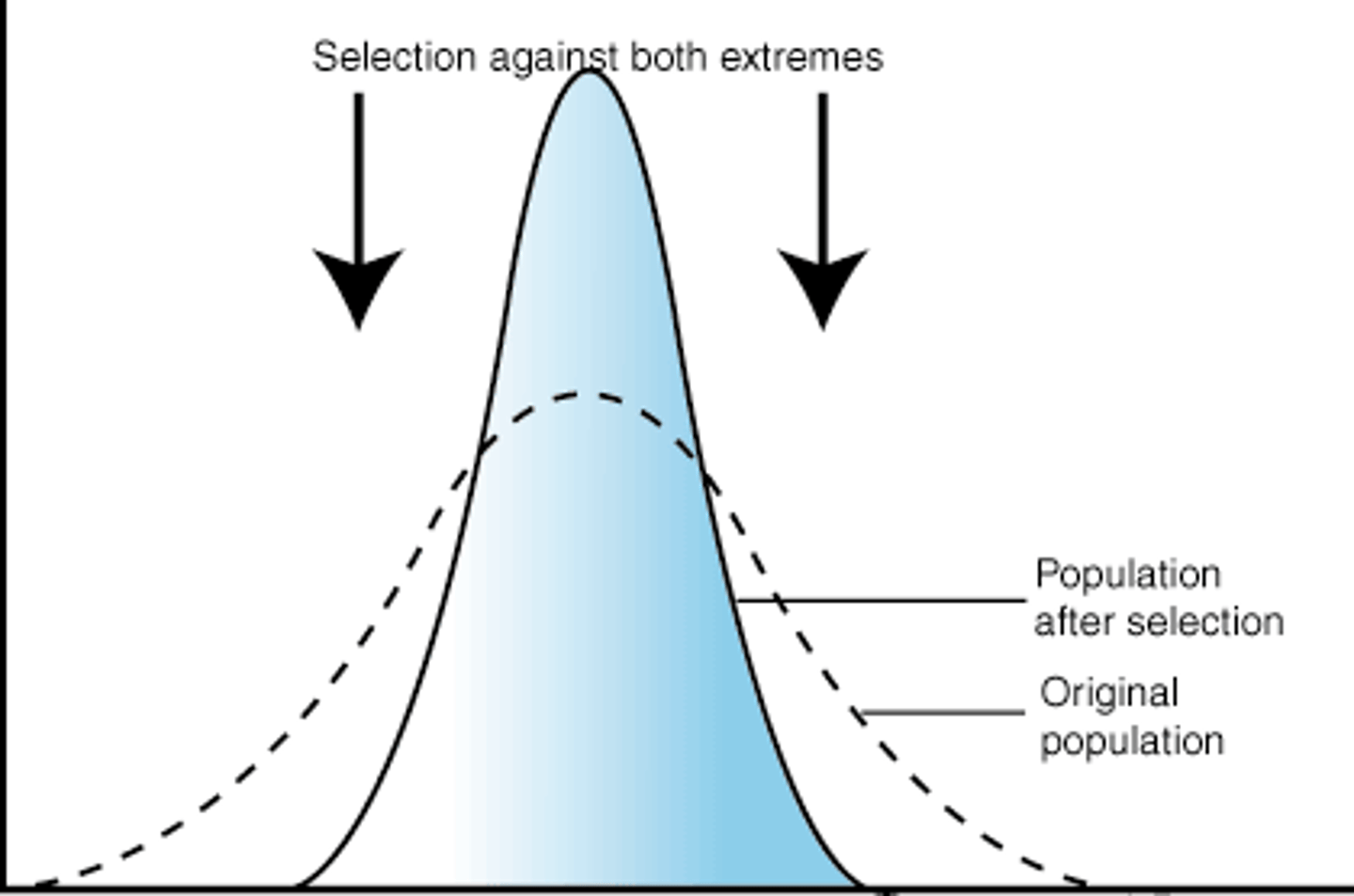
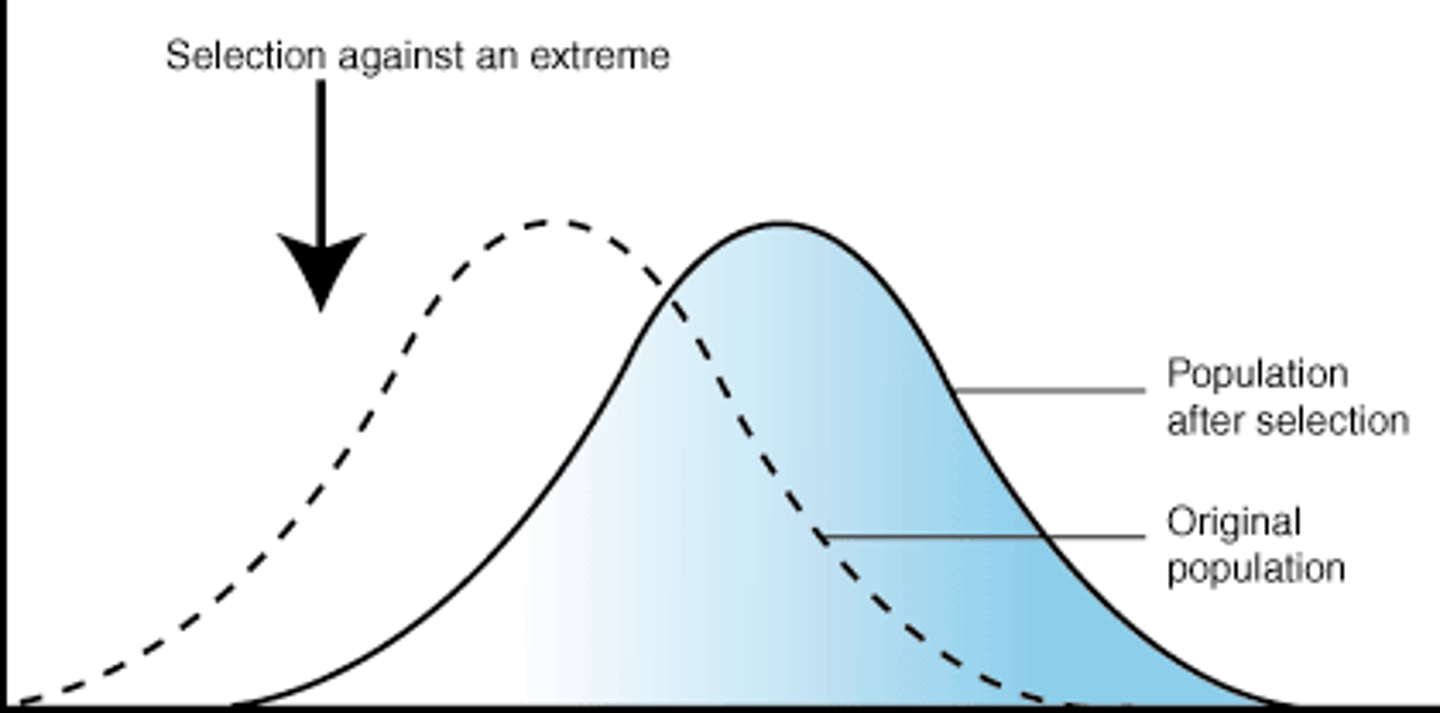
Directional selection
Factor that selects individuals with an extreme phenotype of a range of phenotypes so the population changes over time.
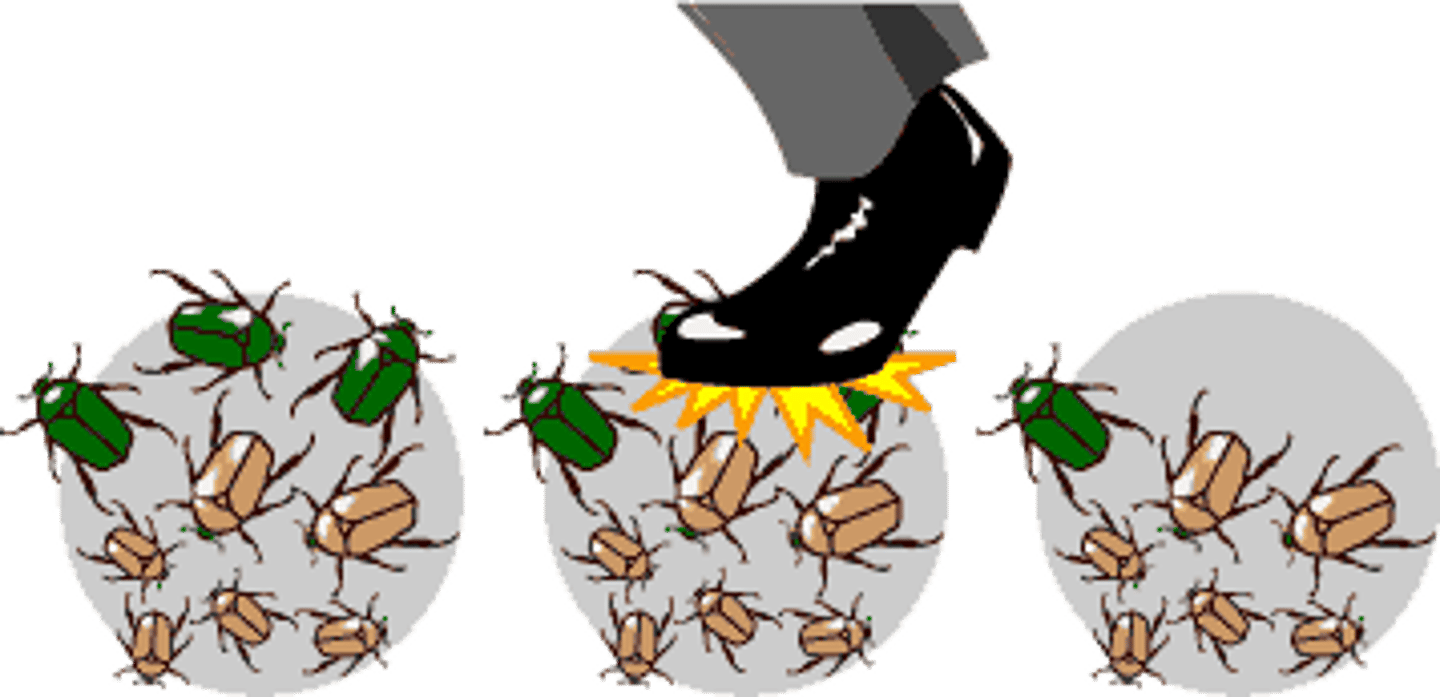
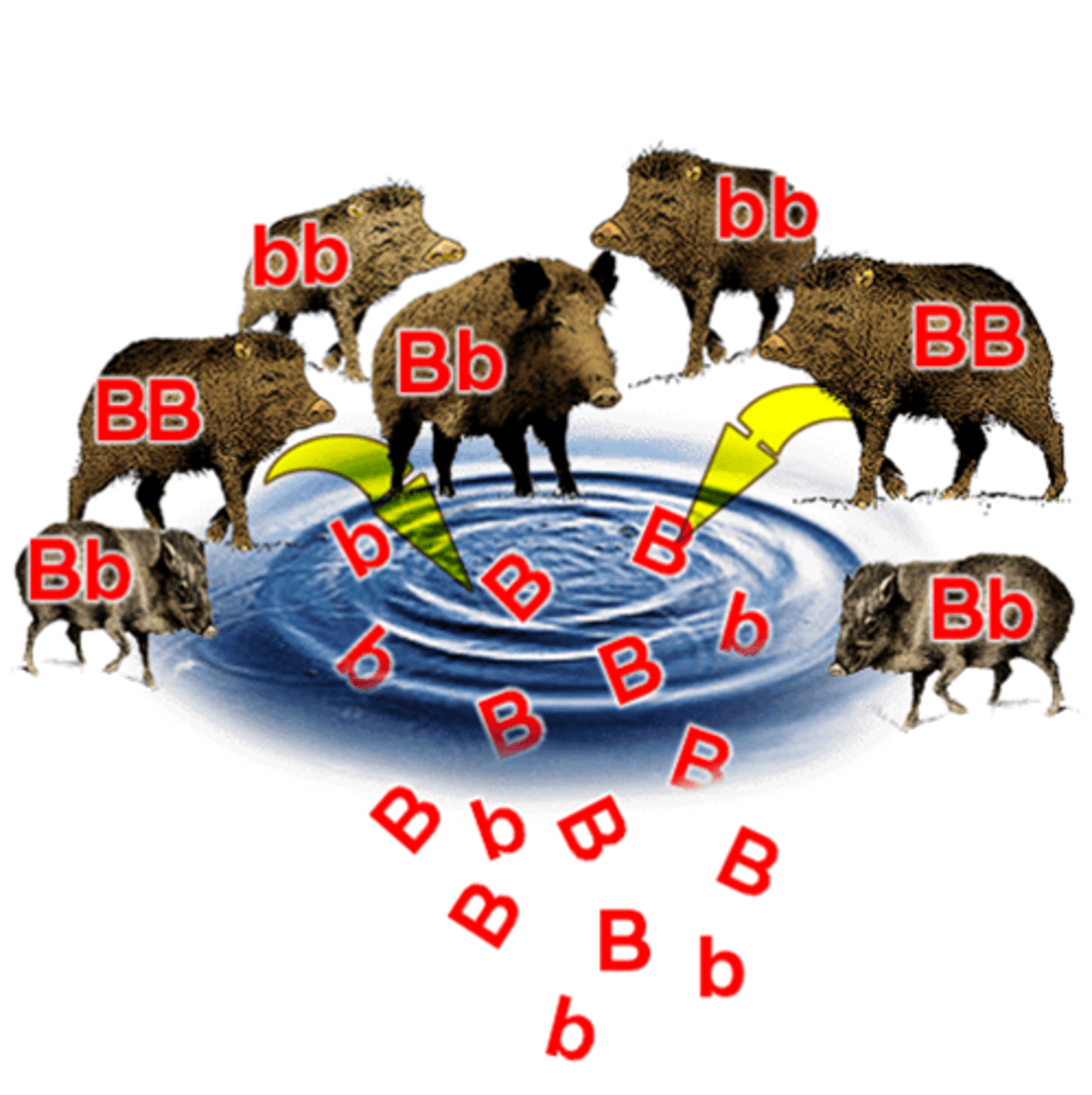
Genetic drift
The increase or decrease in the frequency of alleles as a result of chance events.

Carrying capacity
The maximum population size of a species that a particular habitat can support over time.
Gene pool
The sum of all the alleles in a population at a given time.
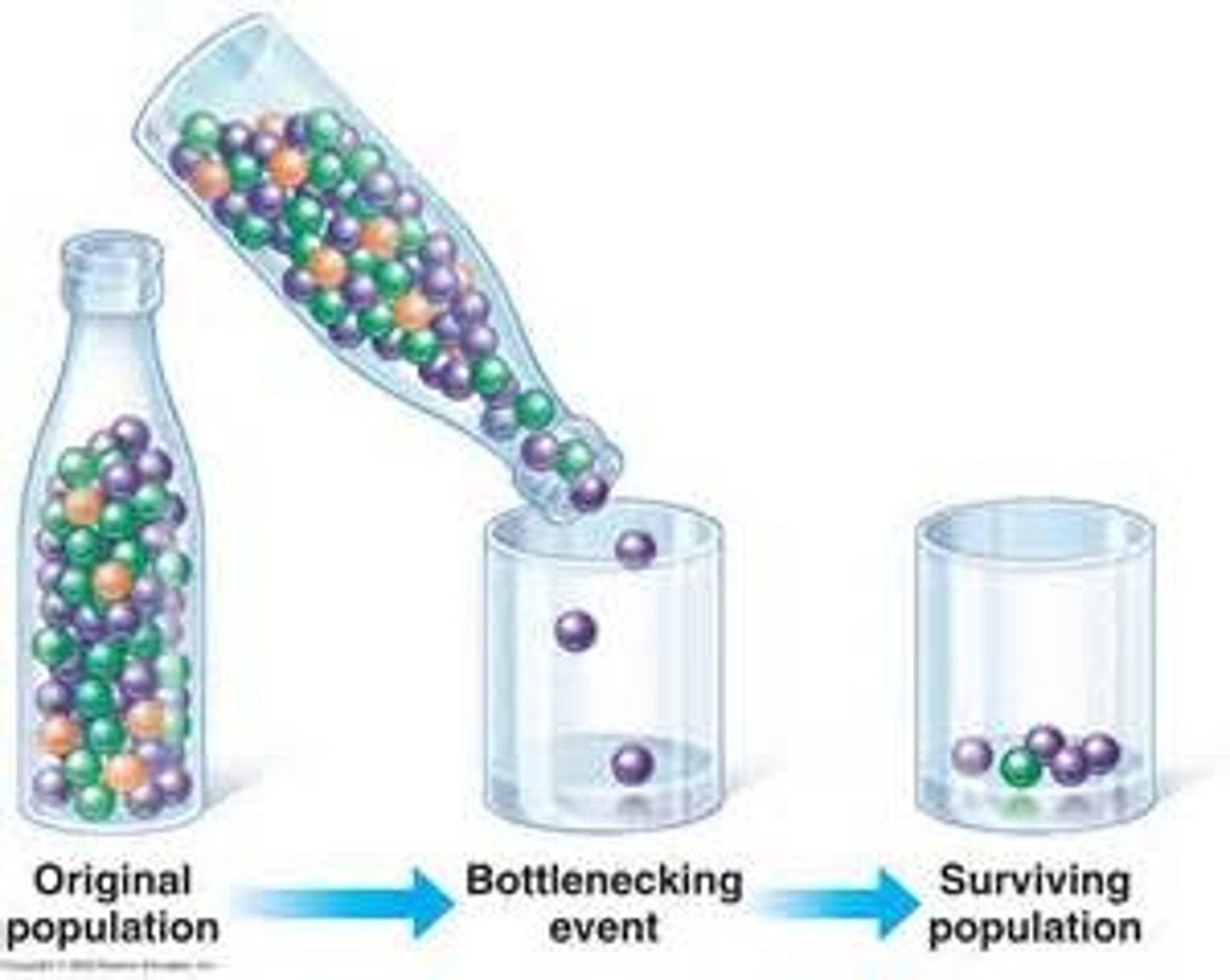
Genetic bottleneck
An event, such as a natural disaster, that causes a large reduction in the size of a population.
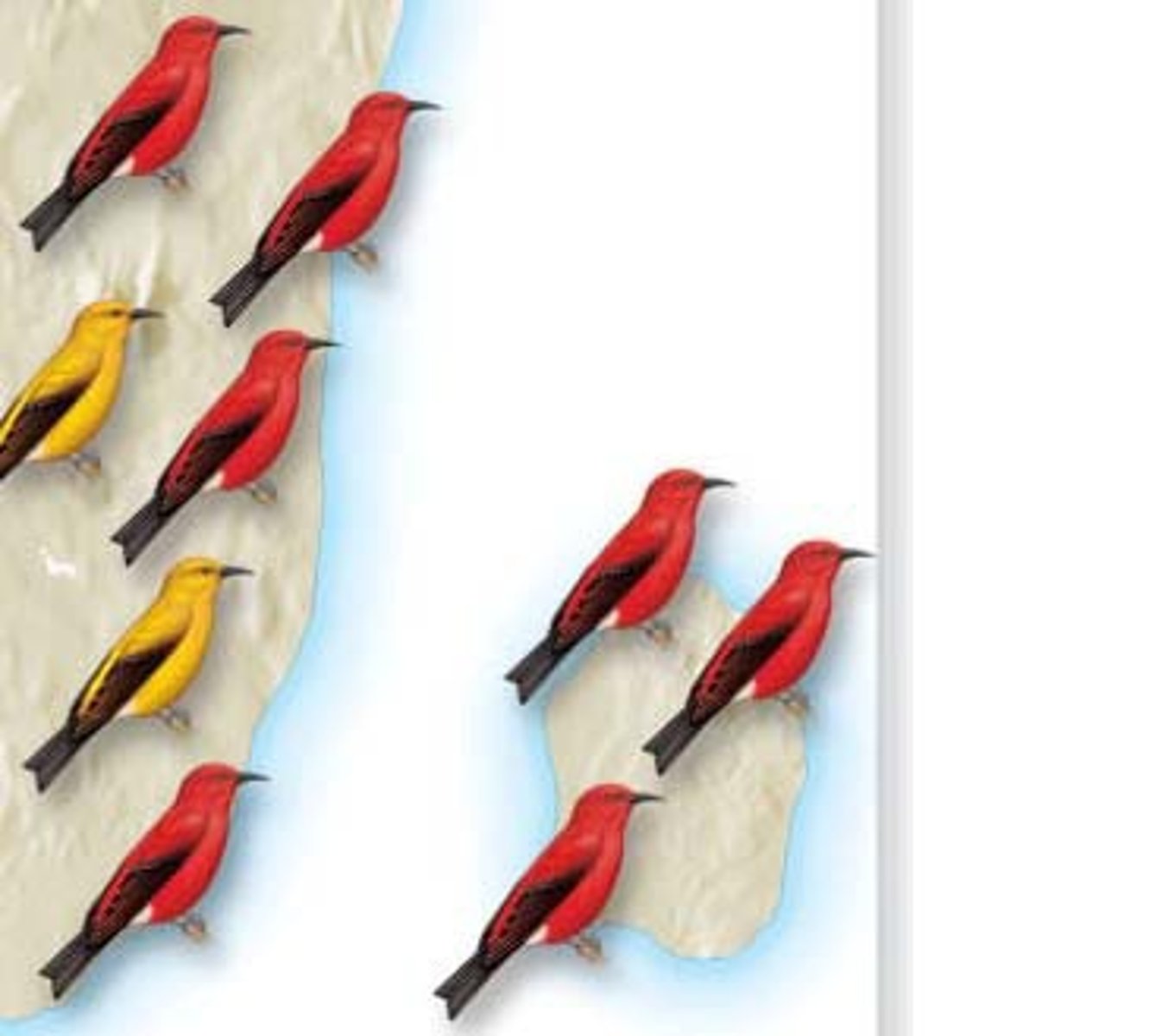
Founder effect
What happens when a small number of individuals start a new population and there is only a small number of alleles.

Species
A group of similar organisms that can reproduce to give fertile offspring.

Allopatric speciation
Populations become geographically isolated and, as a result of natural selection, form new species.
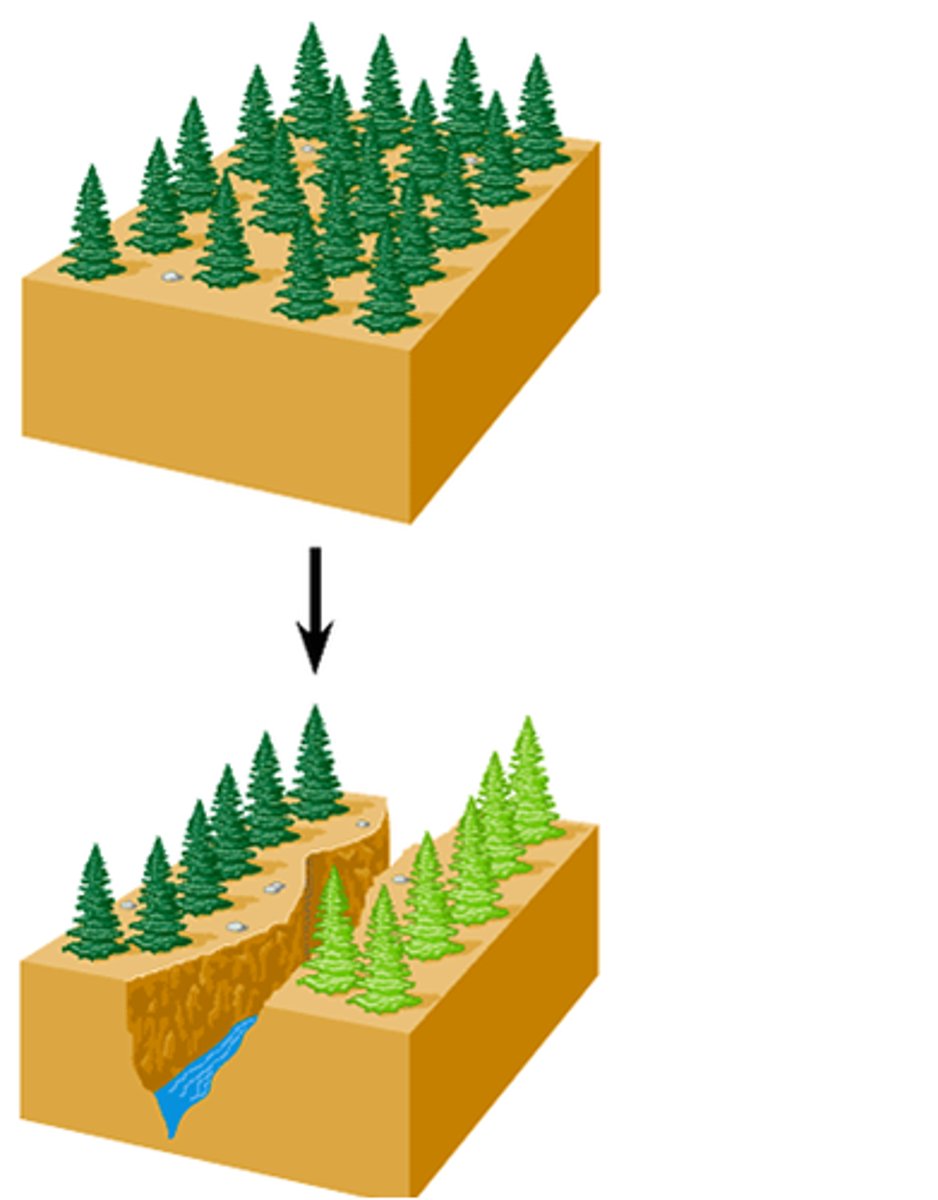
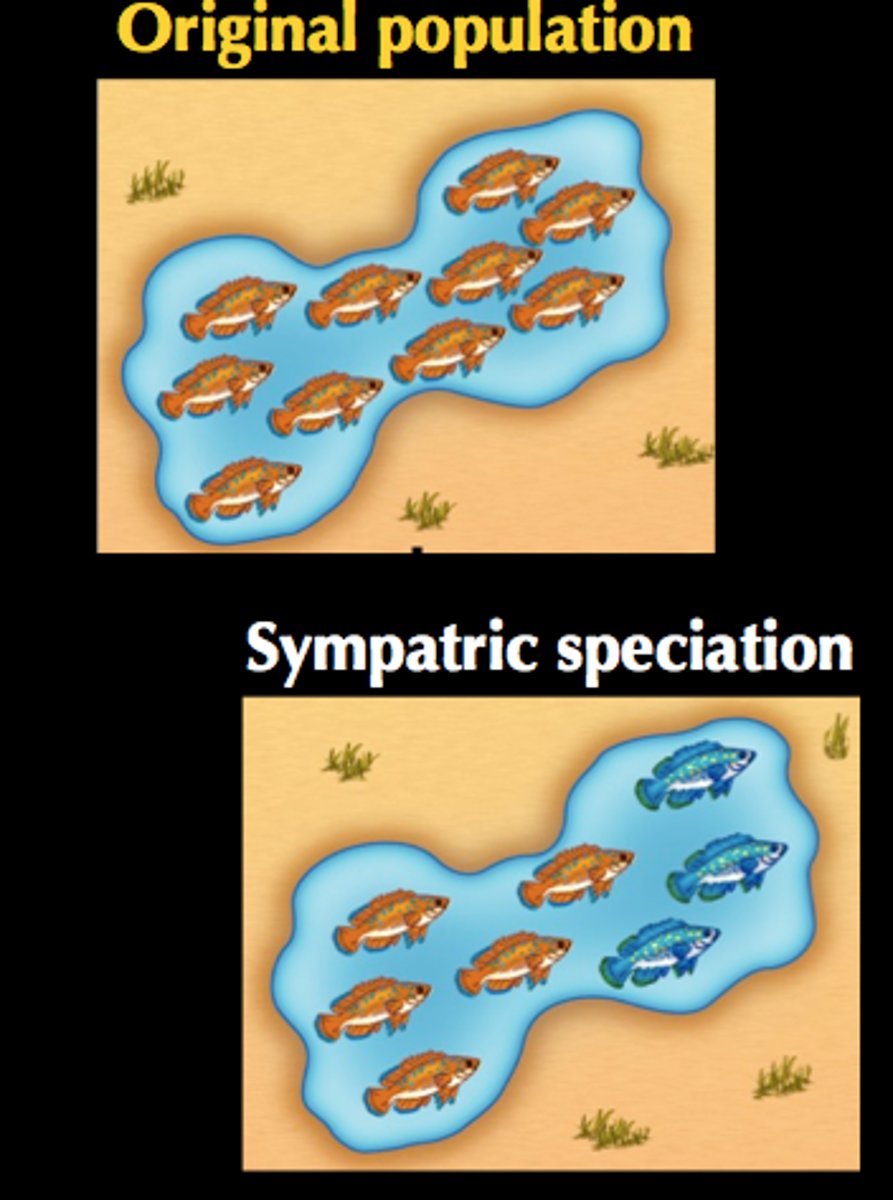
Sympatric speciation
Formation of a new species without geographical isolation.
Reproductive isolation
Populations cannot breed successfully together because of mechanical changes or behavioral changes.

Geographical isolation
A physical barrier such as a mountain range or a desert that prevents gene flow between populations.

Natural selection
The mechanism of evolution.It is the survival of individuals in a population to reproduce and pass on their alleles to the next generation.
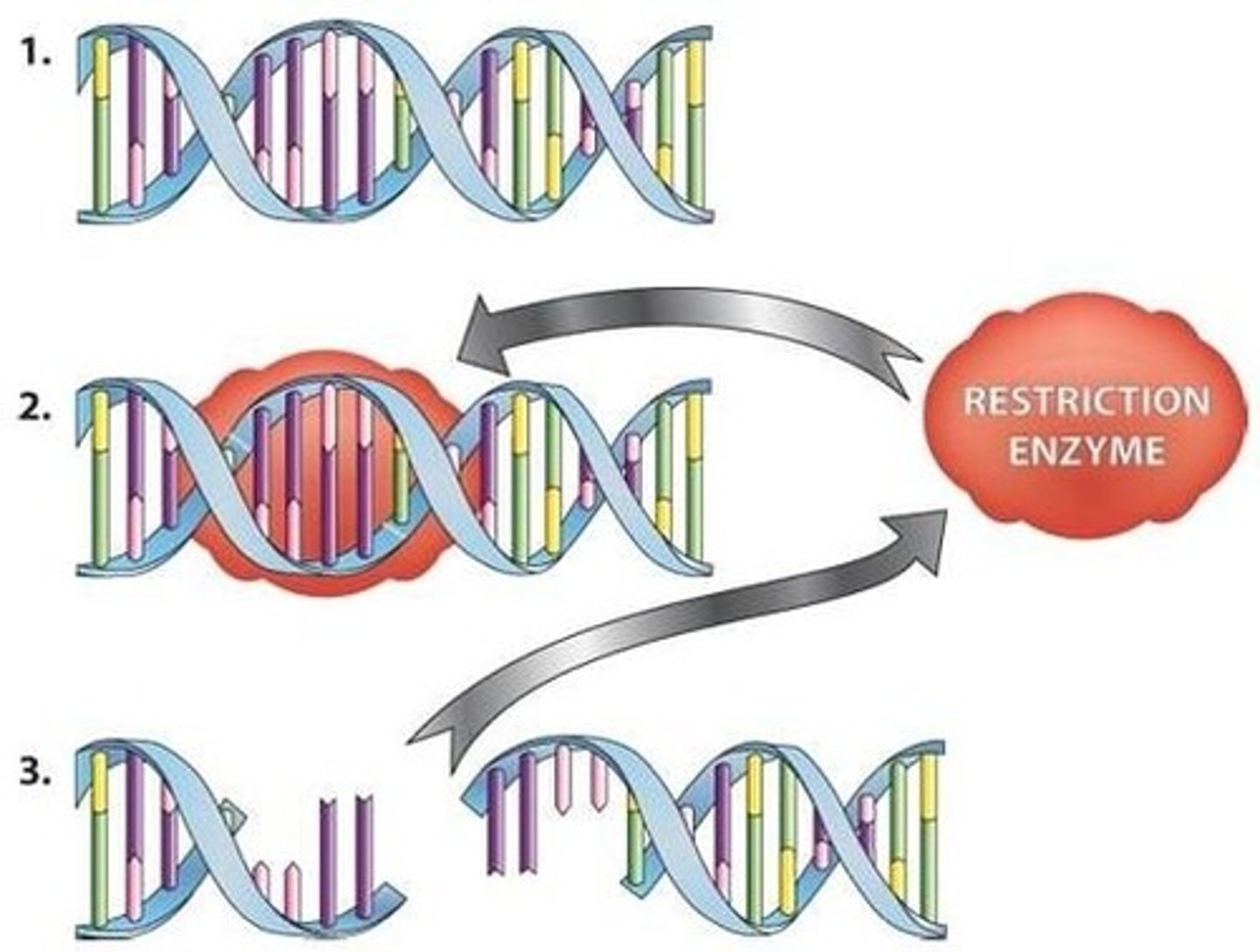
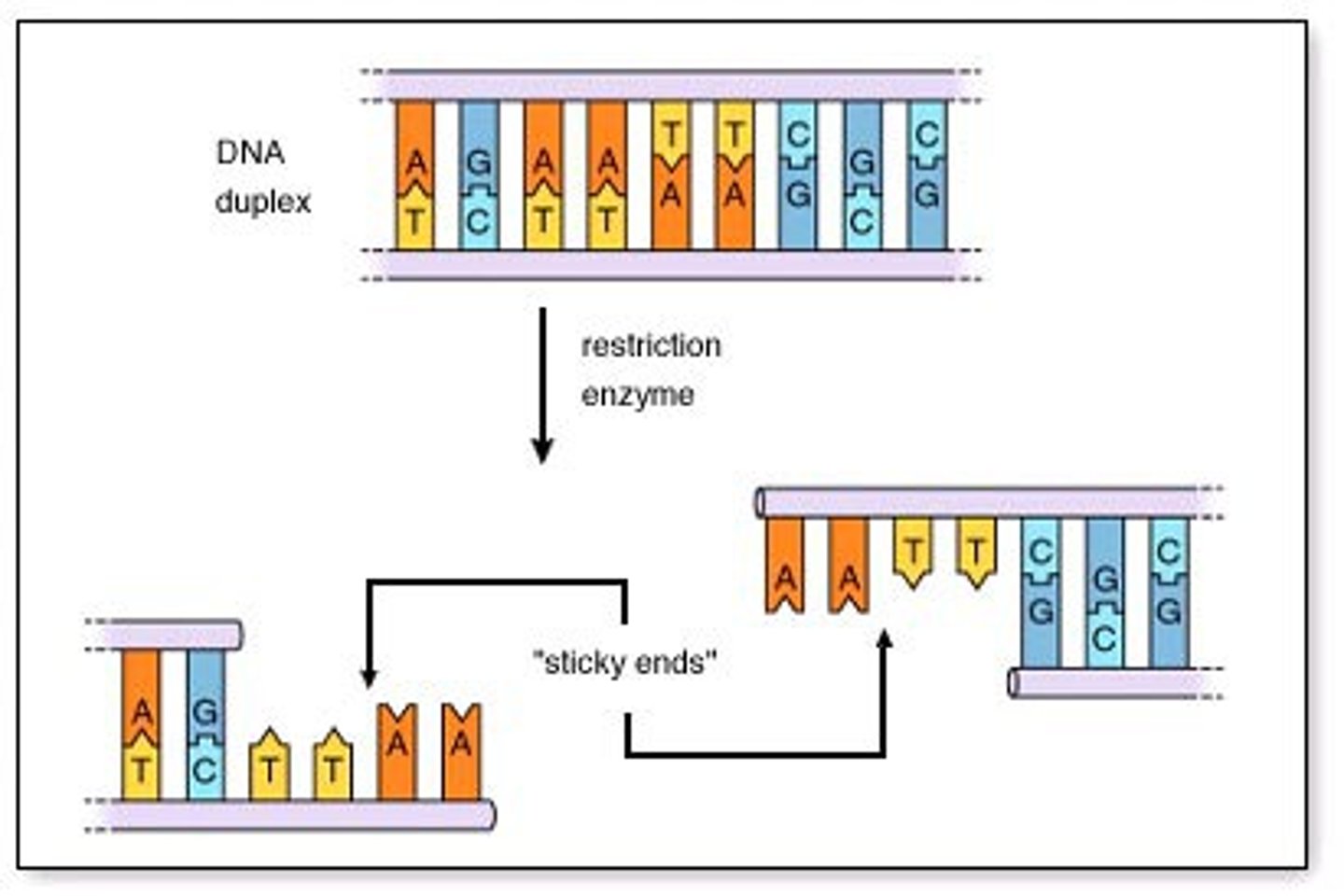
Restriction endonuclease
Enzyme that cuts DNA molecules at a specific sequence of bases.
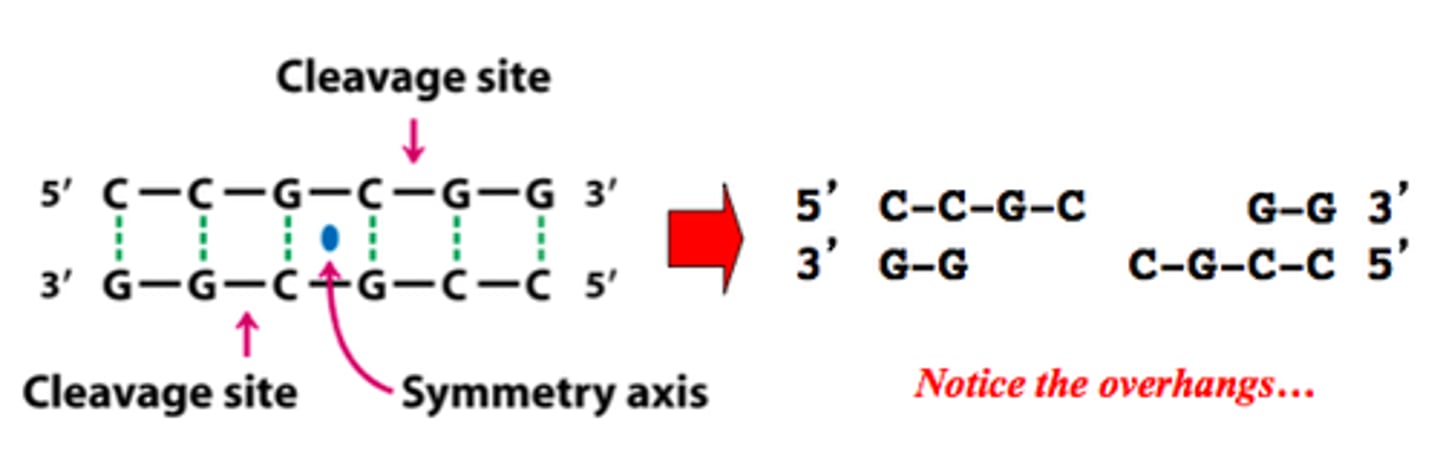
Palindromic recognition site
The specific sequence of bases where a restriction enzyme will cut. The sequence of bases reads the same in opposite directions.
DNA ligase
Enzyme which joins sections of DNA together, catalysing condensation reaction.
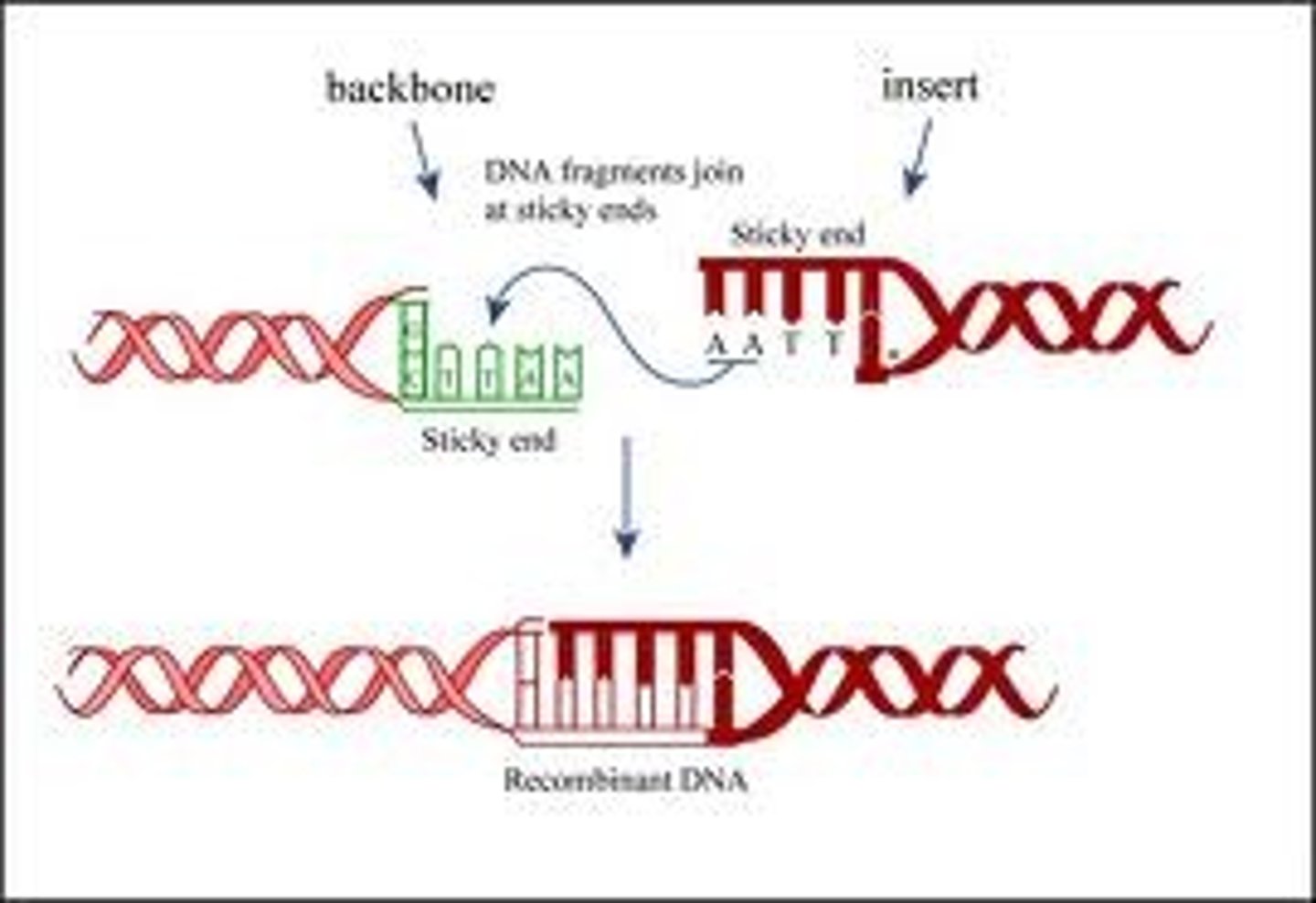
Sticky ends
When a restriction endonuclease cuts DNA and leaves unpaired bases.
Vector DNA
Used to transfer DNA into a cell eg a plasmid or bacteriophage.
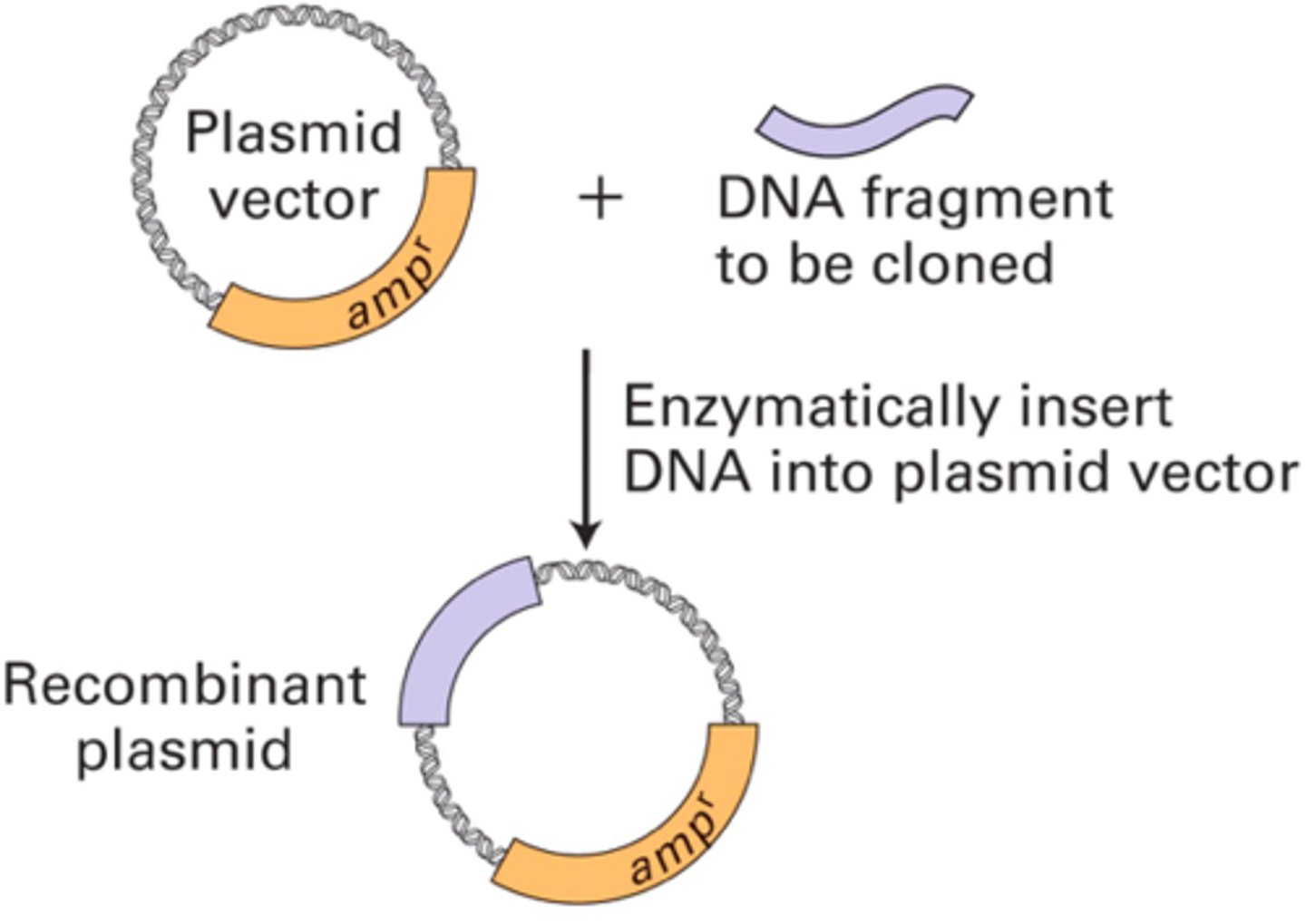
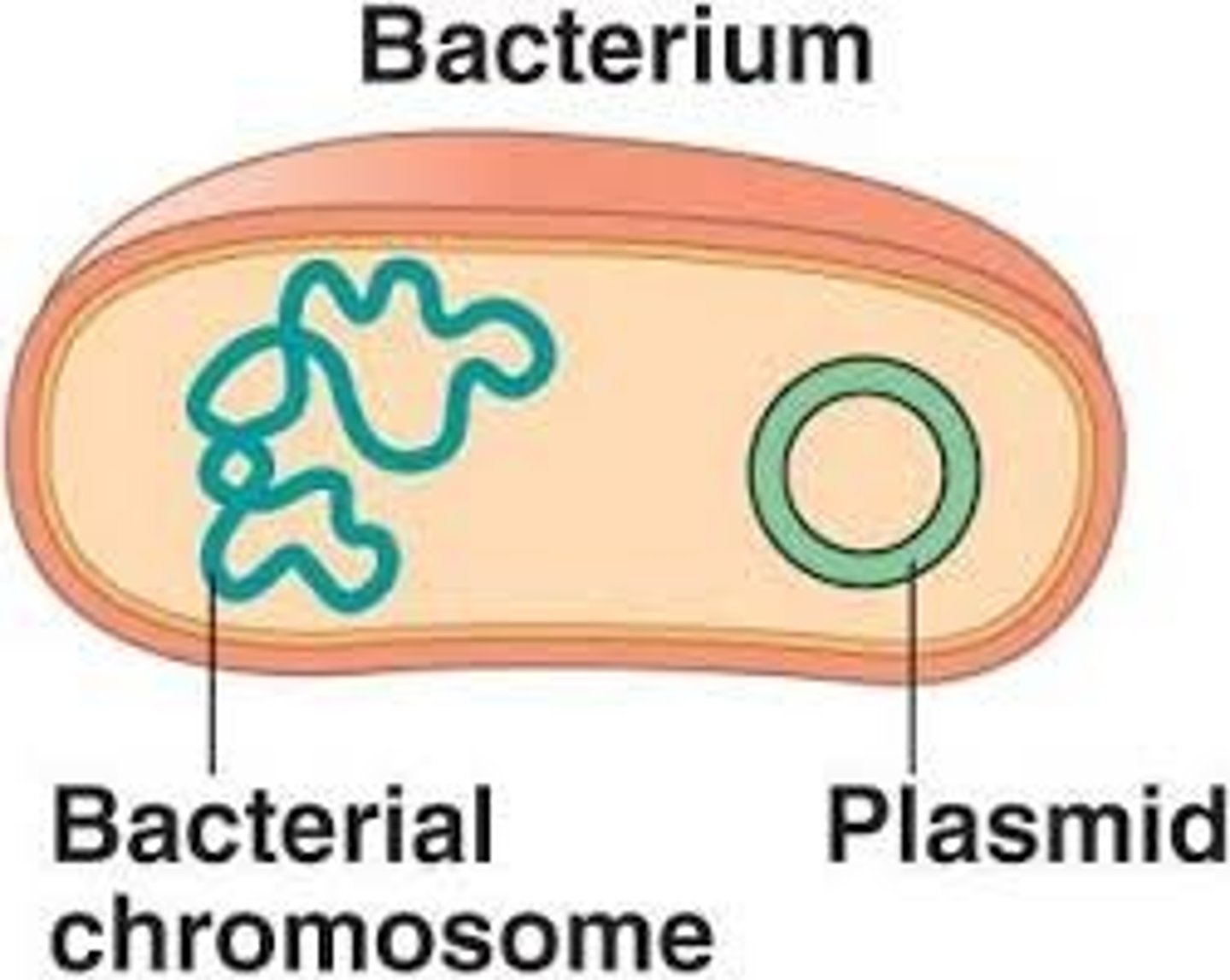
Plasmid
Small, circular molecule of DNA used to transfer DNA into cells.
Bacteriophage
A virus that infects a bacterium and can be used as a DNA vector.
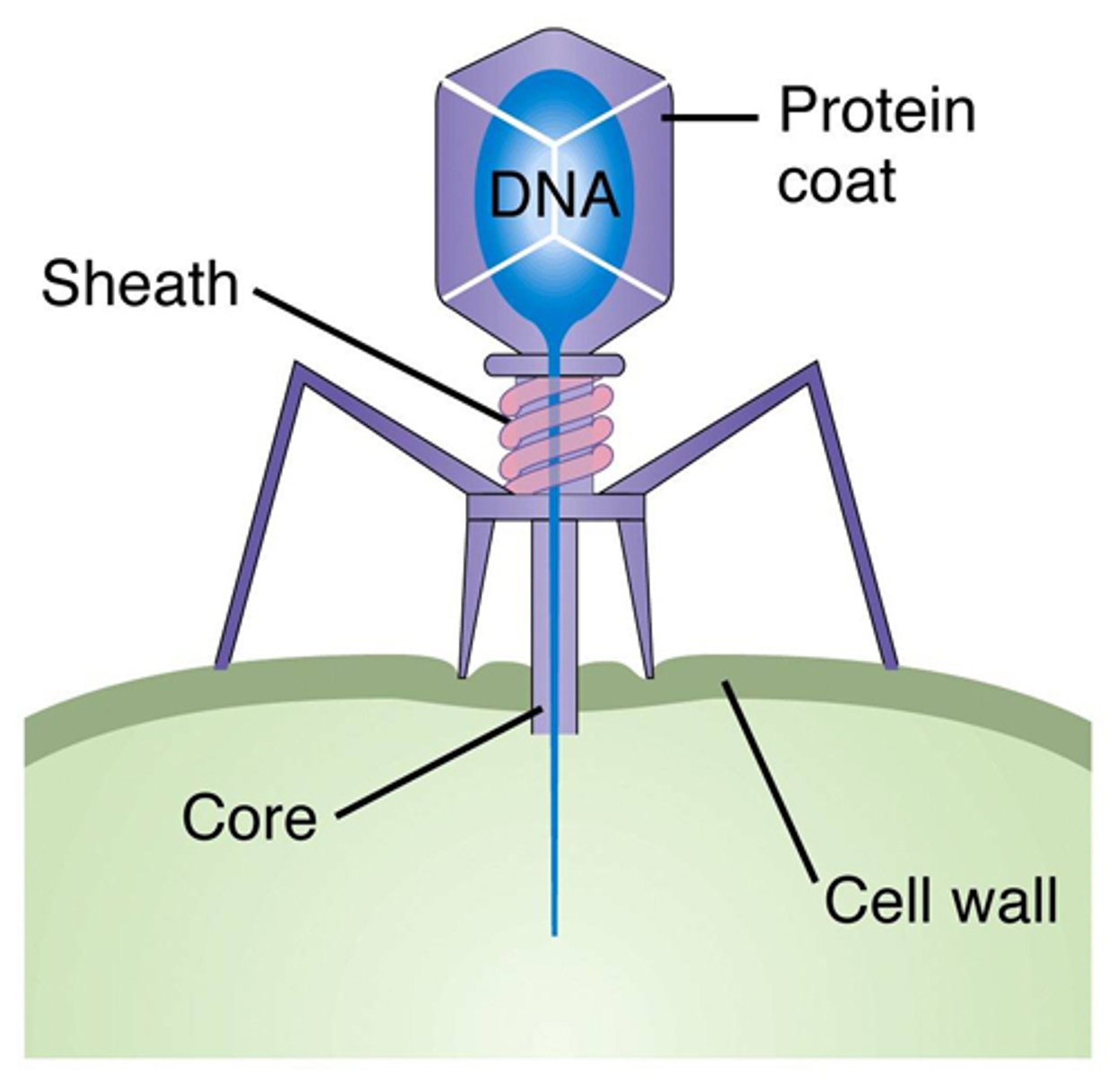
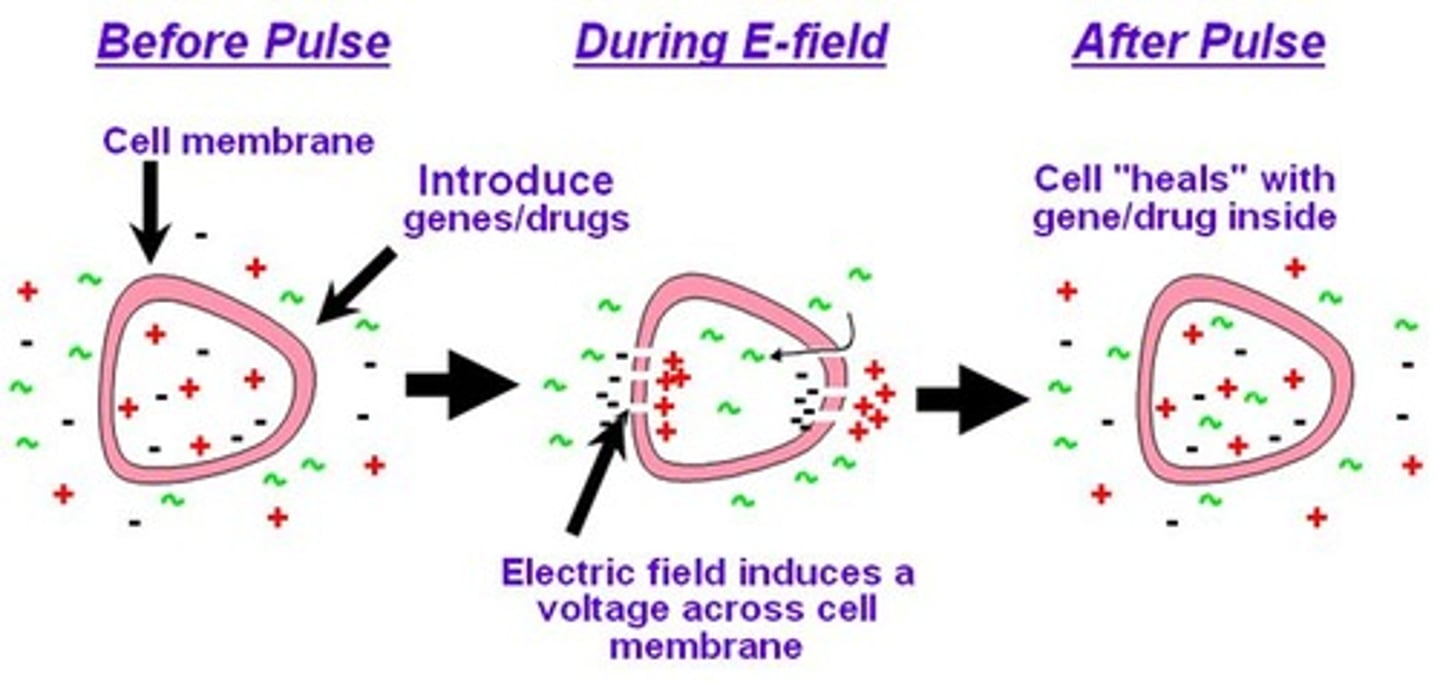
Electroporation
An electric field used to increase the permeability of a bacterial cell membrane so that it takes up plasmids more readily.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
A bacterium used to introduce genes into a plant cell in order to produce genetically modified plants.

Technology transfer
The sharing of knowledge, skills and technology.
Somatic gene therapy
Altering the alleles in body cells in order to treat a genetic disorder.
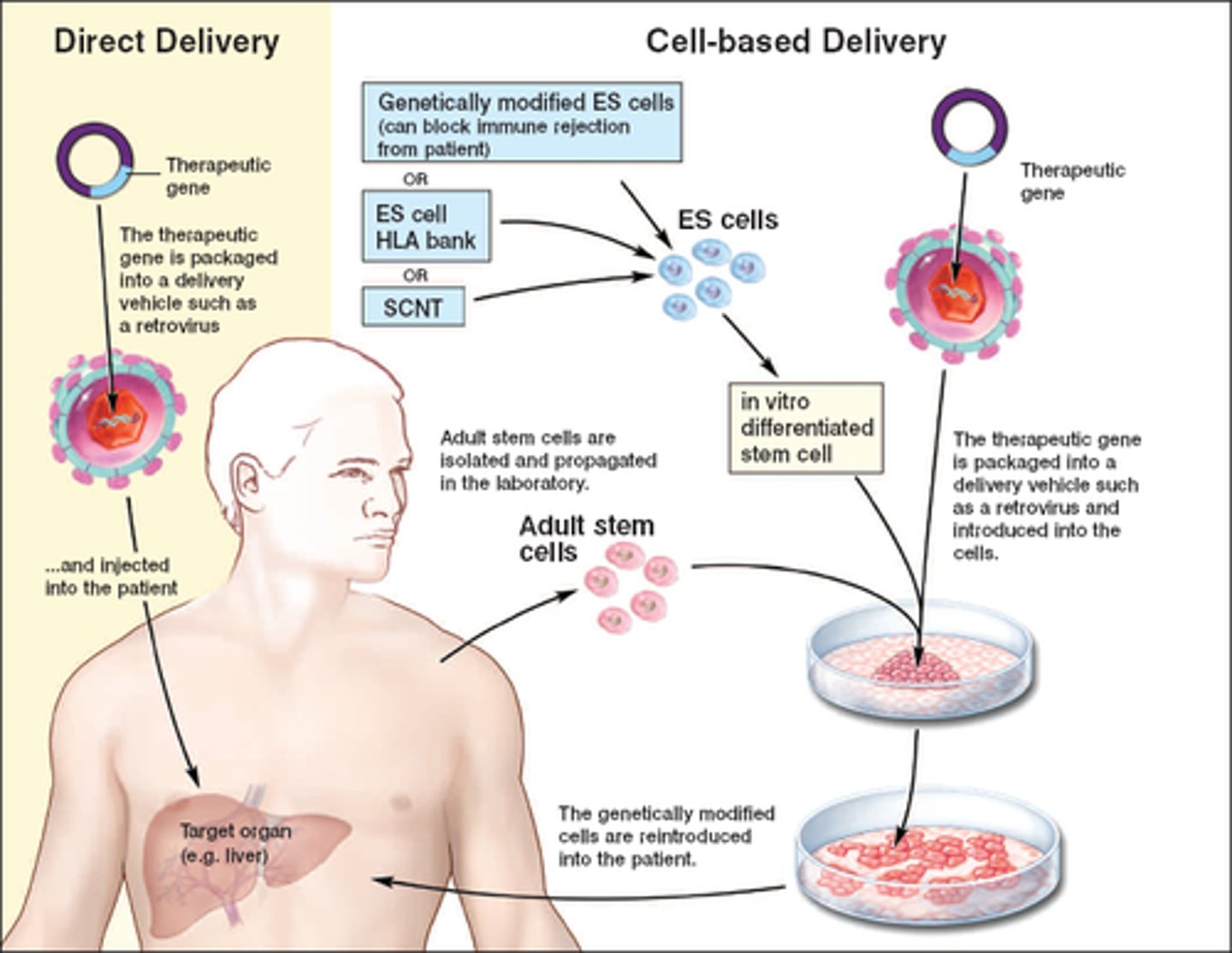
Germ line gene therapy
Altering the alleles in sex cells/zygotes. (Currently illegal in humans)
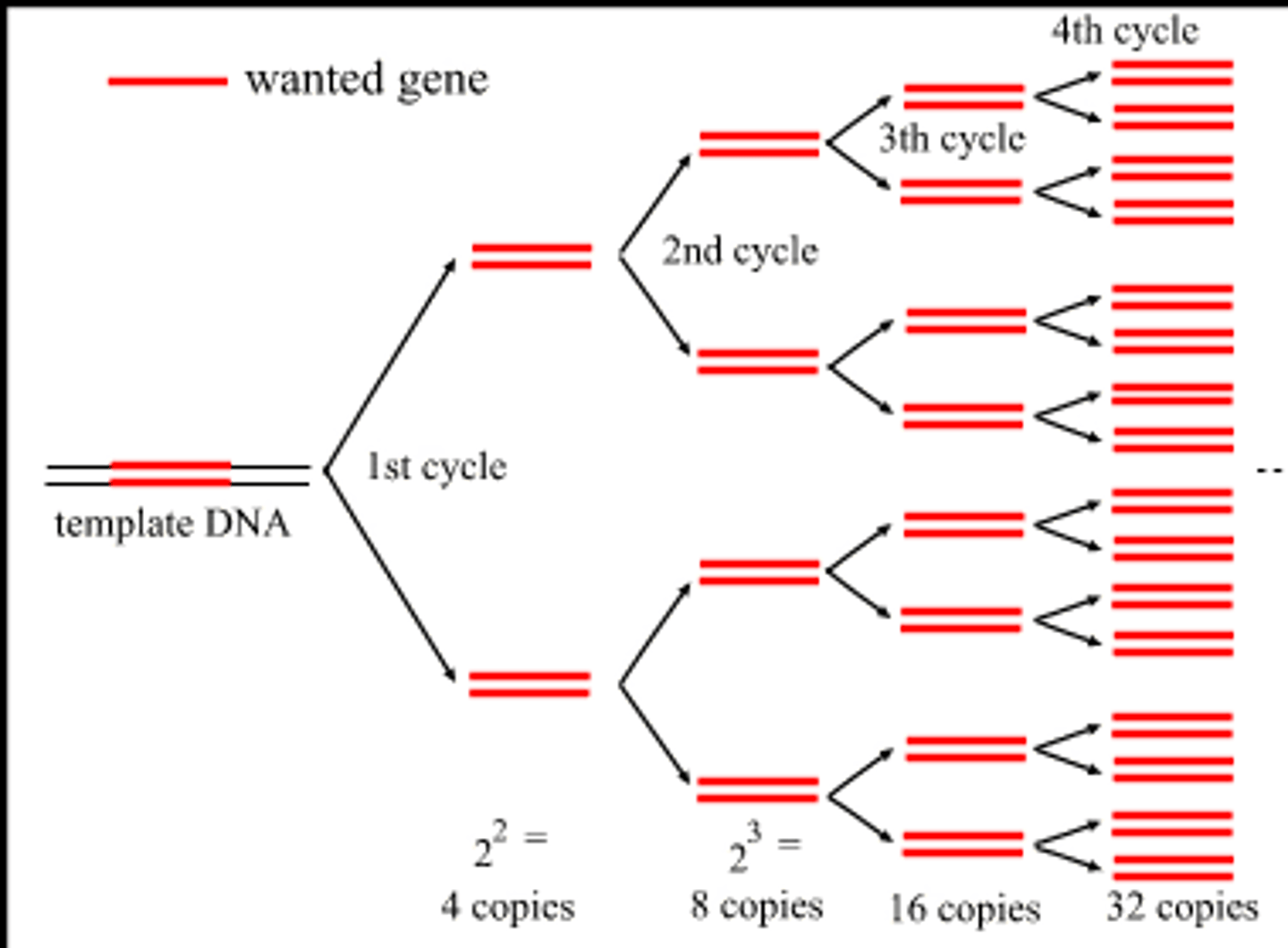
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Technique used to (amplify) copy fragments of DNA millions of times in just a few hours. (Also called in vitro cloning.)
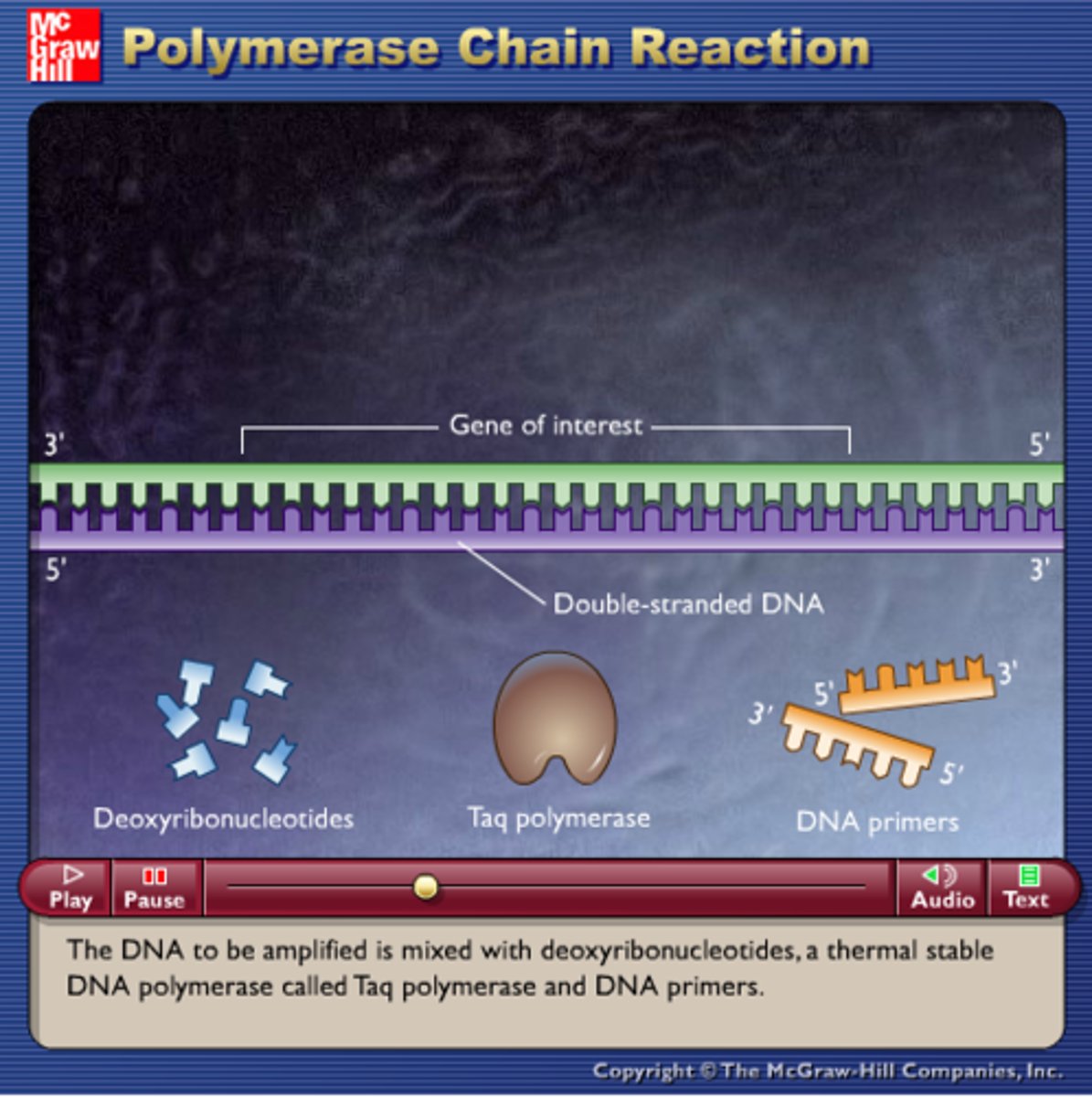
Thermostable DNA polymerase
Enzyme used to copy DNA in PCR which is not denatured by high temperatures.
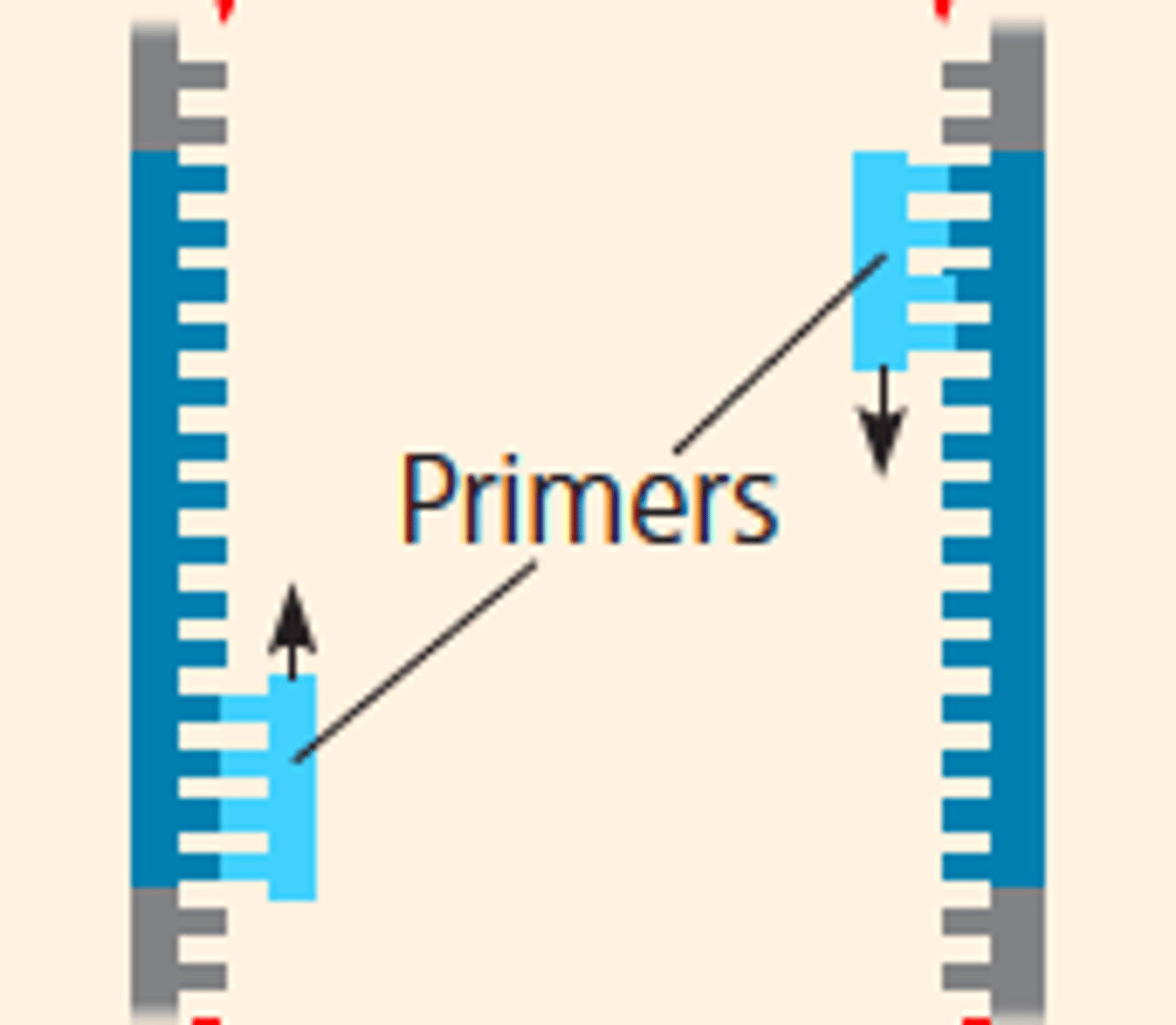
Primer
Short section of single stranded DNA which binds to DNA in PCR and acts as a binding site for DNA polymerase and initiates copying of the DNA.
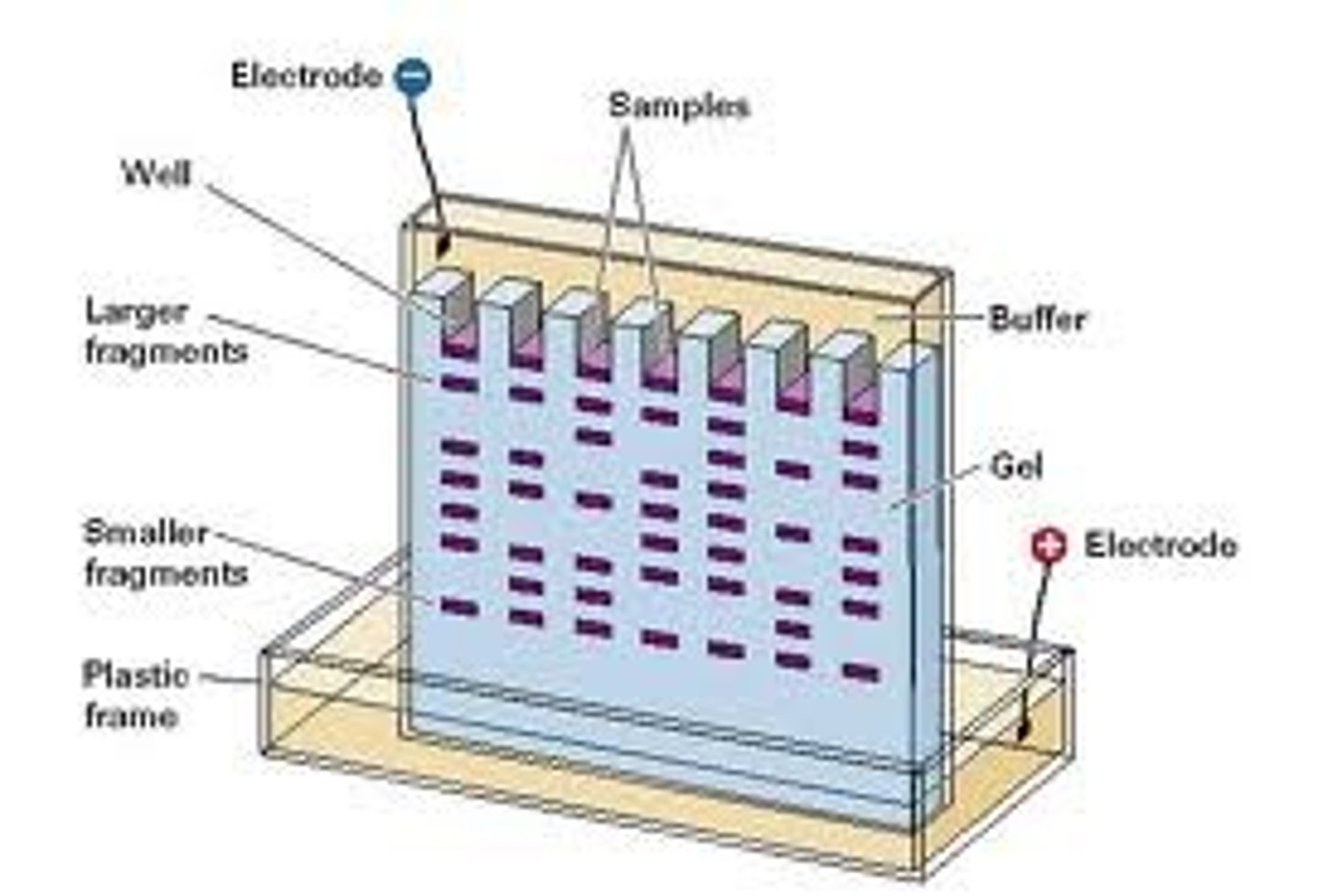
Electrophoresis
Technique that uses an electric field to separate DNA fragments, RNA fragments or proteins, based on their size (and in the case or proteins the charges on the R groups.)
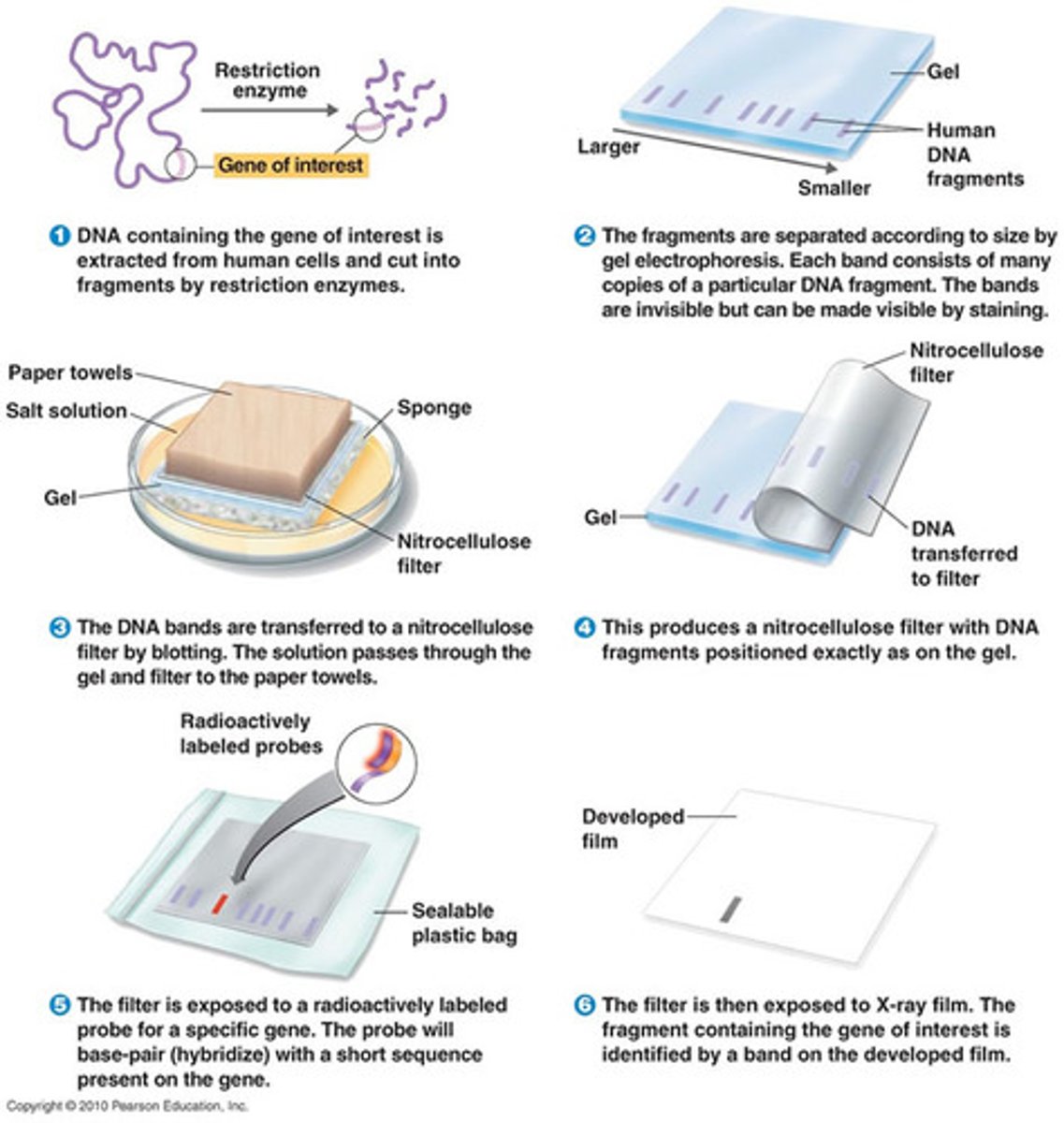
Southern blotting
Technique that transfers DNA fragments from agarose gel to a nylon membrane after electrophoresis
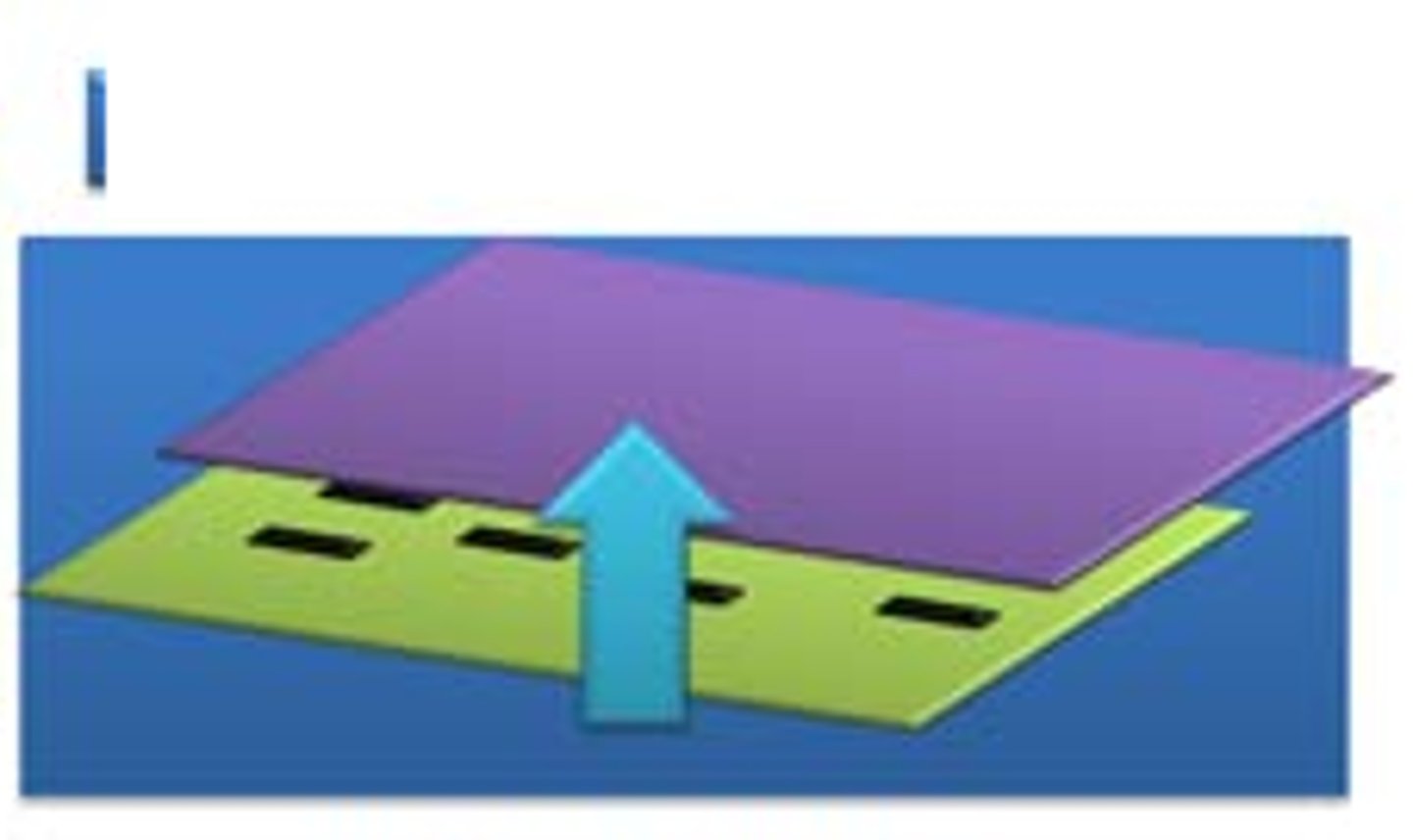
DNA probe
Short section of single stranded DNA used to bind to a complementary sequence of bases. Used to identify specific sections of DNA, following electrophoresis and Southern blotting.
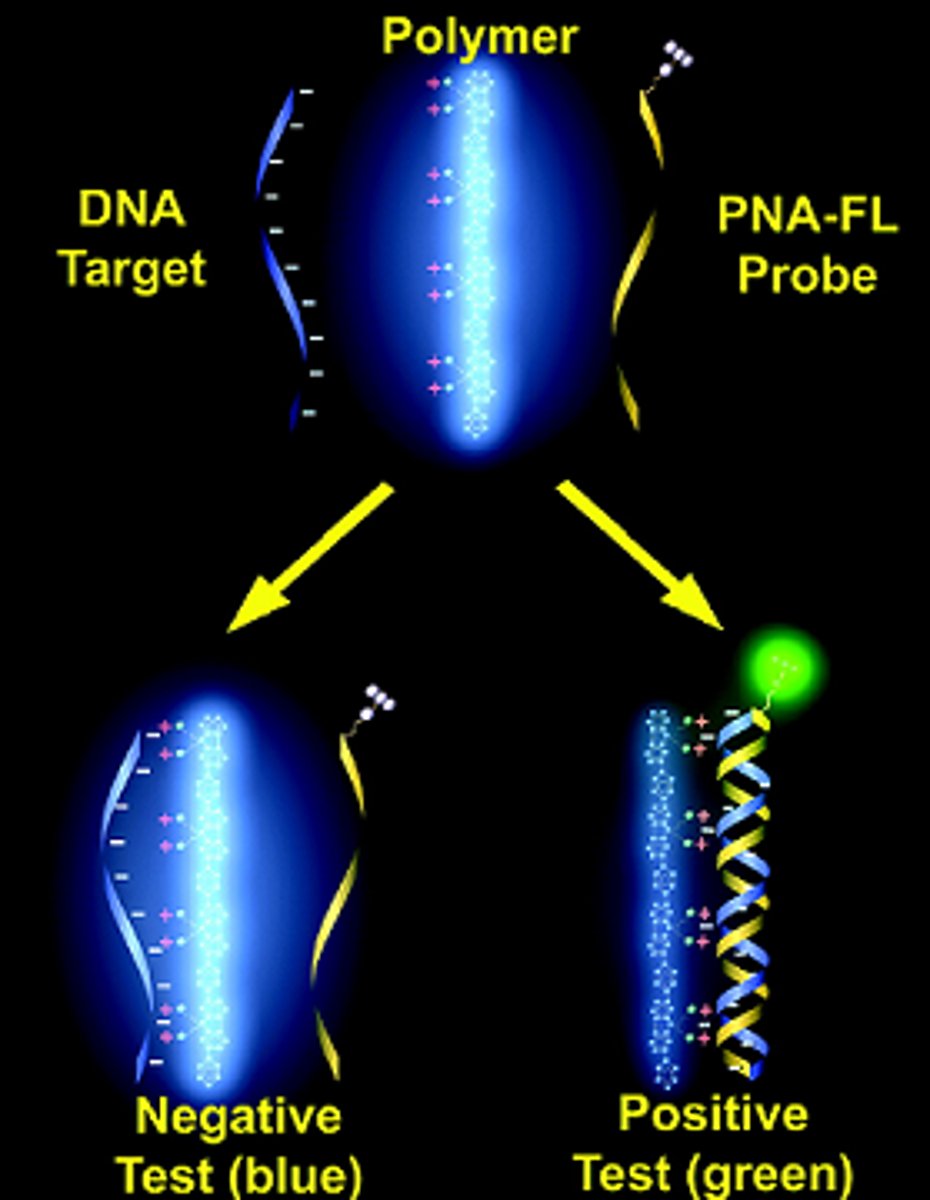
DNA hybridisation
When probes hydrogen bind to DNA fragments, provided that they have a complementary sequence of bases.
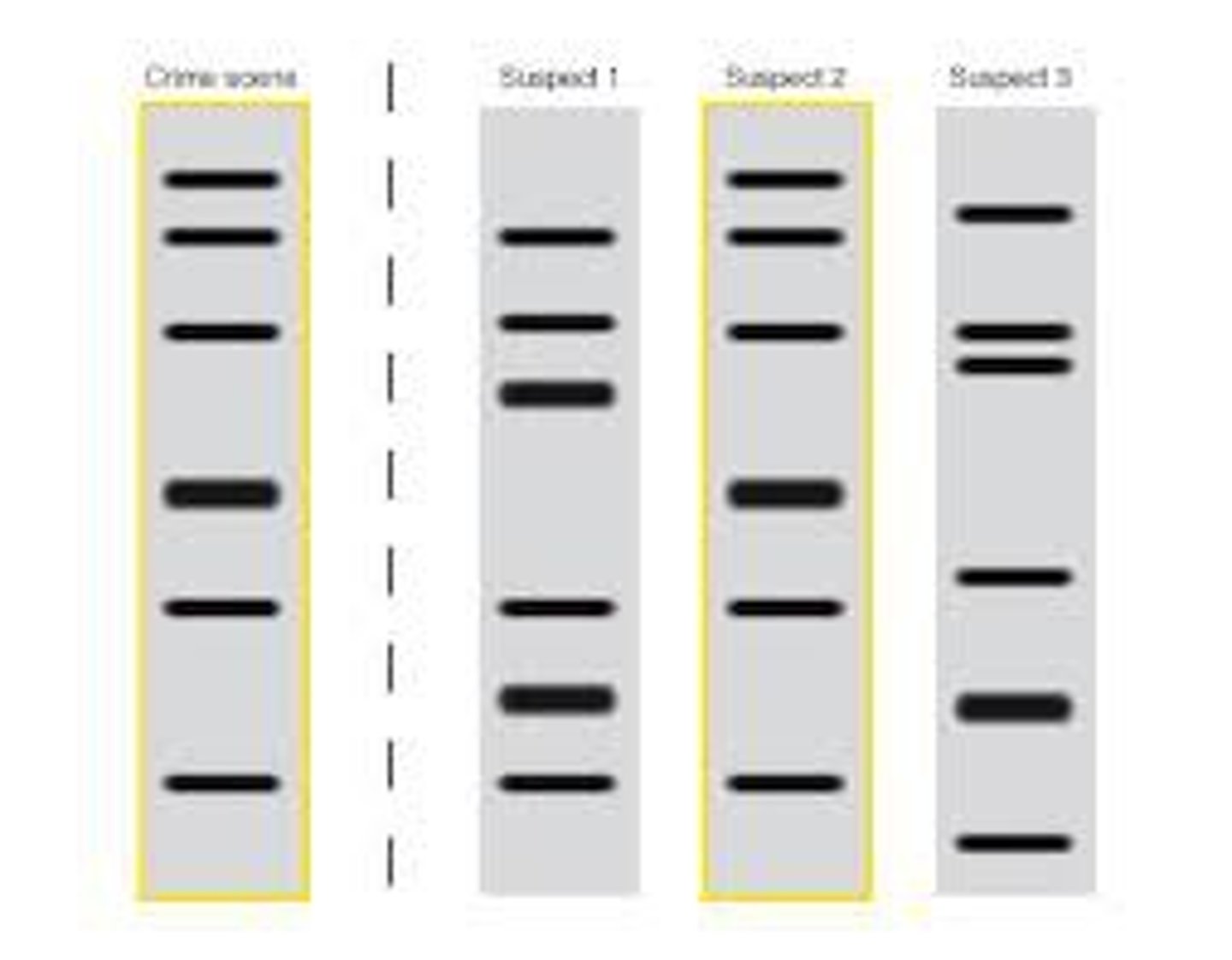
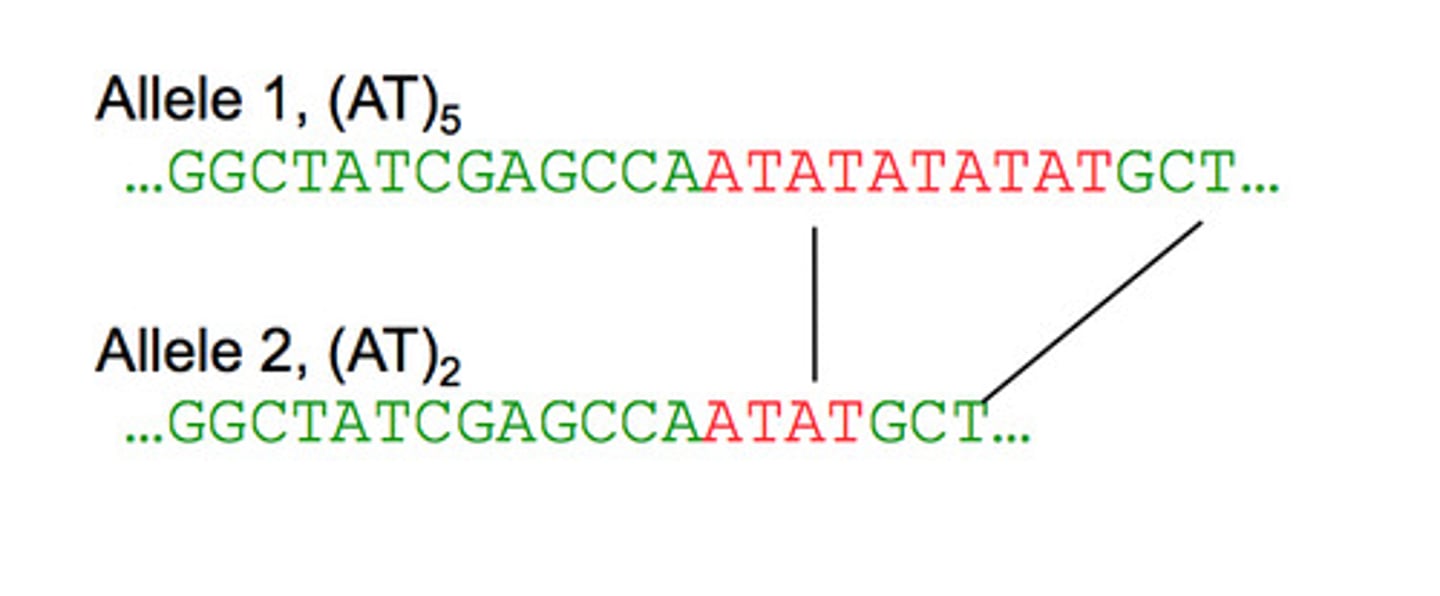
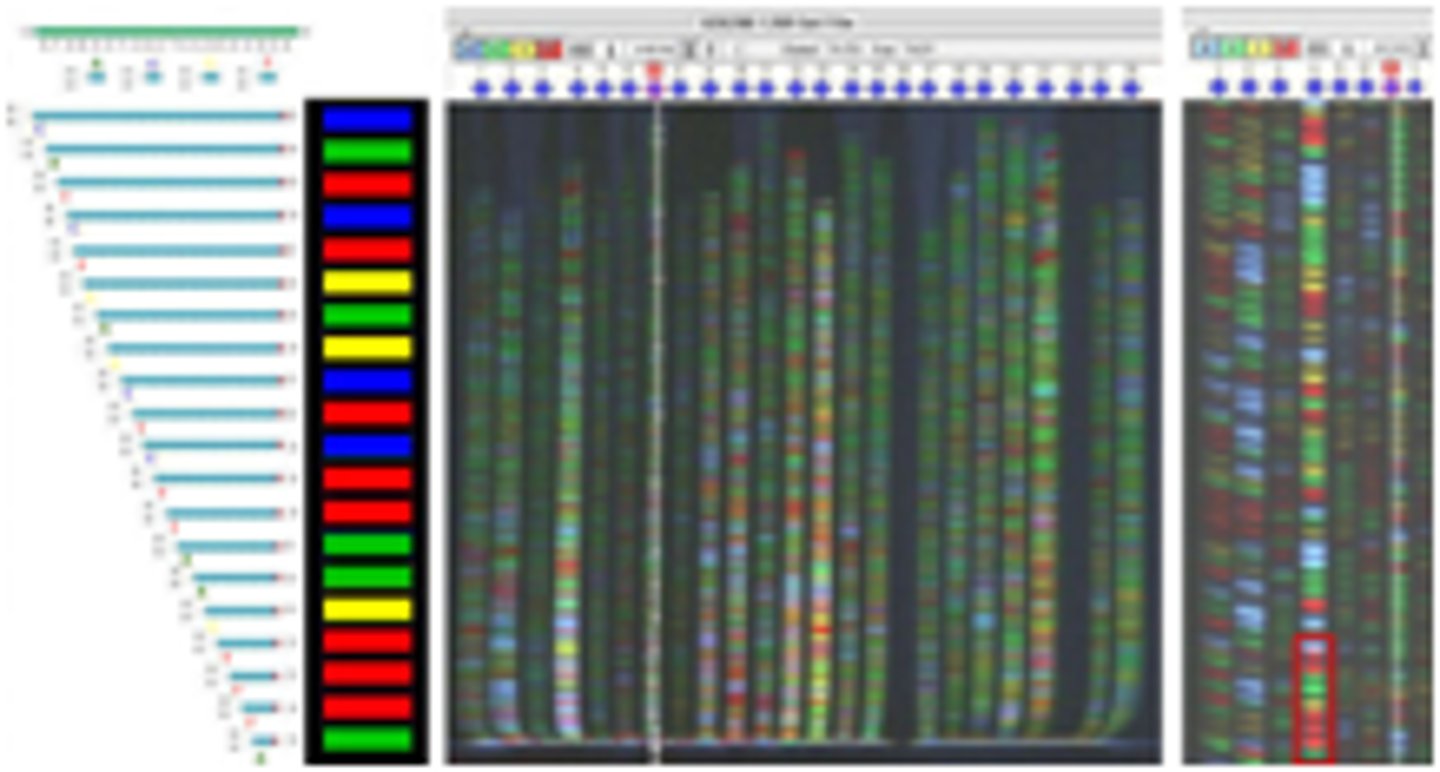
DNA profile
A unique gel produced by DNA electrophoresis that shows the number of times repetitive, non-coding bases sequences are repeated at different loci in an individual.
Variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs) or Minisatellites
Sections of non-coding DNA base sequences that are repeated at different loci and used in DNA profiling.
Genetic screening
A technique that uses electrophoresis and probes to identify, for example, whether individuals are carriers of genetic disorders.
Preimplantation genetic haplotyping (PGH)
DNA sequencing
The process of determining the order of nucleotides within a DNA molecule.
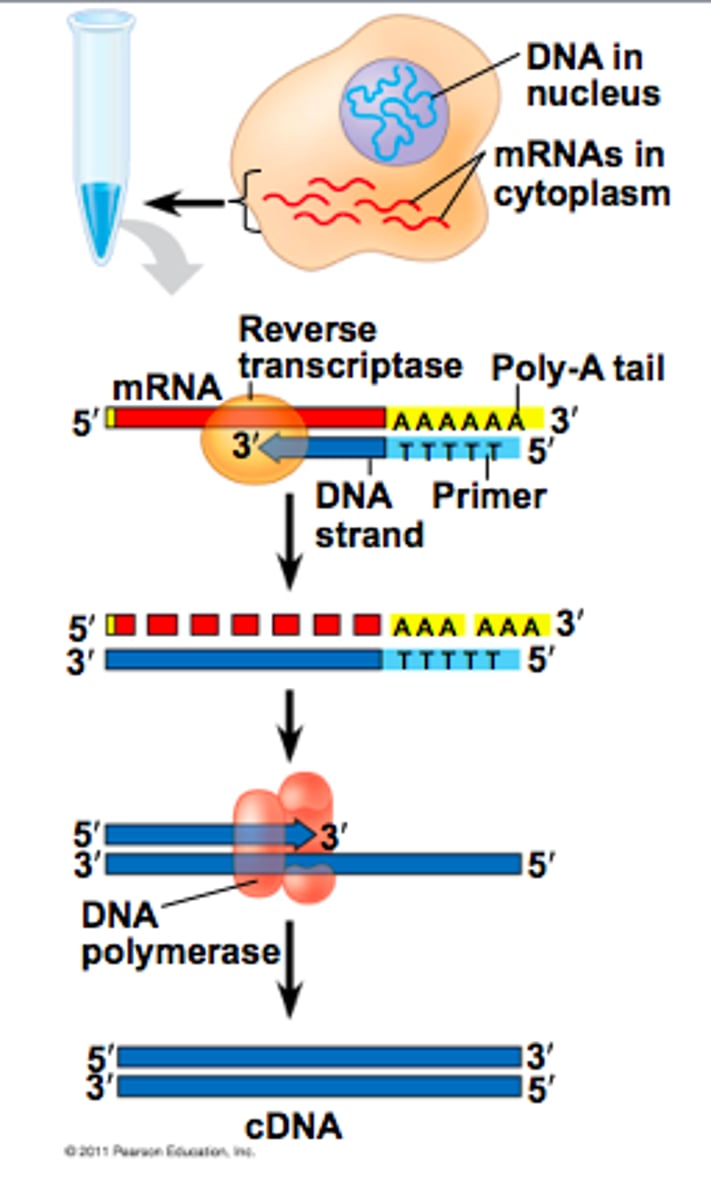
Reverse transcriptase
Enzyme that uses RNA as a template to make complementary DNA (cDNA)
Marker gene
Gene such as that for antibiotic resistance or green fluorescent protein used to identify transformed organisms.
Genome
The minimum quantity of DNA that contains one set of all the genes in an organism, including mitochondrial DNA and the DNA in the chloroplasts of plants.
Recombination DNA
DNA formed by joining together DNA from different sources eg a human gene in a bacterial plasmid.
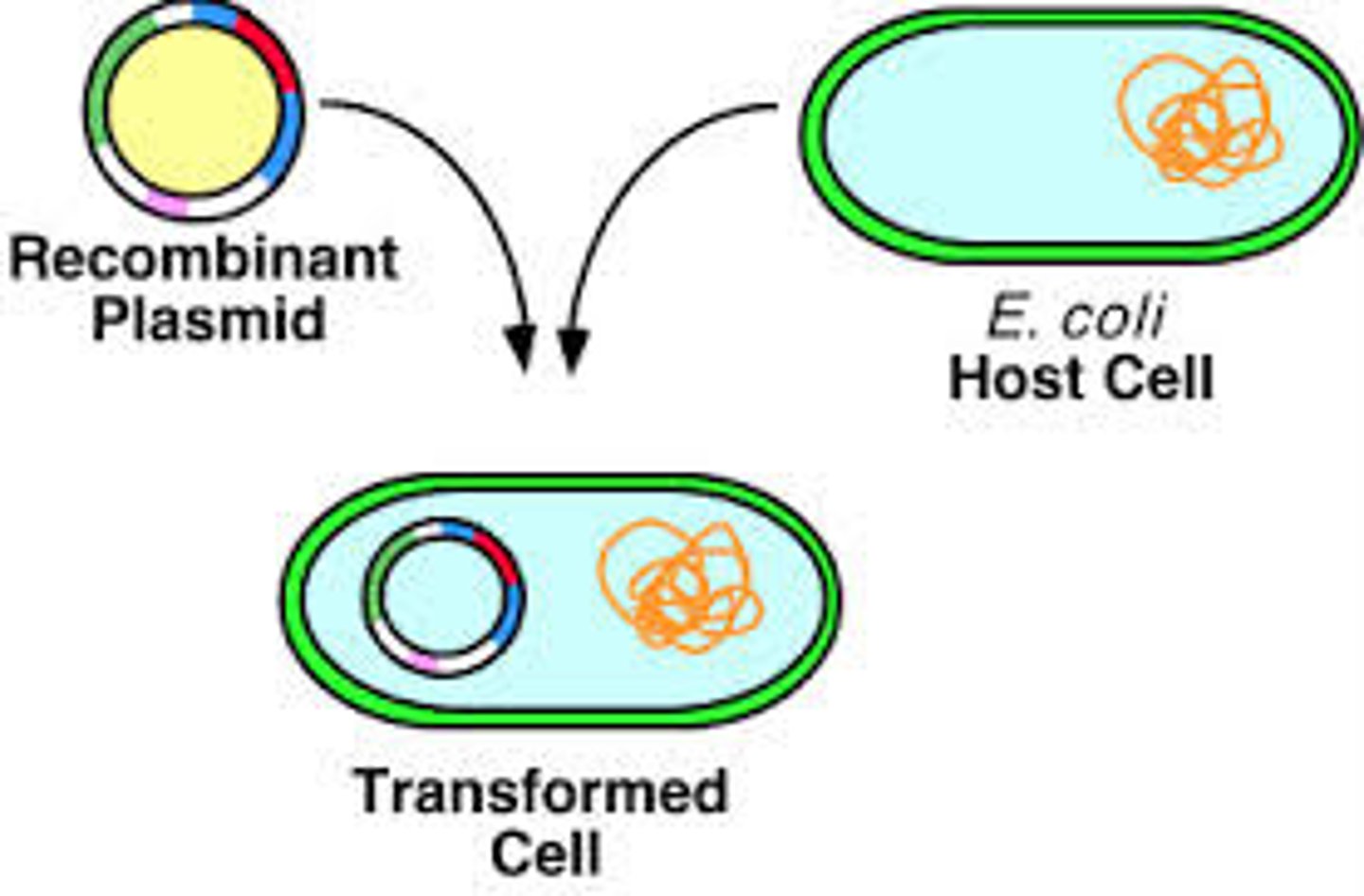
Transformed or Transgenic organisms
Organisms that have been genetically engineered.
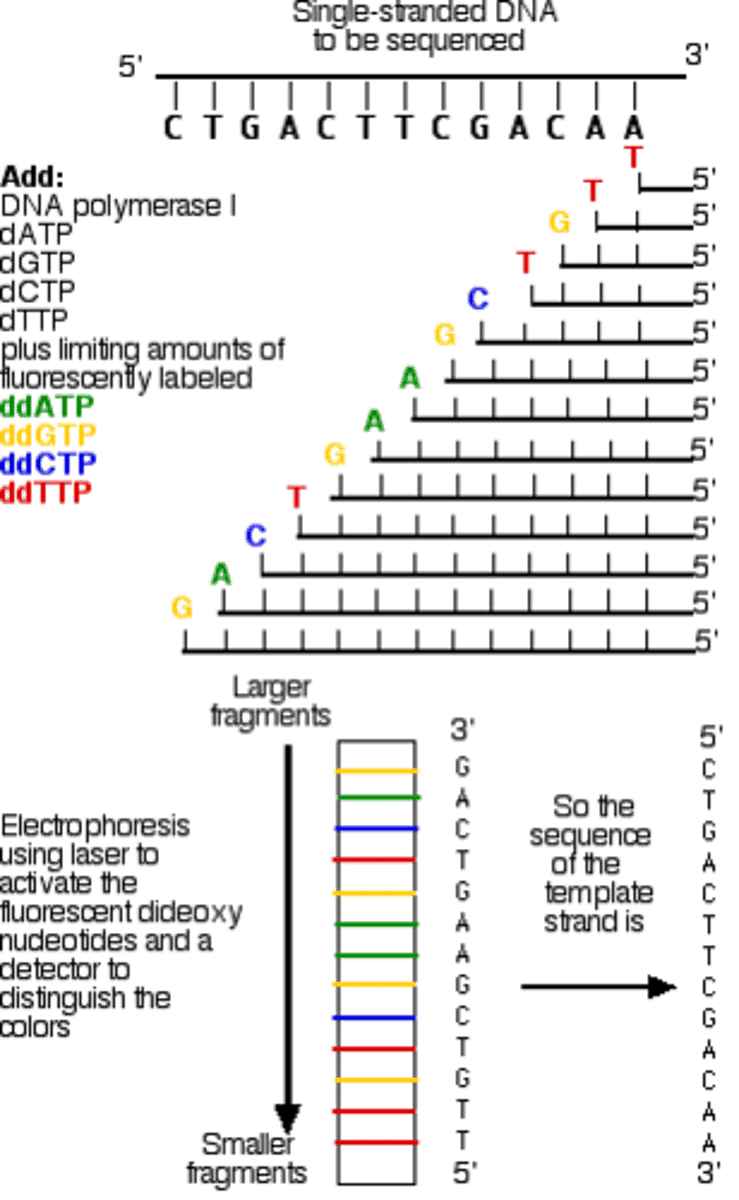
Chain termination method
Method of DNA sequencing that uses dideoxynucleotides.
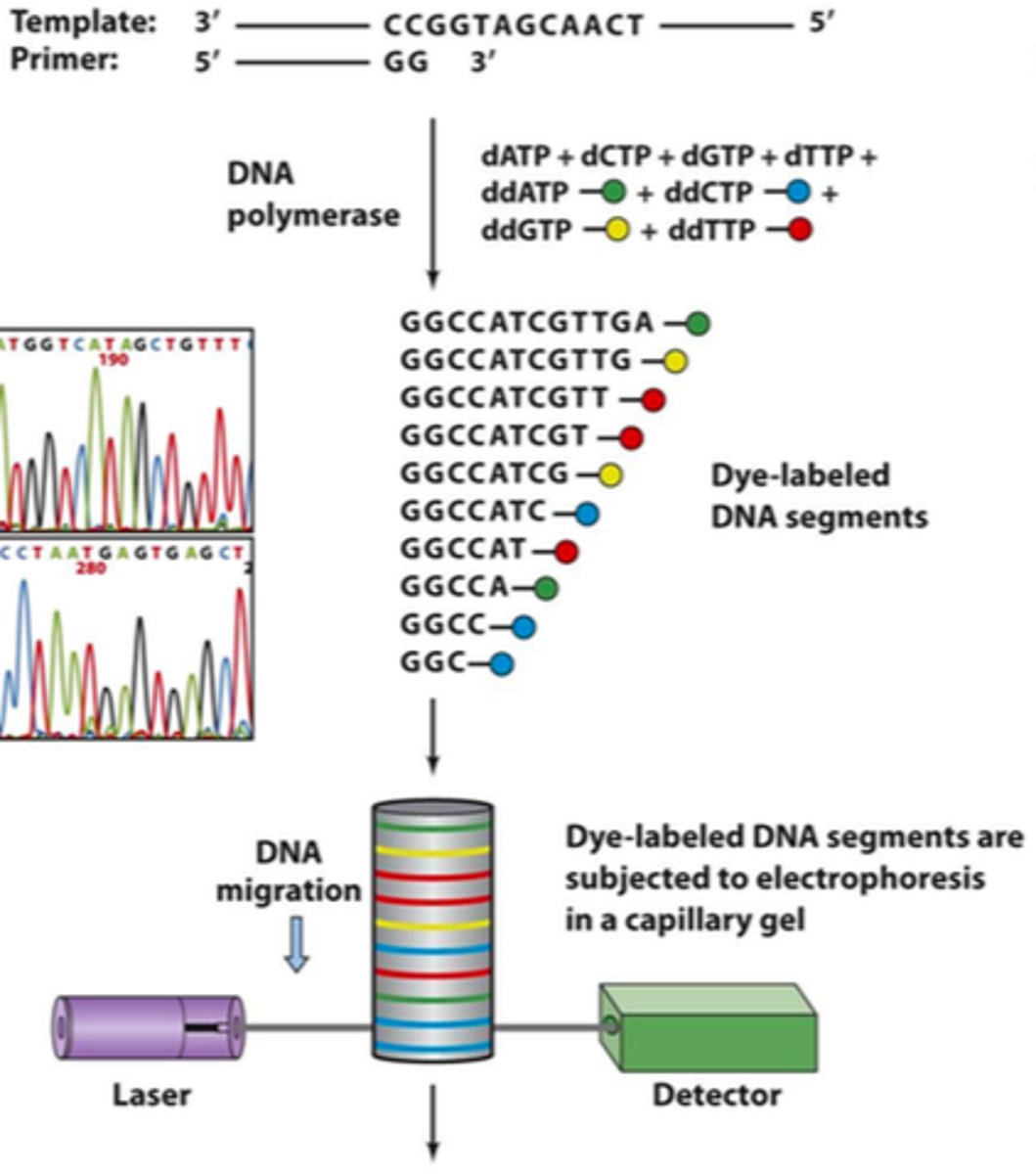
High-throughput sequencing
A faster method of sequencing DNA eg using capillary flow electrophoresis.
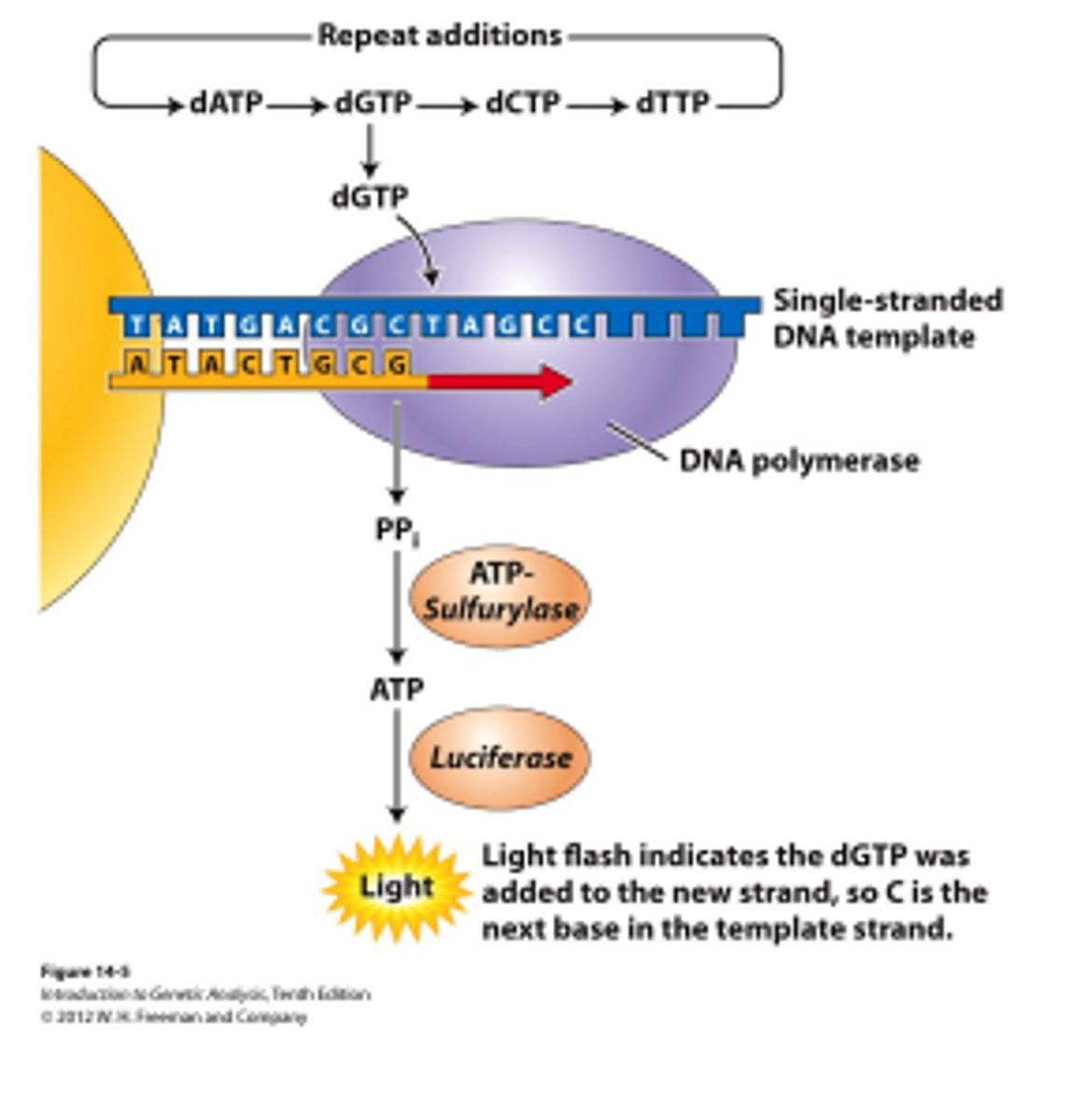
Next-generation sequencing
Method of DNA sequencing that does not use chain termination method eg pyrosequencing.
Synthetic biology
Design of new biological systems and artificially made molecules using our knowledge of DNA and cell biology.
Bioinformatics
The use of computers, software, and mathematical models to process and integrate biological information from large data sets.
Transcription Factors
A protein that binds to DNA and switches a gene on or off by increasing or decreasing the rate of transcription
Promoter
A DNA sequence (located before the structural genes in an operon) that RNA polymerase binds to.
Activator
A transcription factor that increases the rate of transcription
Repressor
A transcription factor that decreases the rate of transcription
Operon
A section of DNA that contains structural genes that are all transcribed together, control elements and sometimes a regulatory gene.
Regulatory gene
A gene that gives rise to a transcription factor.
Structural gene
A gene that codes for a polypeptide (protein)
The lac operon
A gene in E.coli that codes for the production of enzymes that break down lactose. This gene is only turned on in the presence of lactose and is therefore self-regulating.
Intron
A section of DNA that doesn't code for an amino acid
Exon
A section of DNA that codes for amino acids
Splicing
The process that changes primary mRNA into mature mRNA by removing the introns and rejoining the exons together.
cyclic AMP (cAMP)
A molecule that activates proteins inside cells by altering their tertiary structures.
Hox genes
Genes that encode proteins which control body plan development
Homeobox sequence
A sequence in a homeotic gene that codes for the homeodomain.
Homeodomain
Part of a transcription regulatory protein that binds to DNA, allowing the protein to act as a transcription factor.
Apoptosis
A highly controlled process by which cells are broken down. part of programmed cell death.
Mutation
Any change in the DNA base (nucleotide) sequence
Deletion mutation
A mutation where one or more bases are removed and may result in a frame shift.
Insertion mutation
A mutation where one or more bases are inserted and may result in a frame shift
Substitution mutation
A mutation where one or more bases are replaced by another base.
Frame shift mutation
This occurs when a deletion or insertion mutation occurs in a gene. The number of bases in the entire sequence changes, causing a shift in all the base triplets that follow.
Neutral mutation
A mutation that does not affect the phenotype of the organism.
Post Translation Level Control
Modify the protein after it is made by chemical modification or cleavage