PSYC 110 Exam 3 Review
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Episodic Memory
memory for what happened when & where (mentally traveling back to reconnect with something in your past)
declarative memory
refers to semantic & episodic memory collectively
implicit memory
unconscious change, procedural knowledge, skills & priming
explicit memory
conscious recollection, recall, declarative knowledge & recognition
semantic memory
factual knowledge that doesn’t have specific personal experience
pavlovian (classical) conditioning
form of learning where organism, after one or more exposures to neutral stimulus followed by reward or threat, learns to associate stimulus to that reward or threat & acts accordingly
retrograde amnesia
loss of memories prior to trauma
anterograde amnesia
loss of ability to form new memories (like H.M.)
Patient H.M.
(medial temporal lobe removed to alleviate seizures) had amygdala, hippocampus, & parts of adjacent cortices surgically removed; developed anterograde amnesia for events in his life but retained some ability to learn new skills.
Patient E.P.
developed memory impairment following episode of herpes simplex encephalitis
present w: bilateral lesions of medial temporal lobe, severe anterograde amnesia, partial retrograde amenisia, immediate memory & non-mnemonic functions are spared
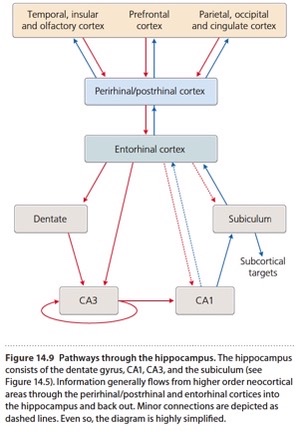
subiculum
part of hippocampus; receives strong projections form CA1 & projects to several subcortical targets as well as entorhinal cortex
hippocampus consists of
dentate gyrus, CA1, CA3, & subiculum
CA1
in hippocampus, “cornu amonts area 1”, receives strong inputs form CA3 & has robust projections to subiculum
CA3
in hippocampus, “cornu ammonisations area 3”, has robust projections to CA1
dentate gyrus
in hippocampus, part that in contrast to most other mammalian brain regions, exhibits high degree of adult neurogenesis
Hippocampus pathway
dentate gyrus→ CA3→ CA1
__________ involved in memory, learning and emotion; holds short term memories & transfers to long term storage in brains.
hippocampus
entorhinal cortex
cortical area that serves as bottleneck for information flowing into out or out of hippocampus, w which it is reciprocally interconnected
perirhinal cortex
cortical area that has reciprocal connections w entorhinal cortex * is needed for object recognition memory
amygdala
almond shaped structure in temporal lobe, major processing center for emotions & links them to memories ( electrical stimulation of lateral amygdala & perirhinal area 36 opens “gate” & spreads activity → entorhinal cortex → dentate gyrus)
recurrent collateral
axonal branch that projects back onto the neuron from which the axon originates
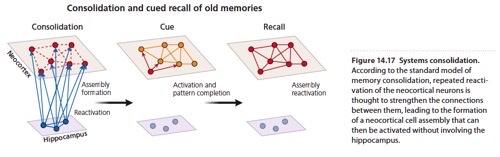
memory consolidation
hippocampus & neocortex (systems consolidation) process where hippocampus guide information stored in neocortex such that it eventually becomes independent of hippocampus
role of attention/ arousal/ emotion for enhancement of memory (recall & encoding)
attention allows information to be taken in and emotions tend to create stronger emotional events which are likely to be recalled more often with more clarity & detail.
Someone who has anterograde amnesia would have an inability to remember which of the following?
a) their mother’s name
b) how they drove to work that day
c) the location of the home they grew up in
d) all of the above
b) how they drove to work that day
Which of the following were important discoveries regarding learning and memory that patient H.M.
contributed to?
a) neuronal activity in the medial temporal lobes is necessary for recalling long-term memories
b) neuronal activity in the medial temporal lobes is necessary for procedural learning
c) neuronal activity in the medial temporal lobes is necessary for the formation of new episodic
memories
d) neuronal activity in the medial temporal lobes is necessary for performing cognitive tasks
c) neuronal activity in medial temporal lobes is necessary for the formation of new episodic memories
The hippocampus is necessary for __________, connecting memories of objects through space and time.
relational memory
Many CA3 neurons project to a dense network of additional neurons creating an
______________network of recurrent connectivity.
autoassociative
Cells that have “wired together” in a cell assembly can spread an input from a subset of neurons to the
entire assembly. This process is called_____________.
a) long term potentiation
b) pattern completion
c) Hebbian synapse
d) sequence learning
b) pattern completion
Memory consolidation requires relocation to the neocortex, which is termed ___________ consolidation.
systems
In rat experiments, it has been shown that the conditioned fear response is mediated predominantly by
the ___________, while the contextual fear response also involves the ______________ .
a) neocortex, amydala
b) hippocampus, amydala
c) amydala, hippocampus
d) thalamus, hippocampus
c) amygdala, hippocampus
hippocampus lesions impair recent memories much more than distant (old) memories resulting in __________.
retrograde amnesia gradient
model of memory in CA3 (recurrent collateral input)
CA3 receives input from 3 major pathways:
entorhinal cortex
dentate
other CA3 neurons
projection from entorhinal cortex to neurons in dentate gyrus & CA3 is called the ____________ because it __________ the boundary between dentate and entorhinal cortex.
perforate path; perforates
entorhinal cortex (EC):
located in medial temporal lobe & is a network for memory, navigation & perception of time.
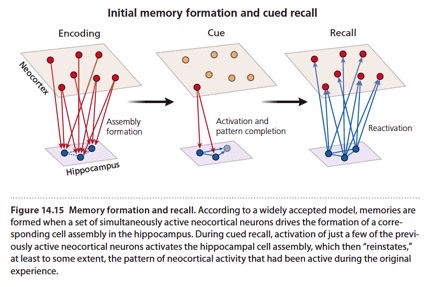
During __________, activation of just a few of previously active neocortical neurons activates hippocampal cell assembly, which then _________, at least to some extent, the pattern of neocortical activity that had been active during the original experience.
cued recall; reinstates
encoding
converting information into a form usable in memory
retrograde vs. anterograde amnesia
loss of memories prior to trauma vs. loss of ability to form new memories (like H.M.)
model of memory formation (hippocampal assembly)
neurons form entorhinal cortex project to dentate gyrus → CA3 → CA1 → subiculum which finally projects out of hippocampus to entorhinal cortex & several subcortical targets (e.g. amygdala, hyothalamus, etc.)
model of cued memory recall (reactivation, pattern completion)
cued recall includes reactivation & pattern completion in figure.
model of memory consolidation (hippocampus & neocortex) → systems consolidation
memory consolidation is the gradual strengthening of memories, the idea that memory consolidation involves relocation of memories to the neocortex
Fear Memory
in rat experiment, it has been shown that the conditioned fear response is mediated predominantly by the amygdala, while the contextual fear response also involves the hippocampus
replay of activity patterns during sleep
6 hoppocampal place cells recorded while rat was running, replay activity during slowaveo sleep just after running the 6 neurons fire in roughly the same sequence as they did during live running, replay activity occurred more frequently than expected by chance
voluntary attention
attention that can be directed at will; for example, when you are looking for a specific item in a cluttered scene or listening for a specific sound embedded in other sounds
involuntary attention
a form of attention in which external stimuli “grab” a person’s attention against their will or, in any case, without them having conscious control
parallel search
several stimuli attended to at the same time
serial search
only one stimulus attended to at a time
overt attention
moving the eyes to point at the location you’re focusing one
covert attention
improves perception, paying attention without moving eyes (ex: someone in martial arts might have trained themselves to attend to things that they are not directly looking at)
salience
“salient” means most noticeable or important; saliency map is a model of spatial attention and predicts attention well
superior colliculus
critical part in neural circuits underlying attention
Frontal Eye Field (FEF)
activity correlates with covert voluntary attention (located in frontal lobe); helps direct voluntary spatial attention
Parietal Eye Field (PEF)
correspond to the lateral intraparietal area of the monkey (located in parietal lobe)
Hemispatial neglect
characterized by inattention to left side of objects or the world; generally caused by lesion of inferior parietal and/or superior temporal cortex on right side of brain (ex. patient asked to copy drawings like a clock or flower, they tend to only copy right side of drawing
arousal
stage in sleep activity that is caused by a change in pattern of brain wave activity
from deep sleep → light sleep or from sleep → wakefulness
slow-wave sleep
low frequencies in EEG
REM-sleep
waves are desynchronized, slow waves disappear
synchronization of EEG
large amplitude, low frequency waves
desynchronized EEG
smaller amplitude irregular EEG traces
locus coeruleus
LC activity responds to external stimuli (loud sounds, stepping on sharp objects, etc.); norepinephrine released
Thalamus
brain & body’s relay station located near the center of the brain
rhythmic oscillations
in cortical neurons, during slow-wave sleep comes from intrinsic neuronal rhythms as well as looping interaction between the neocortex, dorsal thalamus and the thalamic reticular nucleus
thalamocortical neurons
fire rhythmic bursts of action potentials during slow=wave sleep, they are inhibitory
importance of sleep
important for health just like nutrition & exercise
Which of the following is an example of covert spatial attention?
a) Turning your head when you hear a loud crash
b) Being startled awake by a loud thunk in your house
c) Keeping your head facing forward while driving but still paying attention to the conversation you have
with a passenger in the car
d) Diverting your attention back and forth form a powerpoint slide to the lecturer giving the
presentation
c) keeping your head facing forward while driving but still paying attention to the conversation you have with a passenger in the car
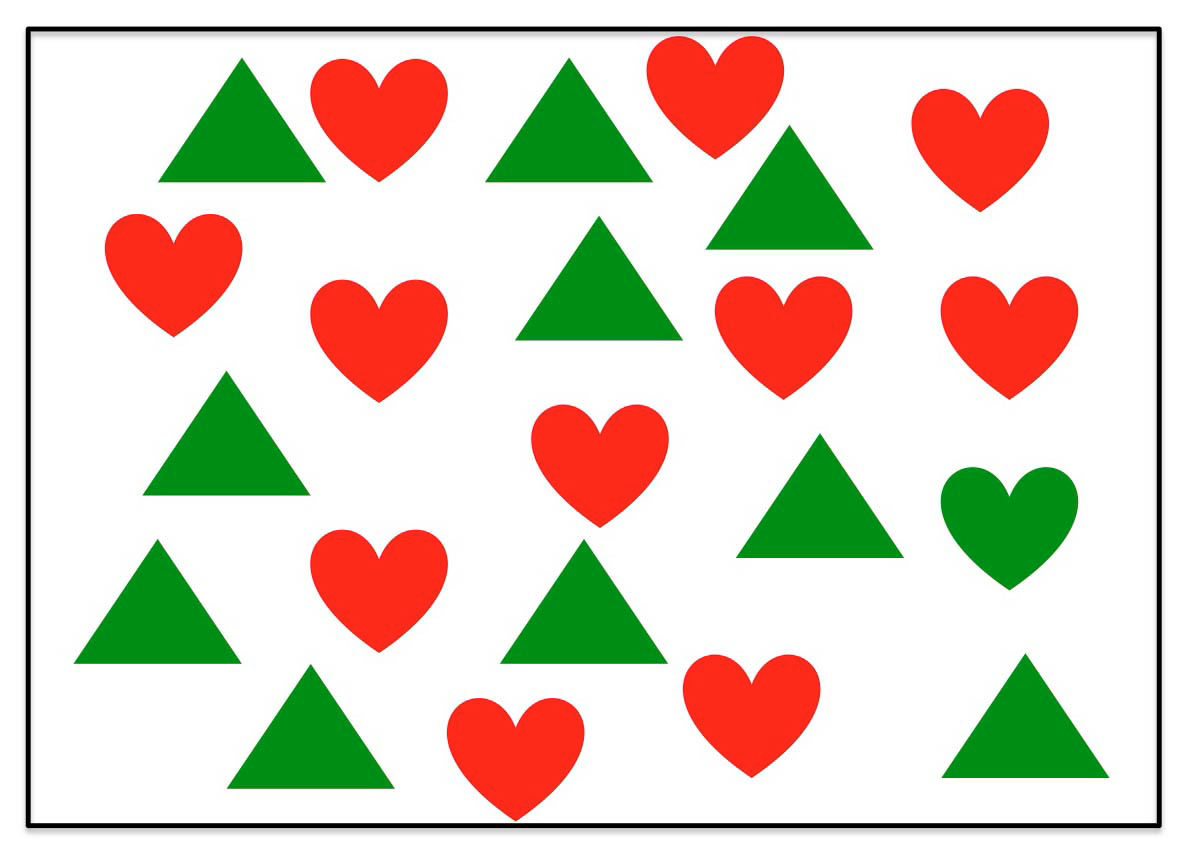
What sort of search are you performing when you identify the green heart in the image above?
a) serial search
b) parallel search
c) salient search
d) all of the above
a) serial search
The amplitude of an EEG of a drowsy individual is _________(than) an individual that is behaviorally
aroused.
a) the same as
b) higher
c) lower
d) slower
e) faster
b) higher
Projections from the_______________, located near that fourth ventral, that are important for the arousal system include the cerebellum, thalamus, neocortex, and brainstem.
locus coeruleus
The feeling of “sleep paralysis” is caused by caused by the hyperpolarization of skeletal muscle neurons in a state called___________.
muscle atonia
Why do we not physically act out our dreams during REM sleep?
motor neurons are hyperpolarized, can’t generate action potentials, body is paralyzed, so don’t act out dreams
Classical conditioning is
passive learning
hippocampus important for remembering
order of sequences
Stages of Memory
Encoding
Storage
Retrieval
Encoding
converting info into a form usable in memory
Storage
retaining information in memory
Retrieval
active process of locating and using stored information
Short term memory
tracks tasks in which brain is currently engaged in; if info is not rehearsed stays in short term memory about 20 seconds capacity is 7 + or - 2, more if chunking
Procedural Memory
memory for motor skills (Ex: testing, riding a bike, & tying shoes); stored in cerebellum & basal ganglia
Episodic memory
mentally traveling back to reconnect with something in your past
Semantic memory
factual knowledge that doesn’t have a specific personal experience
How do animals navigate through space?
animals may either memorize a habitually traveled route or form an allocentric (world-centered) cognitive map aka Place Learning
Tolman’s cross maze & Morris water maze have been used to demonstrate:
that rats are capable of allocentric (world-centered) navigation
Place Grid Cells
pyramidal neuron located in the hippocampus that becomes active when animals enter a particular place int their environement
Grid cells
not in the hippocampus but allows us to understand our position in space aka the entorhinal cortex, name comes from firing fields that form a triangular grid
superior colliculi is important for forming
saliency map
competitive algorithm
determines most salient location, which draws your attention
sleep cycle (circadian rhythm)
2 types: REM & non-REM
5 stages of sleep
1-2 drowsy light sleep
3-4 deep sleep “restorative’
5 REM dreaming & memory consolidation
Large amplitude waves as people become
drowsy & then fall asleep
Small amplitude waves during
REM sleep & when awake
hippocampus is important for
remembering order of sequences
long term memory consolidation
newer memories (hippocampus needed, older memories (10 years ago) hippocampus not needed cortical circuit used instead
associative learning
alzheimer’s disease
characterized by presence of amyloid plaques & neurofibrillary tangles often located in hippocampus
Your roommate dropped a pan in the
kitchen and you turn to see what it was.
This is an example of:
A. Covert attention
B. Overt attention
b. overt attention
An adult with anterograde amnesia would
not be able to remember which of the
following:
A. Their high school graduation
B. Their mother’s maiden name
C. The location of the home they grew up in
D. What they ate for breakfast
d. what they ate for breakfast
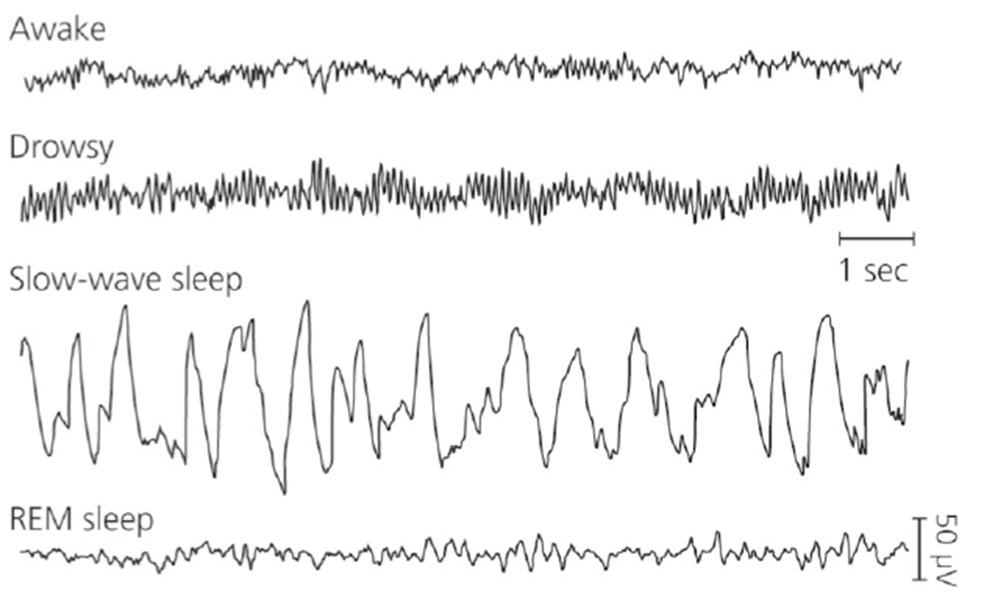
The amplitude of an EEG of a drowsy
individual is _________(than) an
individual that is awake.
A. the same as
B. higher
C. lower
D. slower
E. faster
b. higher
H.M. had what area of the brain removed?
a. cerebellum
b. locus coeruleus
c. inferior parietal lobes
d. medial temporal lobes
d. medial temporal lobes
Which is involved in involuntary attention to salient stimuli
a. hippocampus
b. basal ganglia
c. amygdala
d. superior colliculus
d. superior colliculus
_________ is the stage of sleep where most of our dreams happen.
a. NREM -Stage 1
b. NREM -Stage 2
c. NREM -Stage 3
d. NREM -Stage 4
e. REM
e. REM