Diffraction
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What does diffraction refer too
Diffraction is the interference caused by an object in the path of a wave/waves
Why do we use x-ray diffraction in crystals
X-ray diffraction occurs because their wavelengths are comparable to the separation of lattice planes.
Describe how we use x-ray diffraction for a single crystal and the pattern it makes
A beam of x-rays will be directed at a crystalline solid
The x-rays are scattered by atoms in the crystal lattice. The scattering angles depend on the positions of the atoms.
The x-rays create a series of spots on an image plate - this is the diffraction pattern.
How can we describe the spots and what do they tell us
Spot positions give us the:
Unit cell size
Spot intensities give us the:
Atomic positions
Due to the fact lattice planes exist in three dimensions, each spot needs to be defined by three integers (h,k,l) these are miller indices
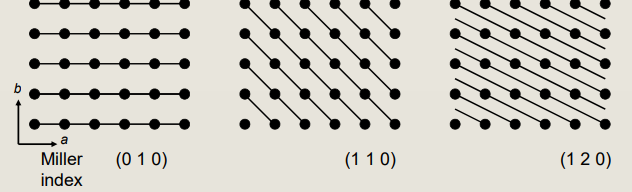
How do we look at just 2 dimensions with the miller indecies
We just look at how the x-rays intersect at each lattice point
Only h and k
The values are dependant on how many repeating units it take until an intersection
Draw out a small sections of (0 1 0) (1 1 0) (1 2 0) diffraction patterns in 2D
Why are h,k,l and nh,nk,nl different
This is because h,k,l are miller indices whereas nh,nk,nl are reflection indices.
h k l are the fundamental plane orientation, with the largest spacing for that direction
nh nk nl are the same orientation but describes a set of planes with a spacing 𝑛
times smaller, which generates a diffraction peak at a different angle according to Bragg's law (𝑛𝜆=2𝑑sin𝜃).
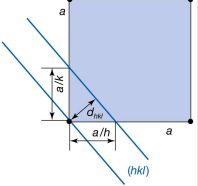
Whats the equation for the separation between lattice distances for a cubic lattice
d² = a² / h² + k² +l²
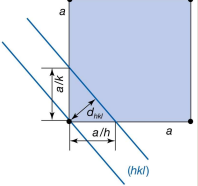
Whats the equation for the separation between lattice distances for more general orthorhombic lattices
1/d² = h²/a² + k²/b² + l²/c²
Why do we see diffraction spots
due to constructive interference of waves
What does constructive interference refer to
Two waves in phase hit different but parallel layers reflecting out still in phase giving rise to a spot of the detector.
Why do we not see diffraction spots in other locations
This is due to destructive interference
What is destructive inteference
Destructive interference refers to, when two waves in phase hit different but parallel layers reflecting out no longer in phase
In the bragg equation what is the difference in path length, and what are the values we see the two types of interference for.
Difference in path length is 2d sin θ
If 2d sin θ = λ, 2λ, 3λ, … we will see constructive interference
If 2d sin θ = λ/2, 3λ/2, 5λ/2, … we will see destructive interference
Condition for constructive interference is therefore 2d sin θ = n λ
What are two ways of looking a the bragg equation in terms of miller indices and cell parameters
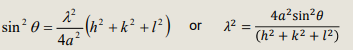
What are systematic absences
specific reflections (or diffraction signals) that are missing from a crystal's diffraction pattern due to the crystal's internal symmetry.