Wound Healing
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Two Key processes in tissue repair
Regeneration
Scar formation
What cells play a central role in repair?
Macrophages
Wound with clean, close edges such as a surgical incision or paper cut. Minimal scarring
Primary Intention
Wound that is larger and more open such as an extraction site, burns, graft site that leads to more granulation and scarring
Secondary Intention
Three cells / tissue that proliferate in regeneration
Injured tissue
Vascular endothelial cells
Fibroblasts
Repair Sequence
Immediately: Clot forms
Day 1: Neutrophils migrate, phagocytose foreign substance
Day 2: Macrophages enter, granulation tissue forms, protected by fibrin clot
Day 3-6: Lymphocytes and Plasma cells enter
Day 7: Clot digested
Day 14: Fibroblast mature, collagen remodeled to form scar tissue
When do Scars form?
When regeneration is not possible
Permanent tissue
Extensive ECM damage
Condition from excessive scar tissue, often seen in chronic inflammation
Fibrosis
What signals the formation of new blood vessels to supply healing nutrients?
VEGF
Migration of fibroblasts is mediated by what?
Fibroblast Growth factor (FGF) made by macrophages
Tissue formed by new blood vessels and fibroblasts, appears red/pink 3-5days post injury
Granulation Tissue
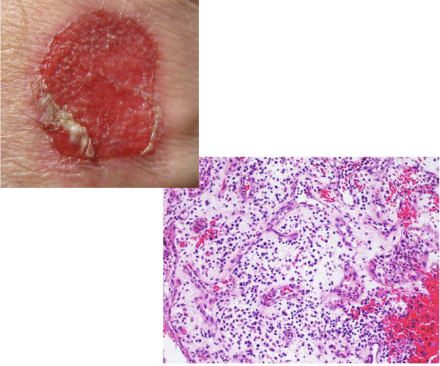
What does this image show?
Granulation Tissue
Fibroblasts depositing collagen is mediated by what?
TGF-beta
Granuloma Vs Granulation Tissue
Granuloma: part of inflamm. process, macrophages, maybe surrounding lymphocytes
Granulation Tissue: created during tissue repair, new BV and fibroblasts
Role of TGF-beta in scar formation
Stimulates production and inhibits breakdown of ECM proteins (and anti-inflamm)
Role of Platelelt derived growth factor (PDGF) in scar formation
Migration and proliferation of fibroblasts and Smooth muscle cells
Role of Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) in scar formation
Fibroblast migration
Role of Cytokine IL-13 in scar formation
Stimulates collagen and fibroblast migration
List factors that can prevent healing and repair
Infection
Nutrition (Vit. C deficiency)
Steroid use
Poor perfusion
foreign bodies
type and extent of injury
Location of injury
Excessive formation of collagen leads to what?
Keloids
What can remodel connective tissue over time?
Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs)
Granulation tissue is primarily composed of which of the following?
Neutrophils and macrophages
Fibroblasts and new BVs
epithelial cells and blood clots
Scar tissue and fibroblasts
Lymphocytes and collagen
Fibroblasts and new blood vessels