Lower leg, Knee, Patella
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
_ is the second largest bone in body
Tibia
Tibia is located on the
medial side
Weight bearing bone (Tibia and Fibula)
Tibia
Does the fibula bear any weight
No
Two prominent and palpable processes on proximal end
medial and lateral condyles
Superior surfaces of condyles
form articular facets (plateaus)
for articulation with the femur
Tibial plateaus
sharp projection between articular facets
intercondylar eminence
Proximal tibiofibular joint is a __ type of joint
synovial, gliding
Lateral condyle has facet on posterior surface for articulation with the ___
head of the fibula
What is located on the anterior surface of tibia, inferior to condyles
tibial tuberosity
The tibial tuberosity serves what purpose
attachment for muscle
Sharp ridge located on the anterior surface of the tibial body
anterior crest
The anterior crest is also known as the
shin
Palpable landmark
forms part of ankle mortise
located at distal end
Medial malleolus
What overlays the fibula and is on the anterolateral surface
anterior tubercle
triangular depression for articulation with distal fibula
fibular notch
The Distal tibiofibular joint is
amphiarthrotic
This is located on proximal end of fibula and articulates with lateral condyle of tibia to make the proximal tibiofibular joint
Head of fibula
Conical projection on lateral and posterior portion of head
Apex of fibula
This is located on distal end of fibula, forms part of ankle mortise, projects lower than medial malleolus
Lateral malleolus
formed by femoral condyles and tibial plateaus
knee
The knee is a synovial, ___ type joint
modified hinge
The knee joint technical name is
femorotibial joint
sesamoid bone
located on anterior surface of femur
Patella
PCL stands for
posterior cruciate ligament
TCL is known as
tibial collateral ligament
The knee is stabilized and cushioned by
menisci
The menisci lies on the
tibial plateaus
The apex of the patella points toward
the knee
largest, strongest and heaviest bone in body
femur
The femur consists of
body and two articular extremities
The body of the femur slants medially how many degrees
5-15 degrees
Distal femur is broadened with two large eminences
medial and lateral condyle
The medial epicondyle contains the
adductor tubercle
The epicondyles can be found on the __ femur
distal
The pateller surface— ____ seperation
anterior
Intercondylar fossa is a
deep depression posteriorly
Proximal tibiofibular is what type of joint
gliding
Patellofemoral is what type of joint
gliding
Femorotibial is what type of joint
modified hinge
caused by irritation of the bone growth plate, causing swelling at tibial tuberosity
Osgood- Schlatters disease
Dressing instructions for lower leg projections
remove everything from waist down
Lower leg projections SID is
44 inches
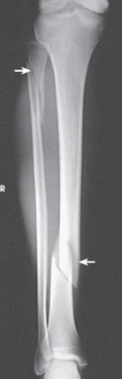
What projection is this
AP Projection leg
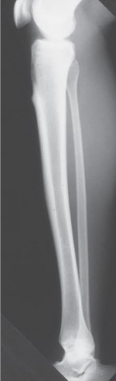
What projection of the leg is this
lateral leg projection
Patient position for lower leg AP projection is
supine
For an AP projection of the leg, femoral condyles are ____ to IR
parallel
CR enters the ____ for an AP leg projection
center of leg
Proximal and distal articulations of tibia and fibula moderately overlapped are seen in a
AP leg projection
What type of lateral is a lateral leg projection
mediolateral
Patient position for a lateral (mediolateral) leg projection is
supine, rotated towards affected side
In a lateral leg projection, femoral condyles are ____ and ___ to IR
superimposed, perpendicular
For a lateral leg projection, the CR enters at
midpoint of leg
Distal fibula superimposed by posterior half of
the tibia
• Slight overlap between tibia and fibular head
• Separation of the tibial and fibular bodies (not at
ends)
seen on a
Lateral leg projection
SID needed for Knee projections
40 inches
Knee projections are done on the
table bucky
Knee 3V routine
AP, Lateral, additional view
Knee 2V routine
AP and Lateral
Knee Routine 4V
AP, Lateral, AP Oblique, 1 additional view
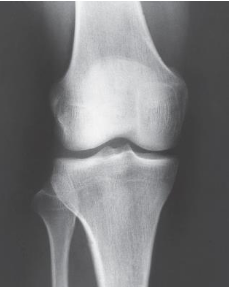
What Knee projections is this
AP Knee
Patient position for AP Knee
supine, no pelvic rotation
In AP Knee, the femoral epicondyles are what to the IR
parallel
The CR in Knee projections are variable depending on the what
ASIS
If Patient’s ASIS is less than 19cm from the table, then the CR angling would be
3 to 5 degrees caudal
If Patient’s ASIS is more than 24cm from the table, then the CR angling would be
3 to 5 degrees cephalic
If Patient’s ASIS measures 19 to 24cm from the table, then the CR angling would be
0 degrees
The CR in an AP knee enters
½ inch below pateller apex
Radiation field for AP Knee is
10 × 12 inch LW
The Patella superimposed on the femur (will
lie slightly to the medial side) is seen on
AP knee
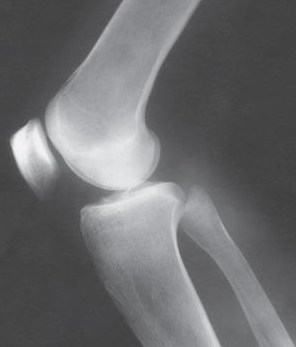
Which knee projection is this
Lateral knee
Patient position for lateral knee is
turned toward affected side, flexed, brought forward
Femoral epicondyles and patella are what to the IR during lateral knee
perpendicular
CR angle in lateral knee is
5 to 7 degrees cephalic
CR enters where for a lateral knee
knee joint 1 inch distal to medial femoral epicondyle
Open patellofemoral joint space seen in
lateral knee
For lateral knee, over rotation results in
less superimposition
For lateral knee, under rotation results in
more superimposition
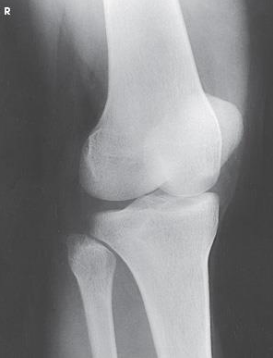
Projection?
AP Medial Oblique knee
Limb is medially rotated how many degrees for an ap oblique medial rotation
45 degrees
Margin of patella projecting slightly
beyond medial side of the femoral condyle
AP Oblique Knee Medial Rotation
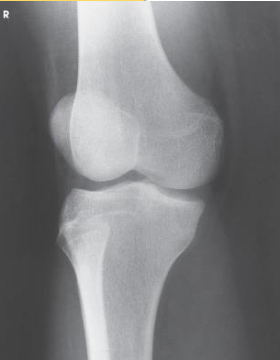
Projection?
AP Lateral Oblique Knee
Patella projected slightly beyond the edge of
the lateral condyle seen on a
AP Oblique Knee
Lateral Rotation
Arthritic knees
Narrowing joint spaces
Varus and Valgus deformities
are seen on a what type of projection
AP Bilateral Weight Bearing
ROSENBURG METHOD is done
PA with knees flexed 45 degrees
CR angled in a Rosenburg method how many degrees
10 degrees caudal
Projections for Intercondylar Fossa (Tunnel)
PA Axial (Homblad)
• PA Axial (Camp-Coventry)
• AP Axial (Beclere
For intercondylar fossa, the CR is ALWAYS
perpendicular to the lower leg
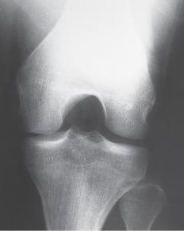
Projection?
PA Axial Holmblad
For the PA Axial Homblad, you must evaluate the what
patient’s ability to safely be placed in one of 3 positions
Patient position for PA Axial Homblad
knee flexed 70 degrees, anterior surface of knee on IR
CR enters where for PA Axial Holmblad
enters superior aspect of popliteal fossa, exits patellar apex
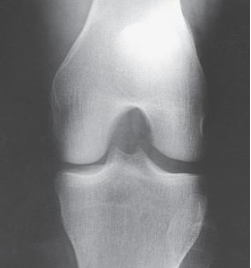
Projection?
PA Axial Camp-Coventry
Patient position for PA Axial (Camp-Coventry)
prone without rotation
The knee is flexed how much in a PA Axial (Camp-Coventry)
40 or 50 degrees
How is the CR angled when the knee is flexed 40 degrees PA Axial (Camp-Coventry)
40 degrees caudal
How is the CR angled when the knee is flexed 50 degrees PA Axial (Camp-Coventry)
50 degrees caudal
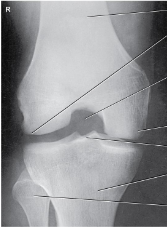
Projection?
AP Axial Beclere
Patient position for AP Axial Beclere
supine without rotation
Knee flexed to place long axis of femur at an angle of 60 degrees to the long axis of tibia in the what projection
AP Axial (Beclere)
Routine 3V Patella
PA, Lateral, Tangential