Classification & Phylogeny I (8)
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Darwin described evolution with the phrase “descent with modification.” What did he mean?
A. Evolution takes a long time—it is not an instantaneous process.
B. Evolution is not “exceptional”—it is a natural phenomenon that is going on today.
C. Closely related species are similar at the genetic, developmental, and structural levels.
D. Populations living today are related (genetically) to populations that lived in the past, but they are not identical.
E. Both C and D apply.
E
What will happen to the size and shape of beaks in medium ground finches, in the future?
A. They will continue to get deeper and wider.
B. They will continue to get deeper, but they should eventually begin to get narrower as well.
C. It depends on changes in the environment.
D. They may fluctuate in size and shape, but they will remain roughly constant over the long term.
C (not enough information in question for other options)
Which of the following could be used as evidence of descent from a common ancestor?
A. Species of tortoise living in close proximity are more similar than tortoise species living far apart.
B. Genes for limb formation have almost identical sequences in salamanders and chimpanzees.
C. Antibiotics can cure the same diseases in rabbits and humans.
D. All of the above could be used as evidence.
D
Analogy vs. Homology
Analogy
same function
different structure
Homology
common ancestor
similar structure
can have different functions
Which of the following is a true statement?
A. An individual with an adaptation is said to have evolved.
B. An individual who is naturally selected has more offspring than an unselected individual.
C. An individual that needs an adaptation to survive is more likely to evolve it.
D. Over time organisms will become increasingly complex as evolution makes them more adapted.
B:
A: individual do note evolve
B: survival and reproduction correlated --> unselected = dead
C: correct state survive and others that don't do not
Next generation has more of survived trait being expressed
D: microbes and bacteria body plan for single celled organisms hasn't changed for thousands of years
What are the predictions based on evolution?
• If life originated on Earth in the distant past and then evolved, we should see evidence in the fossil record
If evolution occurred within lineages, and those lineages sometimes split then we should see change in species or morphology through the fossil record
If creatures share a common ancestry, then we should see transitional forms • We should see evidence of retrodictions and vestigial characters
We should be able to see evidence of natural selection
Why is this not a snake?
Shares more lizard features than snaks
• moveable eyelids
immobile jaw
ear openings
autonomy – can shed tail
shed skin in patches
What is an amniotic egg?
a self-contained, air-breathing egg that provides a protective, moist environment for a developing embryo on land
found in vertebrates
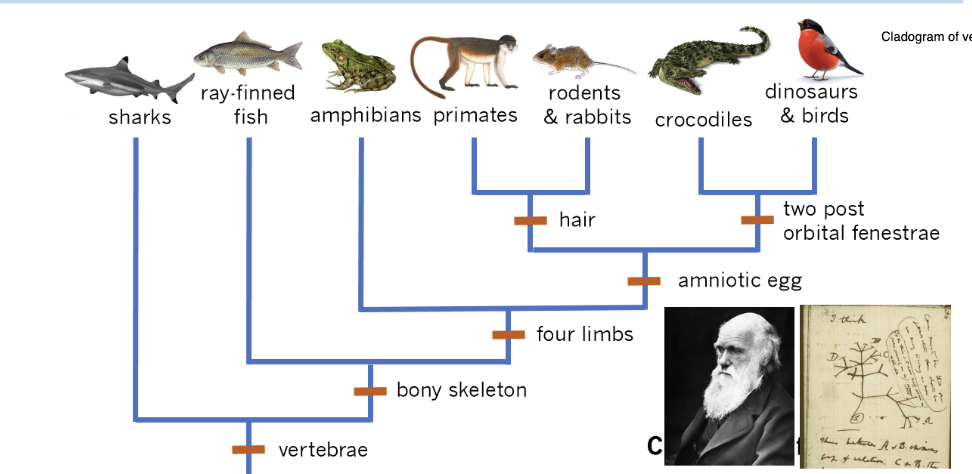
What kind of structure do we use for classification?
Binomial hierarchical naming system: ex (homo sapein = human being)
What are common names?
convey meaning in casual
monkey, finch, lilac
What is the issue with common names?
confusing: some do not accurately reflect type of organism
What kind of names do we use instead?
use Latin scientific names
what does the hierarchy group organisms?
increasingly inclusive categories
How are the Latin names given to organisms?
Genus name + species name
similar enough to be in the same genus, but different enough to be their own species
What is the order of hierarchical classification
• Related Species are grouped into Genera
Genera group into Families
Families group into Orders
Orders group into Classes
Classes into Phyla
Phyla into Kingdoms
and Kingdoms into Domains
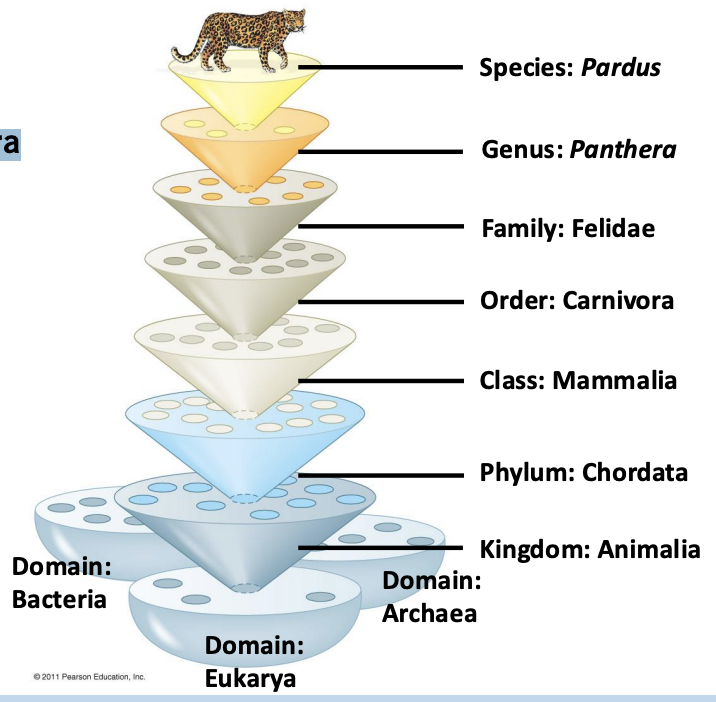
What is a genus (plural: genera)?
closely related species
What is a family?
closely related genre —> grouped to more inclusive branch
What is order?
closely related families
What is domain?
three largest limbs of entire tree
Eukarya, Bacteria, Archaea
What is a node?
where an ancestor diverges into two species or more
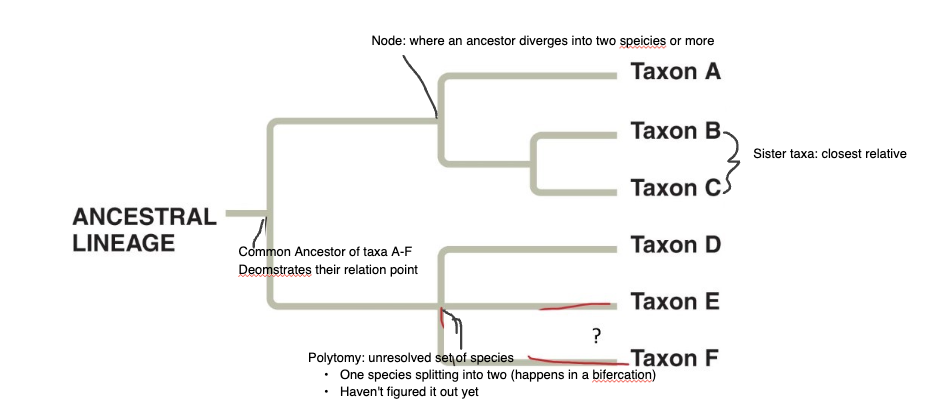
What is sister taxa?
closest relative
two branches from the same node
most related taxa on tree
PT is a set of sister groups —> adding species means finding sister group
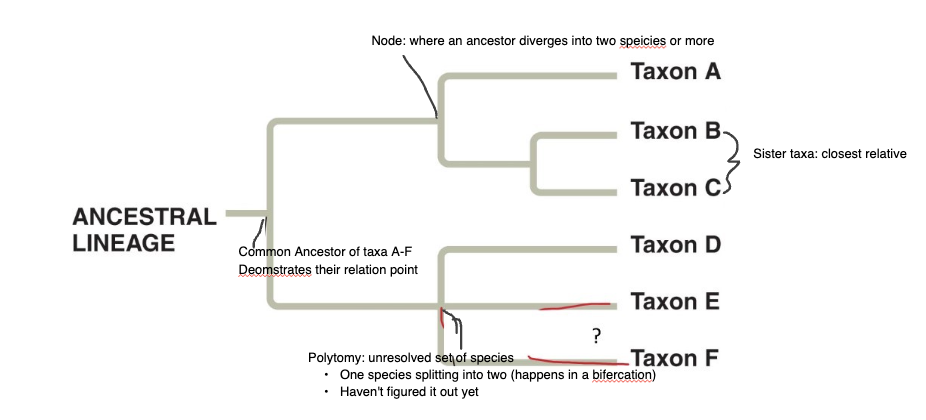
What is a taxa (singular: taxon)
a set of organisms
What is a polytomy?
Common ancestor of two diverging species that is still unkown
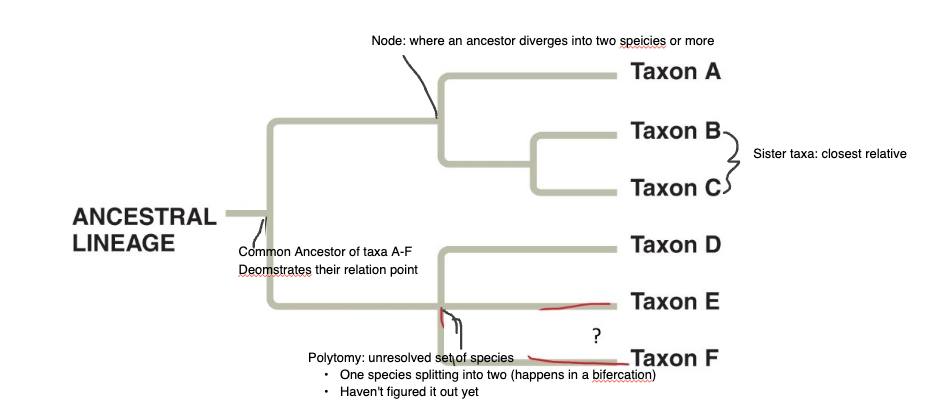
What happens to evolutionary relationships when nodes are rotated?
Nothing changes
order does not impact the relationship
What are phylogenetic trees?
Evolutionary history of a group of organisms can be represented in a grouping diagram
What is phylogeny?
History of descent with branchiing
What differentiates a cladogram and phylogenetic tree?
A phylogenetic tree shows branch order and branch lengths
captures order and timing of splits
Cladogram: branching diagram with no implication of time
What are PTs build from?
analysis of morphological features and molecular attributes
What is systematics?
The science of organizing the history of organismal evolution; use phylogenies
What must characters be to be used in classification?
Independent traits cannot have environmental phenotypic variation
Independent traits must be independent
Why should independent traits not have environmental phenotypic variation for building PT?
Need to focus on traits that is expressed mainly through genetic component
Couldn't create species based on human height because based on environment
What is pleiotropy?
Expression of multiple unrelated traits by a single gene
single gene influencing multiple traits
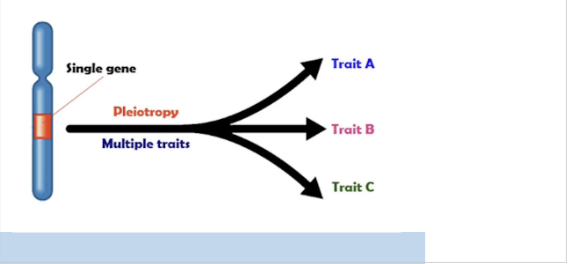
Why should pleiotropy be avoided in PTs?
if gene correlated with multiple traits —> can’t fully distinguish if trait comes common ancestor or other cause
What are frizzles chicken feathers considered?
derived within chickens —> differs from ancestral feather structure
What do phylogenies also represent?
hypotheses that can change as we obtain new data or apply new methods of constructing the phylogeny
When can people be confident about evolutionary relationships?
Only when multiple lines of evidence and multiple methods of analysis converge on the same tree
What are phylogenies often combined with to find timeline of evolution?
fossil record
What can fossil record + phylogenies show us?
give us a glimpse of the temporal patterns of diversification
Ex: bone found between two volcanic events and place it there
What can phylogenies combined with biogeographic data show?
allow us to infer dispersal and vicariance
What is Vicariance?
a lineage splits due to geological events, e.g., the breakup of continents, new island formations the uplifting of a new mountain range
What does the Raffelsia flower show?
dispersal event in Malay archipelago —> new species in tropical rainforest
What can phylogeny also be combined with?
behaviour, ecology or morphology data
What does phylogeny + behavior, ecology or morphology data show us?
understand the origin and loss of traits and predict traits of unstudied species
Ex: Angler fish
Sexual dimorphism --> hard to find mates so male attaches to female
Female can mate whenever she wats, feeds him, or can kick him off
different kinds of male attachment styles can be traced back to common ancestors
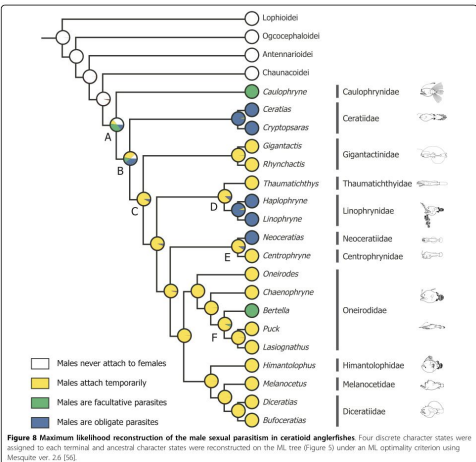
What are facultative parasites?
Angler fish
dependent on female for food
What are obligates (Angler fish)?
male will die if it separates from female
What are the styles of male sexual dimorphism in Angler fish?
White: free living
Yellow: males attach temporally
Green: Facultative parasites
Obligate: will die if he separates
What applications does phylogenies have?
Enhances our understanding of evolution
Control agriculture pests and diseases
Identify endangered species, manage wildlife
Select plants and animals for research
How can P control agriculture disease?
Disease that impacts broccoli will impact cauliflower (same species)
Create plant communities that are better at capturing water based on how they are related
More related they are the more likely they are able to compete
The most different; able to split resources more well
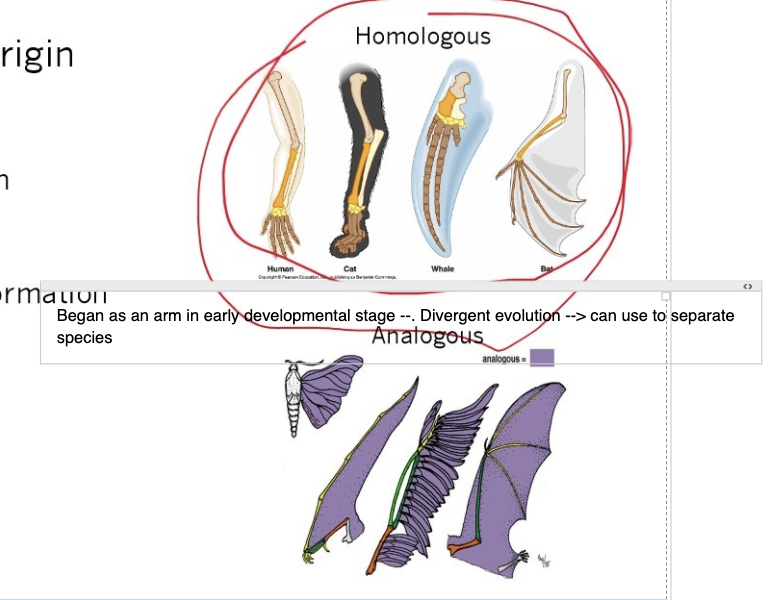
What are homologous traits?
similar origin
Result from common ancestry
Are a product of divergent evolution
Fundamental to systematics
Similar structure and embryonic formation
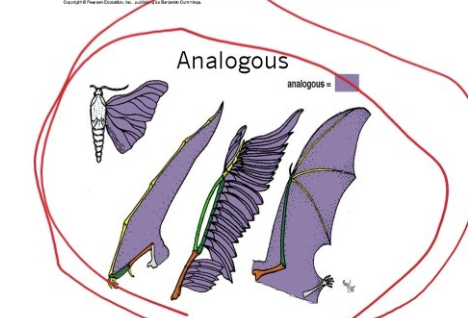
What are analogous traits?
similar function
Do not reflect common ancestry
Not used in systematics
Are the outcomes of convergent evolution
How are analogous traits used in systematics?
they are not used
traits from convergent evolution show no relation to each other through common ancestors
What is convergent evolution?
When two or more different organisms independently evolve the ability to do the same thing
What can convergent evolution be a result of?
adaptive radiations that occur in Allopatry
ex: Placental mammals vs. Australia marsupials
evolved to occupy similar niches but evolved independently
What is allopatry/allopatric?
Describes populations that are geographically separated from each other.
What is homoplasy?
Any similarity in traits that is not due to shared ancestry
What kind of trait are homoplasis?
analogous traits
traits resulting from parallelism
Evolutionary reversal
similar structure —> no common ancestor
What is parallelism?
similar traits evolve independently in different species, not because they are closely related but because they have a similar starting genetic or molecular basis, leading to the same phenotype
What can cause homoplasies?
Same conditions resulting in repeated evolution of same structure independently
Ex: Eye in human and octopus: similar in structure --> evolved independent of each other
simple as gene changes
complex and involve reorganization of multiple systems to converge on a solution
What is evolutionary reversal?
A character reverts from a derived state back to the ancestral state.
Ex: Gastrotheca guentheri regained teeth in the lower jaw after lost in frogs for 200 million years
ancestor of frog had teeth —> lost it —> one species regained it
What is a homologous trait for most insects?
four wings
Why do flies have two wings?
Hind wings replaced by halteres instead
What are the hind wings in flies used for?
gyroscopic mechanisms
What is a gyroscope?
detect deviation of an object from desired orientation
What insect also has hindwings?
twisted wing parasites
also used for gyroscopy
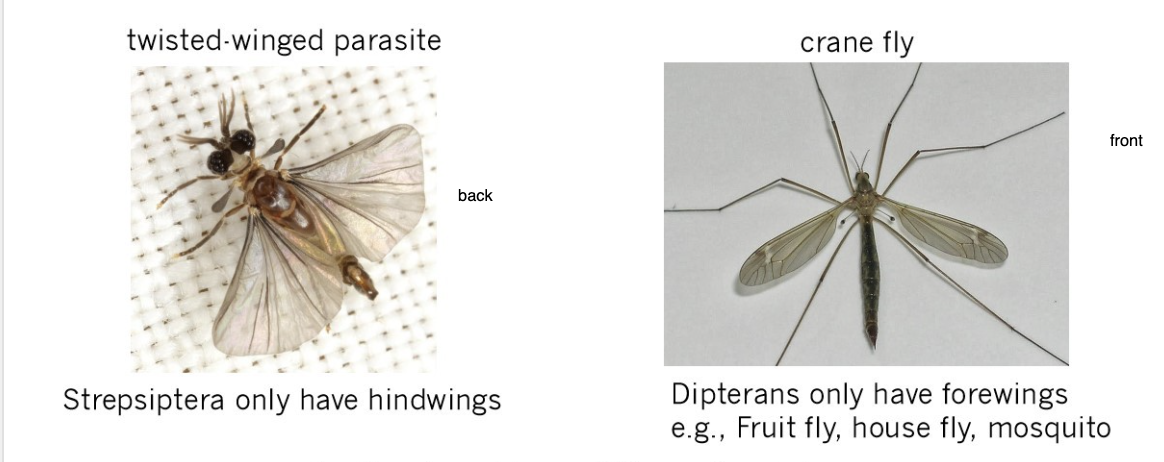
What kind of trait/evolution is this example?
homoplasy
convergent evolution
similar function, different origin
In what two ways can traits appear?
ancestral or derived based on context (point of reference in phylogeny)
What is an ancestral trait?
A trait that was present in the ancestor of a group/clade
What is a derived trait?
A trait that differs from close ancestral trait
What are derived traits a subset of?
subset of ancestral traits common to a group of interest
Ex: bird feathers are ancestral in birds, but are derived when considering all living vertebrates.
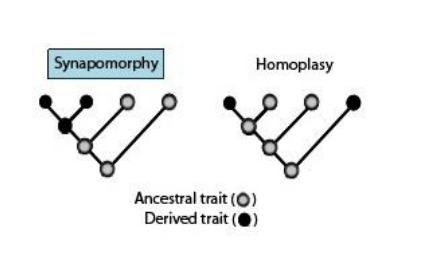
What is synapomorphy?
Derived traits that are shared among a group of descendants and are viewed as evidence of the common ancestry of the group
Ex: the vertebral column is a synapomorphy of all vertebrates when considering all animals
What is milk production considered?
synapomorphy of all mammals when considering for vertebrates
Ex: Monotreme: milk production keeps together even if one develops eggs
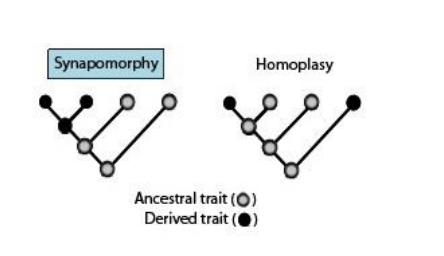
how are derived characters determined?
by comparing with fossils and embryos/larval stage which preserve information about ancestral states and developmental origins
When do derived characters appear?
later in development (novel traits to particular groups of organisms)
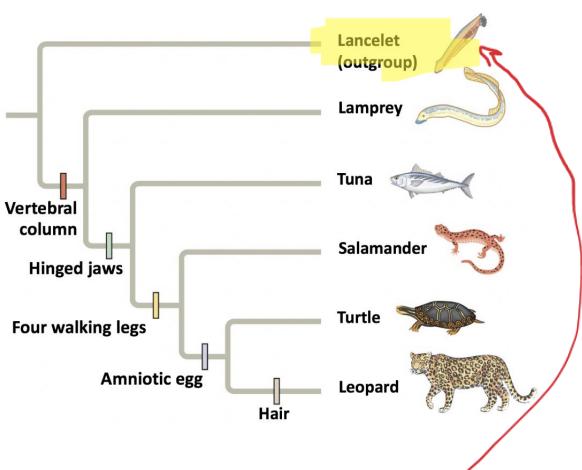
What do derived characters need to be compared to?
outgroup
What is an outgroup?
a lineage that falls outside the group being studied but is closely related to that group
What is a monophyletic group?
includes a common ancestor and all of its descendants.
Shows the entire evolutionary path a group has taken since
its origin.
blue
one cut to separate from PT
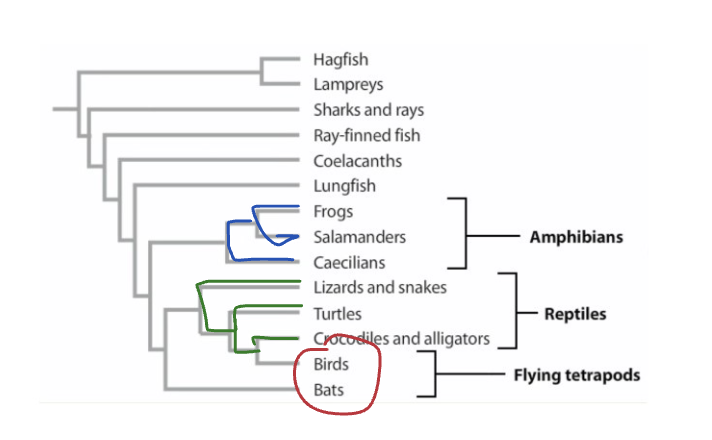
What is a clade?
a monophyletic group
What is a paraphyletic group?
includes a common ancestor and some, but not all, of its descendants
green
two cuts to separate from PT
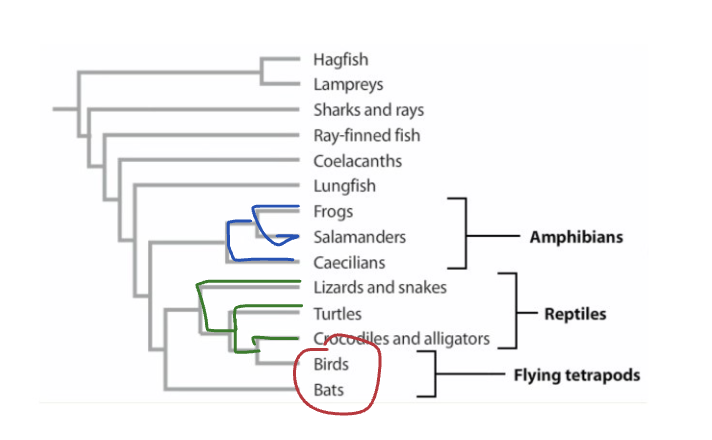
What is a polyphyletic group?
does not include the common ancestor.
members share trait that evolved independently by convergent evolution
red
Ex": Flying tetrapods includes bats and birds: cut out individual species and leaving ancestor out
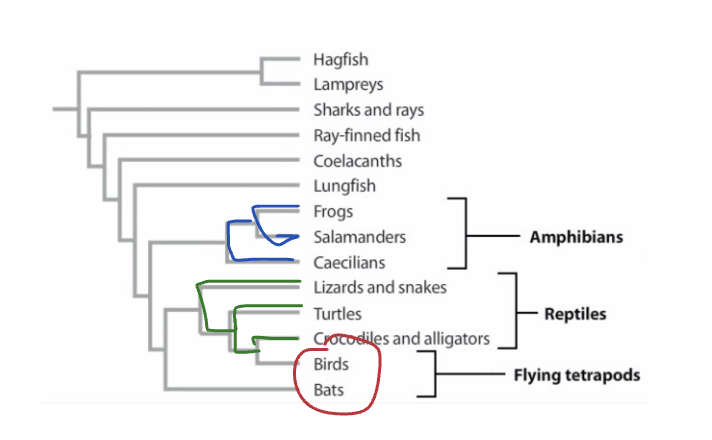
Which group is the only accurate reflection of evolutionary relationships?
monophyletic group
Shows the entire evolutionary path a group has taken since its origin.
Summary

What is the relation between bat and bird wings?
wings of bats and birds are analogous because they evolved independently for flight
forelimbs of mammals are homologous because they share a common skeletal structure inherited from a common ancestor
What is the order of taxonomic groups?
Domain —> kingdom —> phylum —> class —> order —> family —> genus —> species
Doctor King Phillip came over for good soup