Economics - Chapter 4: Government and the Macroeconomy
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/184
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
185 Terms
1
New cards
Define 'economic growth'
An increase in national income (GDP) in a economy over time
2
New cards
Define 'real GDP'
GDP with the effect of price inflation removed so only output is measured
3
New cards
Define 'national income'
Measures the monetary value of the flow of output of goods and services produced in an economy over a period of time
4
New cards
What is national income also known as?
GDP
5
New cards
What is national income and economic growth most commonly measured using?
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
6
New cards
Define 'gross domestic product'
The total value of goods and services produced within a country's borders in a given year
7
New cards
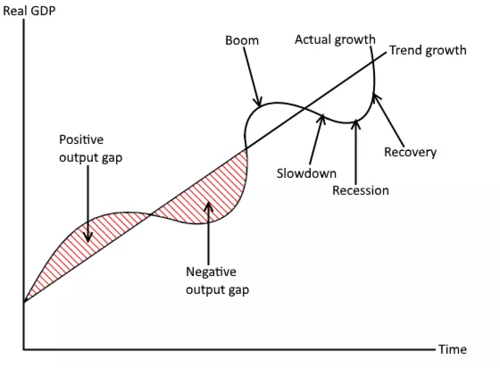
Describe the trade cycle
- boom
- downturn
- recession
- depression
- recovery
- downturn
- recession
- depression
- recovery
8
New cards
Define 'boom'
A sustained period of high GDP growth
9
New cards
Describe the effects of a boom to the economy
- low unemployment
- increasing incomes
- higher investment
- higher confidence
- increased tax revenue
- high inflation
- increasing incomes
- higher investment
- higher confidence
- increased tax revenue
- high inflation
10
New cards
Define 'recession'
2 consecutive quarters of negative (GDP) economic growth
11
New cards
Describe the effects of a recession to the economy
- negative GDP growth
- high unemployment
- decreasing incomes
- low investment
- low confidence
- decreased tax revenue
- low inflation
- high unemployment
- decreasing incomes
- low investment
- low confidence
- decreased tax revenue
- low inflation
12
New cards
Define 'depression'
The bottom of the business cycle when GDP is negative for a sustained period of time
13
New cards
Define 'recovery'
When the economy starts to grow positively again after a recession
14
New cards
What is GDP a widely used measure of?
Economic growth and development
15
New cards
What does a higher GDP per capita generally signify?
A higher standard of living
16
New cards
Define 'GDP per capita'
A measure of average GDP per person in a country
17
New cards
How is GDP per capita calculated?
total GDP ÷ population
18
New cards
Why does higher GDP per capita generally signify a higher standard of living?
Higher GDP per capita = more income per person
More income would lead to higher living standards
More income would lead to higher living standards
19
New cards
In what situation would a higher GDP per capita not signify a higher standard of living?
Hong Kong/NYC - more income does not mean higher living standards as rent is extremely high
20
New cards
Define 'standard of living'
The degree of wealth and material comfort available to a person
21
New cards
Define 'quality of life'
The standard of healthy, comfort and happiness experienced by an individual
22
New cards
List the limitations to using GDP as a measure of economic growth
- inflation
- population changes
- statistical errors
- value of home-produced goods
- hidden economy
- GDP and living standards
- population changes
- statistical errors
- value of home-produced goods
- hidden economy
- GDP and living standards
23
New cards
Describe how inflation is a limitation to using GDP as a measure of economic growth
Economic growth could be mistaken for increases in price - can be fixed by using real GDP
24
New cards
Describe how population changes are a limitation to using GDP as a measure of economic growth
Population changes will lower GDP per capita, even if the economy has grown
25
New cards
Describe how statistical errors are a limitation to using GDP as a measure of economic growth
Large numbers are involved so errors are possible
26
New cards
Describe how the value of home-produced goods are a limitation to using GDP as a measure of economic growth
Carers and parents' output are not counted into GDP but is a valuable service so GDP will be lower
27
New cards
Describe how the hidden economy is a limitation to using GDP as a measure of economic growth
The black market is a hugely lucrative market and should be part of GDP but isn't counted. Cash in hand is also not declared to the government so GDP would be lower
28
New cards
Describe how GDP and living standards are a limitation to using GDP as a measure of economic growth
Assumed that if GDP increases, standards of living increases. This may not occur due to regional imbalances, congestion, pollution and over-population, emphasising inequality from rich and poor.
29
New cards
Name another method of measuring development apart from GDP
Human Development Index (HDI)
30
New cards
How does the HDI give a broader measure of how developed a country is?
HDI includes education, healthy and living standards, designed to give a more well-rounded indication of standards of living
31
New cards
What is HDI a statistic composite index of?
- life expectancy
- education index
- GNI per capita
- education index
- GNI per capita
32
New cards
Define 'education index'
The measure of mean years of schooling and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system
33
New cards
Define 'HDI (Human Development Index)'
The composite index of life expectancy, education and per capita income used to rank countries in terms of human development
34
New cards
List the advantages of economic growth
- increased incomes
- better public services
- greater life expectancy
- more leisure time
- better public services
- greater life expectancy
- more leisure time
35
New cards
How does economic growth lead to increased incomes?
Increases in GDP means that average people have more income. With more disposable income, they can buy more and better quality goods and services \> standard of living improves
36
New cards
How does economic growth lead to better public services?
The government is able to collect more tax revenue as most taxes are linked to income and spending which both increase when the economy grows \> spend this extra revenue on services
37
New cards
How does economic growth lead to greater life expectancy?
Due to economic growth, people are now living longer. People can afford healthier diets and there have been advances in medical technology
38
New cards
How does economic growth lead to more leisure time?
As the economy grows, it is possible to spend less time working. This is due to significant improvements in efficiency and incomes
39
New cards
List the disadvantages of economic growth
- regional differences
- unsustainable growth
- environmental damage
- inflation
- unsustainable growth
- environmental damage
- inflation
40
New cards
How does economic growth lead to regional differences?
Not everyone benefits the same from economic growth so some areas will benefit from others \> lead to discontent
41
New cards
How does economic growth lead to unsustainable growth?
Economic growth uses up non-renewable resources. Once they are used, they cannot be replaced. Economic growth means future generations will have fewer resources
42
New cards
How does economic growth lead to environmental damage?
As the economy grows, more natural resources are used in the production of goods and services and by consumers \> may be damaged or used up in the process
43
New cards
How does economic growth lead to inflation?
If economic growth is too fast, the economy may 'overheat'. Too much aggregate demand can cause inflation \> bad for the economy
44
New cards
Define 'sustainable development'
Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
45
New cards
Define 'unemployment'
The amount of people in the labour force that are willing and seeking work but cannot find employment
46
New cards
Define the ILO definition of 'unemployment'
People who are out of work, want a job, have actively sought work in the previous 4 weeks and are available to start work within the next fortnight
47
New cards
Define 'claimant count'
The number of people claiming unemployment benefits while looking for work
48
New cards
Define 'labour force survey'
Statistical survey conducted in a number of countries designed to capture data about the labour market
49
New cards
Why is the labour force graph always higher than the claimant count graph?
Not everybody who is unemployed will take benefits from the government
50
New cards
List the 5 types of unemployment
- cyclical (demand-deficient) unemployment
- frictional unemployment
- structural unemployment
- seasonal unemployment
- voluntary unemployment
- frictional unemployment
- structural unemployment
- seasonal unemployment
- voluntary unemployment
51
New cards
Define 'cyclical unemployment'
When individuals lose their jobs as a result of a downturn in aggregate demand \> caused by a recession following the business cycle
52
New cards
What type of unemployment is cyclical unemployment in terms of time?
Medium-term unemployment \> should self-correct
53
New cards
Define 'frictional unemployment'
When workers are in the process of searching for and moving from one job to another (in between jobs)
54
New cards
What type of unemployment is frictional unemployment in terms of time?
Short-term unemployment \> not big problem in economy
55
New cards
Define 'structural unemployment'
When certain industries decline because of long-term changes in market conditions \> caused by a mismatch between skills that workers in the economy can offer and skills demanded of workers
56
New cards
What type of unemployment is structural unemployment in terms of time?
Long-term unemployment \> change in industry structure
57
New cards
Define 'seasonal unemploment'
When many individuals are unemployed at certain times of the year, as they work in industries where they are not needed all year around
58
New cards
What type of unemployment is seasonal unemployment in terms of time?
Short-term unemployment \> will revert back to normal by desired seasons
59
New cards
Define 'voluntary unemployment'
When workers choose not to work in the available jobs at the current equilibrium wage rate
60
New cards
List the costs to the individual from unemployment
- no future planned
- decreased standards of living
- decreased standards of living
61
New cards
List the costs to society from unemployment
- more petty crime
- heightened emotions
- heightened emotions
62
New cards
List the costs to the government from unemployment
- lower tax revenue
- high government spending for unemployed
- high government spending for unemployed
63
New cards
List the costs to the economy from unemployment
- waste of economic potential
- negative multiplier effect (cycle)
- negative multiplier effect (cycle)
64
New cards
Define 'inflation'
An increase in the average price level of goods and services in a country \> general persistent rise in prices over time
65
New cards
What do most governments aim the inflation rate to be?
~2% (+/- 1%)
66
New cards
Define 'purchasing power'
The number of value of goods and services that can be purchased with a unit of currency
67
New cards
What happens to purchasing power during inflation?
Inflation causes the purchasing power of money to decrease
68
New cards
Name the formula needed to calculate the index for a given year
CPI = cost of basket in current year ÷ cost of basket in base year
69
New cards
Define 'base year'
The benchmark (start) year that serves as a basis of comparison for prices in other years
70
New cards
Define 'consumer price index (CPI)'
A measure of the general price level (excluding housing costs) used in the UK and across the Eurozone
71
New cards
Describe the method of measuring the CPI
1. every month the government records the prices of ~700 goods and services purchased by over 7000 families
2. the basket of goods is weighted and representative
3. a weighted average of these prices is worked out for each month
4. the average is then converted into an index number with a base year
5. the rate of inflation is expressed in terms of percentage change for the past year
2. the basket of goods is weighted and representative
3. a weighted average of these prices is worked out for each month
4. the average is then converted into an index number with a base year
5. the rate of inflation is expressed in terms of percentage change for the past year
72
New cards
Define 'retail price index (RPI)'
A measure of the general price level which includes house prices and council tax
73
New cards
List the three main reasons why inflation occurs
- demand pull inflation
- cost push inflation
- money supply inflation
- cost push inflation
- money supply inflation
74
New cards
List the costs of inflation
- 'shoe-leather' costs
- 'menu' costs
- reduction of purchasing power
- reduction of value of savings
- reduction in investment
- increase in government spending
- increase in business costs
- decrease in competitiveness
- political instability
- 'menu' costs
- reduction of purchasing power
- reduction of value of savings
- reduction in investment
- increase in government spending
- increase in business costs
- decrease in competitiveness
- political instability
75
New cards
Define 'shoe-leather costs'
Firms and consumers will keep less cash in hand and more interest-bearing bank accounts to counteract the effects of inflation. As they have less cash on hand, they must make more trips to the bank \> waste time and effort and wearing the leather on their shoes
76
New cards
Define 'menu costs'
Rapid inflation means that firms must spend time and resources updating menus and websites to show new prices \> increases costs of production for the firm
77
New cards
How does inflation affect purchasing power?
Decreases purchasing power \> consumers can buy less goods and services with their money and standard of living decreases
78
New cards
How does inflation reduce the value of savings?
Inflation causes money to decrease over time. Money stored as savings will decrease in value if rate of return is lower than rate of inflation
79
New cards
How does inflation reduce investment?
Causes uncertainty, making it harder to predict future levels of demand and potential return on investment \> decreases level of investment in new capital
80
New cards
How does inflation increase government spending?
Unemployment benefits and pensions all increase with inflation, causing government spending to increase \> can worsen budget position and increase national debt
81
New cards
How does inflation increase business costs?
Cost of factor of production to increase so workers will push for higher wages \> increase firms' costs of production leading to further increase in prices
82
New cards
How does inflation decrease competiveness?
Price of your country exports increase so the rate of increase in prices is faster than your trading partners', goods and services will become relatively more expensive \> make domestic businesses less competitive
83
New cards
How does inflation lead to political instability?
Rapid increases in prices decreases the purchasing power of consumer and decreases standards of living. This erodes savings of individuals \> cause discontent and lead to political instability
84
New cards
Define 'hyperinflation'
An extreme and rapid rise in the price level of goods and services of more than 50% A MONTH
85
New cards
What are the problems associated with hyperinflation?
Value of money changes - people can no longer purchase essential items
86
New cards
Why is it concerning that inflation is increasing too rapidly?
- can destroy output and destabilise societies
- society and economy may cripple
- society and economy may cripple
87
New cards
Define 'deflation'
A general and persistent fall in prices over time
88
New cards
What is involved in the construction of a retail price index?
A basket of goods
89
New cards
What is included in the calculation of a consumer prices index (CPI)?
The price of a basket of goods and services
90
New cards
What will help a government reduce the rate of inflation if increased?
Income tax
91
New cards
Define 'aggregate demand'
Total demand for goods and services in an economy
92
New cards
Name the calculation for aggregate demand
AD = C + I + G + ( X - M)
AD = consumption + businesses + governments + (exports - imports)
AD = consumption + businesses + governments + (exports - imports)
93
New cards
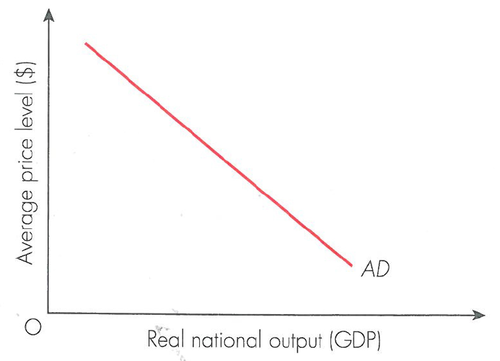
Describe the graph of aggregate demand
- price level (inflation)
- GDP
- AD
- GDP
- AD
94
New cards
Define 'consumption'
Consumers buying and spending on goods and services in an economy (65% of total demand)
95
New cards
When consumer income increases, what happens to consumption?
Consumption increases
96
New cards
When interest rates increases, what happens to consumption?
Consumption decreases
97
New cards
When there is improved confidence in economic outlook, what happens to consumption?
Consumption increases
98
New cards
When there is a decrease in stock and house prices, what happens to consumption?
Consumption decreases
99
New cards
Define 'investment'
Businesses spending on capital and other goods and services in an economy (15% of total demand)
100
New cards
When there is a decrease in corporation tax, what happens to investment?
Investment increases