Human Anatomy Unit 5b - Peripheral Nervous System
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Peripheral Nervous System
All nerves lateral to CNS
Subdivisons of PNS
Somatic system
Autonomic system
Somatic system
Regulates skin & skeletal muscles
Usually voluntary response
Includes reflexes
Protect body from harm
Autonomic System
Regulates cardiac & smooth muscles, and glands
Functions automatically, usually involuntary
Subdivisions of Autonomic
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Sympathetic
Emergency situations: “fight or flight”: increased heart rate & respiration, digestion & excretion inhibited, pupils dilated
Neurotransmitter = norepinephrine (NE)
Similar effects of adrenaline
Parasympathetic
Responses during relaxation: digestion, regular heart rate, pupils contracted
Neurotransmitter = acetylcholine (ACh)
Functions of Nervous System
Gathers info (sensory input)
Interprets info & determines response (integration)
Causes response (motor output)
Sub-divisions of Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS): brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): all neurons lateral to CNS
Neurons
Nerve cells that communicate
Characteristics of Neurons
Long life span
Amitotic (do not reproduce)
High metabolic rate (require constant energy and O2)
Neuroglia
Nerve cells that do NOT communicate
Characteristics of Neuroglia
Nourish neurons to promote growth & health
Scaffolding for cells to climb
Remove debris from dead cells (after injury)
Role in neuron maturation (add myelin)
2 Types of Neuroglia
Astrocytes
Schwann cells
Astrocytes
Nourish neurons
Maintain appropriate chemical environment for neurons (“mop up” toxins)
Schwann cells
Form myelin sheaths around axons
Myelin sheath
Made of lipids and proteins
Surrounds axon of neuron
Allows for quick nerve impulse transmission
Multiple Sclerosis
Autoimmune disorder:
WBC fight cells of myelin sheath —> causes scarring
Results in delayed or blocked signals that control muscle coordination, strength, sensation & vision
Types of neurons
Sensory
Interneuron
Motor neuron
Sensory neurons
(afferent, PNS): receives info from outside and takes it to CNS
Interneuron
(CNS): coordinates info & determines response
Motor neuron
(efferent, PNS): causes response
Dendrites
Receive neurotransmitters
Axon
Send neurotransmitters away to next neuron
Nodes of Ranvier
Periodic gaps along the axon (no myelin)
Allows for rapid conduction of nerve impulses
Synapse
Space in between neurons
Allows for instantaneous communication throughout body
Axon Terminals
Change electrical impulses or action potentials within into chemical messages
Soma
The main cell body
Nucleus
Controls the cell
Nerve Impulses
Necessary for ALL functions of nervous system
Occur due to bioelectric currents (movement of Na+, K+, Ca+2, Cl-)
Resting Potential
Resting axons are POLARIZED (outside of axon is +, inside of axon is - )
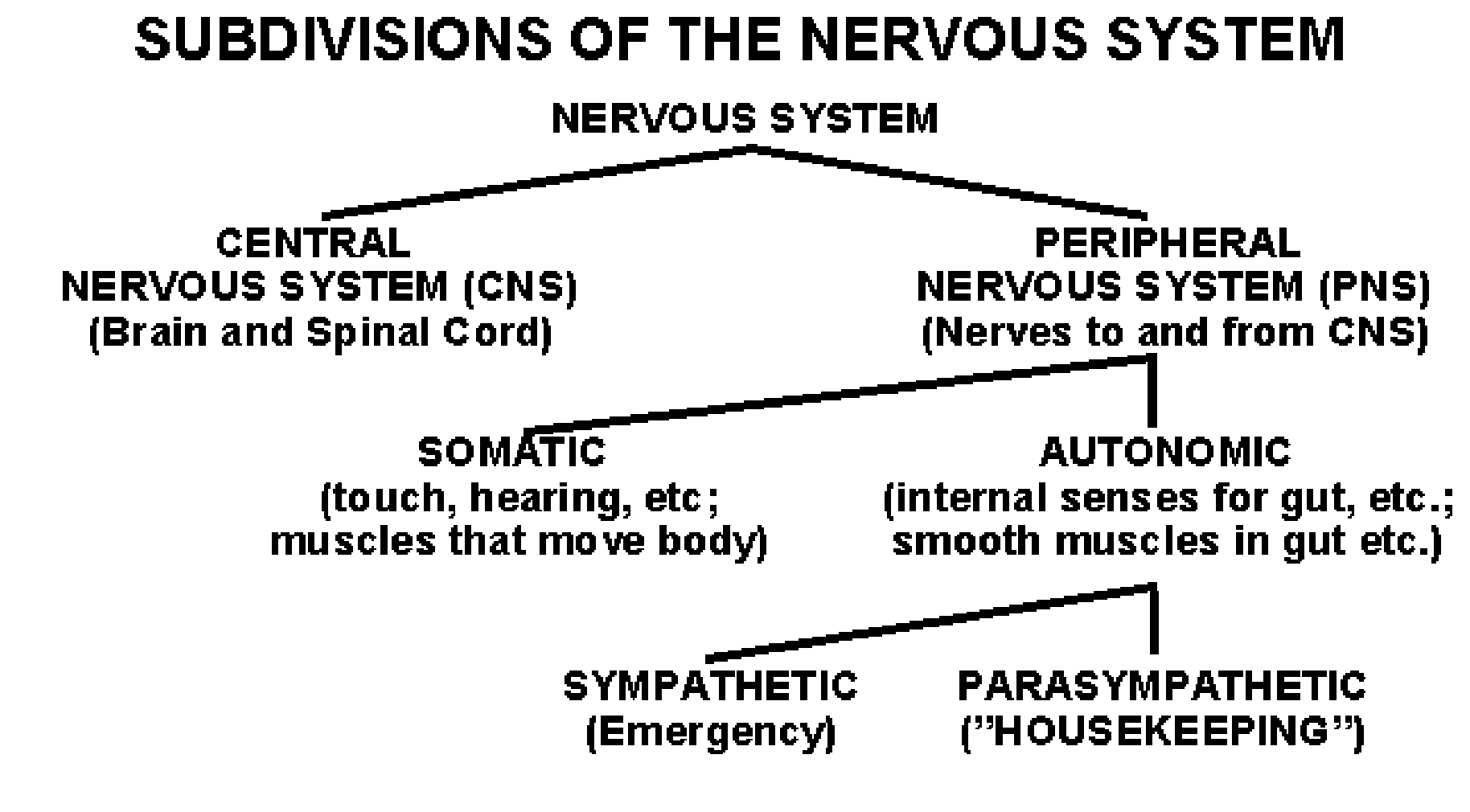
Action Potential
Must occur to conduct a nerve impulse
The polarity inside the axon changes:
Inside of axon becomes positive (depolarization)
Then the inside of axon quickly becomes negative again (repolarization)
All or None response (once it begins, it will complete)
Intensity of message: depends on frequency of action potentials
Speed: depends on diameter of axon & if axon is myelinated
Action Potential Image
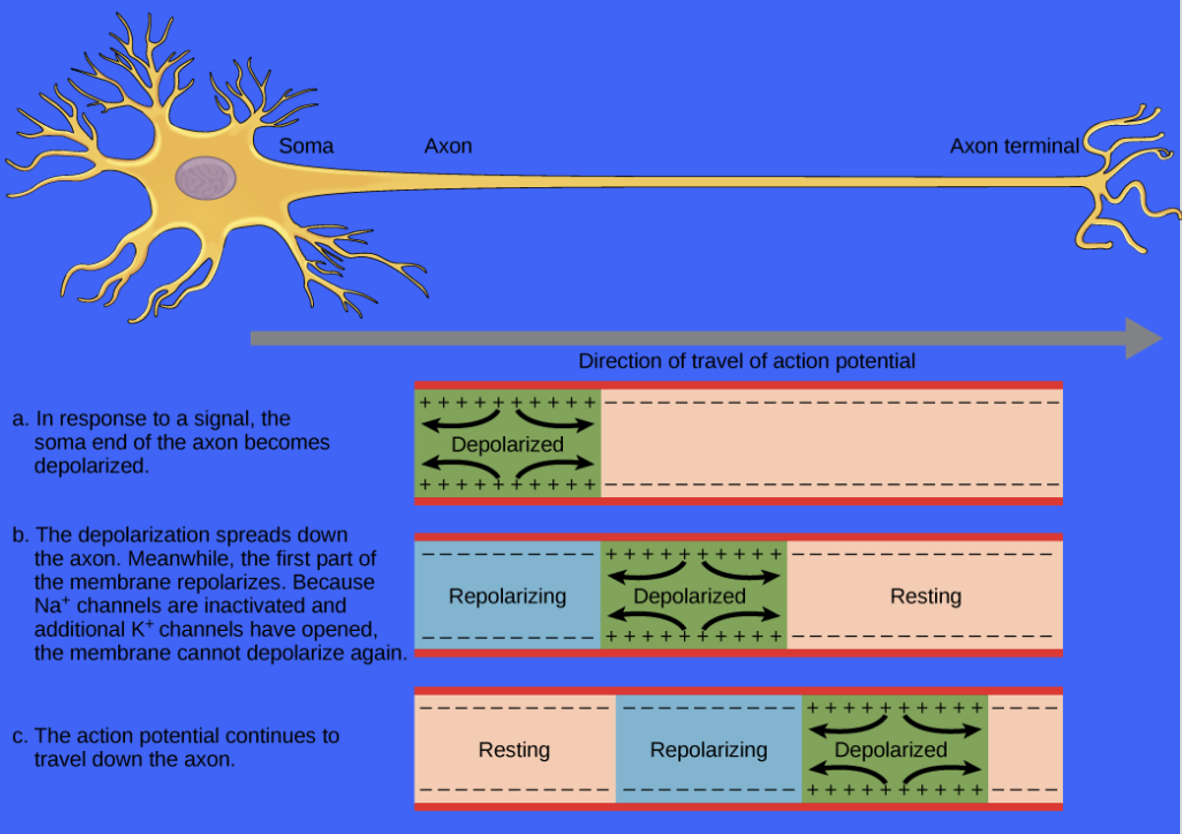
How many Impulse Transmission steps?
3 Steps
Impulse Transmission: Step 1
Axon branches at the end into axon terminals
Impulse Transmission: Step 2
Axon terminals release neurotransmitters across synapse
Impulse Transmission: Step 3
Neurotransmitters received by dendrite of next neuron
Impulse Transmission Image
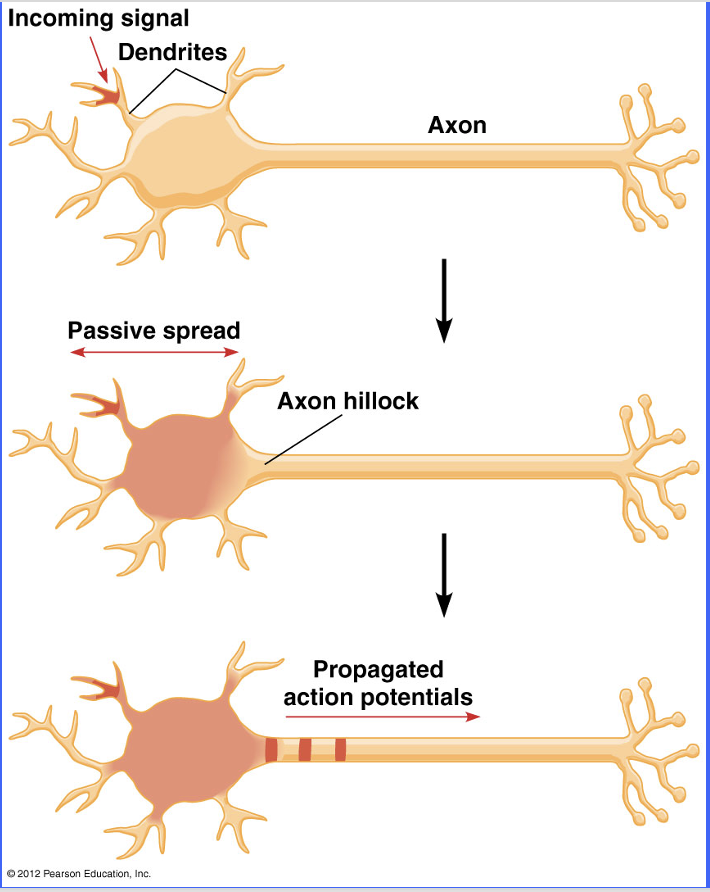
Hearing Step 1
Pinna (outer ear) “catches” sound waves
Hearing Step 2
Sound travels through auditory canal and hits tympanic membrane (ear drum)
Located between canal & middle ear
Muscles keep membrane very taut – therefore membrane vibrates when hit by sound waves
Hearing Step 3
The cochlea (inner ear) must conduct sound through fluid
Requires more pressure to “push” sound waves
Pressure is generated by 3 ossicles
Malleus (hammer)
Incus (anvil)
Stapes (stirrup)
Hearing Step 4
The stapes pushes on the basilar membrane (part of cochlea) causing vibrations in different locations
Cochlea has to convert physical sound waves into electrical signals for the brain to understand
The cochlea is made of 3 separate coiled tubes separated by thin membranes
Hearing Step 5
Organ of Corti (on basilar membrane) contains 1000s of tiny hairs – when vibrations are strong enough, the hairs move and send an electrical impulse to the vestibulocochlear nerve
Hearing Step 6
VB-Cochlear nerve transmits info to brain
Cochlear Implants
The implant device sends its own electrical signals to the cochlear nerve – thus allowing a patient to hear
Ear Image
Cornea
< 1/50 of an inch thick
Cornea must stay clear for light to enter
For the cornea to stay clear:
Stem cells around the cornea produce corneal daughter cells
Daughter cells migrate to center of cornea & form a protective, transparent coat
Replaced every few days
If stem cells are destroyed:
Daughter cells aren’t produced and
blood vessels & sclera grows over
cornea
Corneal Transplants
Discovered by accident
Donor eyes preferably not over 50 years old
Transplanting Stem Cells: Step 1
Surgeon scrapes away growth over recipient’s cornea
Transplanting Stem Cells: Step 2
Surgeon cuts stem cells away from donor cornea & thins from 1 mm to 1/3 mm
Transplanting Stem Cells: Step 3
Place ring of stem cells on recipient’s eye & suture in place
Transplanting Stem Cells: Aftermath
Transplanting stem cells does not result in vision
Takes ~ 4 months for the patient to produce daughter cells & for the daughter cells to forge paths
Transplanting Cornea
Surgeon removes damaged cornea
Transplants new cornea
Laser Eye Surgery
Reshapes cornea to allow light to be better focused on retina (clearer vision)
Make flap in cornea
Remove microscopic amount of corneal tissue with laser (laser uses a cool UV beam to remove tissue and reshape cornea)
Ex: near sighted: goal is to flatten cornea
Ex: far sighted: goal is to make cornea steeper
Ex: astigmatism: goal is to make cornea a more normal shape
Bionic Eye
Uses retinal implant, converts images to mini-video camera in glasses
Not highly detailed vision
Artificial Corneas (Kpro)
A synthetic material that is transparent, regenerates, has high water content, and a unique biomechanics system
Transplanting CNS Stem Cells
Transplant stem cells from olfactory region to spine region, stem cells grew and stimulated regeneration