Final Exam 1, 2, 3 (not finished)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
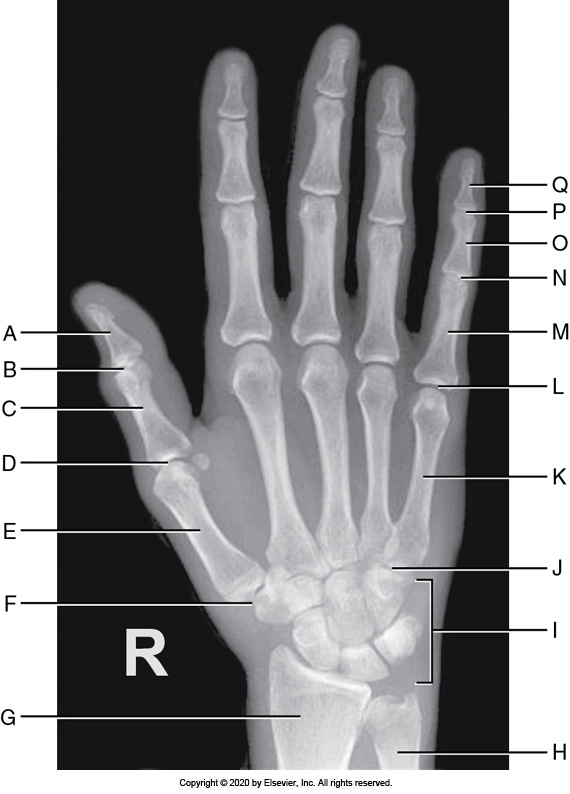
Identify the labeled "B" anatomy below:
Interphalangeal joint
Metacarpophalangeal joint
Radius
Carpometacarpal joint
Interphalangeal joint
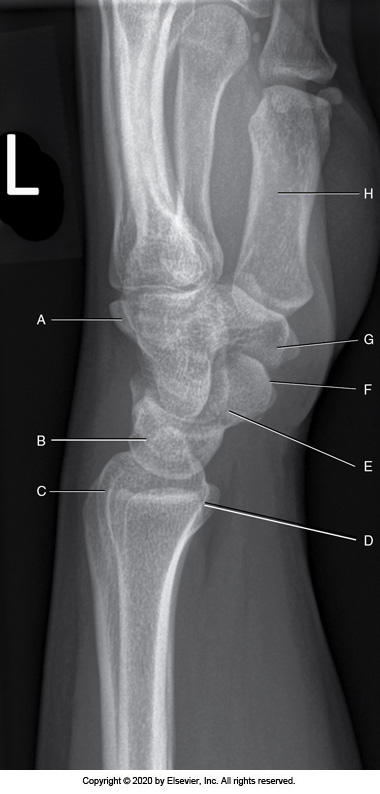
Identify the labeled "G" anatomy in the image below:
Trapezium
Lunate
Pisiform
Capitate
Trapezium
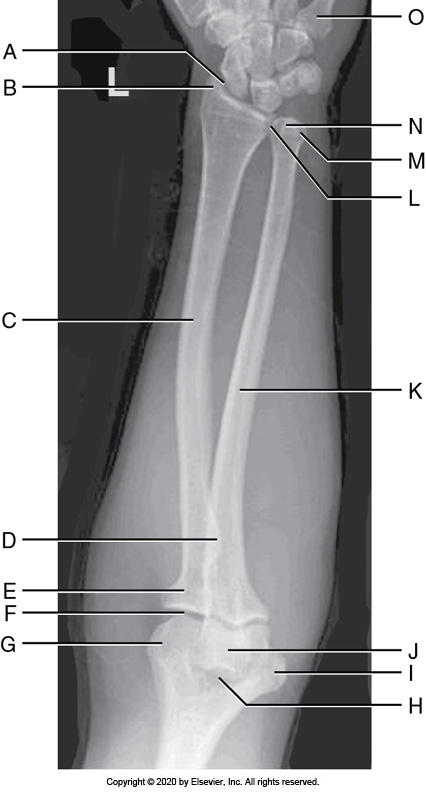
Identify the labeled anatomy "B" in the image below:
Radial tuberosity
Olecranon fossa
Radial styloid
Ulnar styloid
Radial styloid
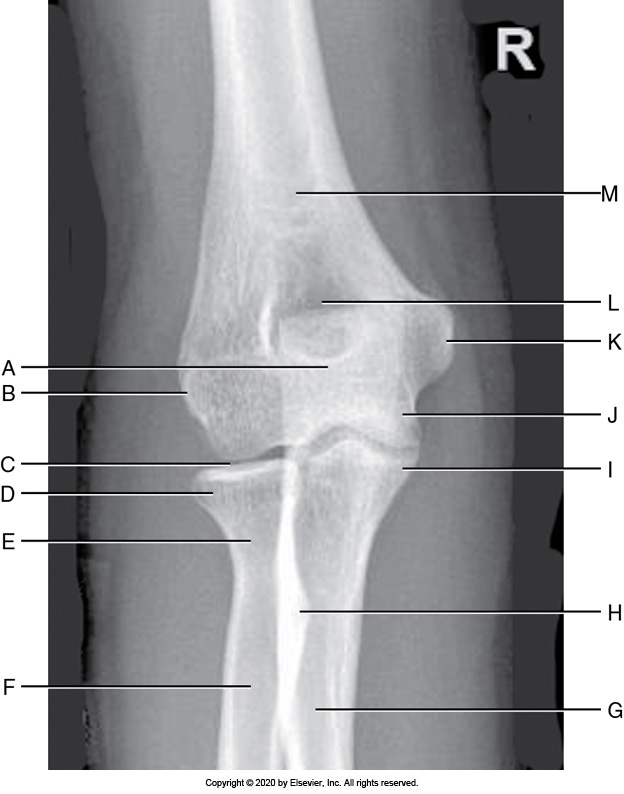
Identify the labeled "K" anatomy in the image below:
Radial head
Medial epicondyle
Lateral epicondyle
Olecranon
Medial epicondyle
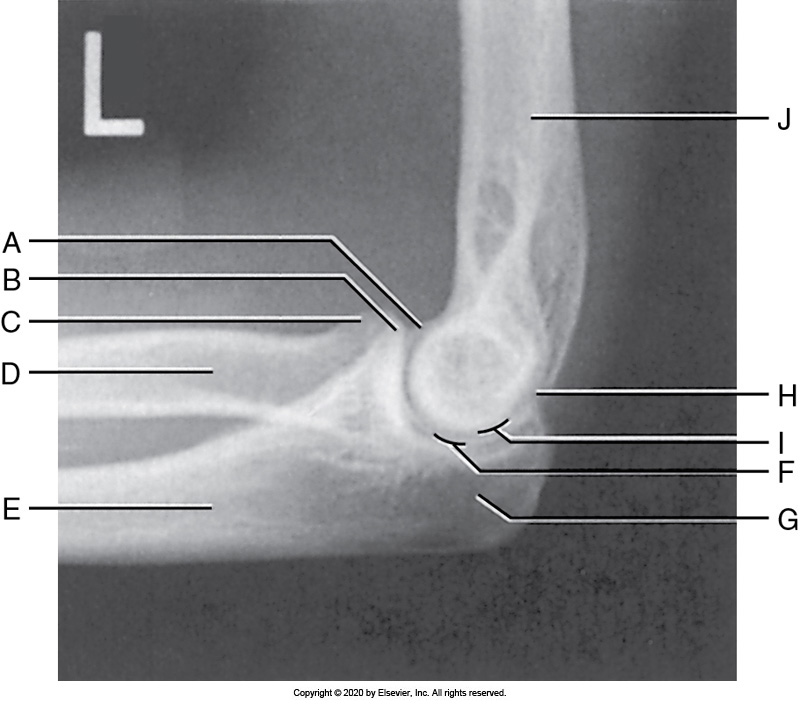
Identify the labeled "H" anatomy inn the image below:
Coronoid
Humerus
Capitulum
Radial head
Capitulum
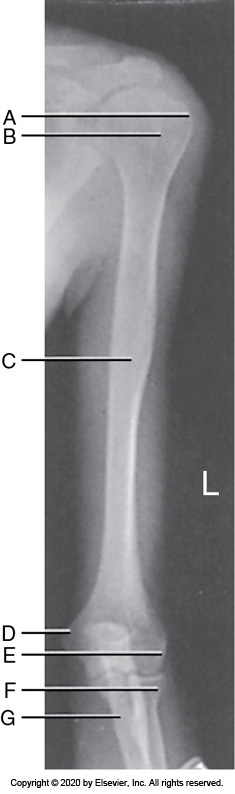
Identify the labeled "D" anatomy in the image below:
Radial head
Greater tubercle
Medial epicondyle
Lateral epicondyle
Medial epicondyle
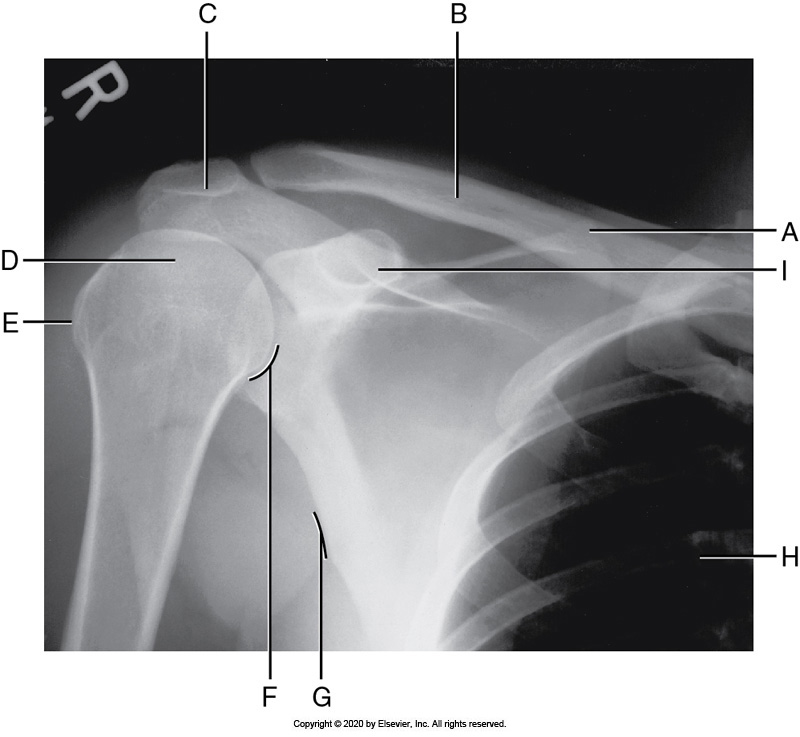
Identify the labeled "I" anatomy in the image below:
Greater tubercle
Coracoid process
Humeral head
Acromion process
Coracoid process
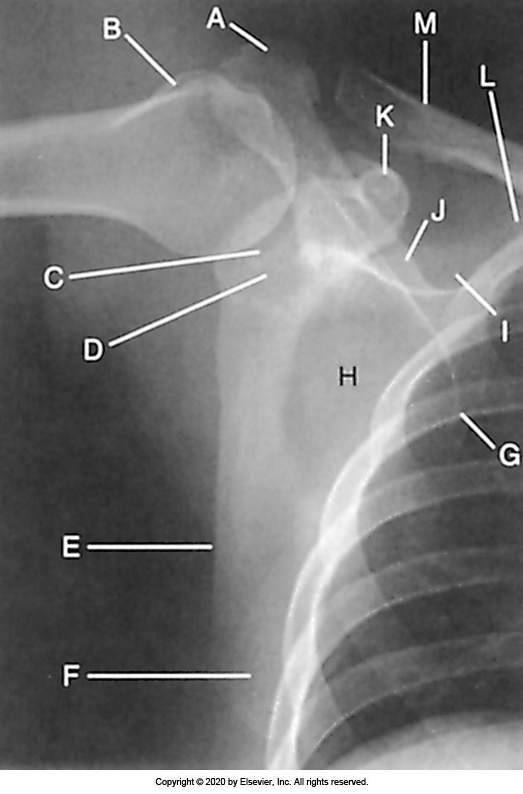
Identify the labeled "E" anatomy in the image below:
Scapular body
Acromion process
Superior scapular angle
Coracoid process
Acromion process
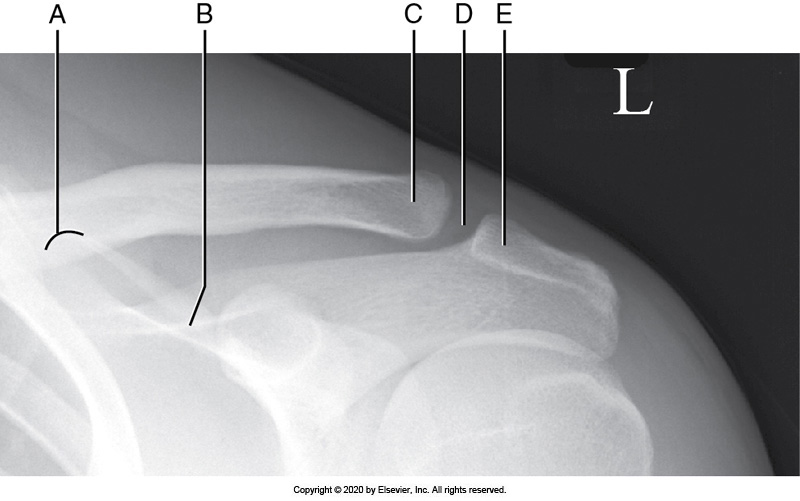
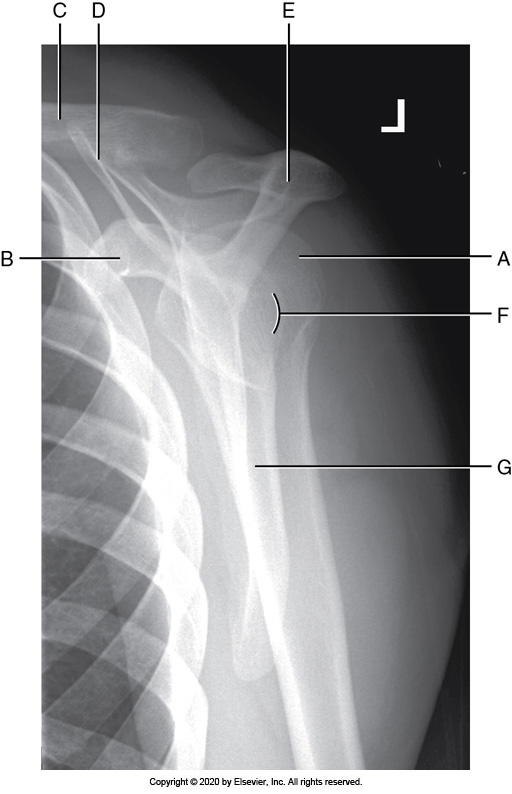
Identify the labeled "D" anatomy in the image below:
AC joint
Scapular spine
Superior scapular angle
Lateral clavicle
AC joint
Identify the labeled "E" anatomy in the image below:
Medial border
Glenoid cavity
Lateral border
Scapular body
Lateral border
The IP joint spaces on finger projections are open and demonstrated without distortion when the
1. central ray is aligned parallel with the IP joint spaces.
2. central ray is aligned perpendicular to the IP joint spaces.
3. IP joints are aligned parallel with the IR.
4. IP joints are aligned perpendicular to the IR.
2 and 4 only
1 and 3 only
1 and 4 only
2 and 3 only
1 and 4 only
A PA wrist projection with accurate positioning demonstrates
1. an open radioulnar articulation.
2. the radial styloid in profile.
3. the long axes of the third metacarpal aligned with the midforearm.
4. open second through fifth MC joint spaces.
1,2,3, and 4
1 and 2
3 and 4
1, 2, and 3
1,2,3, and 4
A poorly positioned PA oblique wrist projection demonstrates superimposition of the trapezoid and trapezium, and the capitate is superimposed by the trapezoid. How should the positioning setup be adjusted to obtain an optimal projection?
Decrease the degree of medial rotation.
Increase the degree of medial wrist rotation.
Increase the hand rotation.
Align the third metacarpal and midforearm, decreasing radial flexion.
Decrease the degree of medial rotation.
A properly positioned AP thumb projection will demonstrate which of the following?
1. Twice as much soft tissue is present on the side of the next to the fingers than the opposite side.
2. Phalanges are not foreshortened.
3. Minimal superimposition of the medial palm soft tissue over the proximal first MC and the CM joint.
4. Hand fully extended.
1 and 3 only
2 and 3 only
2 and 4 only
1 and 4 only
2 and 3 only
An externally rotated PA oblique wrist projection with accurate positioning demonstrates
1. the trapezoid and trapezium without superimposition.
2. an open radioulnar articulation.
3. the ulnar styloid in profile.
4. superimposition of the medially located carpals.
2 and 4 only
2 and 3 only
1,2,3, and 4
1, 3, and 4 only
1, 3, and 4 only
An AP forearm projection with accurate positioning demonstrate the
1. radial styloid in profile laterally.
2. radial head superimposing the ulna by 0.25 inch (0.6 cm).
3. ulnar styloid in profile laterally.
4. humeral epicondyles in profile.
2, 3, and 4 only
1, 2, 3, 4
1, 2, and 4 only
1 and 3 only
1, 2, and 4 only
Which of the following projections is used to prevent crossing of the forearm bones?
AP projection
PA projection
AP projection
For an externally rotated AP oblique elbow projection with accurate positioning, the
1. capitulum is in profile.
2. capitulum-radial joint space is open.
3. coronoid process is in profile.
4. ulna is demonstrated without radial head superimposition.
1, 2, and 4 only
2,3, and 4 only
1 and 4 only
2 and 3 only
1, 2, and 4 only
To properly position an AP humerus, place the elbow at the ______ end of the tube, ______ the hand and wrist, and align the humeral condyles _______ with the IR.
cathode, supinate, perpendicular
anode, supinate, parallel
anode, pronate, perpendicular
cathode, supinate, parallel
anode, supinate, parallel
Which of the following are in profile on an optimally positioned AP humerus projection?
1. Lateral epicondyle
2. Medial epicondyle
3. Lesser tubercle
4. Greater tubercle
1, 2, and 3 only
1, 2, and 4 only
2, 3, and 4 only
1, 3, and 4 only
1, 2, and 4 only
In an AP shoulder projection with external rotation of the humerus, the greater tubercle will be seen
in medial profile
in lateral profile
in partial lateral profile
superimposed with the humeral head
in lateral profile
The arms of the Y on a PA oblique scapular Y shoulder projection are formed by the
1. coracoid.
2. scapular body.
3. acromion.
4. glenoid fossa.
3 and 4
1 and 2
2 and 3
1 and 3
1 and 3
For a PA oblique scapular Y shoulder projection, the patient's
1. humerus is elevated until the hand is placed on the hip.
2. body is rotated toward the unaffected shoulder.
3. body is rotated until an imaginary line connecting the acromion angle and coracoid processes is aligned parallel with the IR.
4. midcoronal plane is vertical.
2, 3, and 4 only
2 and 3 only
1, 2, 3, and 4
3 and 4 only
3 and 4 only
An AP clavicle projection obtained with the patient rotated away from the affected shoulder demonstrates the
1. medial clavicular end superimposed over the vertebral column.
2. medial clavicular end shifted away from the vertebral column.
3. scapular body with increased thoracic superimposition.
4. scapular body with decreased thoracic superimposition.
1 and 3 only
1 and 4 only
2 and 4 only
2 and 3 only
1 and 4 only
Longitudinal foreshortening of the scapula is demonstrated on an AP shoulder projection when the
glenoid cavity is demonstrated on end
superior scapular angle is visualized superior to the clavicle
glenoid cavity is demonstrated in profile
clavicle superimposes the superior scapular angle
superior scapular angle is visualized superior to the clavicle
A PA chest projection with accurate positioning demonstrates
1. 10 posterior ribs above the diaphragm.
2. equal posterior ribs length on both sides of the chest.
3. the manubrium superimposed by the fourth thoracic vertebra.
4. the scapulae outside the lung field.
1, 2, 3, and 4
1 and 3 only
2 and 4 only
1, 2, and 4 only
1, 2, 3, and 4
The IR is positioned _______ for a PA chest projection of a hypersthenic patient.
crosswise
lengthwise
crosswise
A PA chest projection with poor positioning demonstrates vertical clavicles and the manubrium at the same level as the fifth thoracic vertebra. How was the patient positioned for such an image to be obtained?
The central ray was angled caudally.
The shoulders were elevated.
The shoulders and elbows were not internally rotated.
The patient's upper midcoronal plane was tilted toward the IR.
The patient's upper midcoronal plane was tilted toward the IR.
A PA chest projection with poor positioning demonstrates the scapulae in the lung field and elevated lateral clavicular ends. How should the patient be repositioned for an optimal projection to be obtained?
1. Tilt the upper midcoronal plane away from the IR.
2. Depress the shoulders.
3. Coax the patient into a deeper inspiration.
4. Anteriorly rotate the shoulders and elbows.
2 and 4 only
2, 3, and 4 only
2 only
1 and 4 only
2 and 4 only
For a PA chest projection with accurate positioning, the
1. SID is set at 72 inches (183 cm).
2. shoulders are positioned at equal distances from the IR.
3. Upper midcoronal plane is tilted slightly toward the IR.
4. elbows and shoulders are rotated posteriorly.
1, 2, and 4 only
2 and 3 only
1 and 2 only
1, 2, 3, and 4
1 and 2 only
For a lateral chest projection with accurate positioning, the
1. SID is set at 40 inches (102 cm).
2. humeri are positioned vertically.
3. shoulders, posterior ribs, and posterior pelvic wings are aligned perpendicular to the image receptor (IR).
4. midsagittal plane is aligned perpendicular to the IR.
2 and 3 only
3 and 4 only
1 and 3 only
2 and 4 only
2 and 3 only
A left lateral chest projection with poor positioning demonstrates the humeri soft tissue superimposed over the anterior lung apices. How was the patient positioned for such an image to be obtained?
The inferior midsagittal plane was tilted toward the IR.
The humeri were positioned at a 90-degree angle with the body.
The central ray was angled caudally.
The chest was rotated.
The humeri were positioned at a 90-degree angle with the body.
A rotated left lateral chest projection demonstrates the heart shadow posterior to the sternum. Which is the anteriorly positioned lung?
Right
Left
Right
Which side of the patient is positioned against the imaging table or cart for an AP-PA chest projection (lateral decubitus position) to rule out a left side pleural effusion?
Left
Right
Left
For an AP axial chest projection (lordotic position),
1. the shoulders are positioned at equal distances from the IR.
2. the patient's back is arched until the midcoronal plane and IR form a 45-degree angle.
3. a 15-degree cephalad central ray angulation is used if the patient is standing erect.
4. the elbows and shoulders are rotated anteriorly.
1 and 2 only
1, 2, 3, and 4
2 and 3 only
1, 2, and 4 only
1, 2, and 4 only
For AP projection of the chest performed with a portable x-ray unit, placing the IR lengthwise is not appropriate for which body habitus?
Asthenic
Sthenic
Hypersthenic
Hyposthenic
Hypersthenic
For an upright AP abdomen projection, the
1. ASISs are positioned at equal distances from the IR.
2. patient remains in an upright position at least 5 to 20 minutes before the image is obtained.
3. symphysis pubis should be included.
4. patient is instructed to take a deep inspiration before the image is obtained.
1, 2, and 3 only
1 and 2 only
3 and 4 only
2 and 3 only
1 and 2 only
A supine AP abdomen projection with accurate positioning demonstrates the
1. outline of the psoas major muscles and kidneys.
2. symphysis pubis.
3. spinous processes aligned with the midline of the vertebral bodies.
4. long axis of the vertebral column aligned with the long axis of the collimated field.
1, 2, 3, and 4
3 and 4 only
1 and 2 only
1, 2, and 3 only
1, 2, 3, and 4
To best demonstrate intraperitoneal air,
an AP abdomen projection (lateral decubitus position) should be obtained with the patient lying on the right side.
allow the patient to be positioned upright for 5 to 20 minutes before obtaining the exposure for an upright AP abdomen projection.
the left iliac wing needs to be included in an AP abdomen projection (lateral decubitus position) on a patient with narrow hips.
the abdomen projection should be taken after a full inspiration.
allow the patient to be positioned upright for 5 to 20 minutes before obtaining the exposure for an upright AP abdomen projection.
An AP abdomen projection demonstrates greater distances from the left lumbar vertebral pedicle to the spinous process than the right pedicles to the spinous process. The projection
was taken with the patient in an LPO position.
was obtained with the central ray angled toward the right side.
will also demonstrate the sacrum rotated toward the left side.
was taken with the right side of the patient placed closer to the IR than the left.
was taken with the patient in an LPO position.
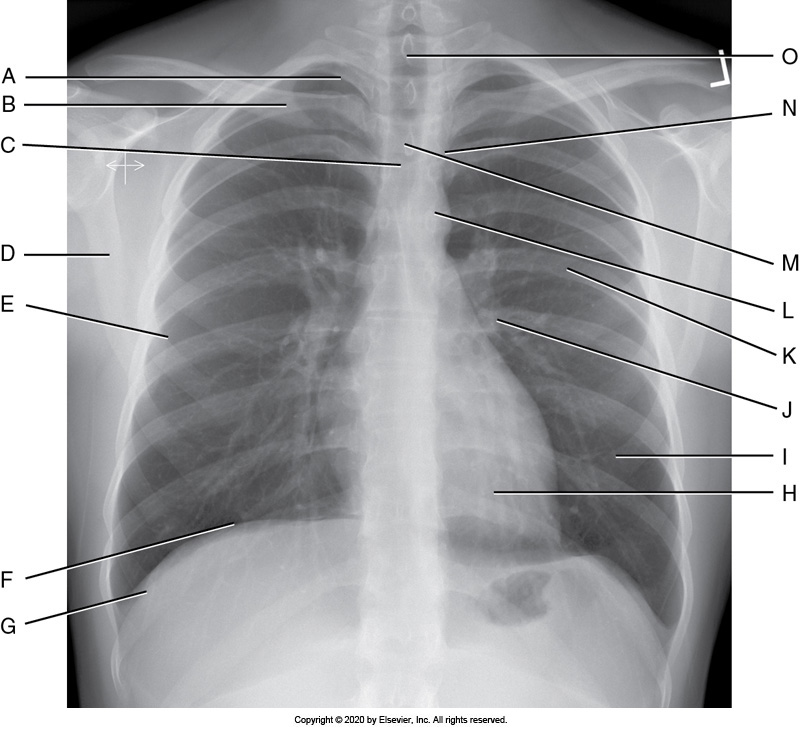
Identify the labeled anatomy " G" on the PA chest projection
Scapula
Clavicle
Lung apex
Costrophenic angle
Costrophenic angle
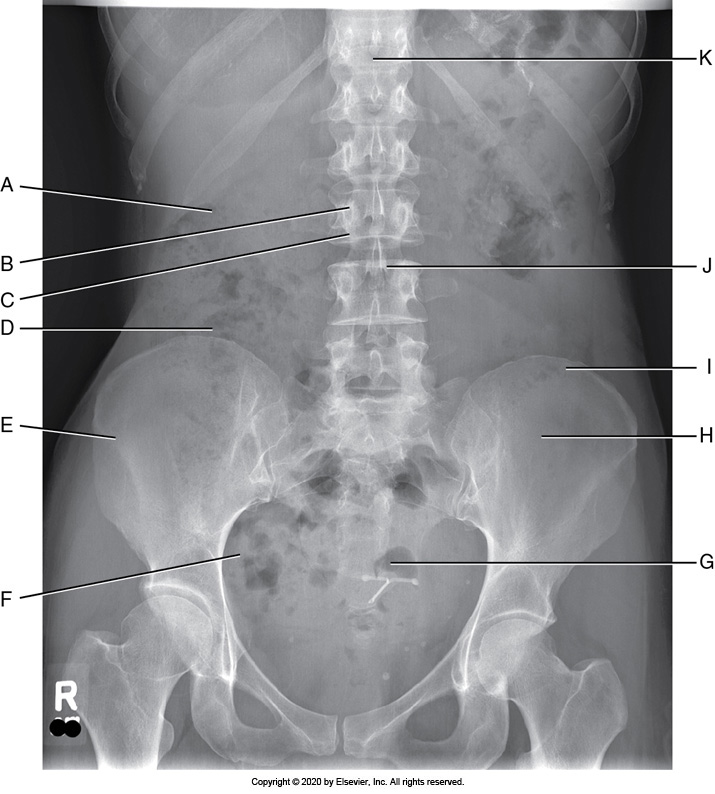
Identify the labeled anatomy "I" in the AP supine abdomen projection
Sacrum
Pedicle
Pubis symphysis
Iliac crest
Iliac crest
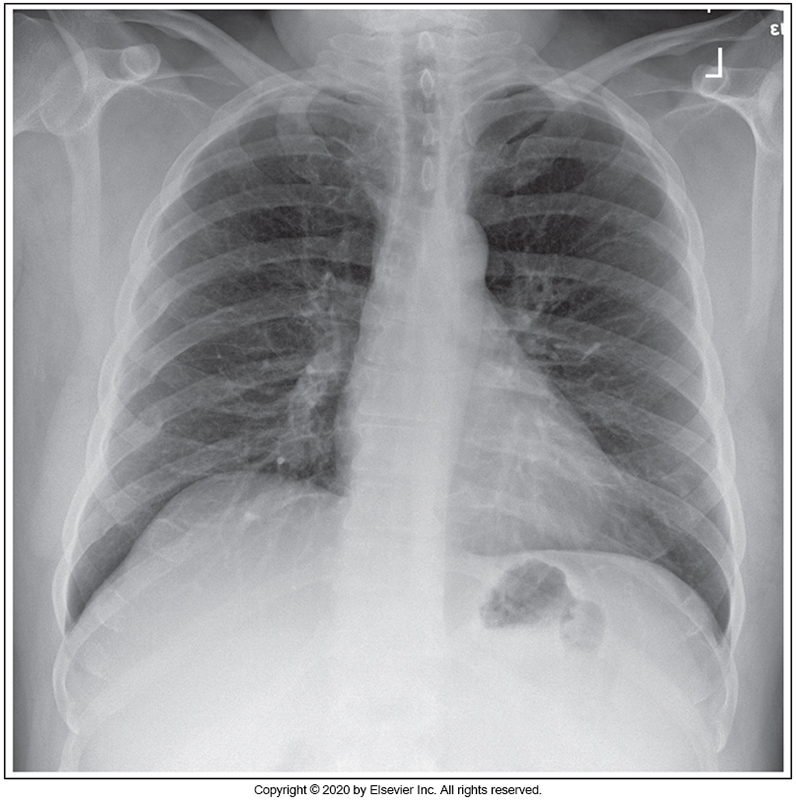
Identify the main problem of the image below (PA chest)
Patient is tilted anteriorly.
Patient is rotated.
Image taken on expiration.
Patient is tilted posteriorly.
Patient is tilted posteriorly.
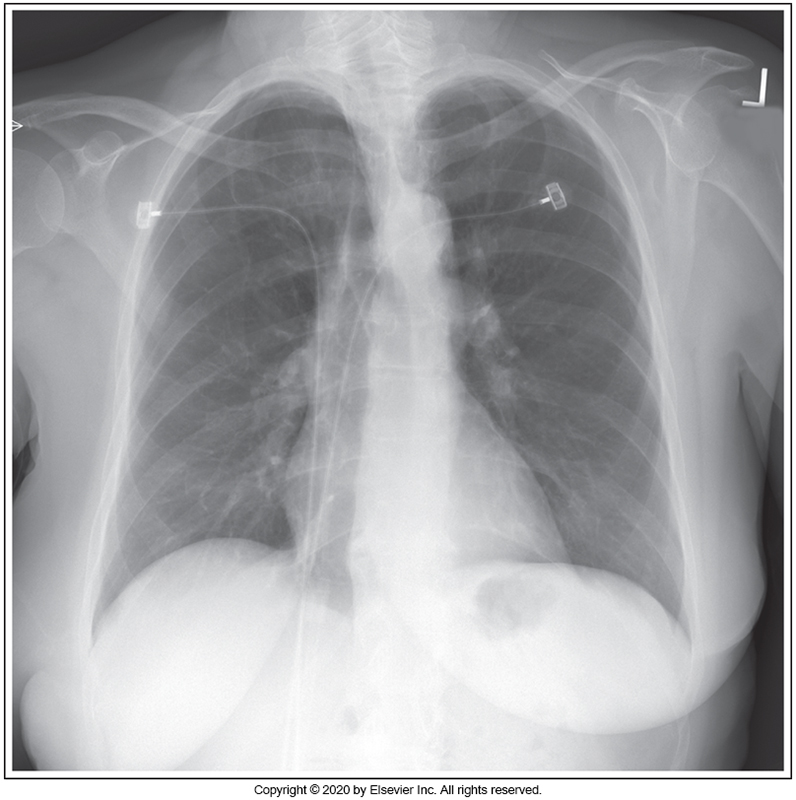
Identify the main problem of the image below (PA chest)
Patient is in an RAO position
Patient is in an LAO position
Patient upper thorax is tilted anteriorly.
Patient's upper thorax is tilted posteriorly.
Patient is in an LAO position
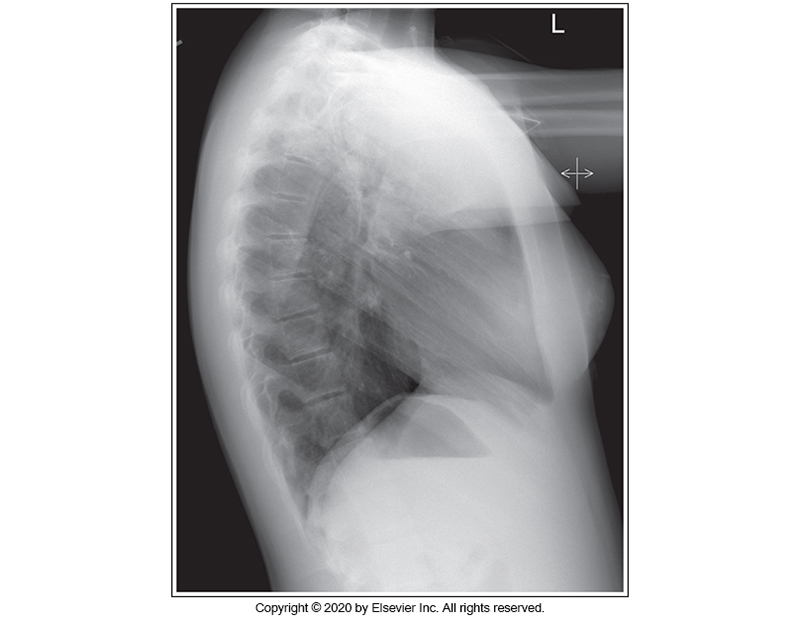
Identify the main problem of the image below (left lateral chest)
Tilt
Humeri not elevated.
CR angulation
Rotation
Humeri not elevated.
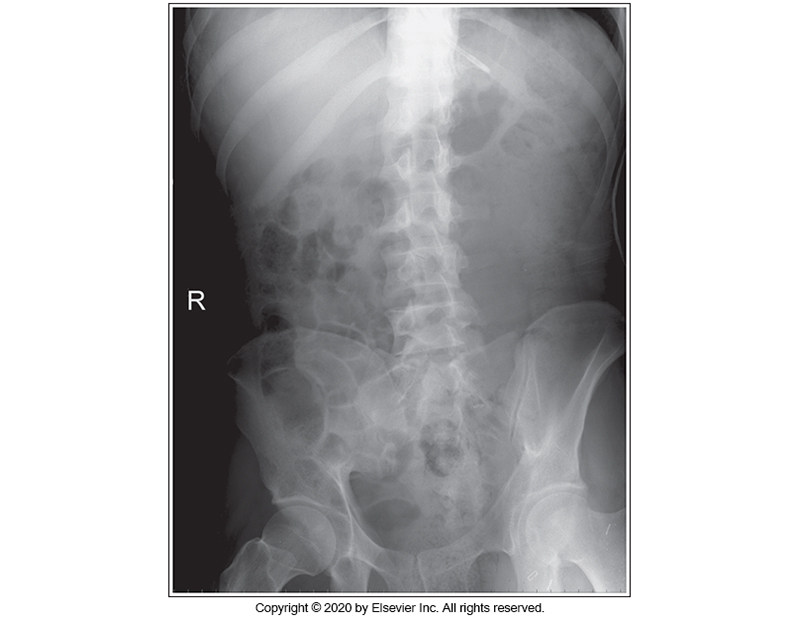
Identify the main problem of the image below (AP Supine abdomen)
The image is taken on full inspiration.
The MCP is tilted anteriorly.
Patient is in an LPO position.
Patient is in an RPO position.
Patient is in an RPO position.
A left lateral chest projection demonstrates the gastric bubble directly beneath the superior hemidiaphragm. Which lung is superior?
Right
Left
Left
For AP chest projection obtained with a mobile x-ray unit, which action is required?
1. The IR is positioned parallel with the midcoronal plane.
2. The image is obtained without the use of a grid.
3. The manubrium is superimposed over the fourth thoracic vertebrae.
4. 10 or 11 posterior ribs are demonstrated above the diaphragm.
1, 2, 3, and 4
1 and 2 only
1, 2, and 3 only
3 and 4 only
1, 2, and 3 only
A PA chest projection obtained in full lung expansion would have which result?
Demonstrates a broader and shorter heart shadow than if obtained in expiration
Demonstrates 10 posterior ribs above the diaphragm
Would have been obtained withe the patient in a seated position
Demonstrates the greatest expansion transversely
Demonstrates 10 posterior ribs above the diaphragm
A rotated left lateral chest projection demonstrates part of a lung field anterior to the sternum. Which is the anteriorly positioned lung?
Right
Left
Right