CompTIA A+ 220-1201 (2.6 - IPv4 and IPv6)
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
IP addressing
• IPv4 is the primary protocol for everything we do
- You probably won't configure anything else
• IPv6 is now part of all major operating systems
- And the backbone of our Internet infrastructure
IPv4 addresses
• Internet Protocol version 4
- OSI Layer 3 address
Public IPv4 addresses
• Each IPv4 address on the Internet is unique
- 1.1.1.1 can communicate to 2.2.2.2
• It is estimated that there are over 20 billion devices connected to the Internet (and growing)
- IPv4 supports around 4.29 billion addresses
- There's an obvious scalability issue
• We've found ways to manage the demand
- Network Address Translation (NAT)
IPv4 addresses format
8 bits = 1 byte = 1 octet
32 bits = 4 bytes
IPv6 addresses format
16 bits = 2 bytes = 2 octets
128 bits = 16 bytes
RFC 1918 private IP addresses
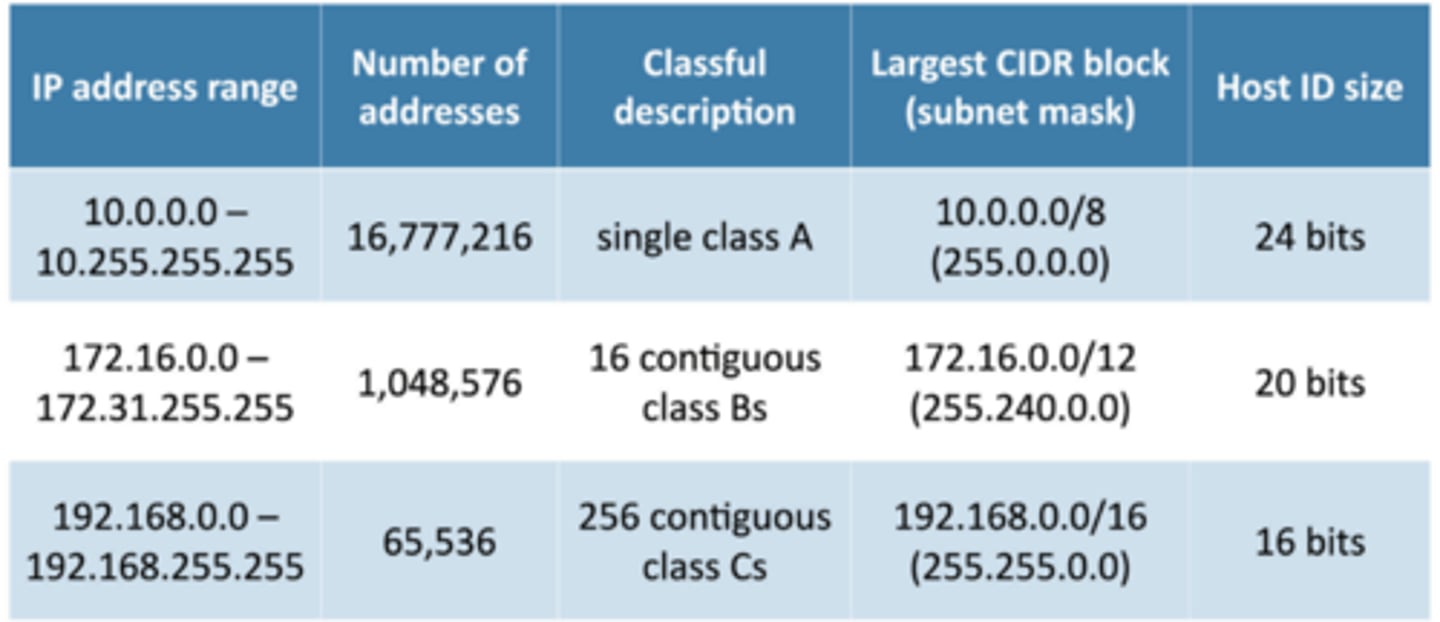
Private IP address ranges
• Large private IP address ranges
- Properly design and scale large networks
• Private IP addresses are not Internet-routable
- But can be routed internally
- Use NAT for everything else
• Defined in RFC 1918
- Request for Comment
IPv6 addresses
• Internet Protocol v6 - 128-bit address
- 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,
431,768,211,456 addresses (340 undecillion)
- 6.8 billion people could each have
5,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 addresses
• Your DNS is very important!
• First 64 bits is generally the network prefix (/64)
• Last 64 bits is then the host network address