BIOL 371 Topic 4 Animals (I made these)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable ______ environment
internal
homeostasis is regulated by ____ ____ loops
negative feedback
describe the flow of negative feedback loops
change in a physiological variable → receptor detects change → integrator processes information → effector produces response
t/f cell location changes how homeostasis occurs
true
t/f cells of exchange surfaces can be either dead or alive
false; must be alive to properly maintain homeostasis
regulation of solute content and volume in extracellular fluid is an example of ______ regulating internal environments
homeostasis
what is osmoregulation
regulation of internal osmotic environment (water/salt/waste)
what is ficks law
the rate in which particles diffuse across a concentration gradient proportional to surface area
what mechanism allows bulk flow to occur
hydrostatic pressure (mechanical)
what is established after letting diffusion occur in a closed space
equilibrium
t/f osmoles are the total number of dissolved particles of solvent per kg of solute
false; solute per kg of solvent
what is osmolality ad what is it measured in
osmotic concentration of a solution'; measured in osmoles
t/f hypoosmotic things have a higher osmolality than its reference solution
false; lower osmolality
what is the difference between isoosmotic and hyperosmotic
iso: same osmolality as solution
hyper: higher osmolality than solution
what is osmosis
tendancy of water to diffuse across a selectively permeable membrane from area with lower conc
t/f osmosis involves movement of solutes across membrane
false; movement of water
what substance has the highest osmotic potential and what is that potential
pure water; zero
t/f less solute = higher (more positive) osmotic potential
true; more solute = lower (more negative) potential
in osmosis water moves from ____ negative to _____ negative volumes
less; more
what happens when pressure potential is added to the side with a lower osmotic potential
flow across membrane decreased, reversed or stopped
water moves from areas of ____ water potential to ___ water potential
high; low
what is the difference in significance between animal and plant cells
animal: cell shrinks or swells
plants: swells based on turgor pressure
how are fluids transported in animals and what is that mechanism reliant on
bulk flow; hydrostatic pressure
t/f bulk flow affects water and solute exchange in open circulatory systems
false; closed systems
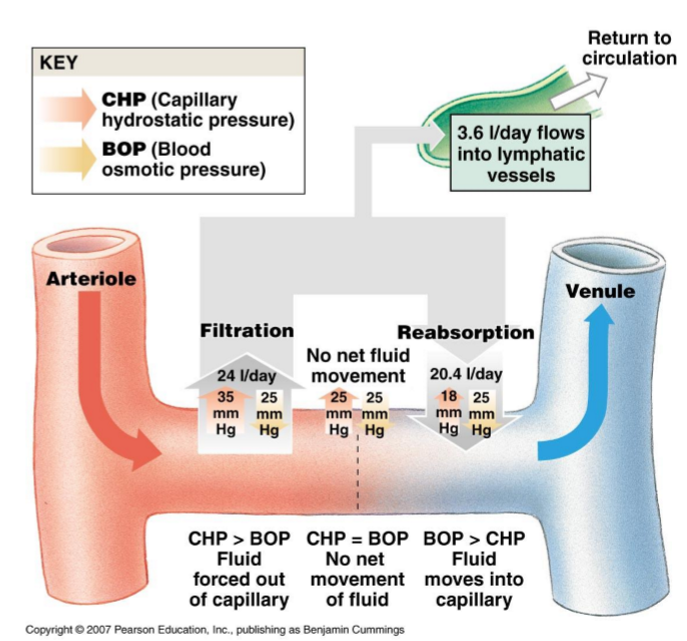
describe how pressure potential impacts water/solute movement in capillaries in relation to osmotic potential and hydrostatic pressure
upstream side of capillary: pressure potential on blood > osmotic potential → water/solutes leave capillary
downstream side of cap: osmotic potential > hydrostatic pressure of extracellular fluid → water/solutes enter capillary
t/f osmoconformers adjust only the extracellular fluid concentration to match with cell concentration
false; adjusts both EF and cell conc to match the environment conc
osmoregulators adjust conc of _____ _____ to match with ____ conc and has a ____ outer layer to protect against the environment conc
extracellular fluid; cell; thick
what is the difference between water loss/gain in fresh vs salt water animals
fresh: body is saltier than environment so water → body (water gain)
salt: environment saltier than body so water → environment (water loss)
marine bony fish are ______ so they are constantly ____ water to their surroundings
hypoosmotic; losing
how do marine bony fish counteract drying out
drink seawater in through gils → filter out sodium, chloride and potassium → produce small urine to get rid of extra solute
freshwater bony fish are ______ so they are constantly _____ water from environment
hyperosmotic; gaining
freshwater bony fish produce _____ amounts of _____ urine
large; dilute
t/f saltwater and freshwater bony fish drink
false; only saltwater
elasmobranches are _______ to seawater
isoosmotic
what makes up for the difference in concentration between elasmobranches and their environment
urea; elasmo less concentrated ions compared to surroundings
what is secreted from the rectal gland of elasmobranchs
very concentrated salt solution
t/f elasmobranchs still experience diffusion of ions through their gills
true
land animals experience constant water loss through ______
evaporation
where does evaporation in land dwellers occur
wet respiratory membrane & skin
why do land dwelling animals need a waterproof outer layer
minimize evaporation
t/f land animals should not limit salt intake
false; salt/electrolyte intake should be limited
excretion is the elimination of _____ from the body
waste
in the excretory tubule, what is the level of selectivity for these stages:
filtration
secretion
reabsorption
non selective filtration (molecules from blood goes into tubule) → selective reabsorption (nutrients/ions/conserved water goes back into blood) → selective secretion (excises ions/toxic products moved into tubule from blood)
what is the specialized layer of cells in excretory tubules that facilitates movement of substances
transport epithelium
the transport epithelium allows active transport of ions between ____ and _____
ECF; filtrate
different functions of the excretory tubule is localized along its ____
length