Alkanes Final
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Uses of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
refrigerators
Propellants for aerosols
CFC properties
Inert
Non-flammable
Non-toxic
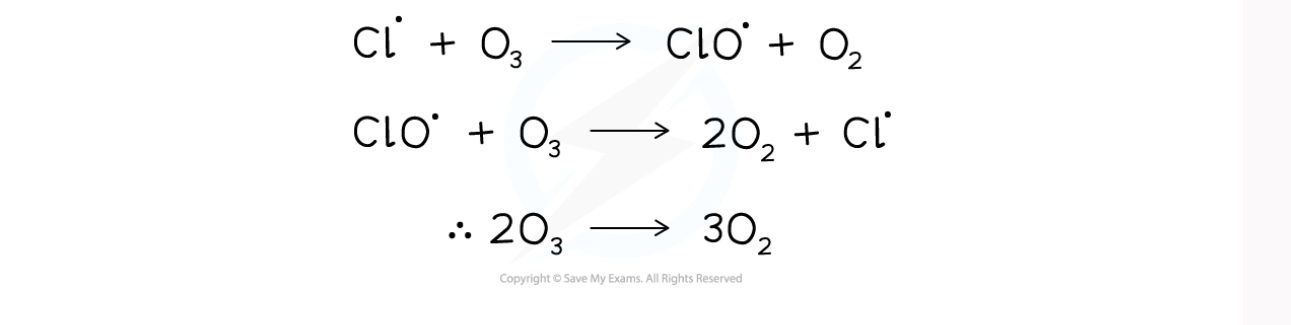
How does the chlorine radical as a catalyst in ozone depletion
the chlorine radical is reformed chemically unchanged from the first step
Benefits of the ozone layer
Absorbs uv light
Reduces rates of skin cancer
Formula for chlorine radicals catalysing the decomposition of ozone (part 1)

Formula for chlorine radicals catalysing the decomposition of ozone (part 2)
Why is the ozone layer important?
It absorbs harmful high energy uv light to prevent it reaching earth
What can uv light cause?
Skin cancer
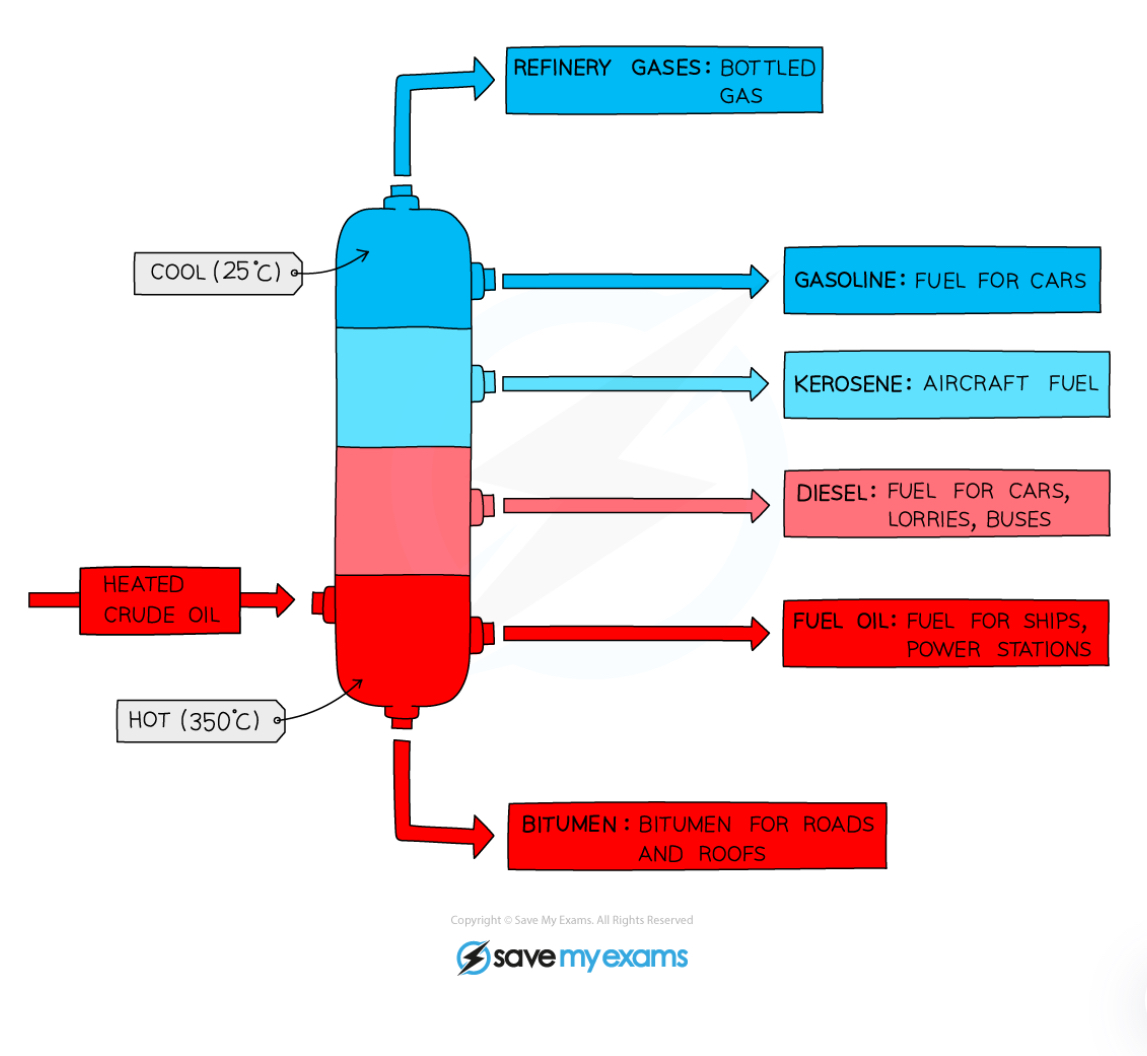
How is crude oil separated?
Fractional distillation
How is petroleum separated?
Fractional distillation
Process: Fractional distillation
crude oil heated to form a vapour
Gas passes into fractionating column with negative temperature gradient
Fractions condense at a height where the temperature is lower than their boiling point
Order of compounds in the fractionating column
Cracking
breaking c-c bonds in log chain hydrocarbons into short chain hydrocarbons
Economic reasons for cracking
most useful fractions contain shorter chain hydrocarbons
Most in demand “””””
Thermal Cracking Condition
Temperature: 700-1200K
Pressure: 7000kPa
Thermal cracking mostly produces
high percentage of alkanes
Catalytic Cracking Conditions
Temperature: 720K
Pressure: 5atm (mild)
Catalyst: Zeolite catalyst
Catalytic cracking mostly produces
Motor fuels
Aromatic hydrocarbons
Features of zeolites
honeycomb structure with large SA
Benefits of catalytic cracking
catalytic cracking is cheaper
Lower pressure used
Complete Combustion of alkanes
sufficient oxygen present
→ carbon dioxide + water
Incomplete Combustion
insufficient oxygen
→ carbon monoxide/carbon (soot(solid)) + water
Pollutants of internal engine combustion
carbon monoxide
Nitrogen oxides
Sulphur dioxide
Carbon Monoxide as a pollutant
a result of incomplete combustion of petrol vapour
Sulphur dioxide as a pollutant
sulphur converted to sulphur dioxide
(Unless removed from atmosphere) forms sulphuric (IV) acid
Forms acid rain
Flue gases
Mixture of waste gases
Removal of sulphur dioxide from flue gases
using calcium oxide/ calcium carbonate in acid-base reaction
Nitrogen Oxides as pollutants
nitrogen has a triple bond
requires a lot of energy to break
High temperatures of engine provide enough energy
Equation for nitrogen oxides
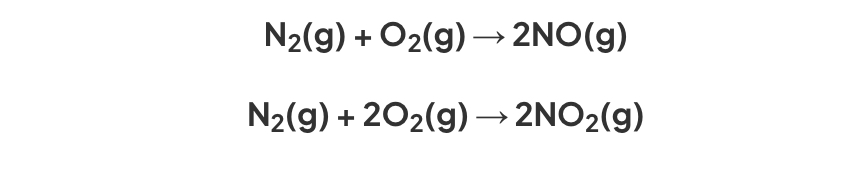
Nitric acid formation
nitrogen monoxide oxidised to nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide reacts with atmosphere to form nitric acid
4NO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + O2 → 4HNO3(aq)
Catalytic converter - how does it work?
Nitrogen oxides oxidise carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide and are themselves reduced

What is used on catalytic converters?
platinum catalyst is used in catalyst converters
What happens to unburnt hydrocarbons in the catalytic converter?
they are oxidised to carbon dioxide and water
Nitrogen monoxide removed from catalytic converters
when reacted with octane
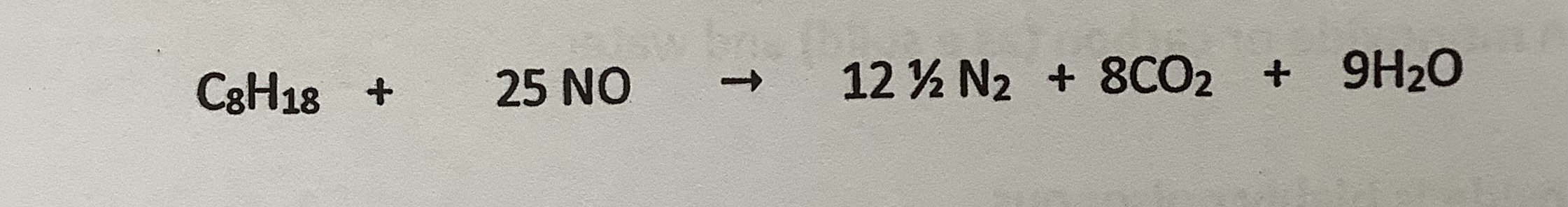
Chlorination of Alkanes Steps
FREE RADICAL SUBSTITUTION
Initiation
Propagation
Termination
Initiation
UV radiation provides energy to break chlorine molecule into 2 chlorine free radicals
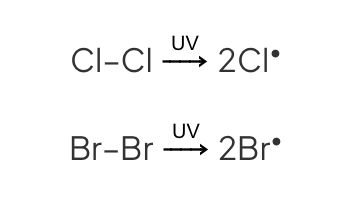
Why does initiation reaction takes place?
The halogen-halogen (name the halogen) bond is weaker than the C-H bond in alkane (name the alkane).
First propogation
chlorine radical reacts with alkane
Halogen halide + alkyl radical
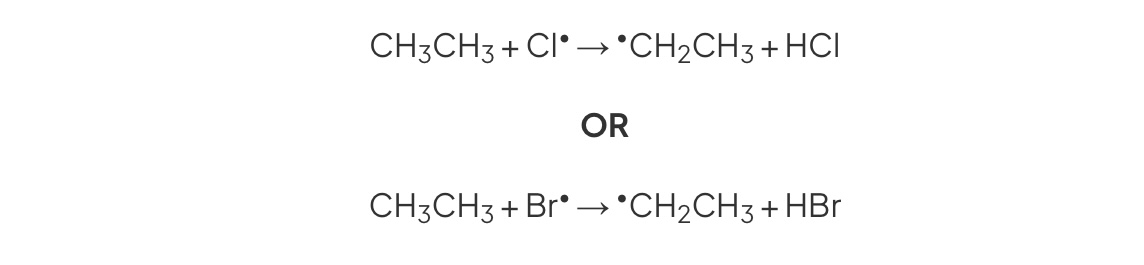
Second Propogation
Alkyl radical reacts with halogen molecule
→ Halogenoalkane + chlorine radical
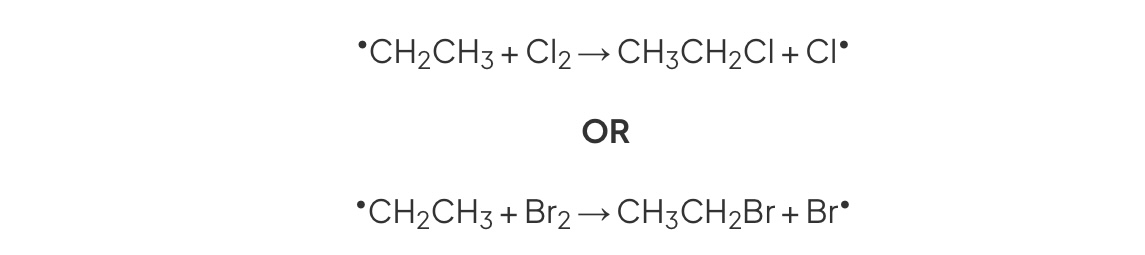
Termination
two radicals react together
How do you prevent further substitution in the chlorination of alkanes?
Excess methane
Requirements for free radicals substitution
UV Radiation
Why does radical substitution not give high yields?
It can lead to further substitution and substitution in different places on long carbon chains.
A combination of radicals can produce a longer carbon chain.
Why is the ozone important?
absorbs harmful high energy uv light and prevents it reaching earth.
uv light caused increased rates of skin cancer,
What bonds do chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) contain?
C-F and C-Cl
How does if radiation affect chlorofluorocarbons?
Uv radiation causes the C-Cl bonds in CFCs to break, releasing chlorine atoms int he form of free radicals.