
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
What pancreatic hormone is anabolic?
insulin
What pancreatic hormone is catabolic?
glucagon
In what step of insulin biosynthesis is insulin separated from C peptide?
conversion of pro-insulin to insulin
What is the significance of measuring C peptide?
can assess beta cell secretion
aka can tell whether or not you can secrete insulin from your b-cells of pancreas
In which form of DM is C peptide absent? Why?
DM1
why? bc in DM1 C-peptide and insulin come from the same AA strand and are co-secreted. So if no insulin like in DM1= no C peptide
What GLUT transporters are present in beta-cells?
GLUT2
What GLUT transporters are present in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue?
GLUT4
In the first step of insulin secretion glucose is turn into ________.
ATP
In the second step of insulin secretion high ATP inhibits what?
K+ channels
In the third step of insulin secretion decreased K+ causes the membrane to ______________.
a. depolarize
b. hyperpolarize
a
In the fourth step of insulin secretion depolarization causes what ion to influx through voltage gated channels? (ex ions: Na+, K+, Ca++, Cl-?)
Ca++
What are the properties of the insulin receptor?
Where is it located?
Does it bind to insulin w/ high specificity or affinity?
It is a dimer made up of what? What type of bond links the dimer?
located in membrane of most tissues
binds to insulin with high specificity AND affinity
It is a dimer made up of 2 COVALENTLY linked monomers
The insulin receptor is a dimer made up of 2 covalently linked monomers. What the the 2 monomers?
alpha subunit
beta subunit
How does signal transduction work in the insulin receptor?
insulin binds to alpha subunit and activates receptor
conformational change occurs and causes beta subunit to close together and phosphorylate
tyrosine kinase activity is directed towards other cytoplasmic proteins
effect occurs
What is the effect of insulin of GLUT4 transporters?
translocation of glucose transporter (moves GLUT4 from cytoplasm to cell membrane)
What is the effect of insulin on each of the following:
glycogenesis
TG synthesis
protein synthesis
glycogenolysis
gluconeogenesis
lipolysis
protein breakdown
glycogenesis- stimulates
TG synthesis- increases
protein synthesis- increases
glycogenolysis- inhibits
gluconeogenesis- inhibits
lipolysis- inhibits
protein breakdown- inhibits
What is the difference between the insulin and glucagon receptor?
insulin- tyrosine kinase
glucagon- GCPR
What is the difference in the effects of glucagon and insulin on gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis?
insulin- inhibits gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis
glucagon- promote gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis
What are incretin hormones? Where are they secreted from?
gastrointestinal hormones (GLP-1, GIP) and secreted from GI tract
What is the stimulus for incretin hormone secretion?
EATING
What are the functions of GLP-1 and GIP?
increase insulin secretion/suppress glucagon secretion
delay gastric emptying
suppress appetite
Answer the following about DM1:
Is it insulin dependent or independent?
What is the cause?
Is or can insulin be produced?
insulin DEPENDENT
cause: autoimmune destruction of beta-cells
NO insulin production
In DM1 is there antibodies to b-cell proteins detected?
yes
In DM1 what is the effect on the following:
glycogenolysis
gluconeogenesis
protein breakdown
fat breakdown
INCREASE ALL
In DM1 it increases the breakdown of adipose tissue (fat) that produce fatty acids and glycerol. Hepatic metabolism of fatty acids produces what? What is the result of excessive amount of this like in DM1?
produces KETONE BODIES
excessive ketone bodies = DKA (diabetic ketoacidosis)
Answer the following about DM2:
Is it non-insulin dependent or dependent?
90% of DM2 cases are due to what?
What happens to beta cells in DM2?
NON- INSULIN DEPENDENT
obesity
impaired beta cells
What are the effects of impaired beta cell function in DM2?
normal insulin levels are not good enough
can’t suppress gluconeogenesis
What cells increase lipolysis and release fatty acids that can cause insulin resistance?
adipocytes
Adipocytokines can cause ___________________________.
insulin resistance
How is HbA1c formed?
a COVALENT reaction of glucose and Hgb
What are the brand and generics of the sulfonyureas?
glyburide- do not need to know brand
glipizide- Glucotrol
glimepiride- Amaryl
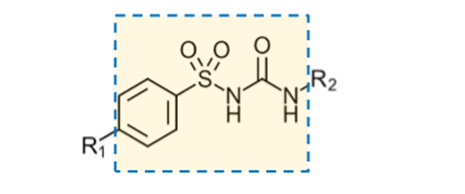
sulfonylurea
be able to recognize this structure within a drug and know it’s a sulfonylurea
What is the MOA of sulfonylureas?
increase insulin release from the pancreas
How? inhibit K+ channels in beta cells
What are 3 common ADRs of sulfonylureas?
hypoglycemia
weight gain
nausea
What is the MOA of repaglinide and nateglinide?
stimulate insulin release (like sulfonylureas)
How? binds to SUR1 (at a different spot then sulfonylureas)
Metformin is considered a _________________.
a. hypoglycemic
b. antihyperglycemic
b
What is the brand name of metformin?
glucophage
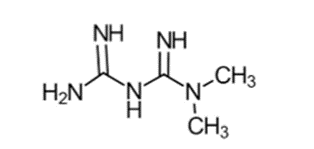
metformin
Is metformin a guanidine or biguanide?
biguanide
What is the MOA of metformin?
increase activity of AMPK (AMP-dependent protein kinase)
(increased AMPK stimulates glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation as well as reduces lipogenesis and gluconeogenesis)
What is the PREDOMINANT effect of metformin?
decrease hepatic glucose production
What is the boxed warning of Metformin? What is the cause?
boxed warning- lactic acidosis
cause- metformin impairs gluconeogenesis—> this impairs hepatic metabolism of lactic acid
What are the most common ADRs of metformin?
GI (anorexia, n/v, diarrhea, upset stomach)
What are the names of the 2 alpha-glucosidase inhibitors?
acarbose
miglitol
What is the MOA of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors? What is their effect?
MOA- inhibit intestinal brush border alpha-glucosidase (basically slows absorption of starch and sugars in the intestines)
Effect- After you eat a meal (post-prandial) there is a slow rise in plasma glucose
What is the most common ADR of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors? What is the cause of this ADR?
GI distress and this is because more carbs are available for fermentation in the gut for bacteria to produce gas