week 5
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
1
New cards
free radical
* uncharged atom or molecule
* that exists with a single, unpaired electron in its outermost shell
* combines with molecules to form toxins
* highly reactive and unstable
* that exists with a single, unpaired electron in its outermost shell
* combines with molecules to form toxins
* highly reactive and unstable
2
New cards
when are free radicals formed?
form when an x-ray photon ionizes with water
3
New cards
what is believed to be involved in degenerative diseases and cancers?
free radicals
4
New cards
What are the two theories of radiation injury?
* direct theory
* indirect theory
* indirect theory
5
New cards
direct theory
* this theory suggest that cell damage results when ionizing radiation directly hits critical areas, or targets, within the cell
* direct injuries from exposure to ionizing radiation occur infrequently
* direct injuries from exposure to ionizing radiation occur infrequently
6
New cards
indirect theory
* this theory suggests that x-ray photons are absorbed within the cell and cause the formation of toxins, which in turn damage the cell
* ex: when x-rays photons are absorbed by the water within a cell, free radicals are formed. the free radicals combine to form toxins
* indirect injuries from exposure to ionizing radiation occur frequently bc of the high water content of cells
* ex: when x-rays photons are absorbed by the water within a cell, free radicals are formed. the free radicals combine to form toxins
* indirect injuries from exposure to ionizing radiation occur frequently bc of the high water content of cells
7
New cards
dose- response curve
used to correlate the response or damage of tissues with the dose or amount of radiation received
8
New cards
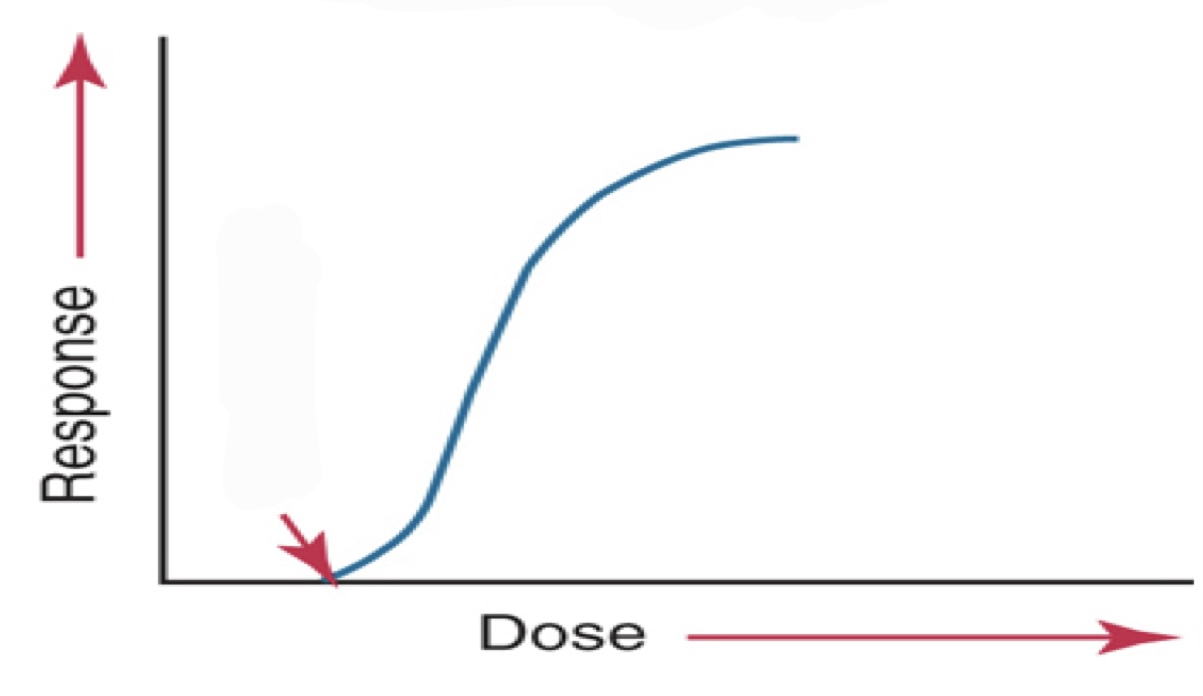
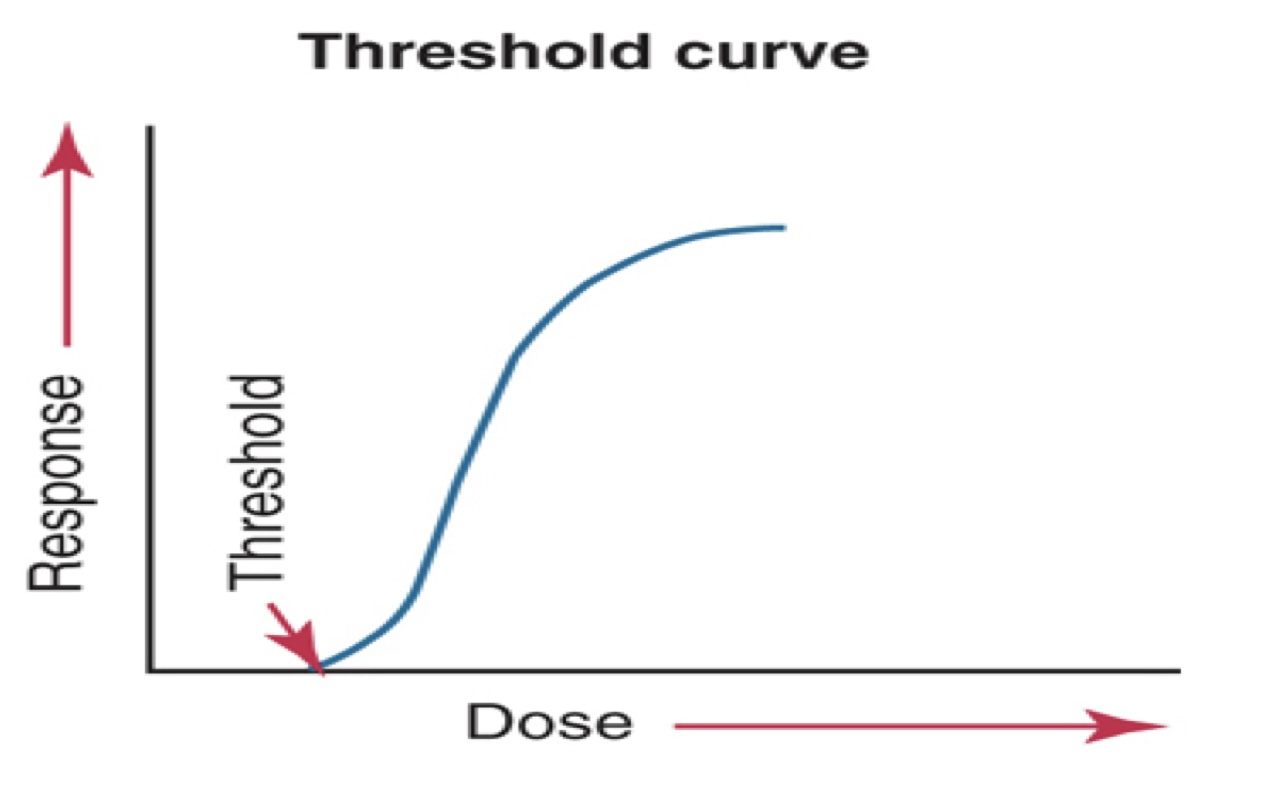
what kind of curve graph is this?
threshold curve
9
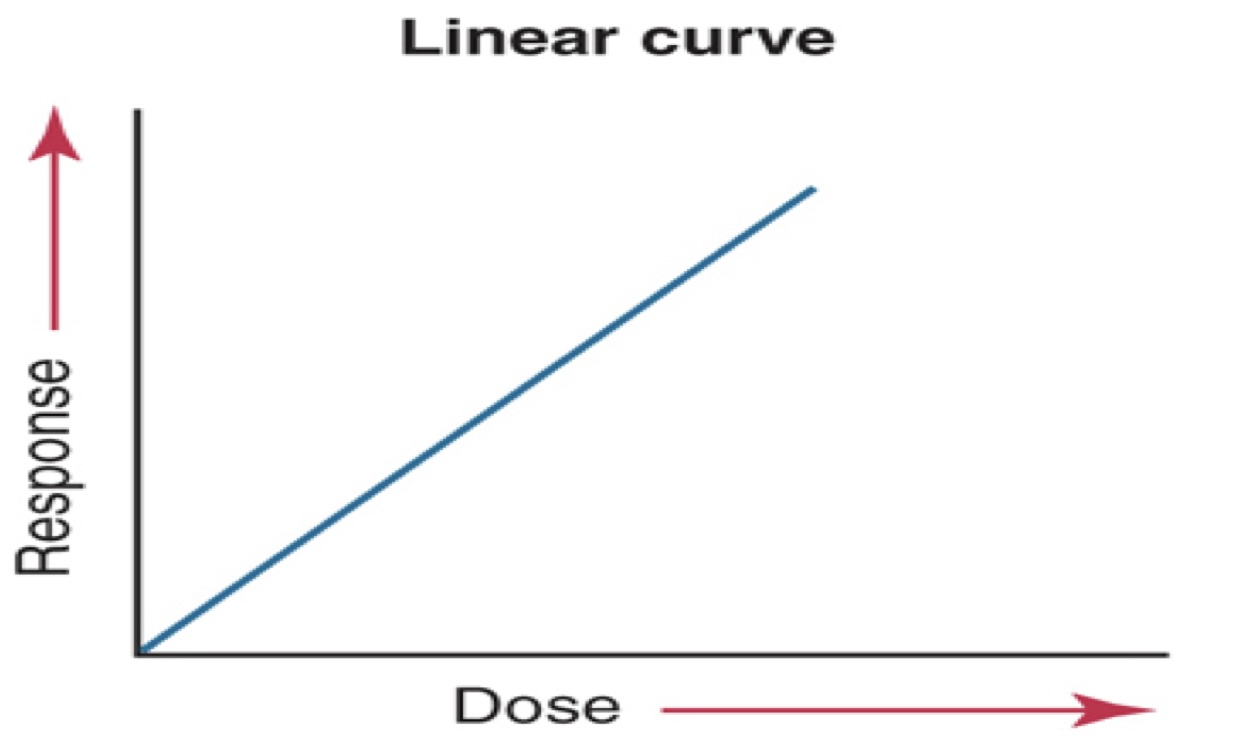
New cards
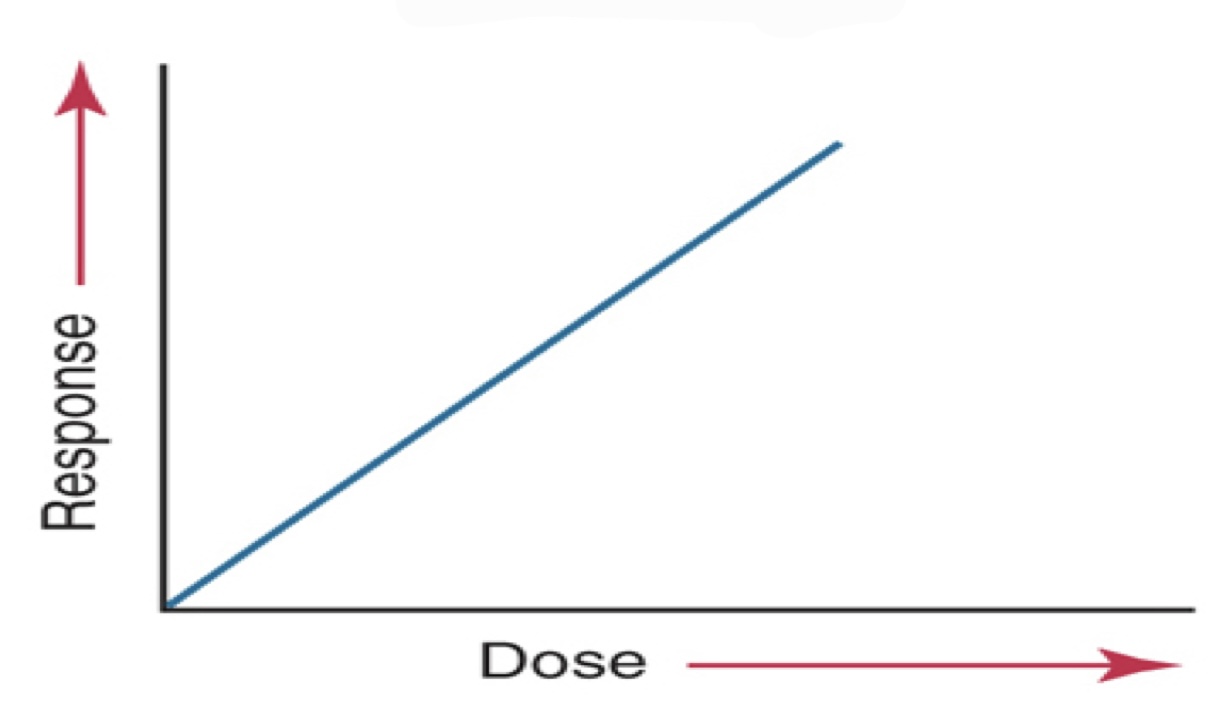
what kind of curve graph is this?
linear curve
* response of tissues is directly proportional to the dose
* response of tissues is directly proportional to the dose
10
New cards
non threshold dose response curve suggests
no matter how small the amount of radiation received, some biologic damage occurs
11
New cards
what are the two types of radiation effects?
* stochastic
* nonstochastic
* nonstochastic
12
New cards
stochastic effects (random)
occurs as a direct function of dose
* effects do not depend on the magnitude of the absorbed dose
* examples: cancer and genetic mutations
* effects do not depend on the magnitude of the absorbed dose
* examples: cancer and genetic mutations
13
New cards
nonstochastic (deterministic) effects
* somatic effects that have a threshold and increase in severity with increased absorbed dose
* effects occur only after a threshold of exposure has been exceeded
* examples: loss of hair, cataract formation, decreased fertilityk, radiation sickness, erythema
* effects occur only after a threshold of exposure has been exceeded
* examples: loss of hair, cataract formation, decreased fertilityk, radiation sickness, erythema
14
New cards
what is the sequence of radiation injury?
explain each.
explain each.
1. ==latent period:== time btw exposure to ionizing radiation an the appearance of observable clinical signs
2. ==period of injury:== cellular injuries may result, changes are observable
3. ==recovery period:== depending on factors, cells can repiar the damge caused by radiation
4. ==cumulative effects:== effects of radiation exposure are additive. unrepaird damage accumulates in tissues. Can lead to cancer, cataract formation, birth defects
15
New cards
what does the latent period depend on?
The latent period depends on the __total dose of radiation r__eceived an the __amount of time (rate)__ it took to receive the dose
16
New cards
the more radiation received and the faster the dose rate, the ______ the latent period
shorter
17
New cards
List the 5 determining factors for radiation injury
1. total dose: quantity of radiation received
2. dose rate: rate at which exposure to radiation occurs and absorption takes place
3. amount of tissue irradiated
4. cell sensitivity
5. age
18
New cards
who is more susceptible to radiation damage?
children and elderly
19
New cards
short term effects
\
* associated with __large doses__ of radiation/__short amount of time__
* can be seen within minutes, days, or weeks
* Acute radiation syndrome (ARS) includes nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, hair loss, hemorrhage
* associated with __large doses__ of radiation/__short amount of time__
* can be seen within minutes, days, or weeks
* Acute radiation syndrome (ARS) includes nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, hair loss, hemorrhage
20
New cards
long term effects
\
* __small doses__ absorbed repeatedly over a __long period__ of time
* effects can be seen after years, decades, or generations
* cancer, birth abnormalities, genetic defects
* __small doses__ absorbed repeatedly over a __long period__ of time
* effects can be seen after years, decades, or generations
* cancer, birth abnormalities, genetic defects
21
New cards
somatic cells
all cells except the reproductive cells
22
New cards
genetic cells
reproductive cells
23
New cards
somatic effects
* seen in the person irradiated
* not seen in future generations
* not seen in future generations
24
New cards
genetic effects
* not seen in the person irradiated
* passed on to future generation
* passed on to future generation
25
New cards
somatic or genetic effect?
\
produces poor health in the exposed animal
\
produces poor health in the exposed animal
somatic effect
26
New cards
somatic or genetic effect?
\
does not effect the exposed animal, but can affect future generations
\
does not effect the exposed animal, but can affect future generations
genetic effect
27
New cards
radiosensitive
a cell that is sensitive to radiation
28
New cards
radioresistant
a cell that is resistant to radiation effects
29
New cards
what is the response of a cell to radiation exposure determined by?
* mitotic activity: cells that divide frequently are more sensitive
* cell differentiation: cells that are immature or not highly specialized are more sensitive
* cell metabolism: higher metabolism are most sensitive
* cell differentiation: cells that are immature or not highly specialized are more sensitive
* cell metabolism: higher metabolism are most sensitive
30
New cards
radiosensitive **organs**
lymphoid tissue
bone marrow
reproductive cells
intestinal mucosa
bone marrow
reproductive cells
intestinal mucosa
31
New cards
What is the **cell** that is most sensitive to radition? It is most susceptible to ionizing radiation
small lymphocyte
32
New cards
radioresistant **tissues**
salivary glands
kidney
liver
kidney
liver
33
New cards
radioresistant **cells**
mature bone
muscle
nerve
muscle
nerve
34
New cards
radiosensitive **cells**
blood
immature reproductive cells
young bone cells
immature reproductive cells
young bone cells
35
New cards
radiosensitive organs are composed of radiosensitive cells and include the
lymphoid tissues
bone marrow
testes
intestines
bone marrow
testes
intestines
36
New cards
critical organ
an organ that if damaged diminishes the quality of a person’s life
37
New cards
what are critical organs that are exposed during dental radiographic procedures?
skin
thyroid
lens of the eye
bone marrow
thyroid
lens of the eye
bone marrow
38
New cards
What are the __traditional__ units of radiation measurements?
* Roentgen
* measures radiation exposure by determining the amount of ionization that occurs in air
* Radiation *absorbed* dose (rad)
* amount of energy(x-rays) *absorbed* by tissue
* ==Roentgen equivalent (in) man (rem)==
* used to compare biologic effects of different kinds of radiation
* measures radiation exposure by determining the amount of ionization that occurs in air
* Radiation *absorbed* dose (rad)
* amount of energy(x-rays) *absorbed* by tissue
* ==Roentgen equivalent (in) man (rem)==
* used to compare biologic effects of different kinds of radiation
39
New cards
Can roentgen measure the amount of radiation absorbed?
no, limited to measurements in air only
40
New cards
what measurement is only used for x-rays and gamma rays?
Roentgen
41
New cards
__SI (newer)__ units of radiation measurement
* coulombs/kilogram
* gray
* ==sievert==
* gray
* ==sievert==
42
New cards
what does Roentgen measure? Is there an SI equivalent?
* R measures radiation by determining the amount of ionization that occurs in air
* there is no SI equivalent
* there is no SI equivalent
43
New cards
RAD SI equivalent is _____
Gray
1 gray=100 rad
1 gray=100 rad
44
New cards
REM SI equivalent is ____
Sievert
1 sievert= 100 rem
1 sievert= 100 rem
45
New cards
natural background radiation
sources include:
* radon in air
* uranium, radium, thorium in the earth
* cosmic rays from outerspace and the sun
* radioactive potassium in food and water
* radioactive material found w/i human body
* radon in air
* uranium, radium, thorium in the earth
* cosmic rays from outerspace and the sun
* radioactive potassium in food and water
* radioactive material found w/i human body
46
New cards
what is the single greatest source of exposure to background radiation in the US?
radon gas arising from the soil
47
New cards
In the US, the average dose of background radiation received by an individual ranges from ______ mrad per year
150--300
48
New cards
What is the greatest contributor to human-made (artificial) radiation exposure?
medical radiation
* medical radiographic procedures
* dental radiography
* fluoroscopy
* nuclear medicine
* radiation therapy
* medical radiographic procedures
* dental radiography
* fluoroscopy
* nuclear medicine
* radiation therapy
49
New cards
ways to decrease pt exposure and dose
film speed
collimation
technique
exposure factors
collimation
technique
exposure factors
50
New cards
TRUE OR FALSE
\
anatomic order refers to how teeth are arranged within the dental arches
\
anatomic order refers to how teeth are arranged within the dental arches
True
51
New cards
Why is an opaque film mount preferred compared to a clear film mount?
it masks the light around each radiograph
52
New cards
who mounts films?
any trained dental professional with knowledge of the normal anatomic landmarks of the maxilla, the mandible, and related structures is qualified to mount dental radiographs
53
New cards
when should films be mounted?
immediately after processing in a area designated for film mounting
54
New cards
what are two types of film mounting methods?
labial and lingual mounting
55
New cards
Curve of Spee
* maxillary =
* mandibular=
* maxillary =
* mandibular=
maxillary= convex
mandibular= concave
mandibular= concave
56
New cards
True or False
\
Use a view box to examine radiographs, avoid holding mounted films ‘up to the room light’ to view
\
Use a view box to examine radiographs, avoid holding mounted films ‘up to the room light’ to view
true
57
New cards
radiographs are placed in the film mount with the _____ side of the identification dot facing the viewer
raised (convex-pimple)
\
pimple not a dimple
\
pimple not a dimple
58
New cards
whos responsibility is it to establish a final or definitive interpretation and diagnosis?
the dentist
59
New cards
two types of bones
cortical bone (compact bone)
cancellous bone (spongey bones)
cancellous bone (spongey bones)
60
New cards
How does **cortical** bones appear on a radiograph?
radiopaque
61
New cards
how does **cancellous** bone appear on a radiograph?
radiolucent
62
New cards
How do prominences of bone appear on a radiograph? What are examples of prominences?
* __process__
* marked prominence or projection
* __ridge__
* linear prominence or projection
* __spine__
* sharp, thorn-like projection
* __tubercle__
* small bump or nodule
* __tuberosity__
* rounded prominence
\
They appear radiopaque(absorb more of the x-rays)
* marked prominence or projection
* __ridge__
* linear prominence or projection
* __spine__
* sharp, thorn-like projection
* __tubercle__
* small bump or nodule
* __tuberosity__
* rounded prominence
\
They appear radiopaque(absorb more of the x-rays)
63
New cards
How do spaces and depressions in bone appear on a radiograph? What are some examples of them?
* __canal__
* tube-like passageway through bone that contains nerves and blood vessels
* __foramen__
* opening/hole that permits passageway of nerves/blood vessels
* __fossa__
* broad, shallow, scooped-out, or depressed area
* __sinus__
* hollow space, cavity, or recess
\
They appear radiolucent (they do not resist passage of x-rays)
* tube-like passageway through bone that contains nerves and blood vessels
* __foramen__
* opening/hole that permits passageway of nerves/blood vessels
* __fossa__
* broad, shallow, scooped-out, or depressed area
* __sinus__
* hollow space, cavity, or recess
\
They appear radiolucent (they do not resist passage of x-rays)
64
New cards
Septum
* a bony wall or partition that divides two spaces/cavities
* radiopaque
* radiopaque
65
New cards
suture
* an immovable joint
* thin radiolucent line
* thin radiolucent line
66
New cards
What does the maxilla form?
floor of the orbit of the eye
sides and floor of the nasal cavity
hard palate
sides and floor of the nasal cavity
hard palate
67
New cards
incisive foramen
* hole located at midline of hard palate
* radiolucent
* radiolucent
68
New cards
superior foramina of the incisive canal
* two tiny openings in bone on the floor of the nasal cavity
* radiolucent
\
* radiolucent
\
69
New cards
median palatal suture
* immovable joint between the two palatine processes of the maxilla
* radiolucent thin line
* radiolucent thin line
70
New cards
lateral fossa
* smooth depressed area of maxilla
* aka canine fossa
* radiolucent
* aka canine fossa
* radiolucent
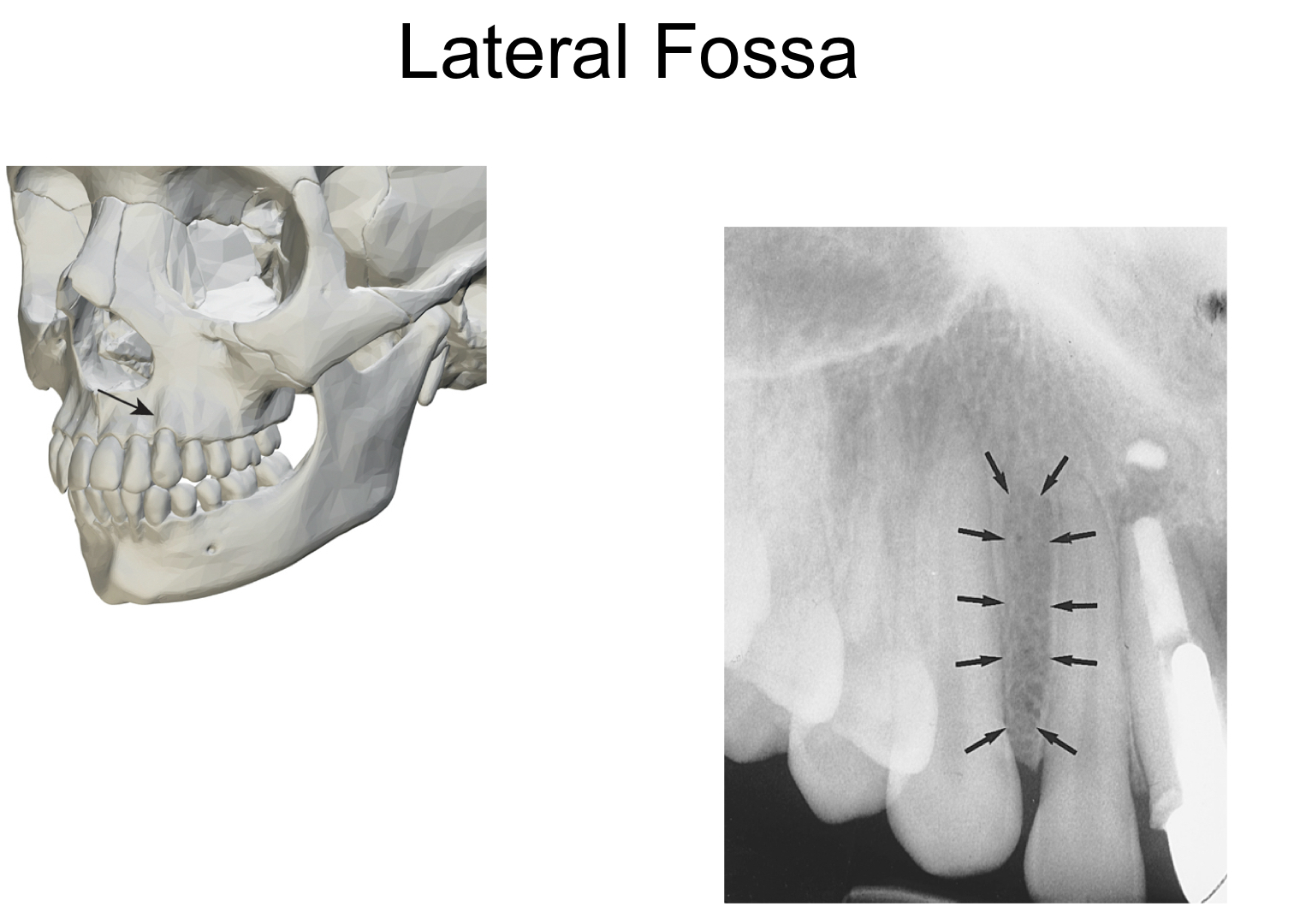
71
New cards
nasal cavity
* pear shaped compartment of bone located superior to maxilla
* radiolucent
* radiolucent
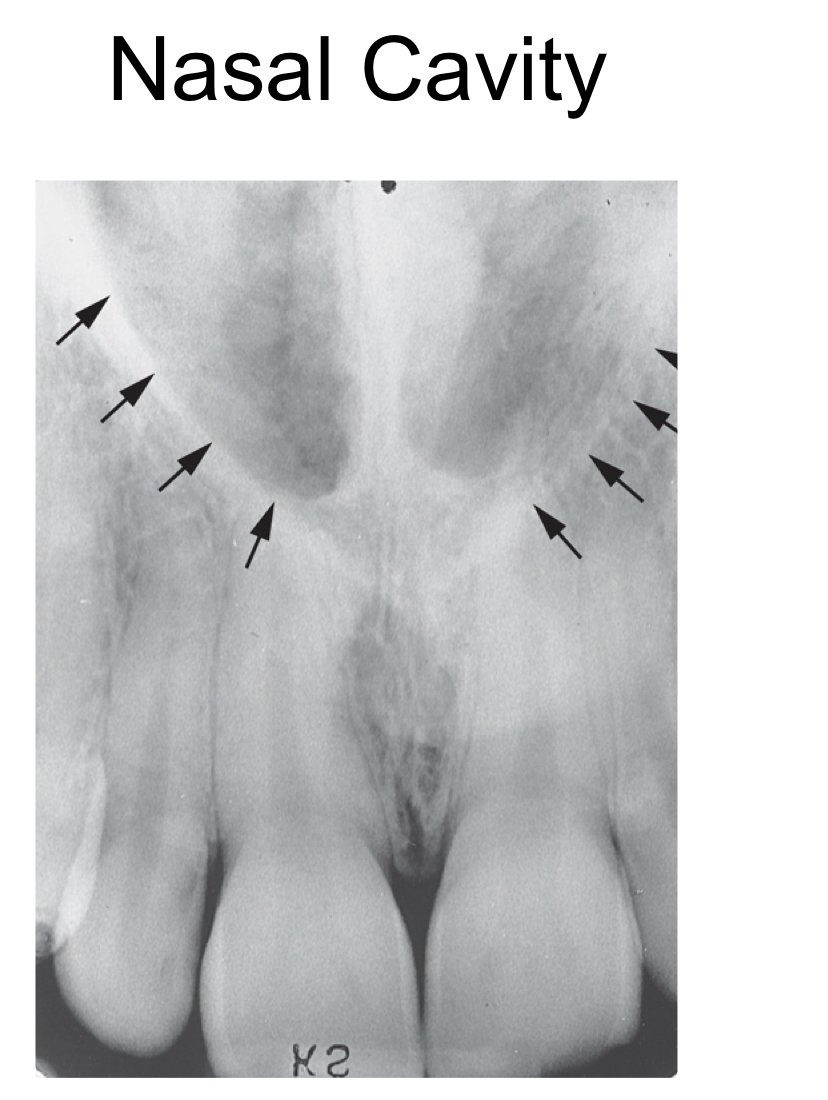
72
New cards
nasal septum
* vertical bony wall
* radiopaque
* radiopaque
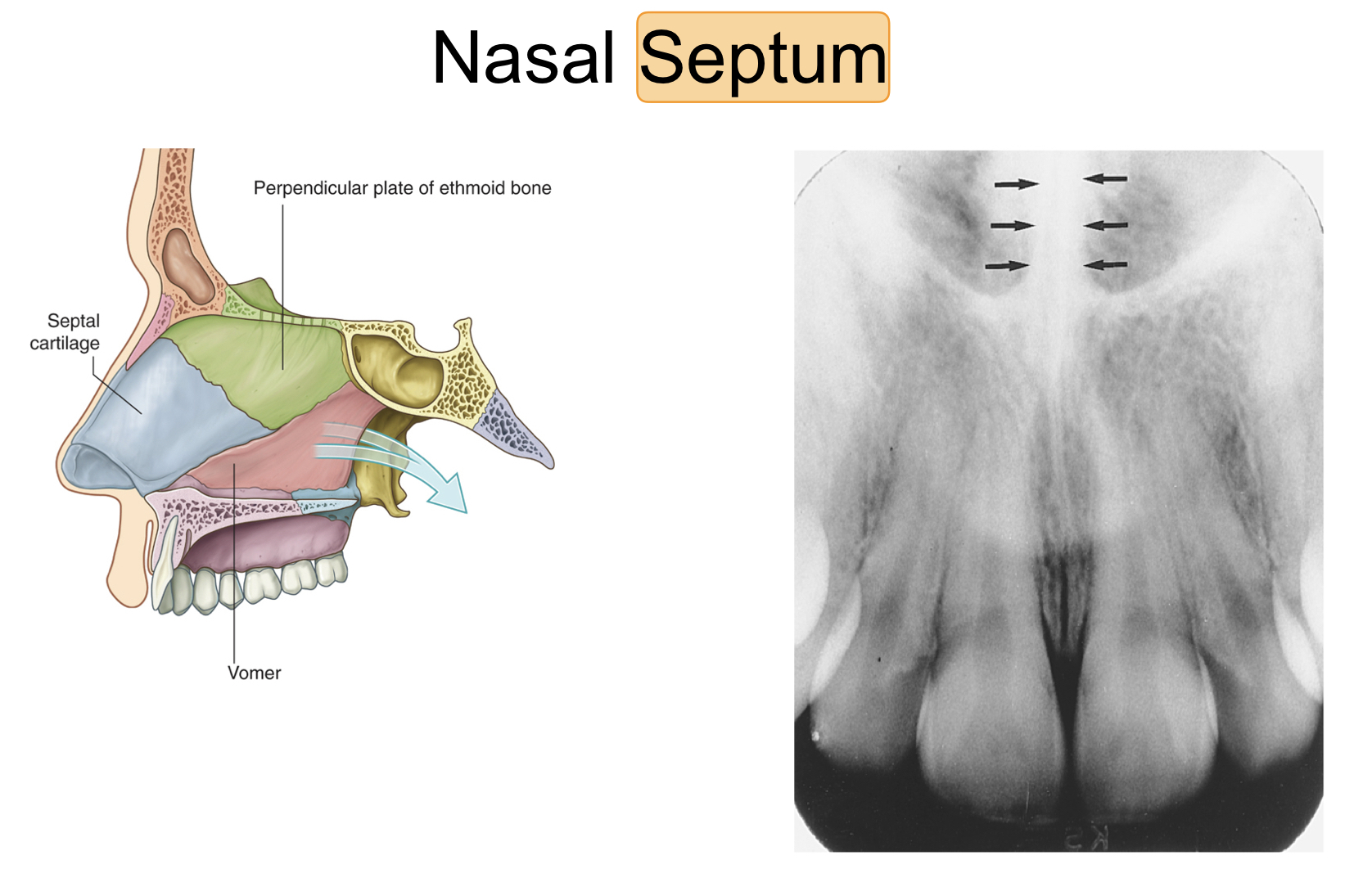
73
New cards
floor of nasal cavity
* bony wall formed by palatal processes
* radiopaque
* radiopaque
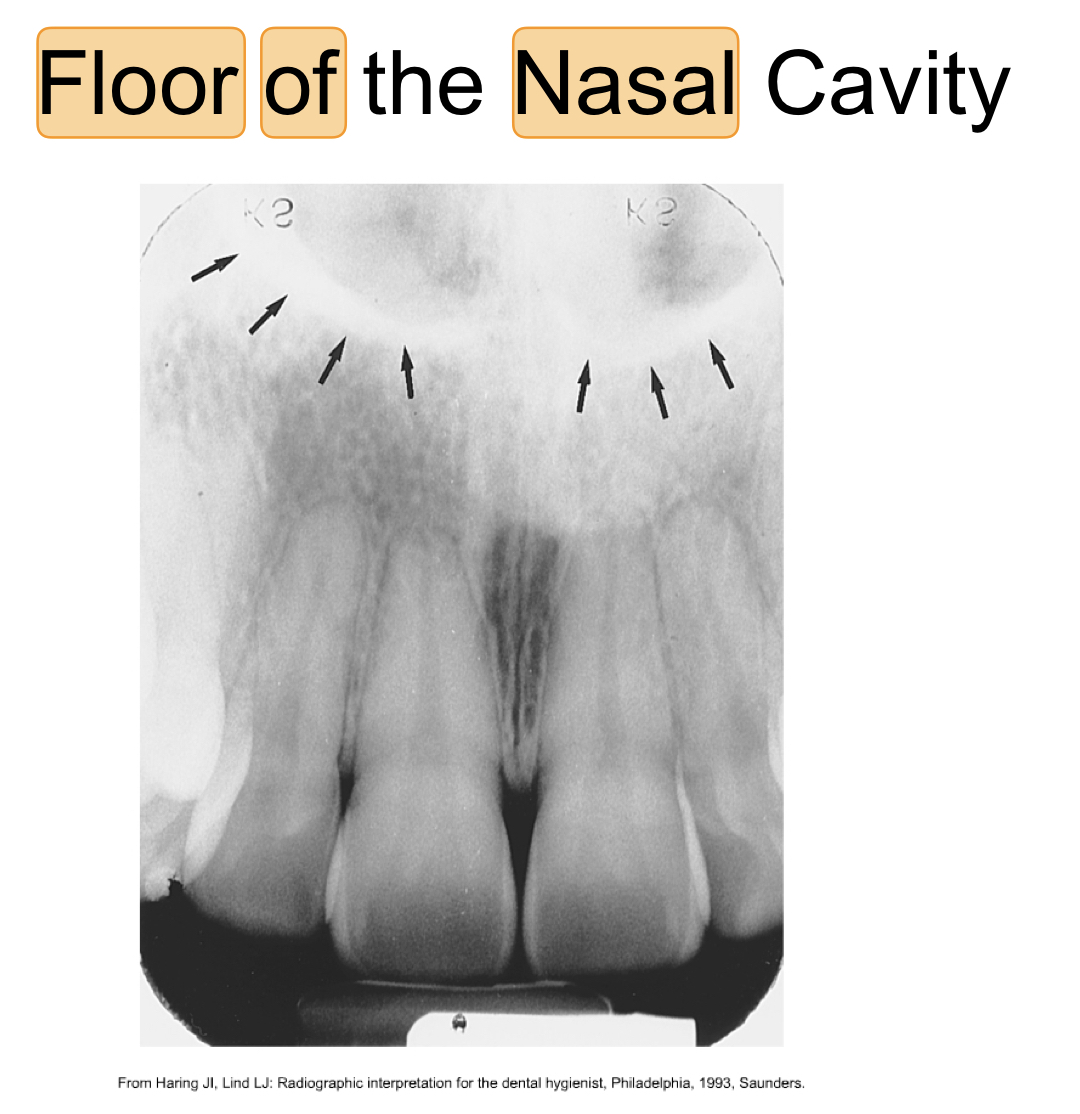
74
New cards
anterior nasal spine
* sharp projection of maxilla
* radiopaque
* radiopaque
75
New cards
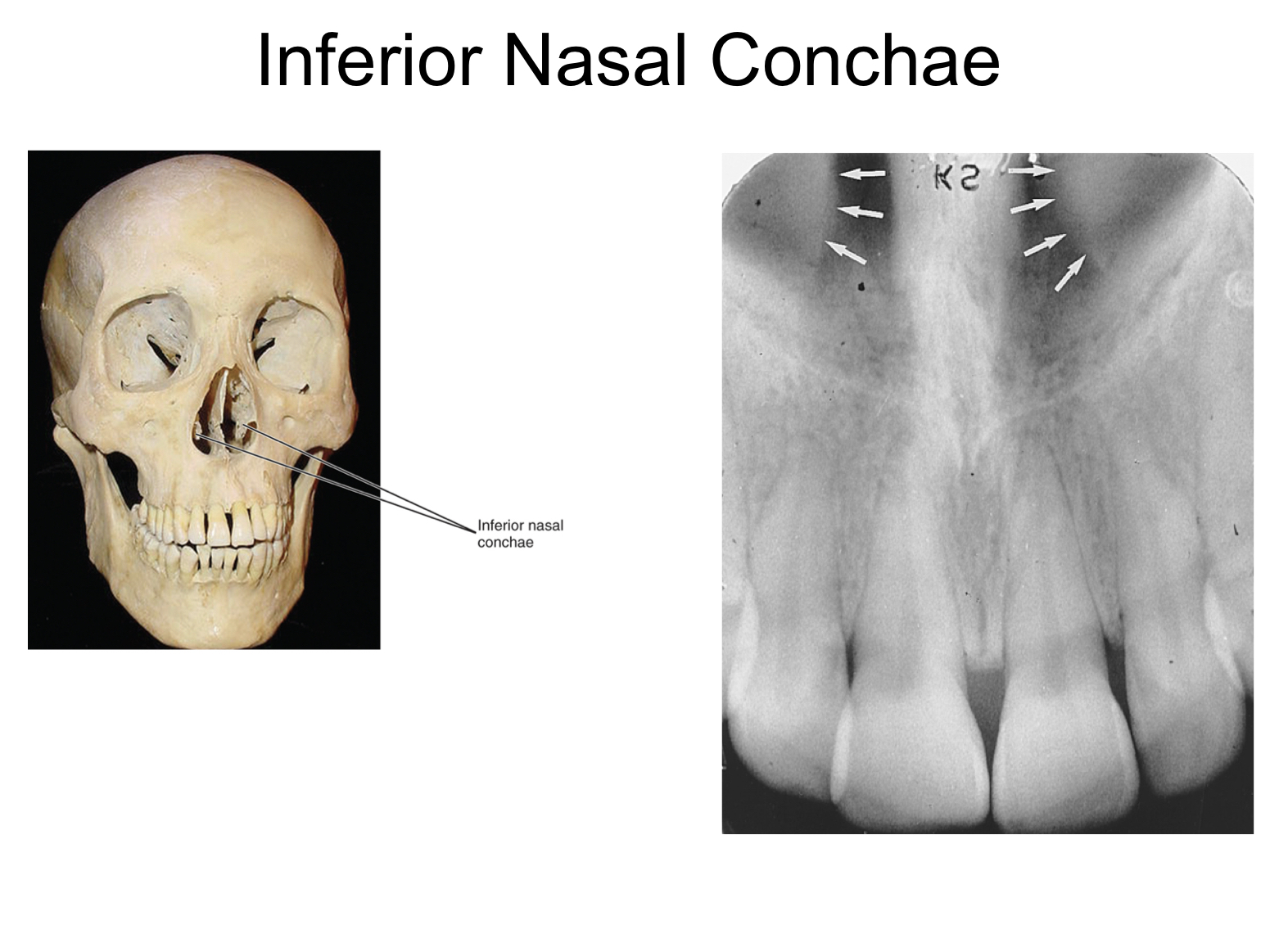
inferior nasal conchae
* wafer thin curved plates of bone extend from lateral walls of nasal cavity
* radiopaque
* radiopaque
76
New cards
maxillary sinus
* paired cavities of bone located within in maxilla
* radiolucent
* radiolucent
77
New cards
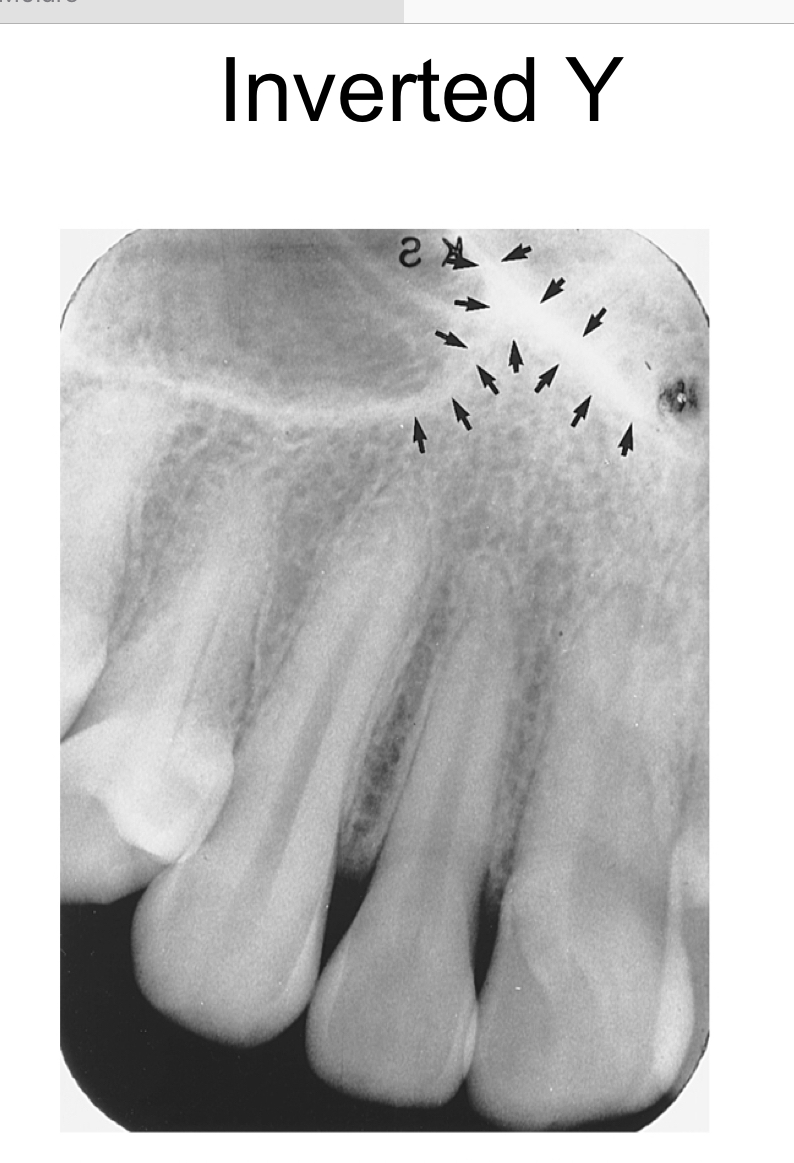
inverted y
the intersection of the maxillary sinus and the nasal cavity
radiopaque upside down Y
radiopaque upside down Y
78
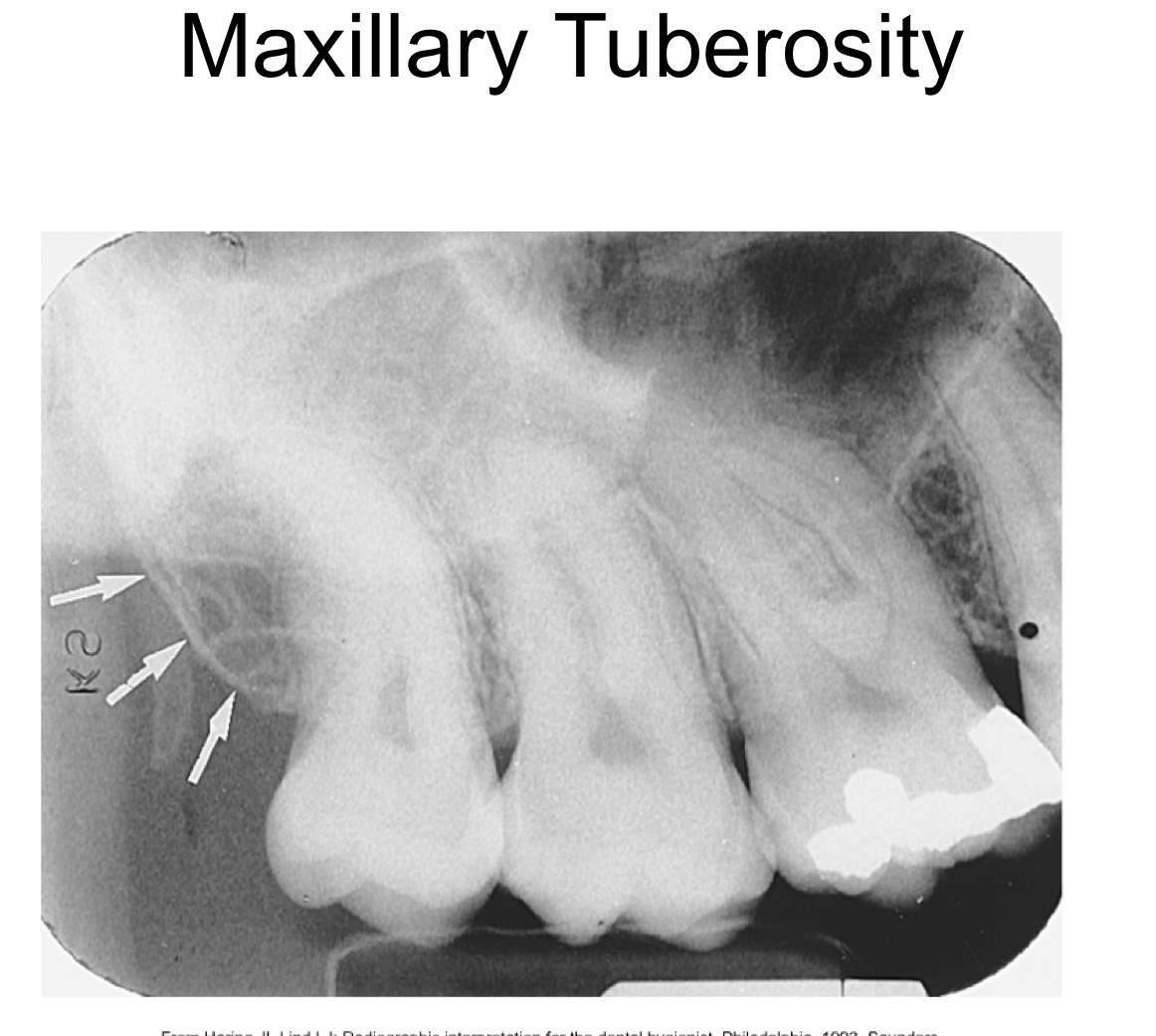
New cards
maxillary tuberosity
radiopaque bulge distal to the third molar region
79
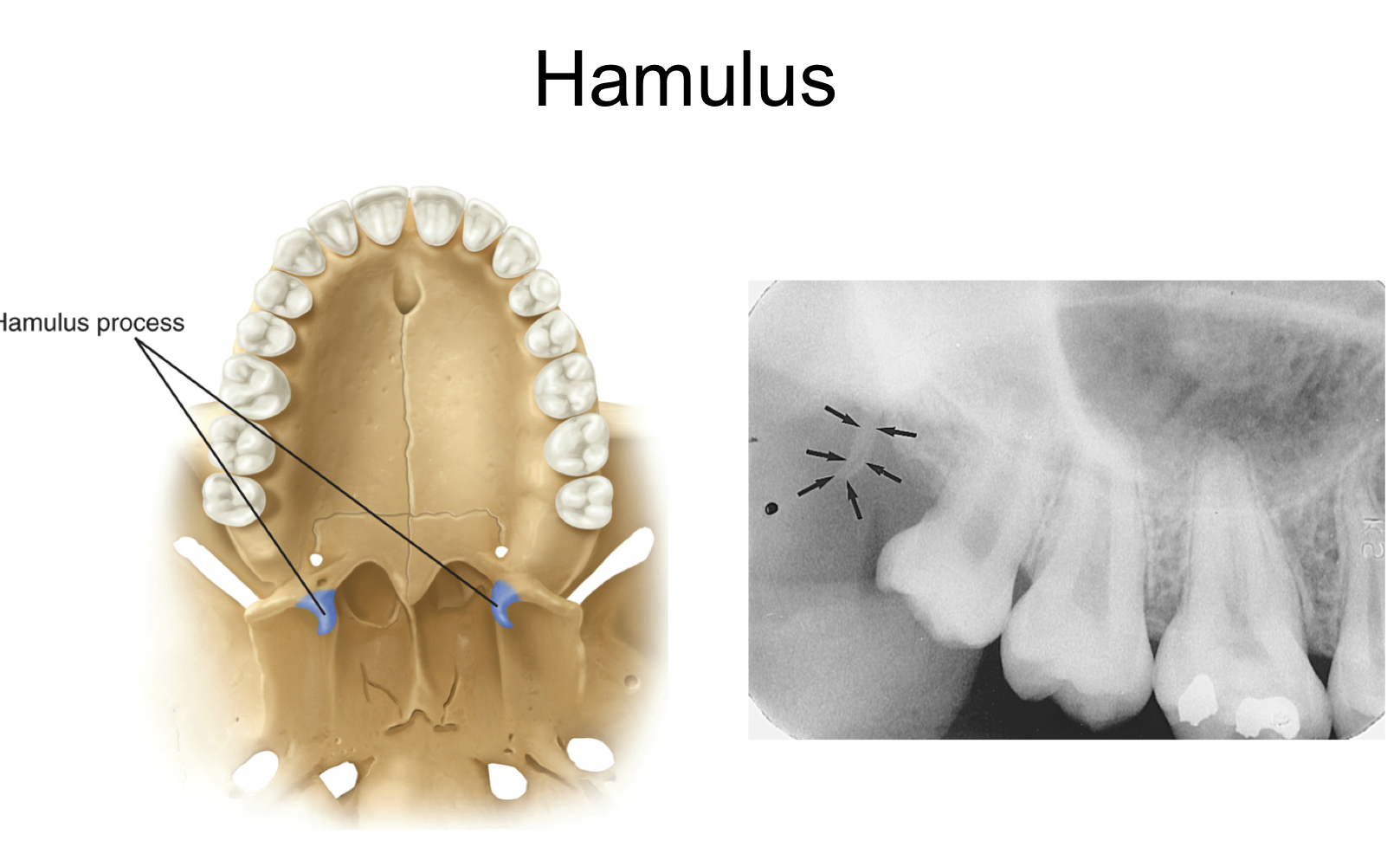
New cards
hamulus
* small hook like projection
* aka hamular process
* radiopaque hook like projection
* aka hamular process
* radiopaque hook like projection
80
New cards
the mandible
* the only moveable bone of the face
* divided into three parts
* ramus
* body
* alveolar process
* divided into three parts
* ramus
* body
* alveolar process
81
New cards
where is the coronoid process visualized?
in the maxillary molar PA
82
New cards
lamina dura
* made of **dense** **corticol** bone
* radiopaque
* radiopaque
83
New cards
alveolar crest
* radiopaque
* 1.5-2 mm below the CEJ
* 1.5-2 mm below the CEJ
84
New cards
Periodontal ligament space
radiolucent line around the root of a tooth
85
New cards
what does a normal alveolar crest appear? anterior and posterior regions
==__anterior: pointed and sharp__==
==__posterior: flat and smooth__==
==__posterior: flat and smooth__==
86
New cards
interpret
to offer an explanation
87
New cards
interpretation
an explanation
88
New cards
image interpretation
an explanation of what is viewed on a dental image, the ability to read what is revealed by a dental image
89
New cards
diagnosis
the identification of a disease by examination or analysis g
90
New cards
who interprets images?
any dental professional with training in interpretation can examine images
91
New cards
why should the dental radiographer must have an established sequence in interpretation?
to prevent erros
92
New cards
All interpretation must be be documented and must include:
* description of bone/ supporting structures
* description of artifacts
* indication of any areas that require additional images or evaluation
* description of artifacts
* indication of any areas that require additional images or evaluation
93
New cards
descriptive terminology allows the dental professional to describe what is seen on a dental image _____ implying a diagnosis.
With out
94
New cards
how to describe lesions
* appearance (most radiolucent lesions appear uni or multilocular)
* location
* size
* location
* size
95
New cards
unilocular lesion, corticated borders
well demarcated radiopaque rim of bone at the periphery
96
New cards
unilocular leson, noncorticated borders
does not exhibit a thin radiopaque rim of bone. instead, the periphery appears fuzzy or poorly defined
97
New cards
inter-radicular location
lesion located ==between the roots o==f adjacent teeth
98
New cards
periapical location
lesion located ==around the apex== of a tooth
99
New cards
pericoronal location
lesion located around the crown
100
New cards
alveolar bone loss
loss of bone in max or mand that surrounds and supports the teth