Sensory Systems (Chap 9)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Structures specialized to detect and respond to changes in the environment are known as…
Stimuli
The brain interprets the sensory input, creating a ____ or understanding of the info.
Perception
The response of a sensory receptor is an ______________ _______.
Electrochemical message (a change in the charge difference across the plasma)
Receptors include: and what their response le for
Mechanoreceptors - touch, pressure, hearing equallibrium
Thermoreceptors - changes in temperature
Photoreceptors- light intensity
_________ - Respond to chemicals (taste, smell, oxygen levels, etc)
Pain receptors
Chemoreceptors
Encapsulated nerve endings
A connective tissue capsule enclosed and protects the tips of the dendrites of sensory neurons
Meissner’s corpuscles
Encapsulated nerve endings that tell us where we have been touched (common in hairless sensitive skin areas - lips etc)
Pacinian corpuscles
Onionlike layers of tissue surrounding a nueve ending, respond when pressure is first applied and quickly adapt.
Muscle spindles
Special muscle fibers wrapped in sensory nerve endings - monitor the length of a skeletal muscle
Tendon organs
Branched nerve fibers located in tendons - measure the degree of muscle tension.
Referred pain
Pain origination in an internal organ but perceived/expressed in an uninjured organ
Sclera is the ______
White part of the eye (protects and shapes eye ball)
Cornea
Window through which enters the eye (bulges out a bit - front and center)
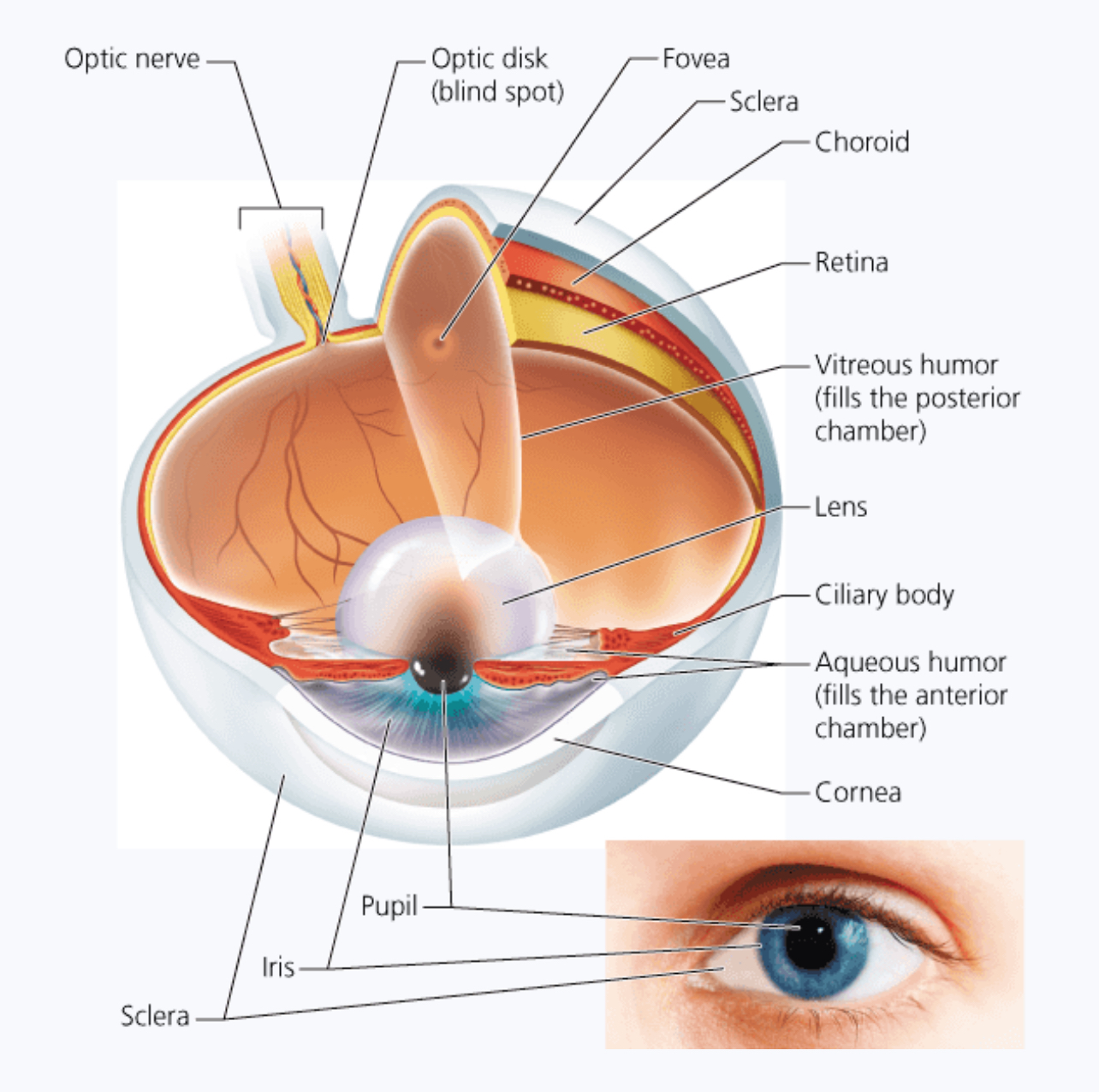
Choroid
Layer of the eye containing many blood vessels and supplies oxygen to the eye. - turns into the ciliary body (encircles the lens)
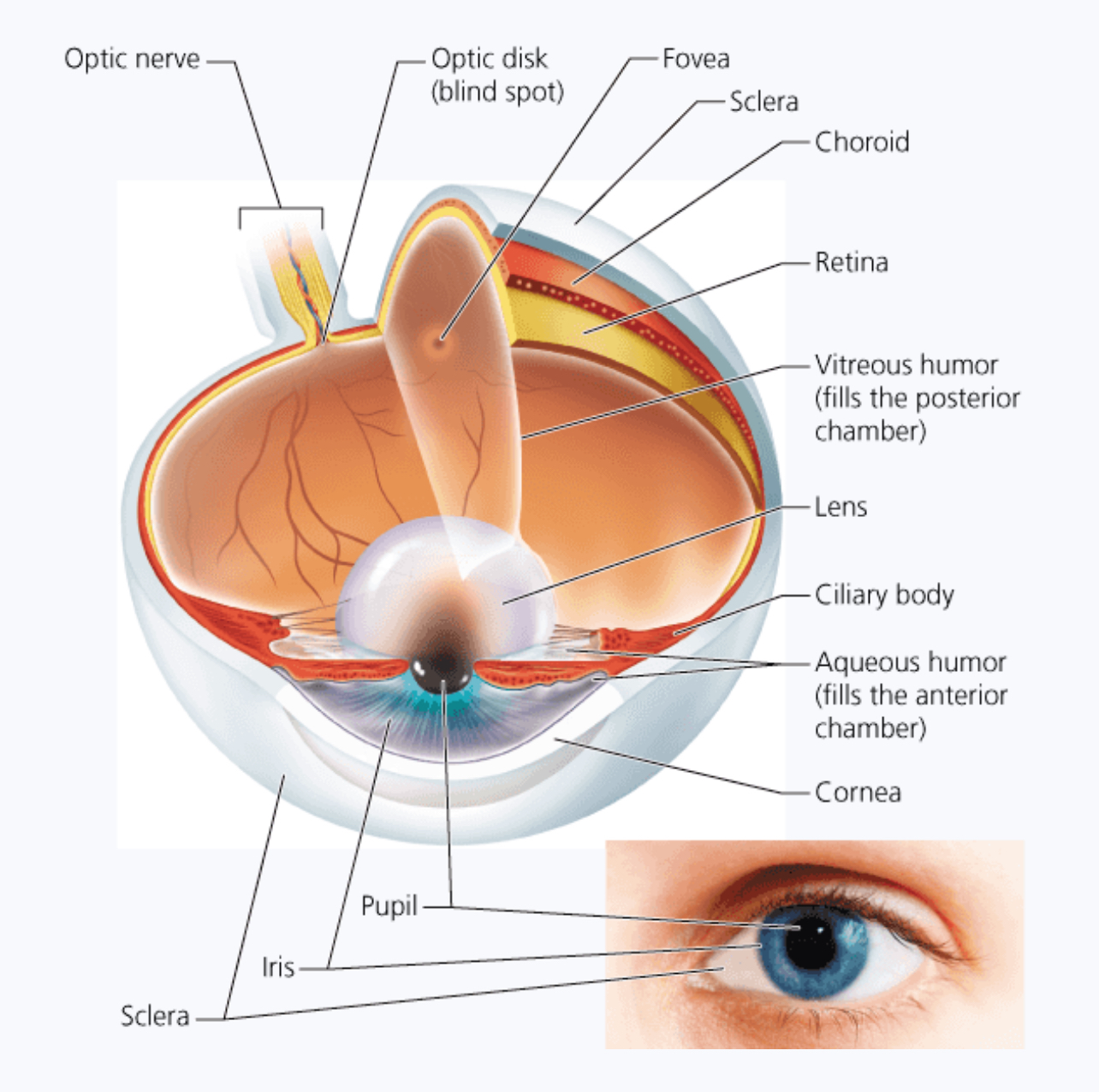
The iris is the..
Colored portion of the eye
The retina contains almost a quarter billion _________
Photoreceptors - rods and cones - most focused on the small center part of retina: the fovea
What does the optic nerve do?
Carries the message from the eye to the brain to be interpreted.
Vitreous humor
Jellylike fluid between the lens and the retina - keeps eye from collapsing
Aqueous humor
Fluid between the cornea and the lens - supplies nutrients and oxygen to these parts
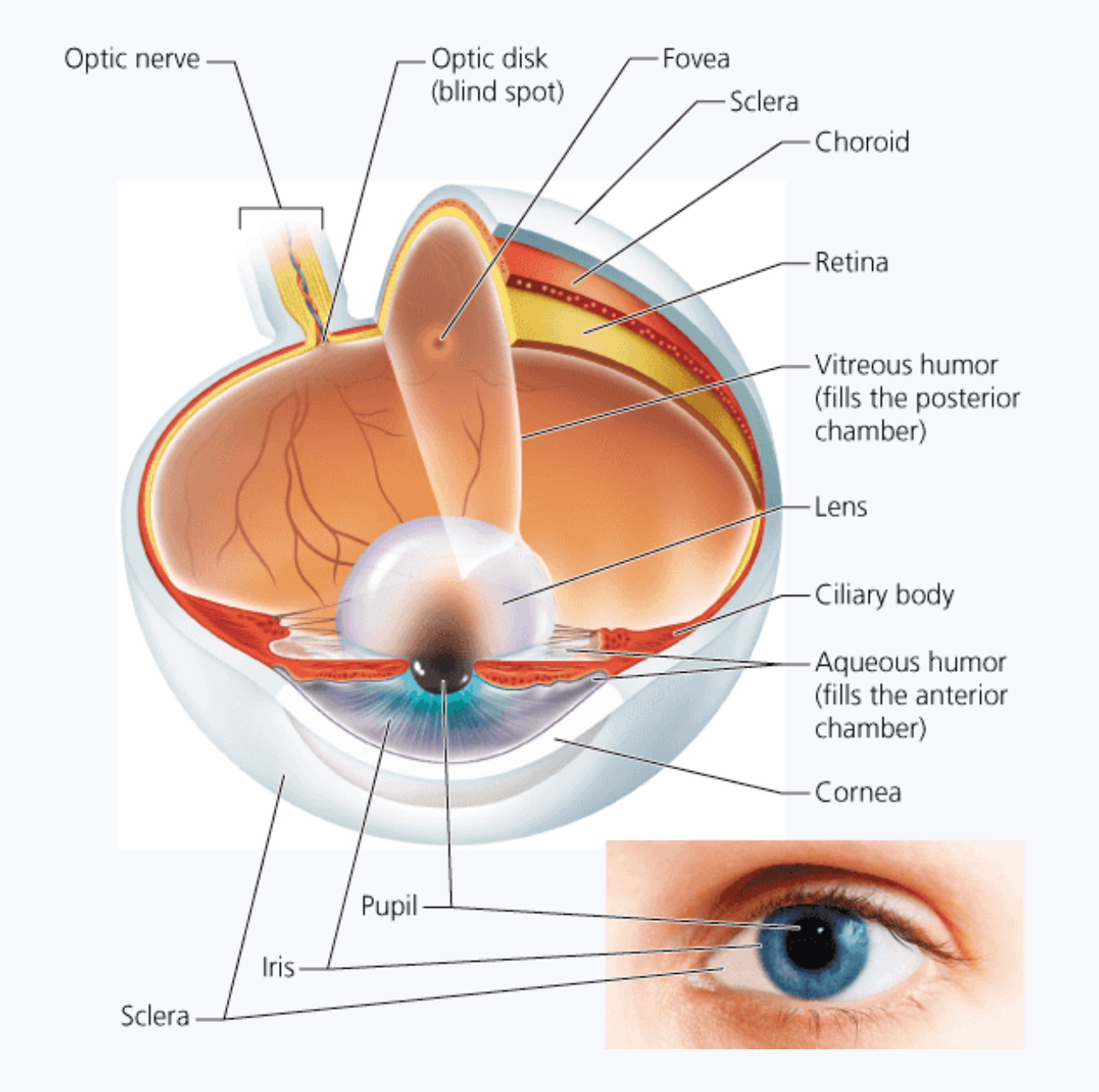
Aqueous humor is replaced bit by bit about every ______
90min
Focal point =
Point of focus
Changing the shape of the lens to alter the bending of light is called….
Accommodation
The lens gets round close objects and _____ with distant objects. - changes are controlled by the ciliary muscle
Flattens
A cloudiness in the lens, usually a result of aging. - leading cause of blindness.
Cataract
______ are the photoreceptors responsable for black-and-white vision. - allow us to see in dim rooms and pale moonlight.
Rods
Pigment in rods =
Rhodopsin - packaged in membrane-bound disks - stacked like coins.
The pinna is the….
gathers sound and funnels it into the external auditory.
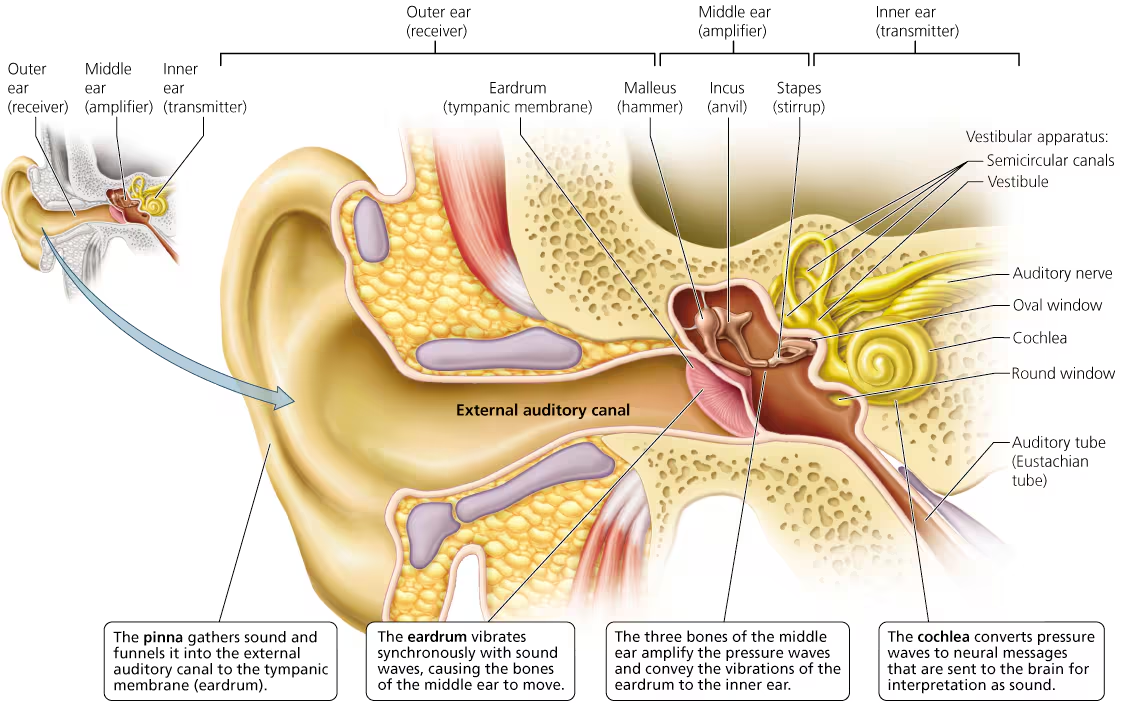
The eardrum is also known as the….
Tympanic Membrane
The smallest bones in the body can be found in the ear (middle part):
malleus (hammer)
_____(avil)
Staples (stirrup)
These stir up the sound to the Oval window (threshold of the inner ear)
incus
cochlea is located in the…
inner ear
conductive hearing loss results when…
obstruction anywhere along the rout prevents sounds from being conducted through the external auditory.
Sensorineural loss results from
damages hair cells or nerve cells.
fluid-filled maze of chambers and canals in the inner ear - monitor head position and movement.
Vestibular apparatus
semicircular canals
three canals in each ear that contain sensory receptors and help keep balance - located in the vestibule apparatus
vestibule
part of the Vestibule apparatus, it is important for static equilibrium (balence what moving)
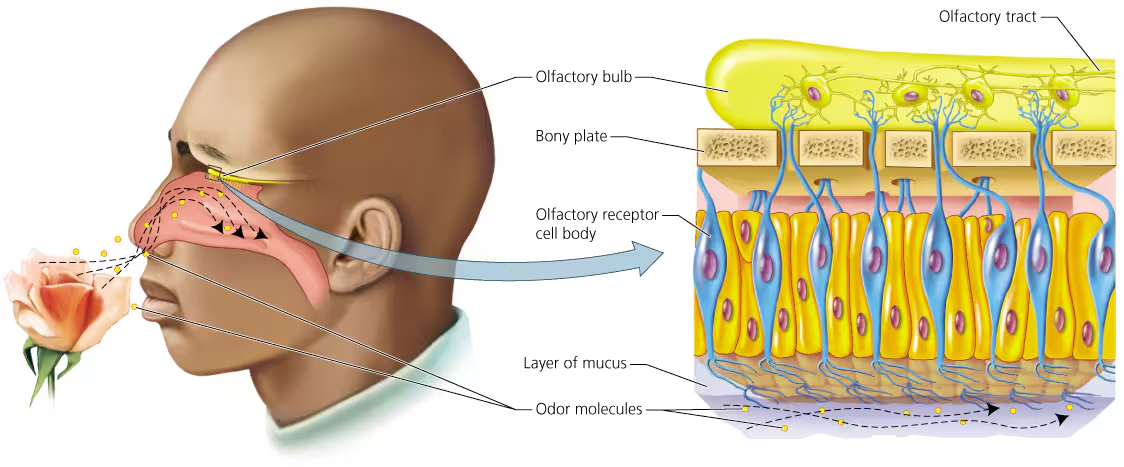
olfactory receptors are located in..
small patch of tissues in the roof of each nasal cavity.
Most taste buds are located in the ______ on the tongue.
papillae
Layer of the eye that holds the cornea.
The fibrous tunic
What treats nearsightedness?
Concave glasses