Physics - Circular motion unit test
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
YOU Got thIS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Why is an object in a circle accelerating?
Acceleration is the change in velocity, over time. Velocity has 2 components speed and direction. In a circle the speed of velocity is constant ( magnitude) but the direction is always changing, therefore the velocity is changing.
If the velocity is changing the object must be accelerating
define centripetal acceleration
the acceleration of an object moving in a circular path, directed towards the centre of the circle.
Centripetal force
The force that keeps an object moving in a circular path, provides the centripetal acceleration.
Newtons Law of Gravitation
every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses , and inversely proportional the square distance between their centres
F=Gm1m2/r²
every particle attracts every other particle;everything has a gravitational field
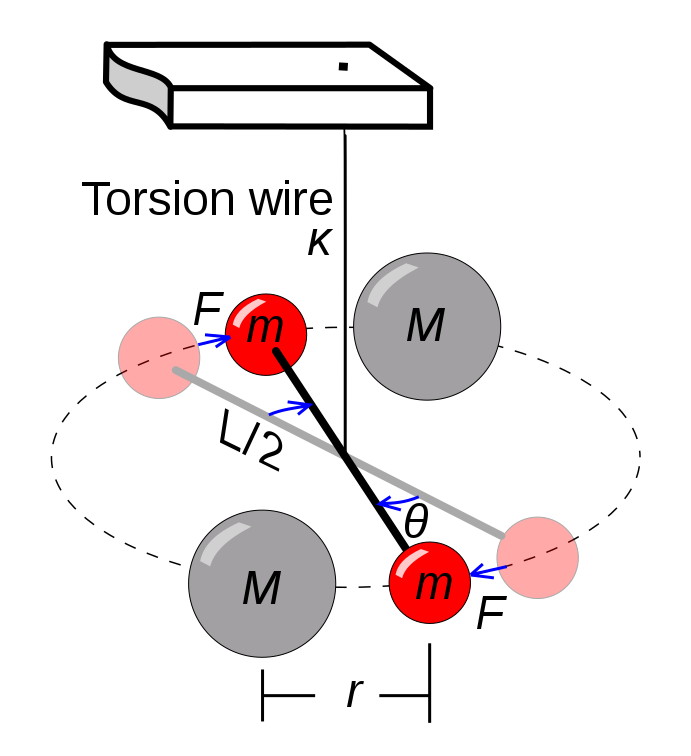
Cavendish experiment
Henry Cavendish
first experiment to measure force of gravity between masses
provided first accurate gravitational constant + mass of earth
He used a horizontal rod suspended by thin wire, with small spheres attached to each side of the rod
placed larger spheres near the smaller ones , saw that the gravitational attraction between masses caused rod to twist
he equated the angle of rotation to force, and measured that angle to determine force
where do units in gravitational constant come from
the equation fr²/m1m2 - which breaks down into Nm²/kg²
definition of gravitational fields
g = Fg/m , this measures the intensity of field at any point on the earth - weight to mass ratio of object ( this is not formula we use tho)
gravitational field eqs
for object producing force : g=Gm/r²
for object in field : g=fg/m
Why is gravitational potential energy negative
at infinity there is no pe, thats reference point. gravitational potential energy represents the energy needed to push the object from its current spot - infinitely far away ( outside of gravitational field).
As you get further away from the gravitational pull the work you have to do to fight said pull is less, so the number is less negative.
negative because the work is against the gravitational pull.
Orbiting Deets
An object in orbit is in continuous free fall
things in orbit are always falling towards the earth, but the earth curves away at the same rate
curvature is why things in orbit dont crash into the earth, the keep falling around it due to their forward motion and earths curved surface
Infinity as a concept
Infinity is a concept to indicate a large distance, rather than a literal place
think of it like a zone, that once entered the gravitational pull is zero, its a zone in the sense that it can still keep moving after it hits infinity
explaining energy lingo
parabolic has no final Ke
Hyperbolic has addiontla Ke

Calculator note
always be really careful with brackets, if diving two massive terms ( like multiplying lots on top, lots on bottom and then dividing) , make sure to always use brackets to seperate whole top and bottom term, or multiply them seperately the divide!!! VERY IMPORTANT
Whats always positive
centripetal force !
vertical circle
if you have a vertical circle, like a ferris wheel, be very careful about which direction fn @ top is going. Is the object going upside down at the top, or is it staying up right?
In a stable orbit
KE is half magnitude of PE
totale E is half PE
total orbit energy is opposite of KE ( total is negative, KE is positive)
centrifugal force
its an imaginary force - basically the force of when your body tries to stick to its initial inertia, when being turned
ex, turning in a car , your head jerks to teh right because it was initially going straight - centrifugal force acting ( not a real force, a side affect almost)
apparent weight - or how you feel
refers to Fn