Ointments/Creams/Gels
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Ointments, creams, gels and pastes are referred to as ____________________
semisolid
Ointments, creams, gels and pastes are referred to as semisolids meaning
less pourable than a liquid, and less rigid than a solid
semisolid dosage forms are applied to any ___________ body surface
external
physical properties of semisolids
1. smooth texture
2. elegant in appearance
3. non-dehydrating/gritty/greasy/staining
physiological properties of semisolids
1. non-irritating/interference
2. biocompatibility
application of semisolids
1. easy to apply (spreadability)
2. efficient drug release
semisolid preparations intended for external application to the skin or mucous membranes
ointments
A cream is a semisolid dosage form containing one or more drug substances dissolved or dispersed in a suitable base
creams
Ointments and creams may be differentiated by the ________ from which the semisolid is formed
base
Creams are traditionally made from ________-containing bases (more cosmetically acceptable)
water
Ointments are usually made using _________________ bases
oleaginous or anhydrous
categories of bases for ointments/creams
1. hydrocarbon bases
2. absorption bases
3. W/O emulsion bases
4. water removable bases
5. water soluble bases
hydrocarbon bases characteristics
1. water-insoluble/ not water washable
2. Oily/greasy, occlusive; Lack cosmetic appeal (WORST)
3. prevent water loss from skin
absorption bases characteristics
1. Water-insoluble, will absorb water to form W/O emulsion (BETTER absorption)
2. occlusive, lack cosmetic appeal, emollient (dry skin)
When an W/O emulsifier (emollient) is added to an oleaginous base, the mixture becomes ________________ that is capable of absorbing large amounts of water or hydro-alcoholic solutions
absorption (anhydrous) base
Remember the bases containing water are subject to microbial growth and the USP requires that these contain __________________
preservative
characteristics of W/O emulsion bases
1. Water-Insoluble, less occlusive (compared to oleaginous bases); contain water
2. More cosmetically acceptable; spread more easily on the skin; emollients
3. useful for hydrophilic drugs
characteristics of water removable bases (O/W emulsion)
1. Water-washable; can be diluted
2. Non-occlusive but cosmetically elegant; Easily removed from skin
3. ensure patient cooperation
Aqueous phase exceeds the oil phase in volume
O/W type emulsions
Usually incorporates three components of O/W type emulsions
1. oil phase
2. emulsifier (anionic, cationic, nonionic)
3. water
for water removable bases store in tight containers and add _______________ agents such as glycerin, propylene glycol to retard dehydration
auxiliary
characteristics of water-soluble bases
1. Water-soluble and washable
2. can absorb water, no oil phase
3. non-occlusive and non-greasy
additional characteristics of water soluble bases
1. preservative needed
2. no emollient properties
3. stability prone to oxidation
methods for preparing ointments
1. fusion
2. levigation
Components of the ointments are combined together and melted and cooled with constant stirring until congealed; mix ingredient in the melting state (Melting; Mixing, Cooling and Stirring)
fusion method
when preparing using the fusion method
1. add ingredients in order of decreasing mp
2. heat to fusion point
In the fusion method Ingredients with ____________ melting point are melted first. The heat is then reduced and the ingredient with the next highest melting point is added and melted. Continue the process.
highest
components of fusion
1. melting
2. mixing
3. cooling
4. stirring
when to use fusion method
Solids that can not be easily triturated
Mechanical incorporation
levigation
preparation of levigation
1. must reduce powder
2. use geometric dilution to add powder
when to use levigation
When all ingredients can be triturated
Note that a levigating agent should be physically and chemically _________________ with the phase into which the drug is dispersed
compatible
other additives to ointments
1. perfumes
2. chelating agents
3. antioxidants
4. preservatives
Most Ointments are non-sterile except ___________ ointments
Ophthalmic
Ointments must meet minimum standards for __________ contents
microbial
Ointments containing __________ are good source for microbial contamination.
water
o USP suggests tests for Staphalococcus aureus and pseudomonas aeuroginosa, because both these microbes can cause _________ infection
skin
Examples of preservatives for topical formulations
parabens
Semisolids consisting of suspensions made up of either small inorganic particles or large organic molecules interpenetrated by a liquid
gels (jellies)
classification of gels
1. single phase
2. two phase
- uniform dispersions of particles in a liquid with no apparent boundaries between dispersed particles and the medium
single phase
when the network of small discrete particles are noticeable.• Consists of small dispersed particles
two phase
homogeneous physically distinct portion of a system that is separated from other portions of the system by bounding surfaces
phases
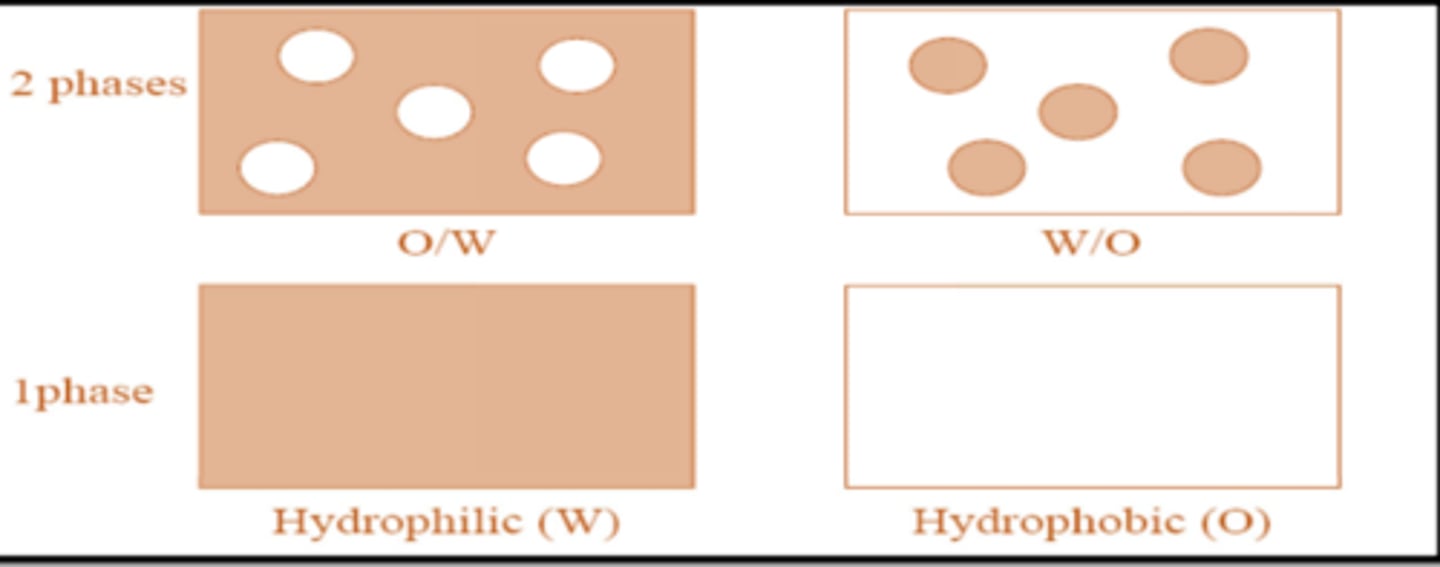
characteristics of gel single phase
1. clear water appearance
2. translucent of polymer is not fully dissolved
characteristics of gels-two phase
1. typically inorganic
2. opaque
3. thixotropic
semisolid dosage forms that contain one or more drug substances intended for topical application.
pastes