final exam apk2100c ahlgren UF PART 2
1/226
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
227 Terms
muscles and glands
effectors of nervous system
sensory and motor
PNS breaks down into
somatic and autonomic
motor (efferent) division breaks down into
sympathetic and parasympathetic
autonomic divison breaks down into what
afferent (sensory) neurons
conducting TOWARDS the CNS
efferent (motor) neurons
conducting AWAY from CNS
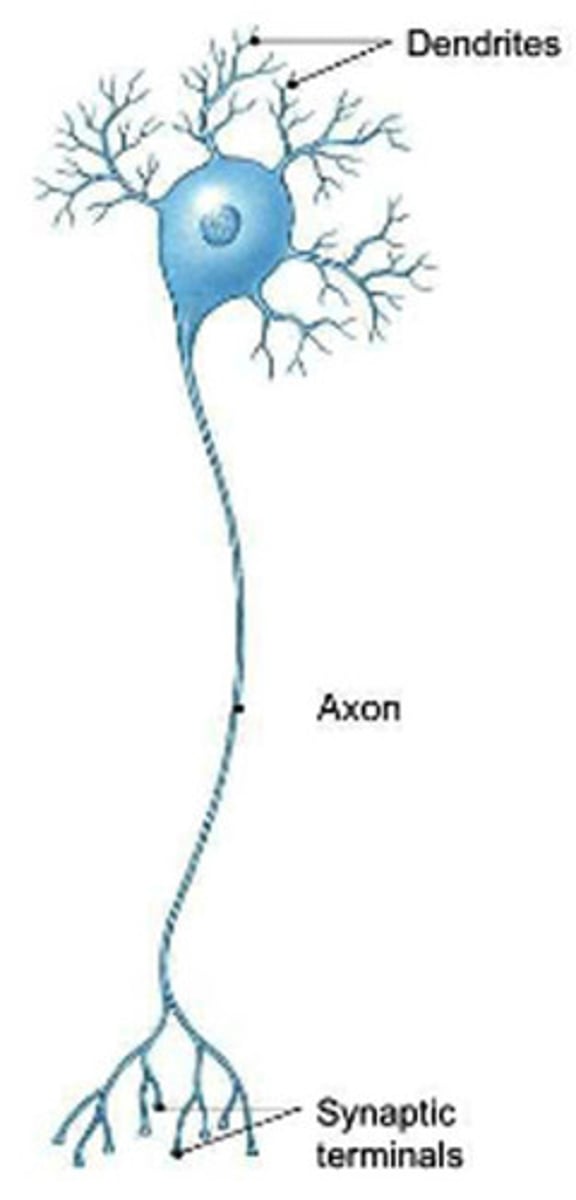
multipolar neuron
most common type of neuron in CNS
Dendrites
receive sensory info from neighboring neurons
Axons
fibers that extend from the cell body and subdivide into branchlike endings called terminal boutons
----receives info form cell body and transmits it to other cells thru the axon terminals
axon hillock
part of soma, not an axon
-area where membrane potentials are summated before they are transmitted to the axon
initial segment of the axon - trigger zone
very first place of the axon that receives an action potential from axon hillock
-not covered in myelin sheath
synaptic cleft
that actual space where that communication occurs -- its the part that separates the two neurons communicating from one another
myelin sheath
wraps around the length of axon with occasional gaps called nodes of ranvier
-impulses jump BW the nodes
synaptic gap/synapse
space bw neurons/neurons communicate with one another across the synapse thru neurotransmitters
Terminal boutons (axon terminals)
end of the axon where it enlarges and secretes neurotransmitter from the cells
glial cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
multipolar neuron
A neuron with a single axon and multiple dendrites; the most common type of neuron in the nervous system.
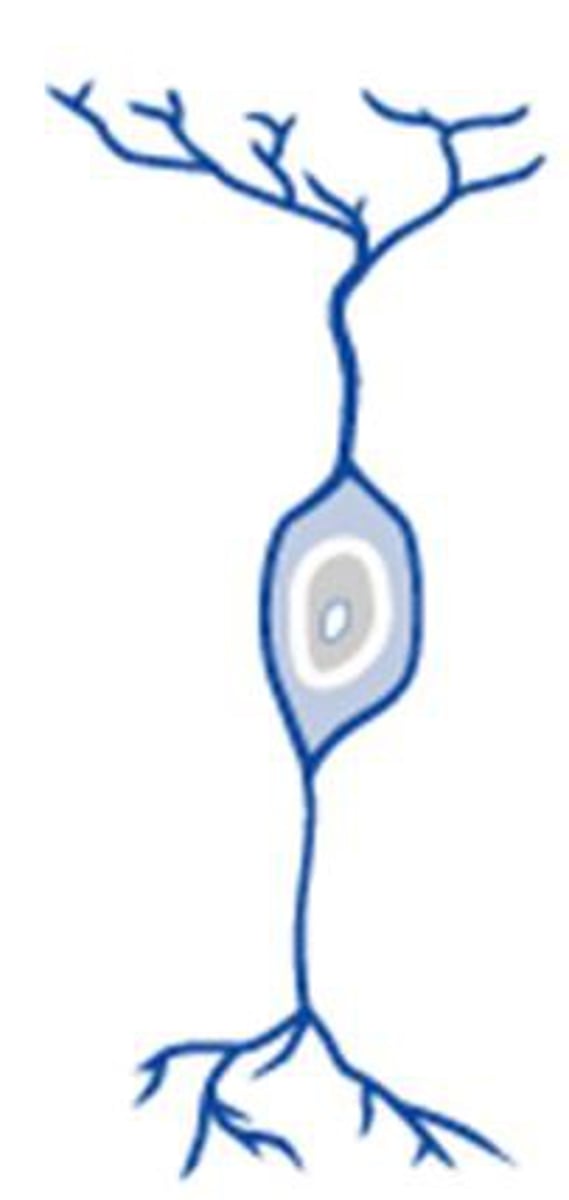
bipolar neurons
A neuron that has only two projections (one axon/one dendrite) from the cell body
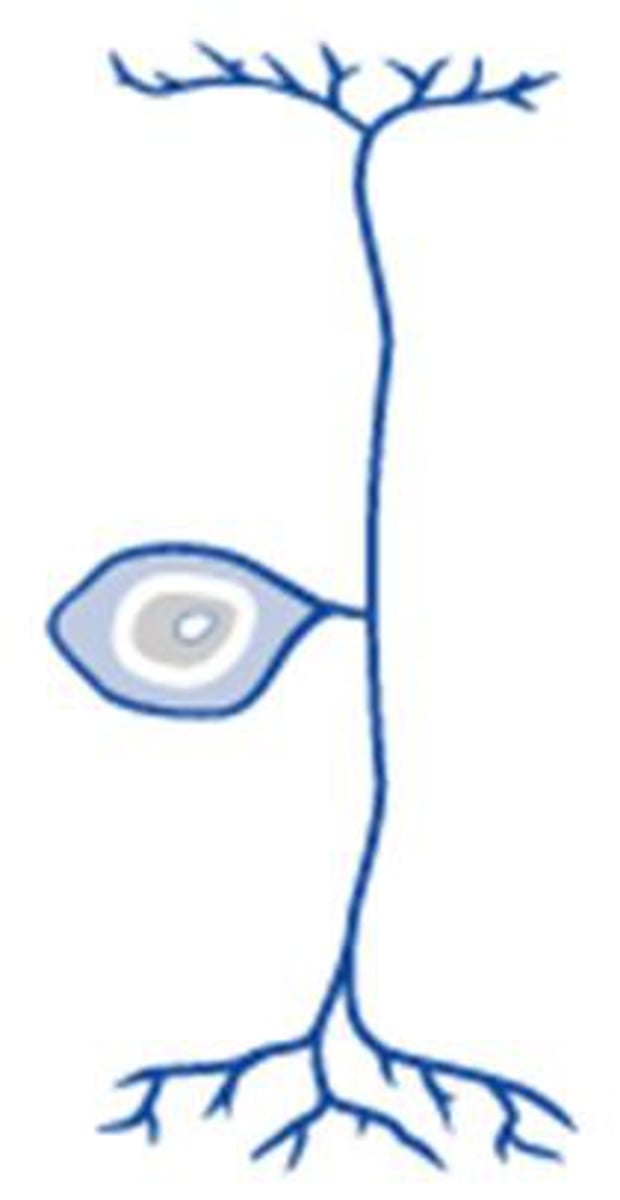
unipolar neuron
a neuron with one process extending from its cell body
CNS
interneurons are only found in the
Oligodendrocytes
produce myelin sheaths in CNS
Schwann cells
produce myelin sheaths in PNS
Myelin
multilayered lipoprotein that serves as an electrical insulation for the axon by preventing ions from moving across the plasma membrane
nerve
cluster of axons in PNS
tract
cluster of axons in CNS
Nucleus
cluster of somas in CNS
ganglion
cluster of somas in PNS
white matter
large amounts of myelinated and unmyelinated axons
gray matter
large amounts of cell bodies of interneurons and motor neurons
Epineurium
CT that surrounds the entire nerve
Perineurium
CT surrounding fasicles, which are bundles of axons arranged parallel to one another
Endoneurium
CT found WITHIN the fascicles, surrounding the individual schwann cells that surround individual axons
receptor, sensory neuron, integration center, motor neuron, effector
five components of reflex arc
Rostral
towards the snout
Caudal
towards the tails
Sulci
shallow grooves
Gyri
ridges of the brain
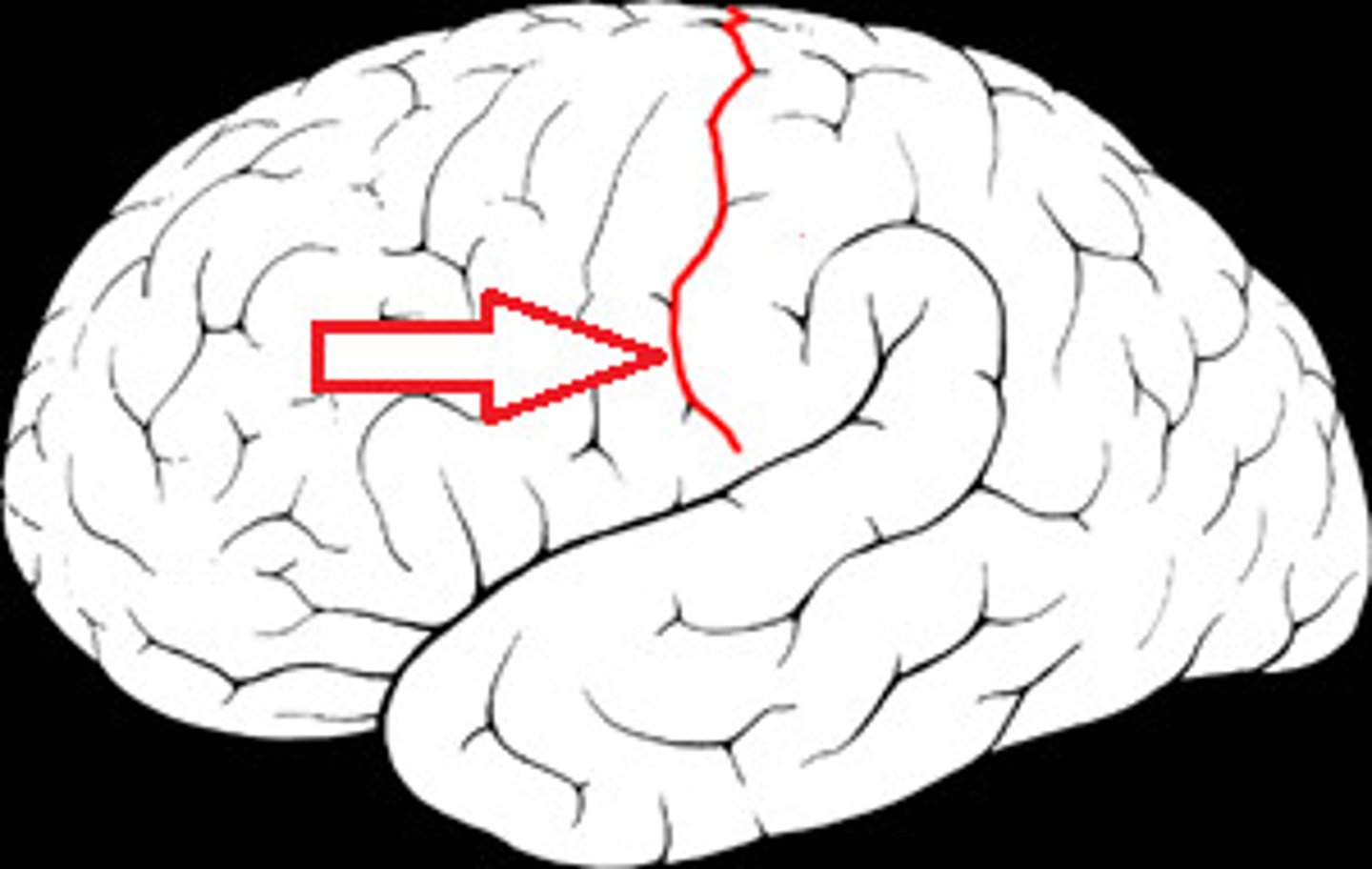
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
parieto-occipital sulcus
separates occipital and parietal lobes
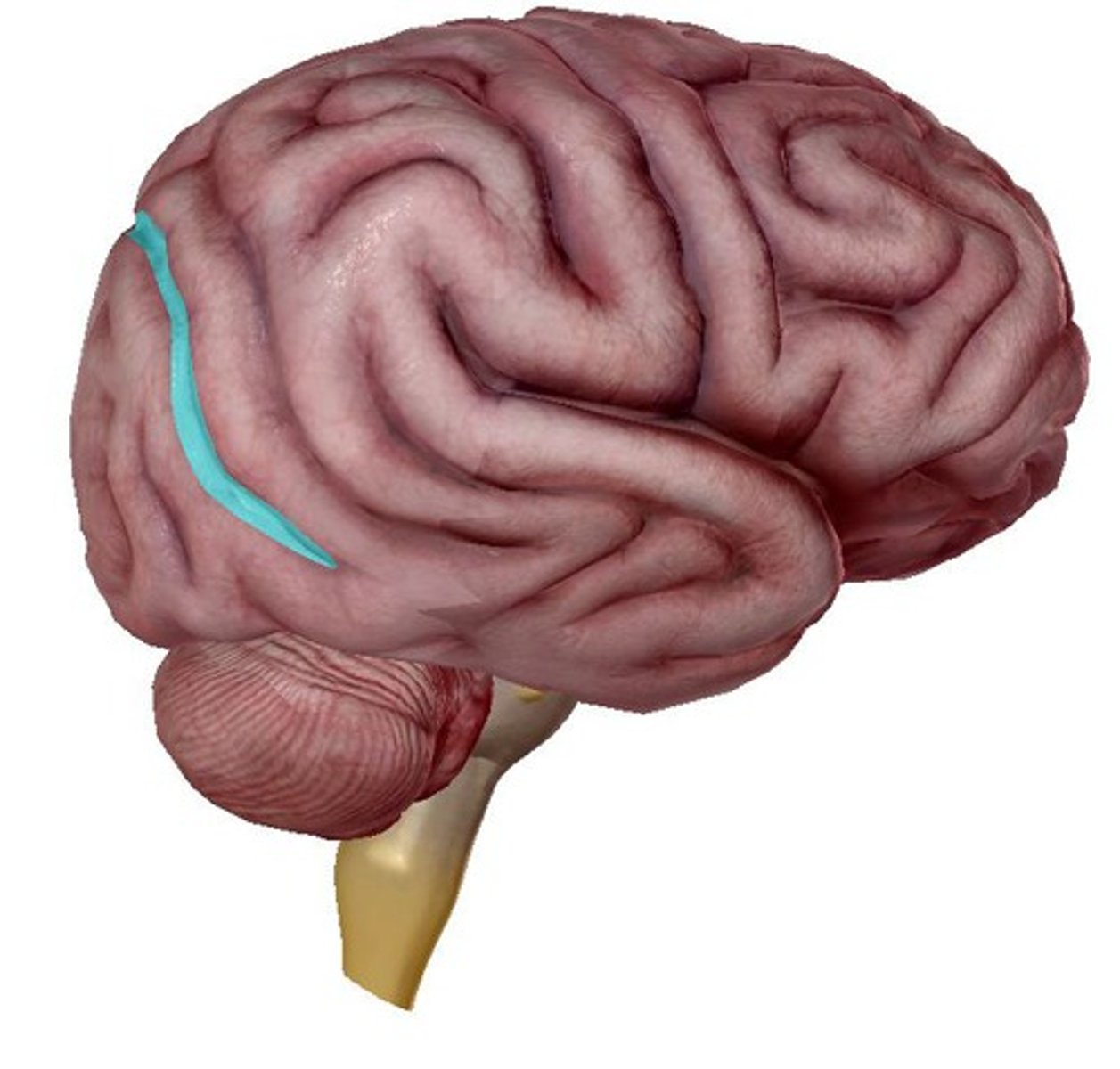
lateral sulcus
Separates temporal lobe from parietal and frontal lobes
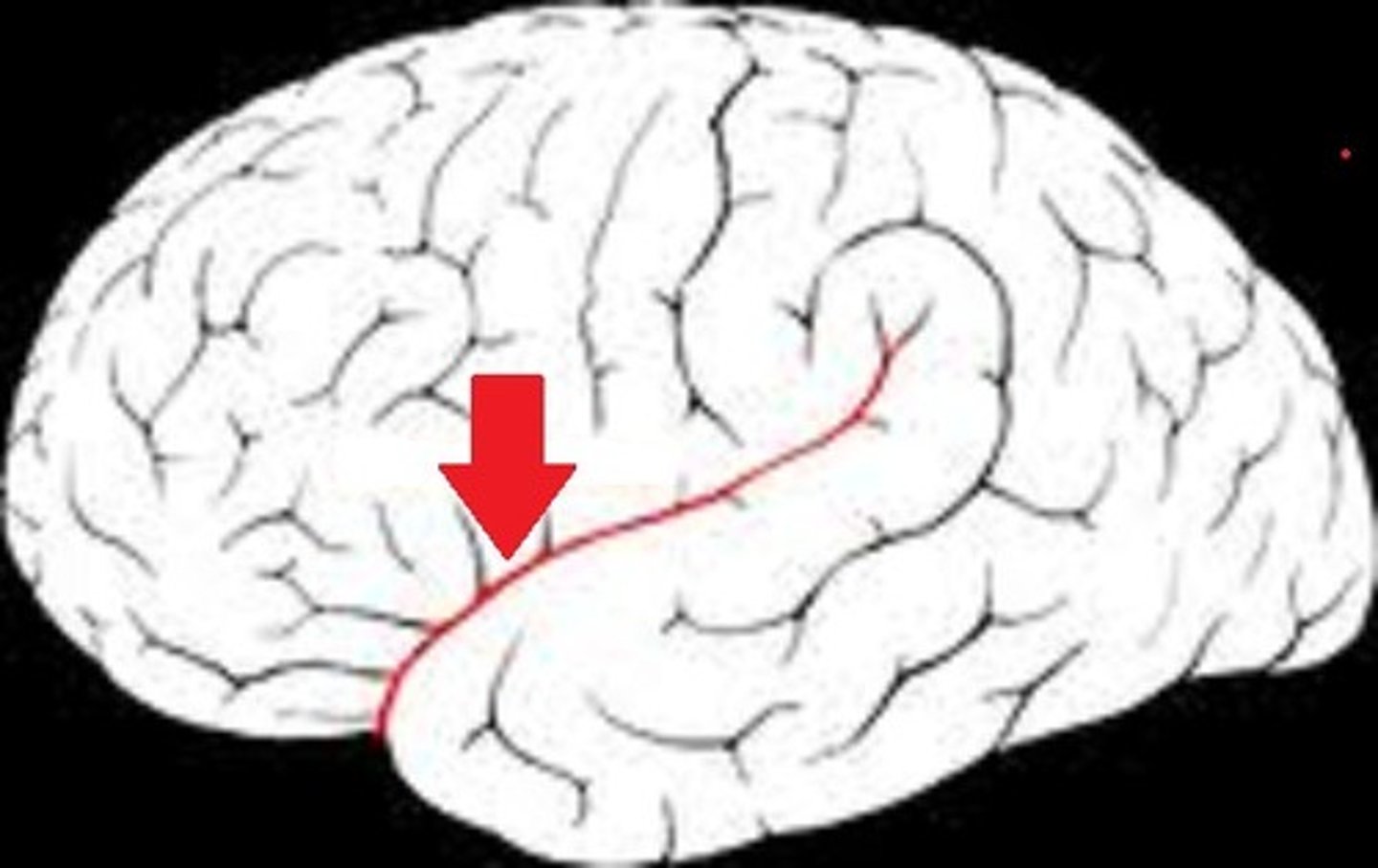
Fissures
deep grooves in the brain
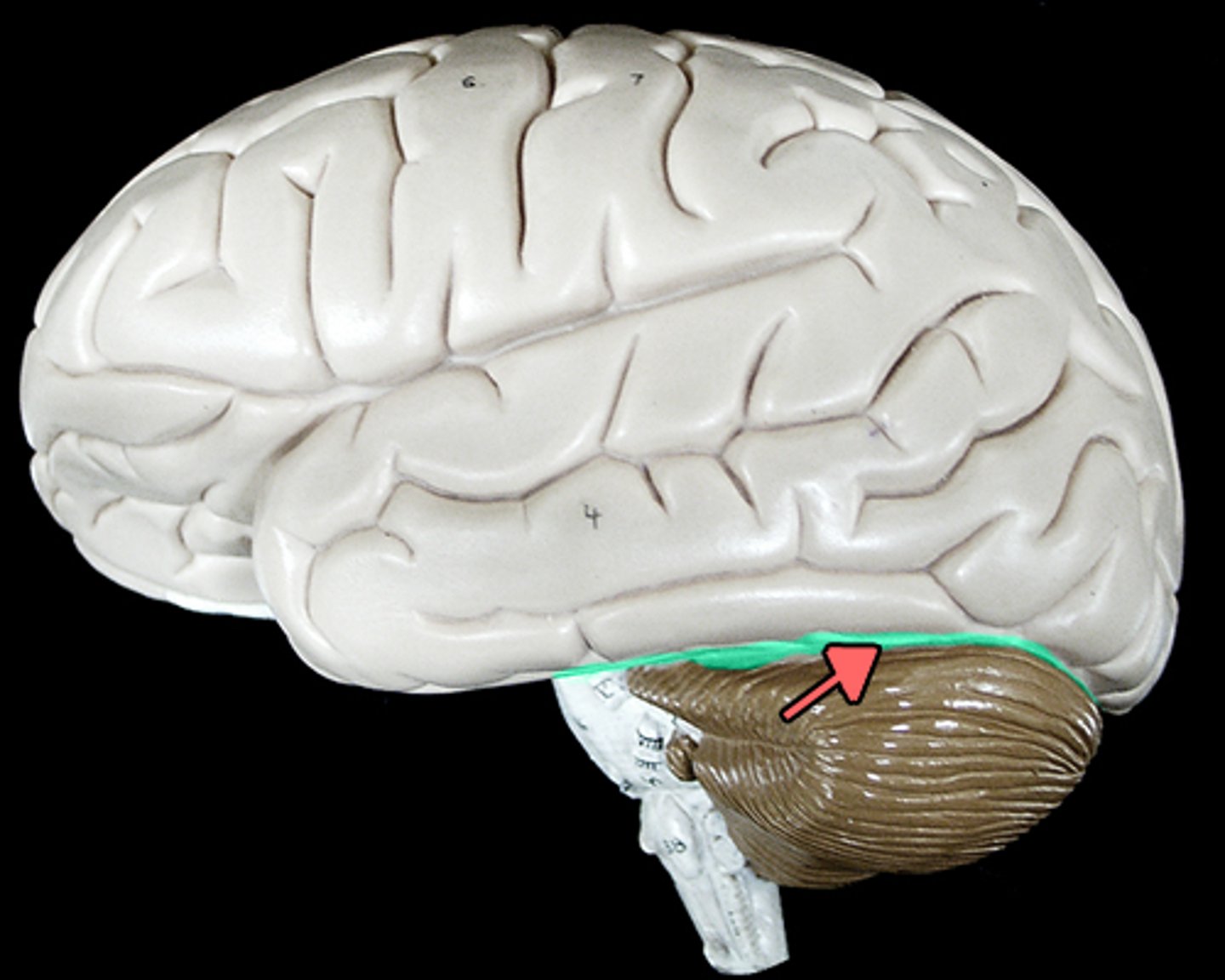
transverse cerebral fissure
separates cerebrum and cerebellum
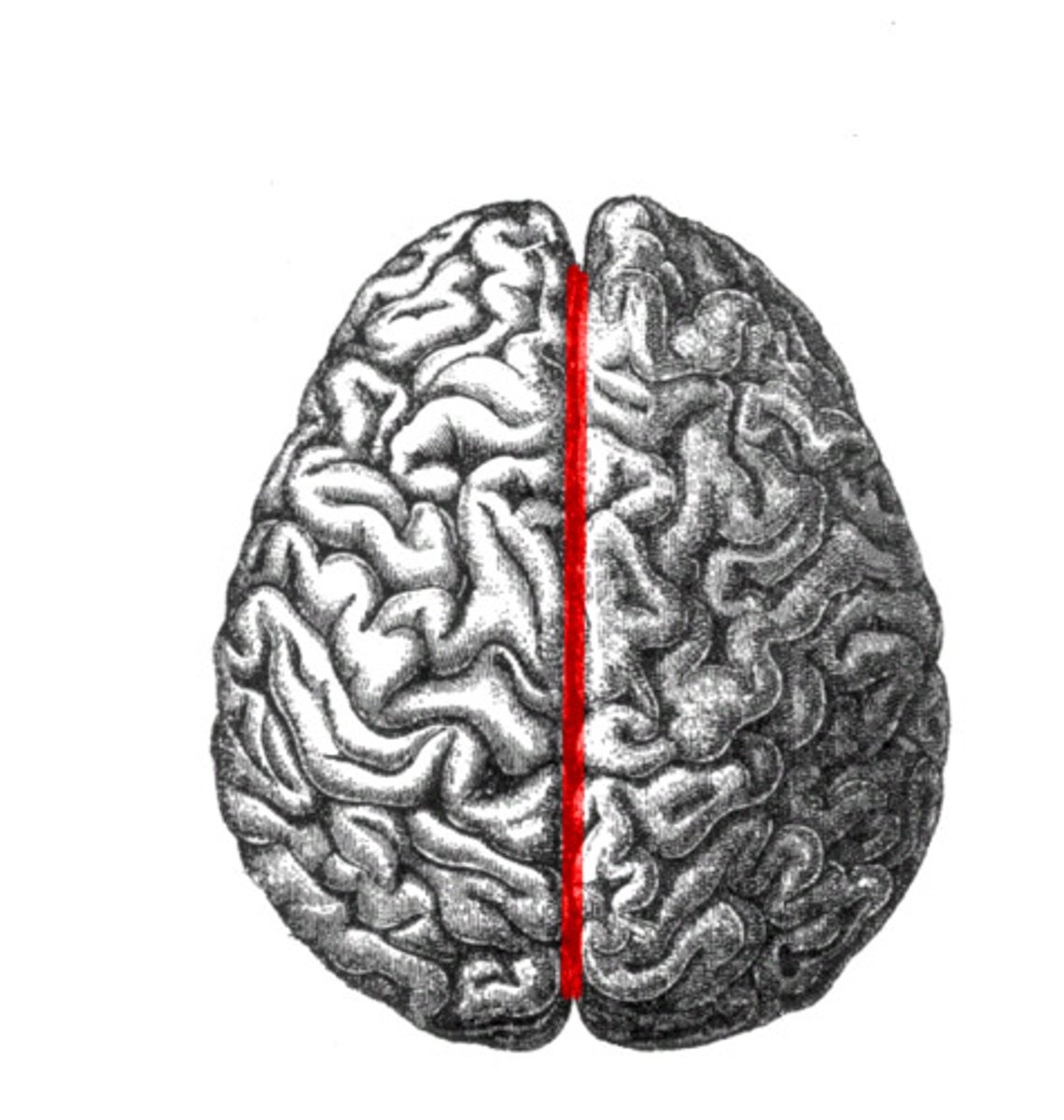
longitudinal fissure
separates cerebral hemispheres
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
list the meninges from superficial to deep
dura mater
thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
arachnoid mater
weblike middle layer of the three meninges
pia mater
thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges
---highly vascularized and delicate
---clings to the surface of the brain and spinal cord
third ventricle
The midline ventricle that conducts cerebrospinal fluid from the lateral ventricles to the fourth ventricle.
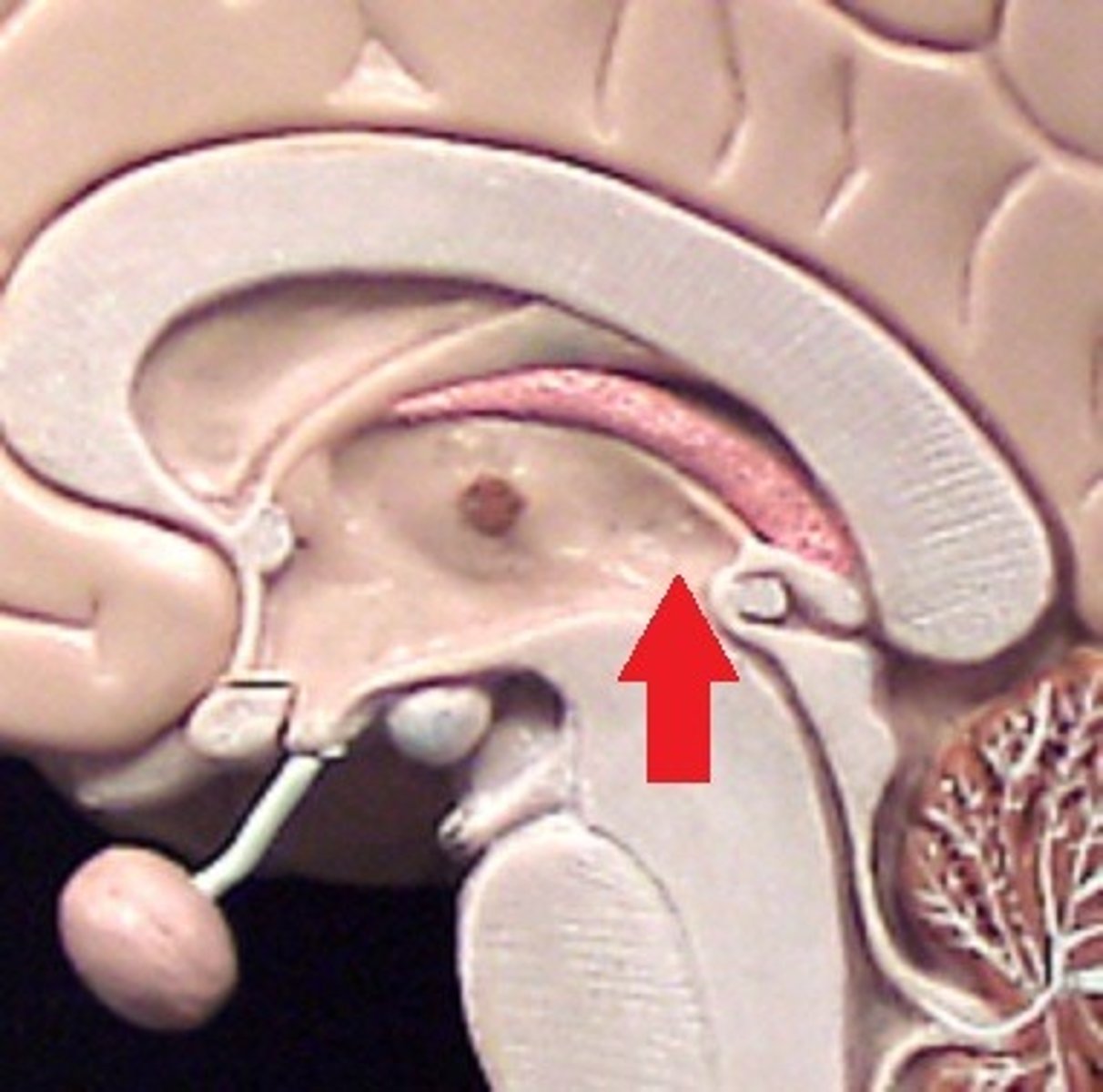
Fouth ventricle
Immediately in front of cerebellum
anterior horn
supplies frontal lobes and parietal lobes
posterior horn
supplies occipital lobes
inferior horn
supplies temporal lobes
Diencephalon
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
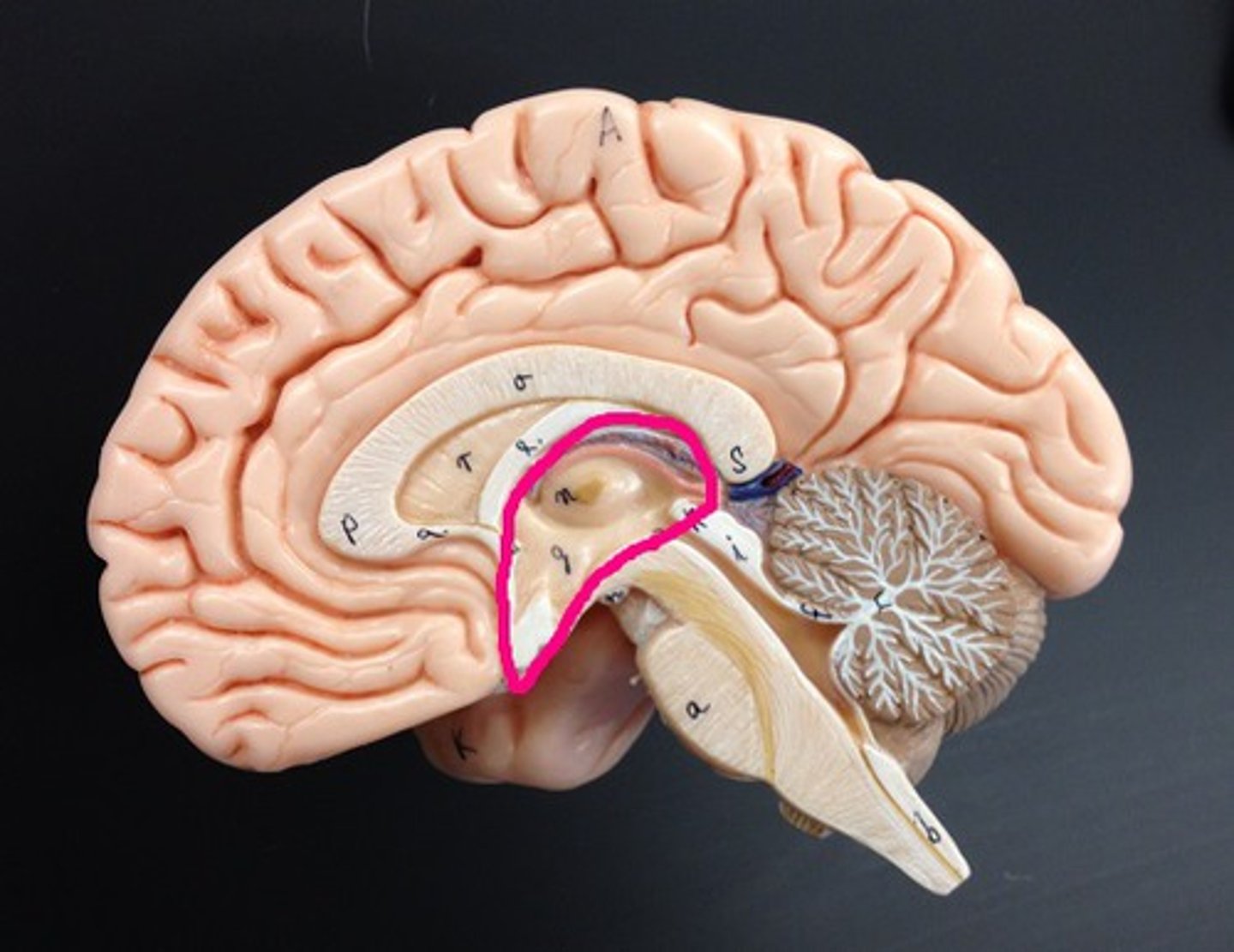
Thalamus
Relay station for sensory information
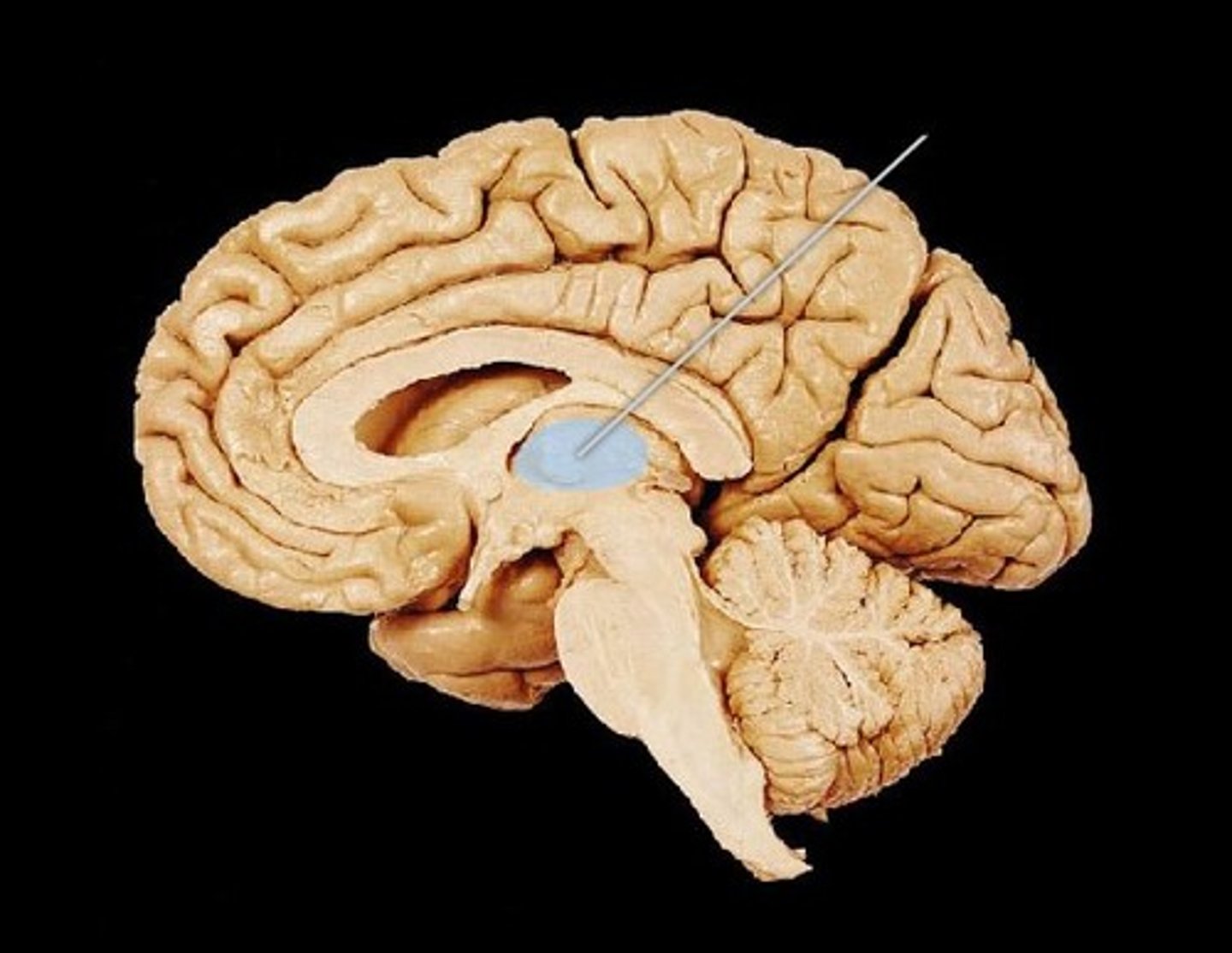
Hypothalamus
homeostasis
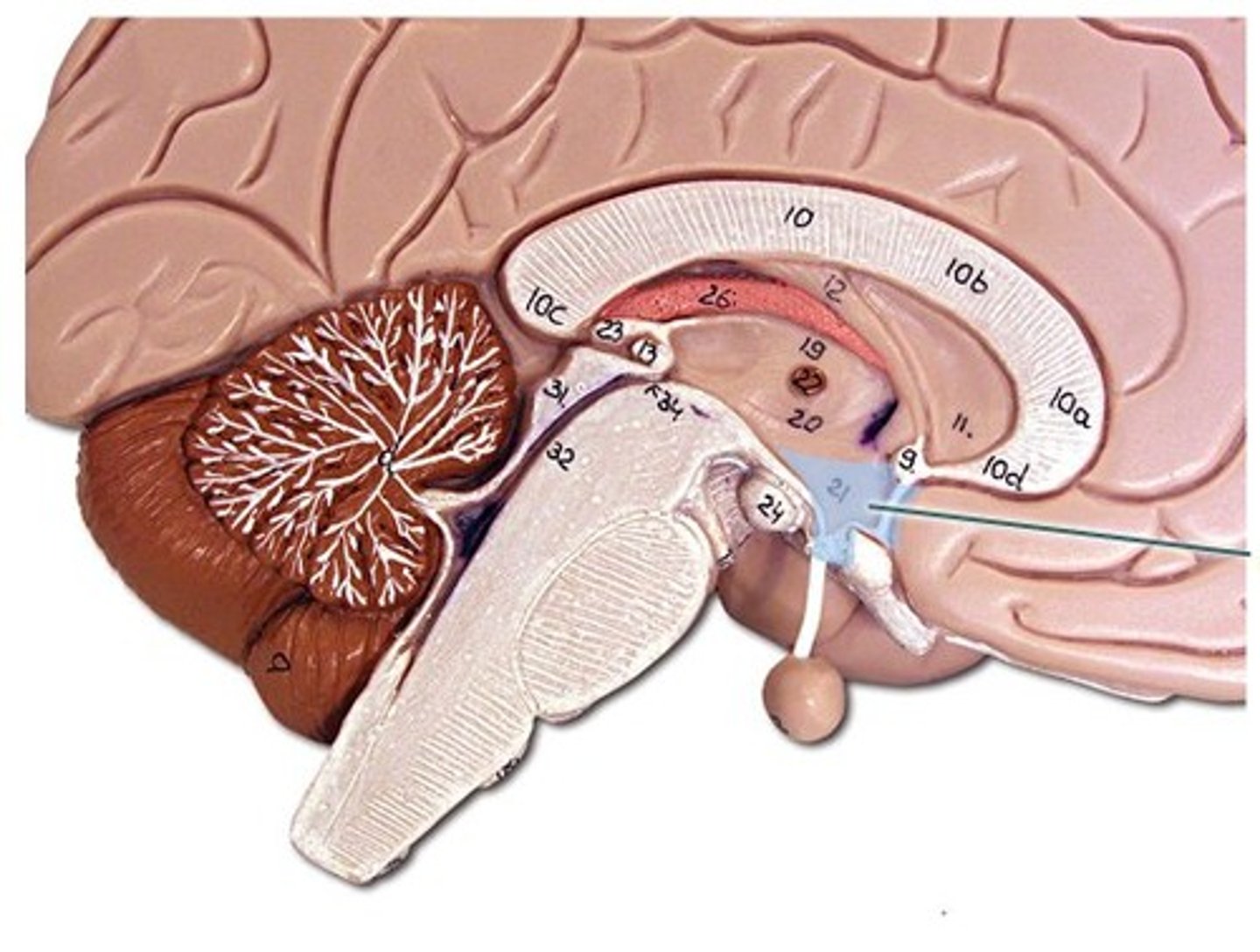
Midbrain
Region between the hindbrain and the forebrain; it is important for hearing and sight.
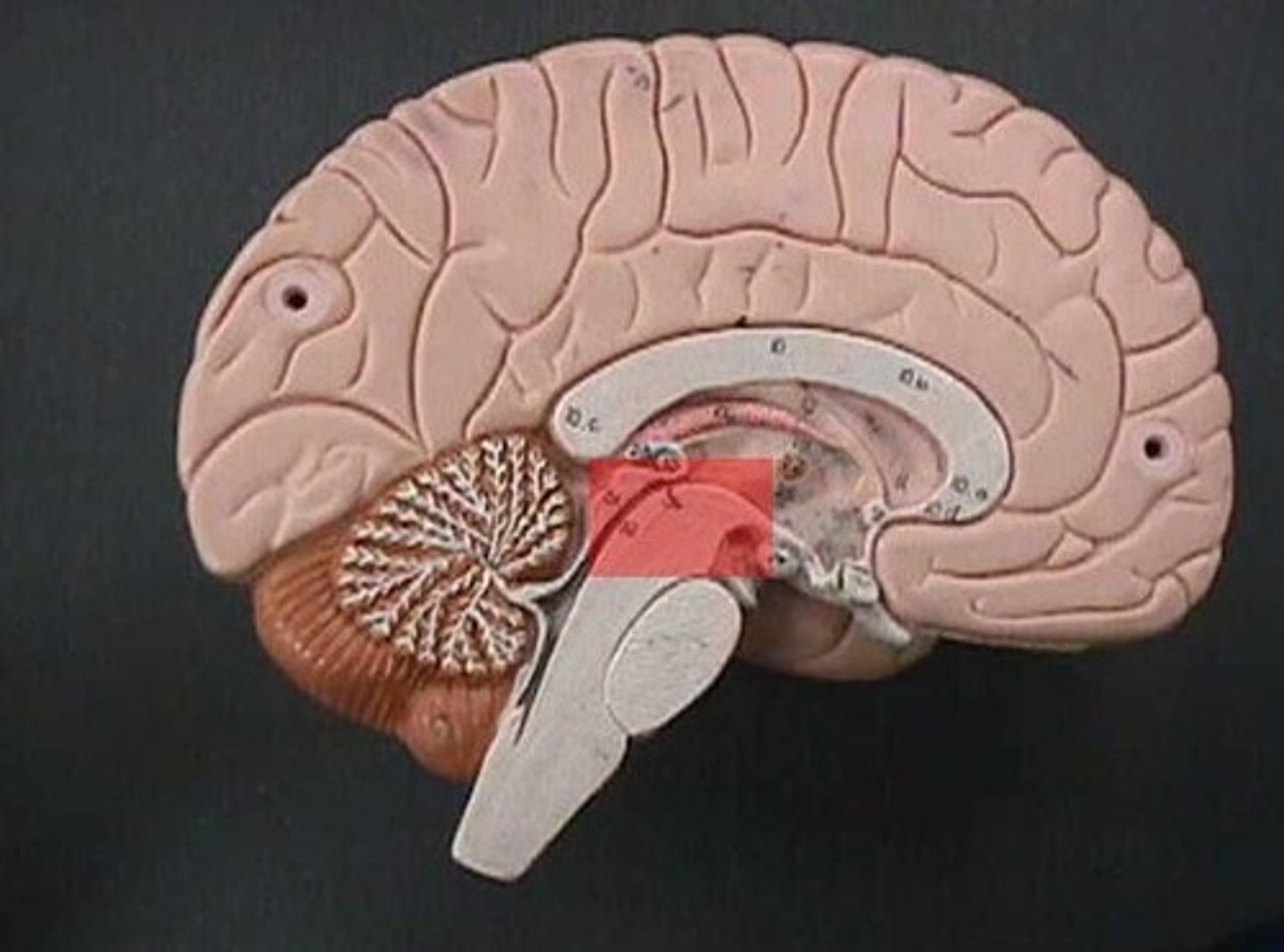
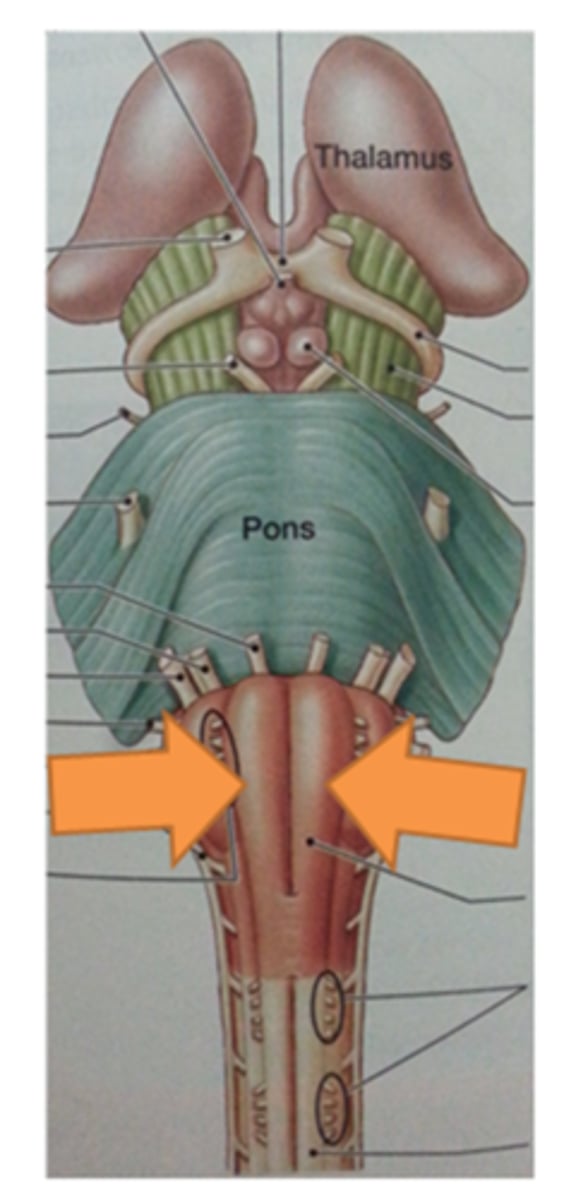
Pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
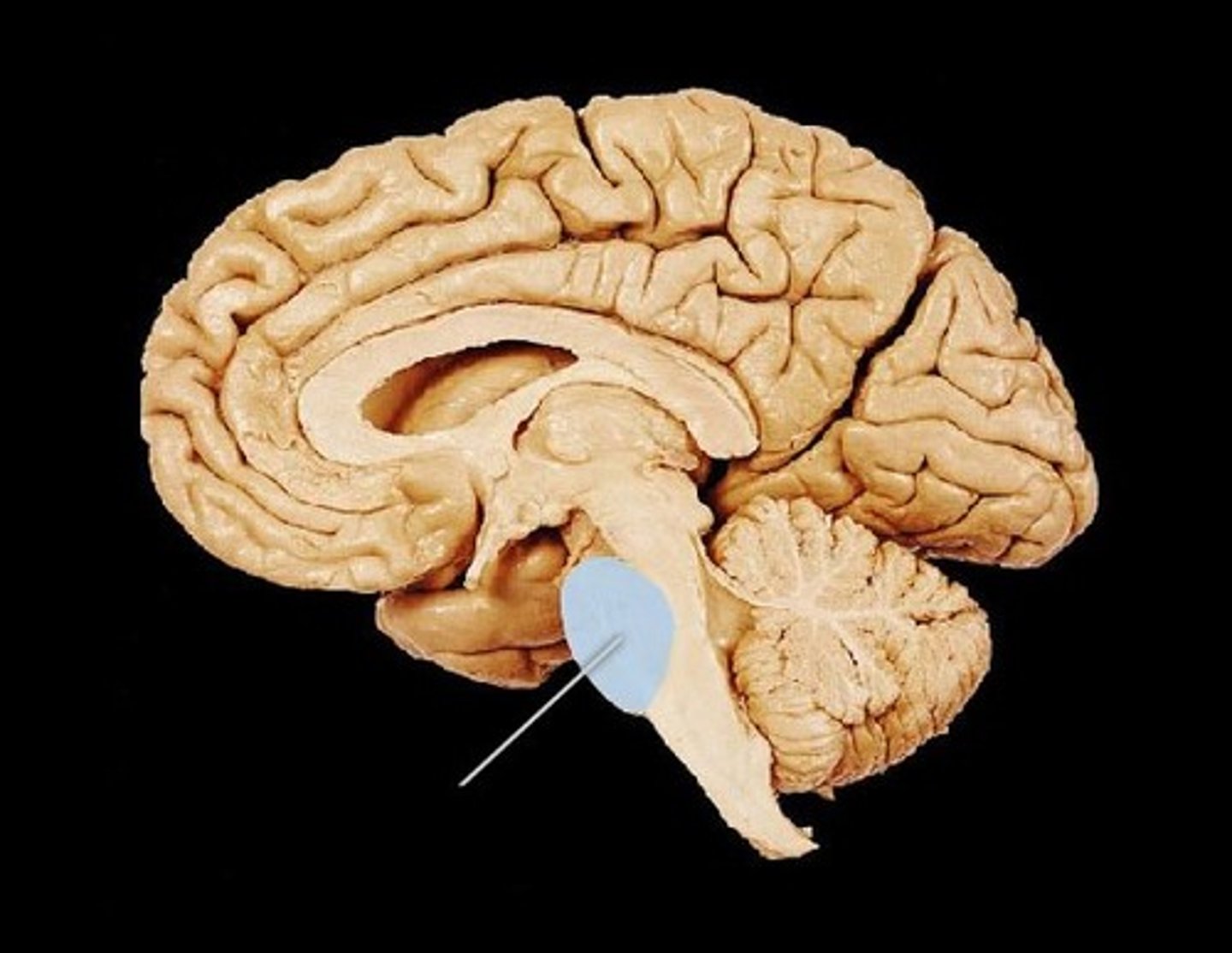
medulla oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
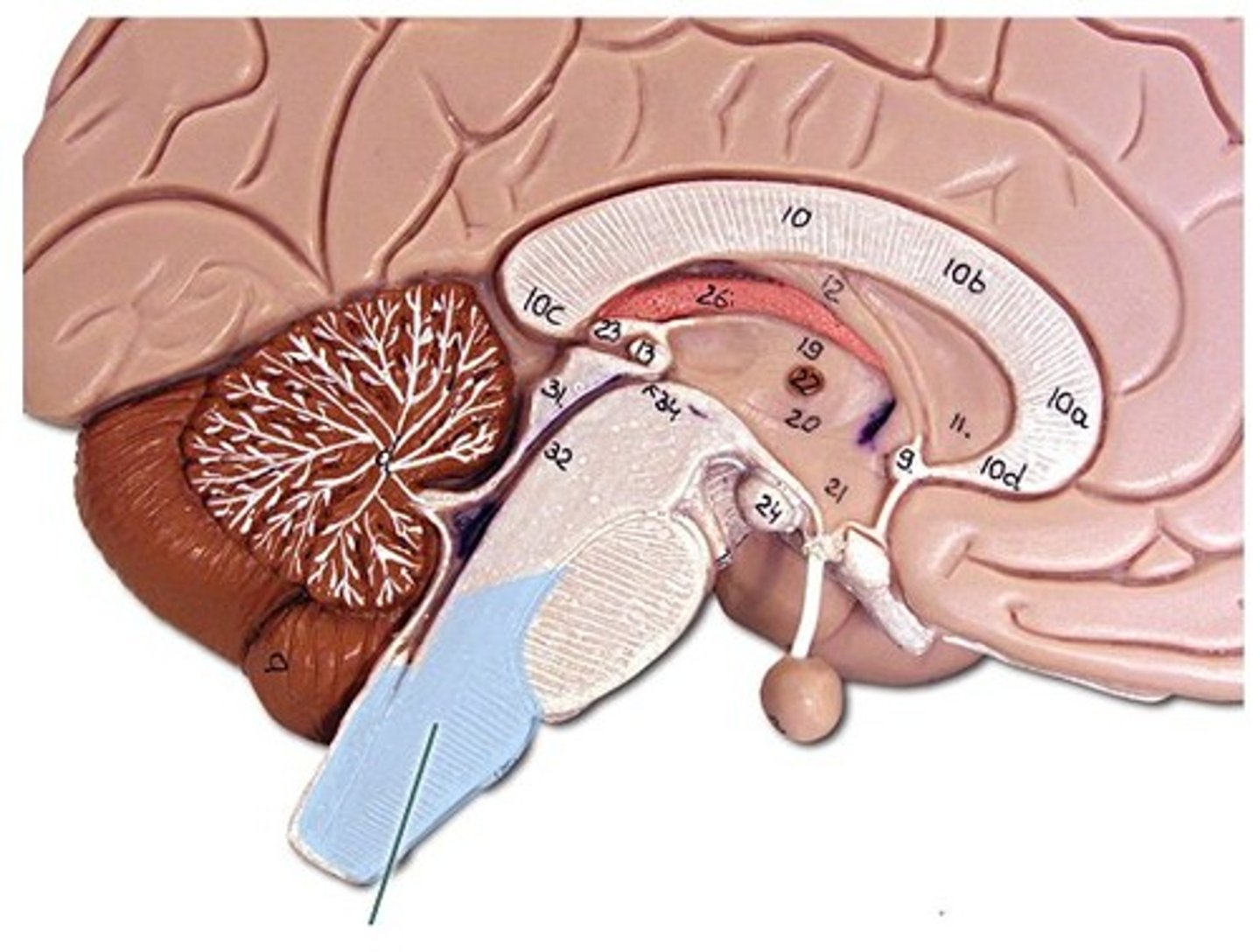
olives of medulla oblongata
rounded; protrude from anterior surface. Nuclei within help regulate balance, coordination, modulation of sound from inner ear
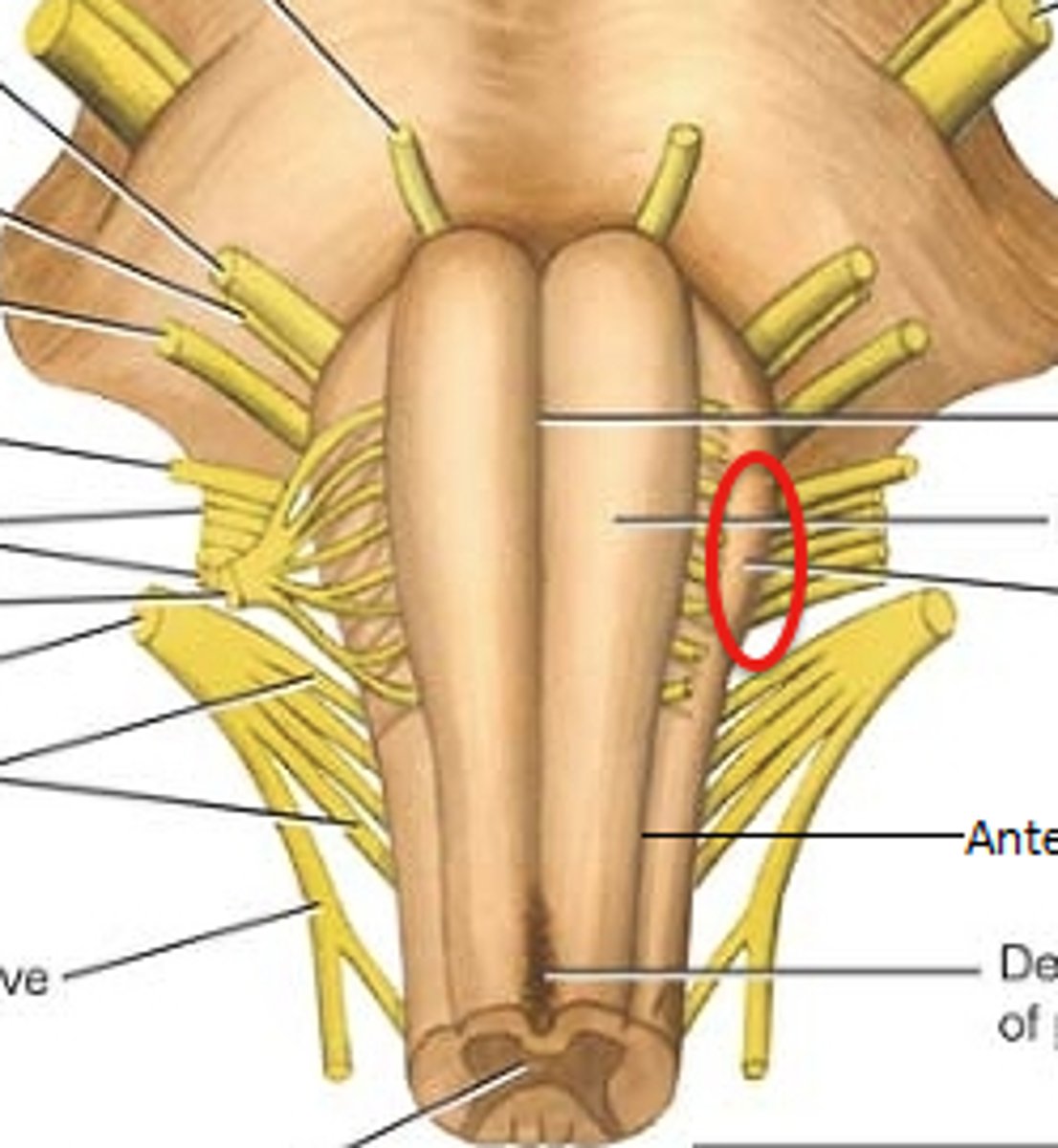
pyramids of medulla
ventrally located columns containing descending motor neurons
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
regions of the vertebral column from rostral to caudal
externally
in the spinal cord, white matter is located....
internally
in the spinal cord, gray matter is located...
dorsal horn
sensory
ventral horn
motor
root
horns give off small axons that accumulate together to form a...
cell bodies of sensory neurons
The dorsal root ganglia mainly contain
axons of motor neurons
ventral roots contain
cranial nerves
12 pairs of nerves arising from the brain
spinal nerves
31 pairs of nerves arising from the spinal cord
plexus
interlacing network of axons
ventral rami
which rami forms plexuses?
dorsal rami
which rami does NOT form plexuses
C1-C4; phrenic nerve
cervical plexus, innervates diaphragm
C4-T1; brachial plexus
gives rise to ulnar nerve, medial nerve, radial nerve, axillary nerve, and muculocutaneous nerve -- innervated antebrachium and brachium
L1-L4, obturator and femoral nerves
lumbar plexus, helps innervate thigh
L4-S4, sciatic nerve
sacral plexus, supplies lower regions like leg, hamstrings, and buttocks
I Olfactory
SENSORY nerve
-sense of smell
II Optic
SENSORY
-vision
III Oculomotor
motor, eye movement: superior rectus, medial rectus, inferior rectus, inferior oblique muscles
IV Trochlear
motor, eye movement: superior oblique muscle
V Trigeminal
mixed nerve
-chewing and sensation of face
VI Abducens
motor, eye movement: lateral rectus muscle
VII Facial
mixed nerve
facial expression, taste on 2/3 of the tongue, ear sensation, salivary production
VIII Vestibulocochlear
sensory
hearing and balance (equilibrium)
IX Glossopharyngeal
mixed nerve
tongue sensation 1/3 of tongue, swallowing, taste
X Vagus
mixed
swallowing and vocalization, taste in epiglottis, helps the parasympathic nervous system function (heart and digestion)
- only cranial nerve that leaves the head to the ventral cavity
XI Accessory
motor
innervates your upper trapezius fibers and sternocleidomastoid ----- moves your head and neck
XII Hypoglossal
motor
innervates the tongue form under, moves the tongue
Some Say Marry Money But My Brother Says Big Brains Matter More
trick to remembering if a nerve is motor, sensory, or mixed (in order from 1-12)
somatic motor division of PNS
-neurons can only activate skeletal muscle
-impulses are sent form the spinal cord to the skeletal muscle via the neuron of a single axon
visceral (autonomic) nervous system
-neurons can activate or inhibit smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, or glands
-The ANS uses two neurons to send impulses: a preganglionic neuron and postganglionic neuron
lateral horn of spinal cord
-soma of sympathetic preganglionic neuron exists here
-of the thoracocolumbar spinal cord (T1-L2)
T1-L2
preganglionic fibers arise from spinal cord segments :
preganglionic
extends from soma in CNS to ganglion (cell bodies in PNS)
postganglionic
releases acetycholine into synaptic cleft, activating a second neuron in the PNS called postganglionic neuron
---then its sent to the effectors
Norepinephrine
is the neurotransmitter released onto an effector organ in the sympathetic nervous system
Acetylcholine
neurotransmitter released onto an effector organ in parasympathetic nervous system
hypothalmus
regulates autonomic tone
-regulates the balance of sympathetic and parasympathetic activity == autonomic tone
parasympathetic - rest and digest
-salivation
-constriction of pupils
-constriction of bronchi
-slowing of heart beat
-constriction of urinary b ladder
-stimulation of peristalsis
-secretion, bile release