Forces And Motions
movement and position
speed and velocity
{{total distance [m] = average speed [m/s] x total time [s]{{
- speed is shown as ‘==20m/s==’ which is the ==magnitude== [size = magnitude]
- velocity is shown as ‘==20m/s== ^^→^^’ which is ==magnitude== and ^^direction^^
| scalar [magnitude] | vectors [magnitude and direction] |
|---|---|
| speed | velocity |
| mass | force |
| time |
acceleration
- a change in velocity is known as acceleration since acceleration can act to increase or decrease velocity- it has a direction and is therefore a vector.
{{acceleration = gain in velocity / time{{
{{acceleration [ms^-2] = final velocity [m/s] - initial velocity [m/s] / time [s]{{
{{a = v-u / t{{
- acceleration can be related to the distance by using the equation below:
{{(f@@inal speed)^2 @@= ^^(initial speed)^2 ^^+ (2 x ==acceleration ==x %%distance moved%%){{
{{@@v^2 @@= ^^u^2 ^^+ (2 × ==a ==× %%s%%){{
speed [velocity] time graphs
gradient = acceleration
area under the graph = distance
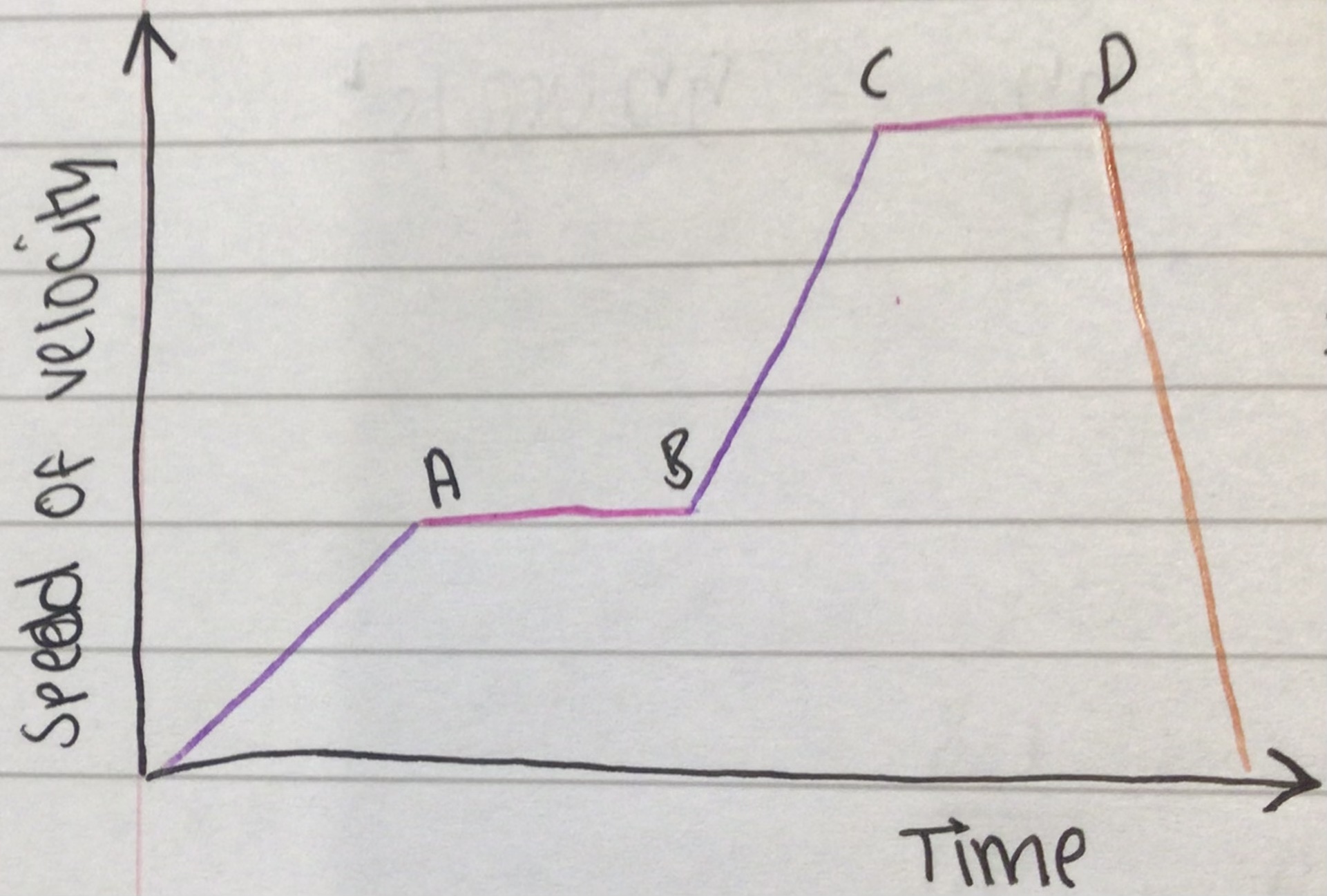
[purple = blue]
<<0 → A<<
- <<constant positive gradient, therefore acceleration<<
[[A → B[[
- [[zero gradient, therefore zero acceleration ie constant speed[[
<<B → C<<
- <<constant positive gradient, therefore acceleration [but greater than from 0→A]<<
[[C → D[[
- [[zero gradient, therefore zero acceleration ie constant speed, but greater than A→B[[
]]@@D → E@@]]
- ]]@@constant negative gradient, therefore deceleration@@]]
distance time graphs
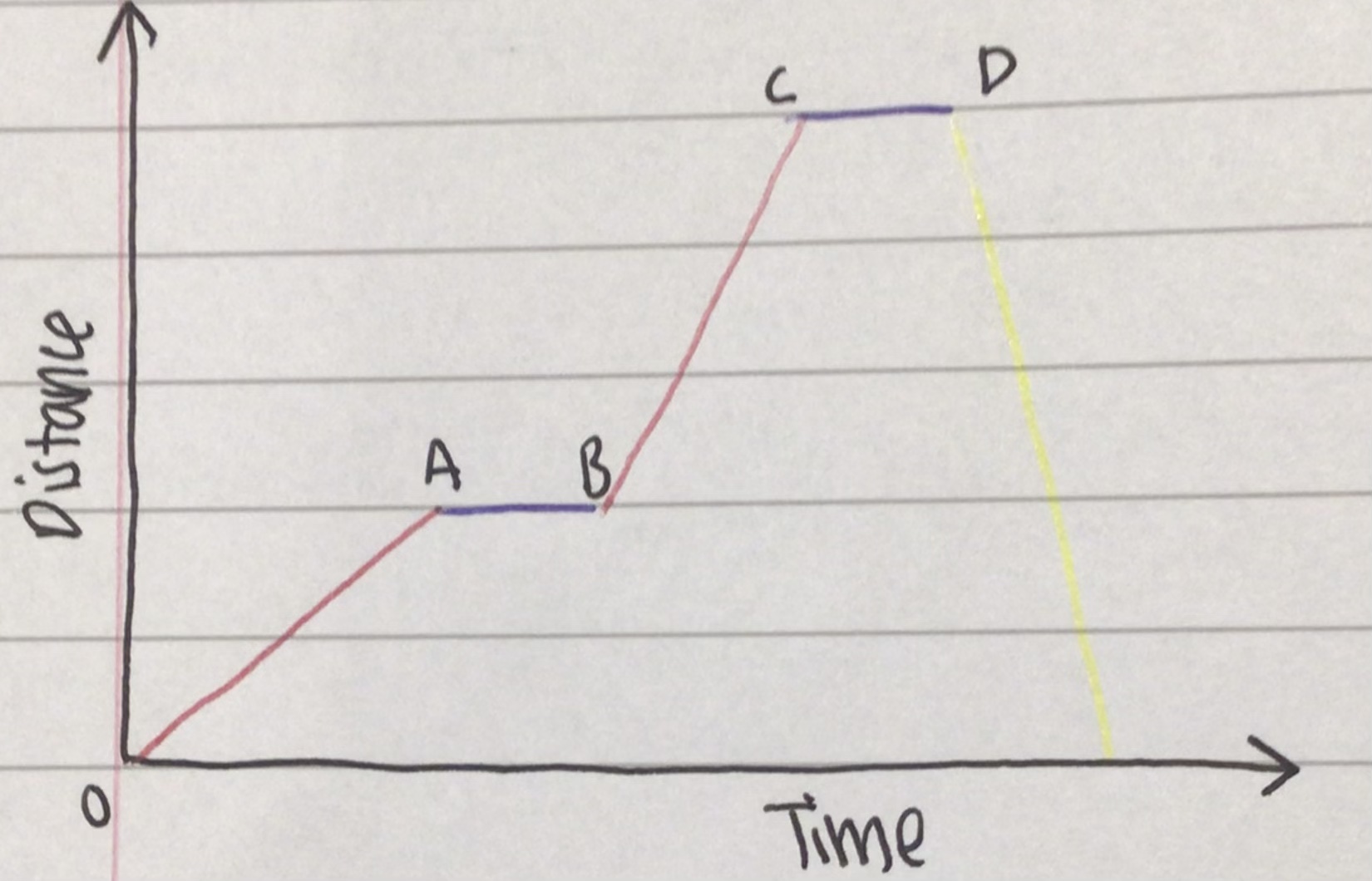
[[0 → A[[
- [[constant velocity away from starting point, since the gradient is constant & positive[[
<<A → B<<
- <<stationary [ie zero velocity] since the gradient is zero<<
[[B → C[[
- [[constant velocity away from starting point, since the gradient is positive & constant [but velocity greater than 0 → A since the gradient is steeper][[
<<C → D<<
- <<stationary, since the gradient is zero and therefore velocity is zero<<
{{D → E{{
- {{constant velocity back toward starting point since the gradient is constant & negative{{
forces, movement, shape, and momentum
forces
- pulling force = tensile force [e.g a dog pulling on a lead]
- pushing force = compressive force [e.g person pushing on a wheelbarrow]
- forces always come as a pair of equal and opposite forces.
- for example, the force of the dog on the person is equal and opposite to the person on the dog.
- this is summarised in Newton’s third law which states,
^^“To every force, there is an equal and opposite reaction.”^^
- forces can be shown on a diagram by using a solid-headed arrow, usually, the length of the arrow is in proportion to the size of the force.
- where there are two or more forces that can be combined to yield one resultant [overall or net force]
- forces are vector quantities, they have both size [magnitude] and direction
- scalar quantities only have size
| contact forces | non-contact forces: |
|---|---|
| drag [air or water resistant] | gravitational |
| push/pull | electrostatic |
| thrust | |
| friction |
weight
- weight - the force due to gravity
- the weight of an object is the force by which gravity pulls it down
- mass is the amount of matter in an object
{{weight [N] = mass [Kg] x gravitational field strength [N/Kg]{{
{{w = m x g{{
- ==Earth = 10N/Kg==
- ==Mars = 4N/Kg==
- ==Moon = 1.6N/Kg==
investigating mass and weight:
- electric balance gives the mass
- force meter gives the weight
an experiment to investigate friction:
- frictional forces always oppose motion
- the graph shows that the weight of an object increases so does the frictional force, since the graph is a straight line through the origin it shows a proportional relationship
terminal velocity
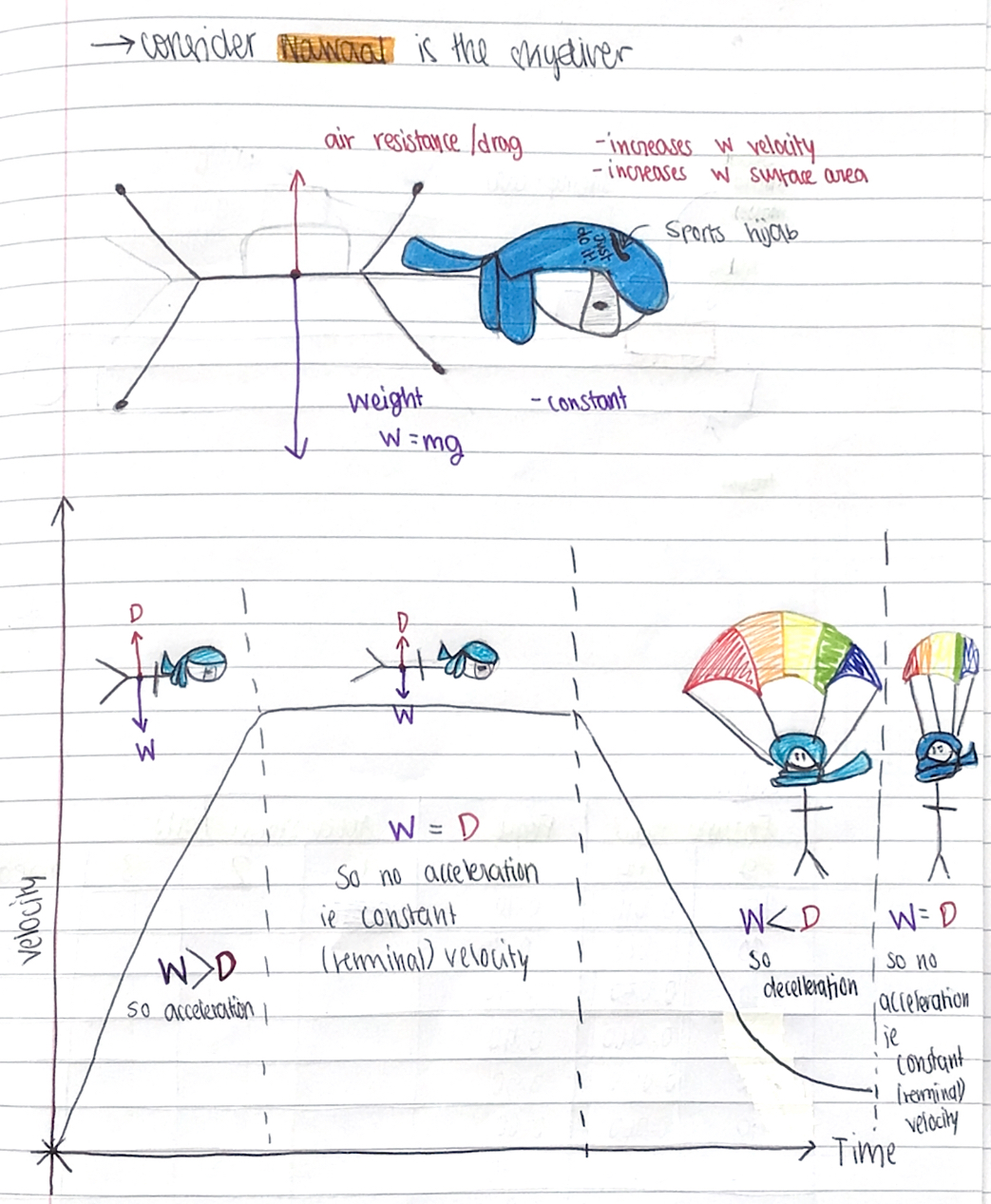
force and acceleration
- the resultant force on an object and the acceleration are related by the equation below:
{{force[N] = mass[Kg] x acceleration[m/s^2]{{
{{F = m x a{{
stopping distances
{{thinking distance + braking distance = stopping distance{{
factors which increase the thinking time:
- increased thinking time due to alcohol, drug use, distractions [eg use of phone, other people, music], tiredness, etc.
- increased initial velocity
factors which increase braking time:
- poor weather eg ice, snow and rain
- worn tyres
- poorly maintained brakes
- increased initial velocity
hooke’s law
- hooke’s law works up to a certain limit- this is the elastic limit. when an object goes after the elastic limit it is now permanently deformed this is plastic behaviour
- elastic behaviour: when an object is returned to its original shape when the force is removed
- plastic behaviour: when an object does not return back to its original shape when the force is removed and the is permanently deformed
momentum
{{momentum[Kgm/s] = mass[Kg] x velocity[m/s]{{
{{P = m x v{{
- provided that no external forces act on a system the total momentum is conserved
{{momentum/before = momentum/after{{
{{Pbefore = Pafter{{
safety features in cars:
- people are injured in car accidents when their bodies experience large features as they come to rest
- the force of the body can be calculated using
{{force[N] = change in momentum[Kgm/s] / time[s]{{
- modern cars have airbags. these inflate very quickly in the event of an accident and then deflate as the person hits them to gently slow the person down.
centre of mass
symmetrical object:
- for a symmetrical 2d object, its centre of mass is along its line of symmetry. if the object has more than one line of symmetry, then its centre of mass is where the lines meet.
irregular object:
- to find the centre of mass for an irregular object you must hang it thrice:
- place a hole through the object and allow it to swing freely
- hang a plumb line and mark that line on the irregular shape
- rotate the object and hang it through another hole, mark the plumb line
- the point at which the plumb line meet is the centre of mass
moments
- a moment is the turning effect of a force. a moment will work around a pivot. a moment can work clockwise or anticlockwise
{{moment[Nm] = force[N] x perpendicular distance to the pivot[m]{{
- if the force is further away from the pivot than the load it will multiply the force
principle of moments = when an object is balanced it is in equilibrium
{{anticlockwise moment = clockwise moment / f1 d1 =f2 d2{{
{{moment[Nm] = force[N] x distance[m]{{