Economics: Market Power-Quant & Market Characteristics & graphs
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Total Product(TP)
No. variable factors(V) × Average Product(AP)/Total output firm produces in given time period
Average Product(AP)
TP/V; output produced on average by each unit of variable factor
Marginal Product(MP)
ΔTP/ΔV; extra output produces by using extra unit of variable factor
Total Fixed Cost(TFC)
No. fixed factors × Cost. fixed factors; total cost of fixed assets firm uses in given time period
Total Variable Cost(TVC)
No. variable factors × Cost. variable factors; total cost of variable assets firm uses in given time period
Total Cost(TC)
TFC + TVC; total cost of all fixed & variable factors used to produce certain output
Average Fixed Cost(AFC)
TFC/Q; fixed cost per unit of output
Average Variable Cost(AVC)
TVC/Q; variable cost per unit of output
Average Total Cost(ATC)
AFC + AVC or TC/Q; total cost per unit of output
Marginal Cost(MC)
ΔTC/ΔQ; increases of total cost of producing extra unit of output
Total Revenue(TR)
P × Q; total amount of money firm receives by selling a product
Average Revenue(AR)
TR/Q=P×Q/Q=P; revenue firm receives per unit of sales
Marginal Revenue(MR)
ΔTR/ΔQ; extra revenue gained by firm selling 1 more unit of the product in given time period
Perfect Competition
Large no. firms
Price takers; each firm so small compared to the size of the industry
Homogeneous goods; no brand names
No barriers to entry/leave for firms
Perfect knowledge of the market by producers & consumers
No long-run abnormal profits/losses
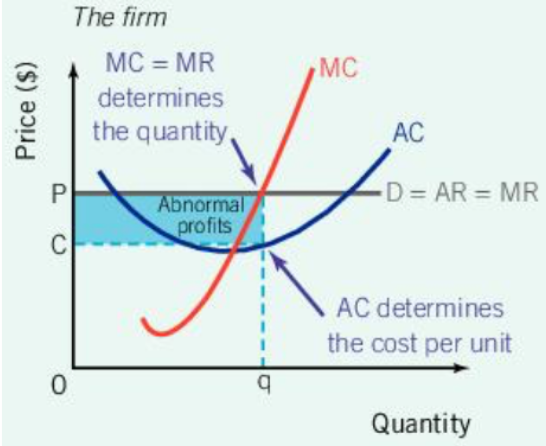
Short-Run Abnormal Profit: Perfect Competition
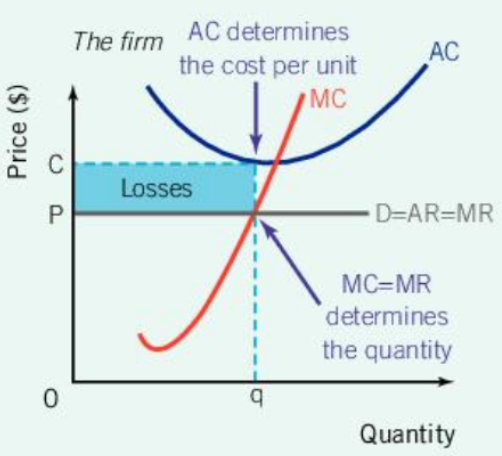
Short-Run Loss: Perfect competition
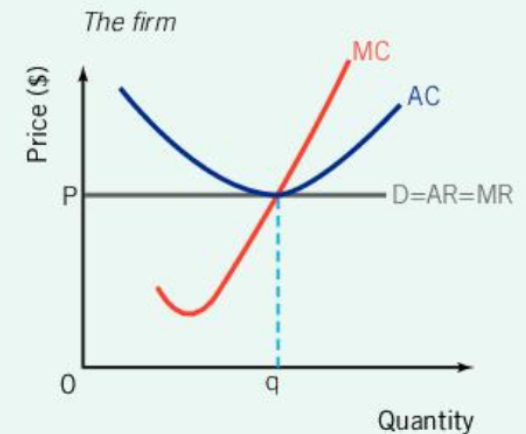
Long-Run Normal Profit: Perfect Competition
Monopolistic Competition
Large no. small firms
No barriers to entry/exit
No long-run abnormal profits/losses
Firms produce slightly differentiated products; branding→Price makes to some extent; some market power but small relative to size of industry(relatively elastic demand curve)
Monopoly
Only 1 firm producing a product; firm=industry
Existing barriers to entry→Keep out new firms/maintain monopoly/make long-run abnormal profits
Oligopoly
Few firms dominating an industry
Produce nearly identical products, highly differentiated products, or slightly differentiated products
Distinct barriers to entry such as large-scale production or distinct branding
Price rigidity
Non-price competition: firms don’t compete w/prices; brand names, marketing, advertising, packaging
Interdependence: 1 firms’ action have major effects on others
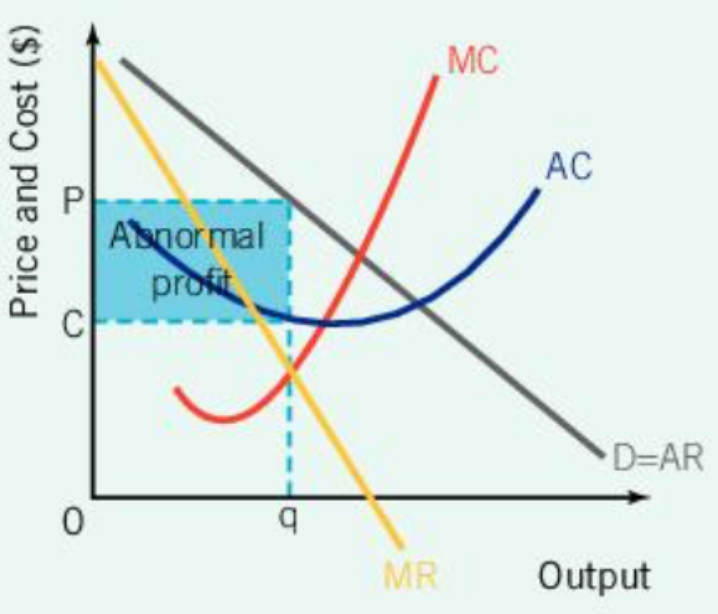
Short-Run Abnormal Profit: Monopolistic Competition, Monopoly, Collusive Oligopoly
Short-Run Loss: Monopolistic Competition, Monopoly
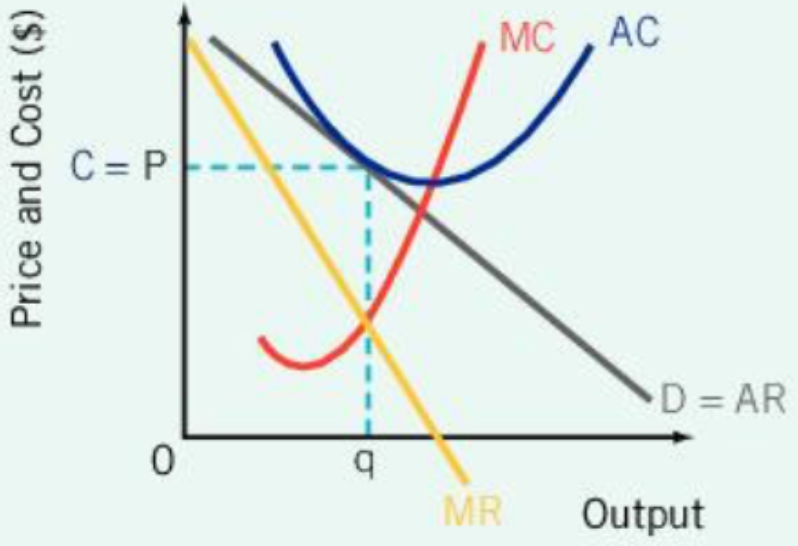
Allocative Efficiency
MC=AR; suppliers of firms produce optimal mix of G & S required/desired by consumers
Productive Efficiency
MC=AC; Firms combine resources most efficiently & resources are not wasted by inefficient use