The Human Eye
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Stimulus
a chemical or physical change in the internal or external environment which is detected by receptors eliciting a response
Transduction
when stimulus energy (kinetic, force, heat) is converted into chemical energy in the form of nerve impulses
Biological Transducers
receptor cells
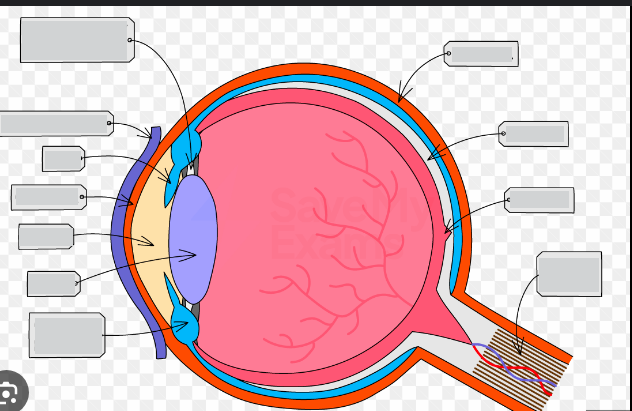
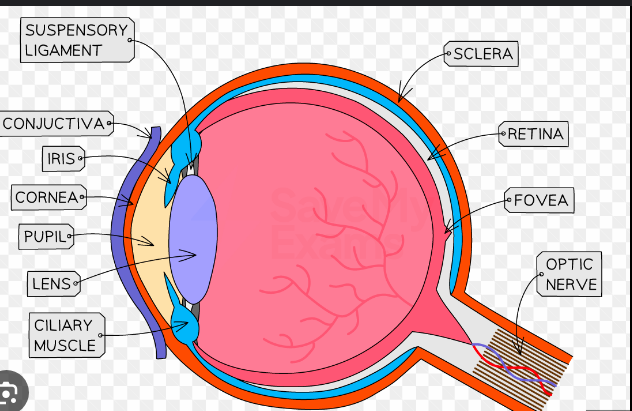
cornea
iris
lens
sclera
retina
choroid
fauvea
optic disc
optic nerve
vitreous body
suspensory ligaments
ciliary body
anterior chamber filed with aqueous humor
pupil
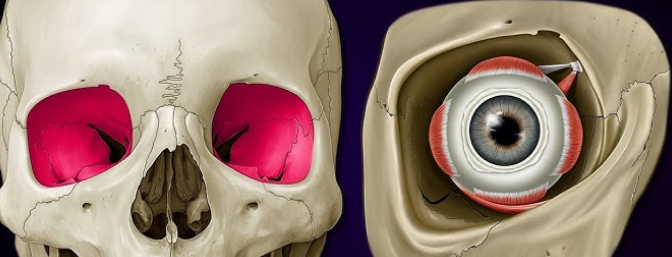
Orbits
eye socket which holds the eye
has a tiny hole at the end
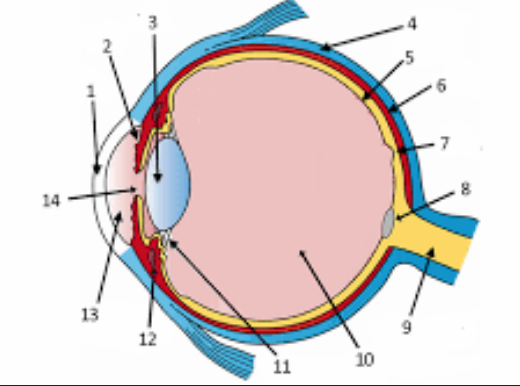
What is the spherical shape of the eye maintained by
sclera
aqueous and vitreous humors → create hydrostatic pressure to support the eye shape
list the outermost to innermost tissue layers of the eye
sclera and cornea
choroid, ciliary body, lens, iris
retina
Ancillary Structures
external structures but necessary for eye functioning
eyebrows and eyelids
conjunctiva - on the sclera and eyelid
transparent mucous membrane
lubricates eye surface
secretes lysozyme to destroy bacteria
Tears
produced by the lacrimal gland
consist of
water/salts
mucilage
oils
antibodies and lysozyme
drain into lacrimal canaliculi and lacrimal sac
surplus tears drain into nasal cavity
Sclera
outermost layer of the eye
opaque whitish-yellow appearence due to collagen fibres
protects, supports the eye
Cornea
transparent dome over iris
refracts light
aqueous humor behind it increases the refractive index
(angle light rays to retina for clearest image)
Iris
circular muscular diaphragm
controls the PUPIL
pigment over iris muscles determines eye color
separates the anterior and posterior aqueous humors.
Pupil
black due to absorption of light
opens/closes to let light in
opening in the iris
red pupil effect
when a bright light enters the eye and the light reflects off the choroid blood vessels inside
The Pupil Light Reflex
iris muscels are smooth muscles controlled by the autonmic nervous system
when the circular muscles contract
pupil contracts - allowing less light in
radial muscles contract
pupil dilates - allowing more light in
this is a reflex
Choroid
blood rich to supply retina
pigment cells absorb light - no reflection
WHY INSIDE THE EYE APPEARS DARK
Accommodation Structures
ciliary body - marks where sclera joins cornea
muscles + blood vessels
secretes aqueous humour
suspensory ligaments join ciliary body to lens
ciliary muscles
circular and longitudinal bring about lens accomodation
Lens accommodation
where the lens shifts its forward or backward so an image always forms on the retina
3 words for the lens + describe how lens focuses light
plastic, biconvex and transparent
focuses light via refraction
when object is far away the lens thins due to relaxation of ciliary muscles
when object is close lens becomes more rounded due to contraction of ciliary muscles
The Retina
composed of photoreceptor cells
Rods - which work best in dim light
Cones - which work best in high light intensity
Optic Disc
blind spot, neurons meet at the optic nerve to take information to the brain
Fovea
most sensitive spot due to a large number of cone cells
highest image clarity and sharpest image
Aqueous Humour
salt solution located behind the cornea which refracts light
secreted by ciliary body
drains into blood vessles via canal of schlemm
blockage of this canal causes glaucoma
Vitreous Humour
clear semi-solid gel
refracts light even more
supports eyeball via hydrostatic pressure
Layers of the retina
photoreceptor layer
rods and cones
embedded in the choroid, prevents light bouncing back
intermediate layer
bipolar neurons which connect the photoreceptor and internal surface layer
internal surface layer
ganglion cells
axon and dendrites of optic nerve
4 main parts of the rods and cones
Outer segment
photosensitive part - flattened membranous vesicles containing photosensitive pigments
transform light into a generator potential (graded pot - which results in an action p)
Constriction
cytoplasm constricts due to pinch in outer membrane
Inner Segment
nucleus, mitochondria needed for polysomes for protein sysntehsis (pigments and membranous vesicles) and energy
metabolically active part of the cell
Synaptic Region
connect bipolar neurons
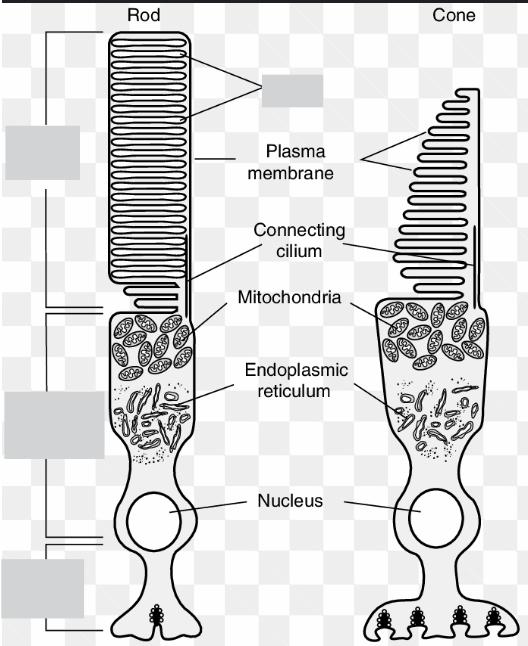
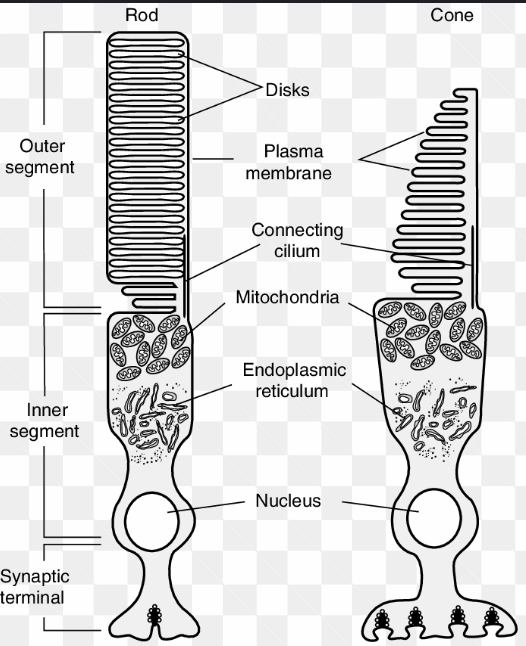
Main difference between Rods and Cones
Rods have multiple connections to bipolar neurons allowing for synaptic convergence
Cones only have one connection to each bipolar neuron - high visual acuity.
What cells help with image processing
Horizontal Cells and Amacrine cells help with image processing
Distinguish between rods and cones
rods | cones | |
convergence | visual acuity | |
work best in low light (scotopic vision) absent in fovea periphery of retina monchromatic vision | used for vision in bright light (photopic vision) concentrated in fovea center of retina trichromatic (Color) vision |
convergence
multiple rods are connected to a single bipolar neuron
this allows for summation of a generator potential
this makes the rods more sensitive to dim light - as summation will result in an action potential being generated
decreases visual acuity as the brain cannot tell which rod the signa came from producing a fuzzy image (in dim light shapes appear fuzzy)
Visual Acuity
related to the sharpness of vision
visual acuity is the ability to distinguish two or more stimuli of identical intensity as two distinct stimuli
cones have individual connections to bipolar neurons
the brain can tell exactly from which con the stimulus is coming from - each cone triggered is a separate stimulus
stimulus must be strong enough to generate a GP → AP
ONLY POSSIBLE IN BRIGHT LIGHT
THUS OBJECTS LOOK THE SHARPEST WHEN IN BRIGHT LIGHT AND DIRECTLY LOOKED AT (fovea)
Sensory Transduction
in the dark an inhibitory neurotransmitter called glutamate which prevents bipolar neurons from exciting the ganglion cells
then in the light glutamate is inhibited, hence the cell is no longer hyperpolarized
ganglion cells are excited and generate impulses leading to the brain
Rhodopsin
photosensitive pigment found in rods
made up of 11-cis retinal + opsin
in the light 11-cis retinal becomes all-trans retinal
As a result opsin bleaches (no longer fit)
Once released (bleached) opsin triggers a cascade in the cells causing Na+ channels to be inhibited
this causes a hyperpolarization
prevents the release of glutamate
How is a hyperpolarization achieved
in the dark there is a dark current
where na+ flows from the inner segment into the outer segment
in the presence of light → opsin is released
opsin causes cGMP(cyclic guanosine monophosphate) to change into GMP
cGMP keeps the Na+ channels open, while GMP closes them
the hyperpolarized membrane now no longer releases glutamate
bipolar neurons depolarize and generate an AP
generates AP in ganglion cells
sends impulse to brain
Cones in Humans
3 cones with different opsin molecules
S- cones → blue
M Cones → Green
L - Cones → Red
TRICHROMATIC VISION
most animals have dichromatic vision
sea turtles have extra cones so can see UV light aswell
Color Blindness
sex linked on the X-chromosome
deficiency of one or more cones causes this
most common is red-green
Nocturnal Vision - adapations
only rods and no cones
wide eyes - allow more light in
reduced eye movement (eyes are too big for their skull)
hence they have incredible neck rotation ability
larger pupils - let more light in
tapetum lucidium which reflects light back into the retina
spherical lens + wide cornea to increase refraction