Exam 1 Physiology IUPUI Dr. Fahim
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
160 Terms
Levels of organization
cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
Cells are classified into 4 groups:
neurons, muscle cells, epithelium, and connective tissue
neurons
Short and rapid communication, some can process information
neuron to brain length
long path
neuron to spinal cord length
short path
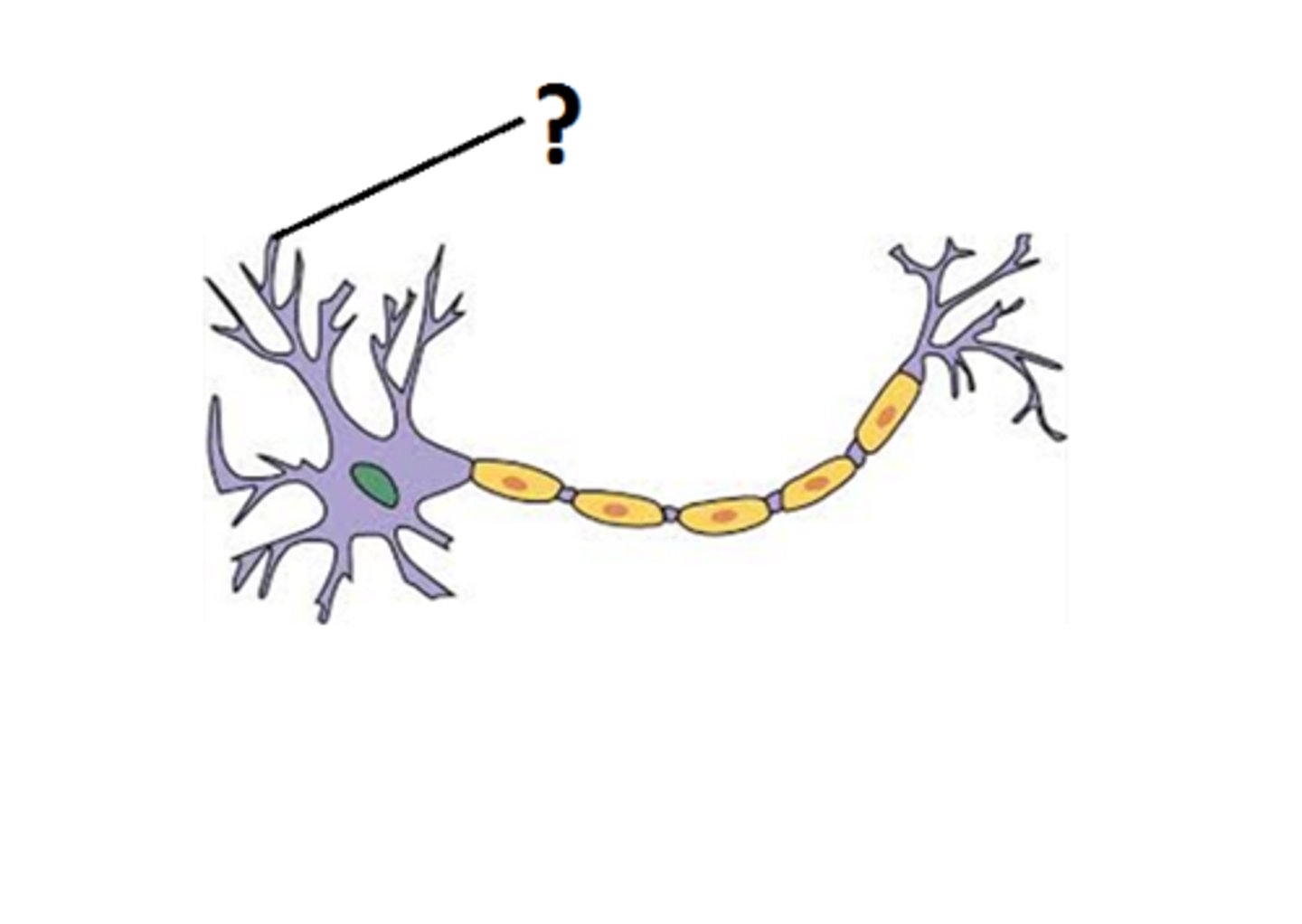
dendrites
recieve information
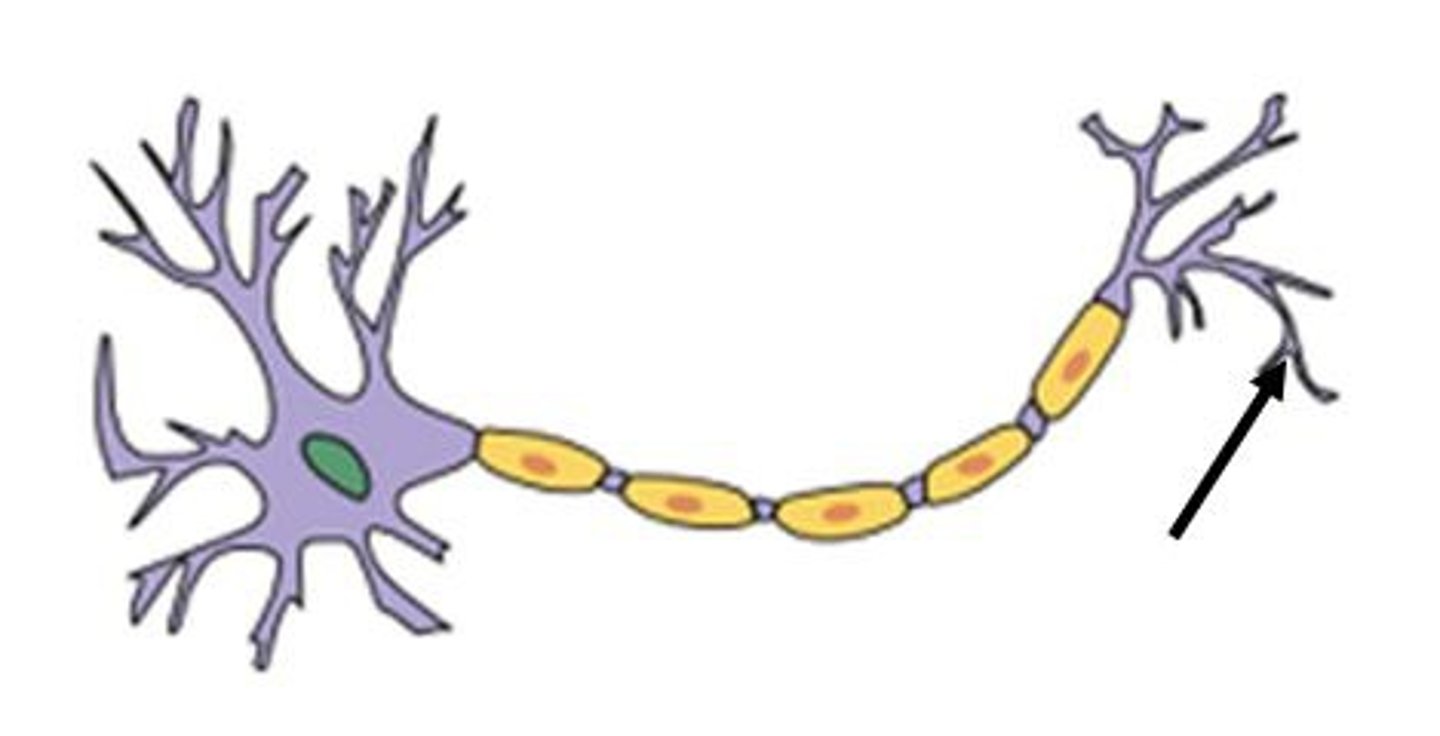
axon terminal
send information out
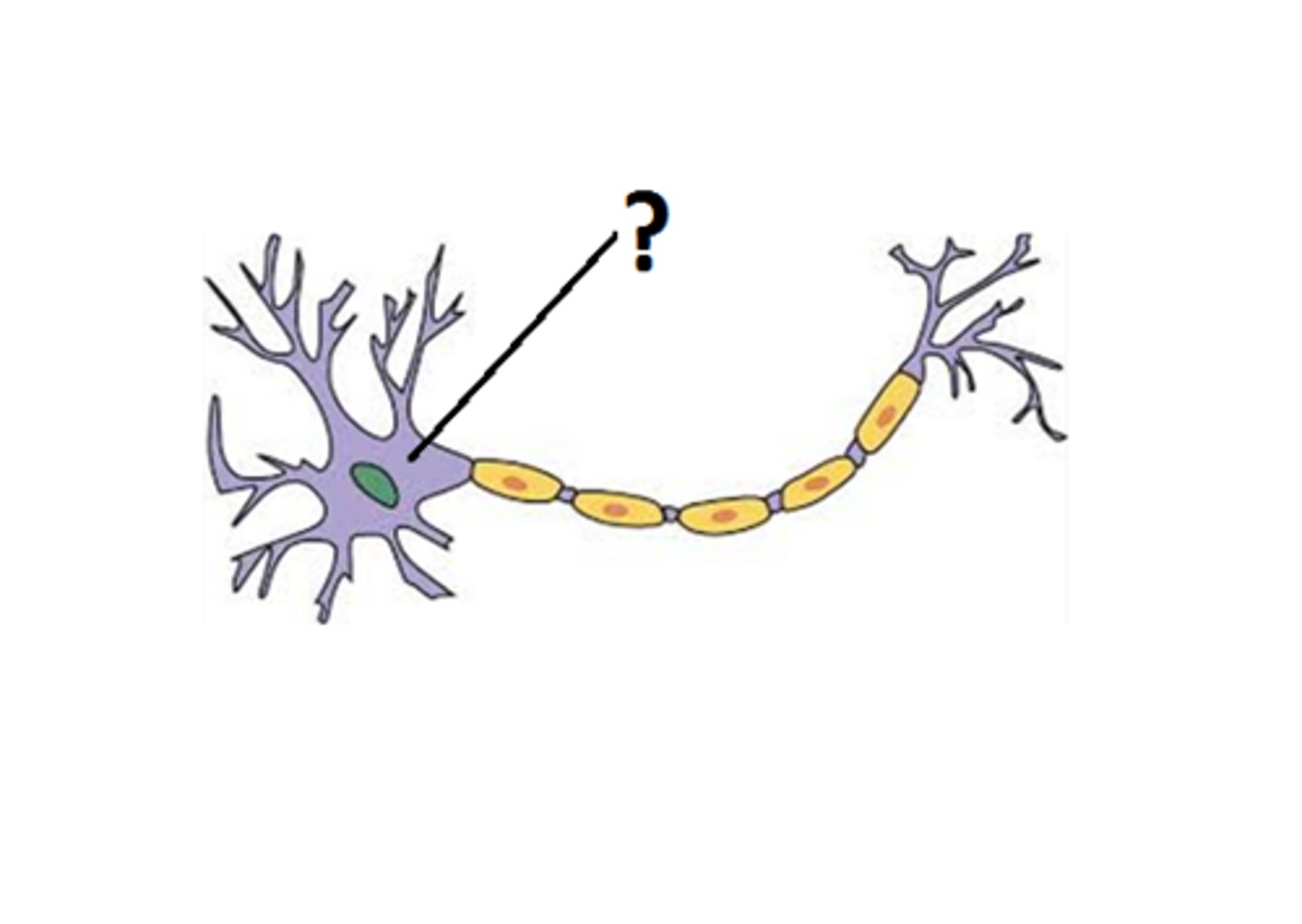
soma
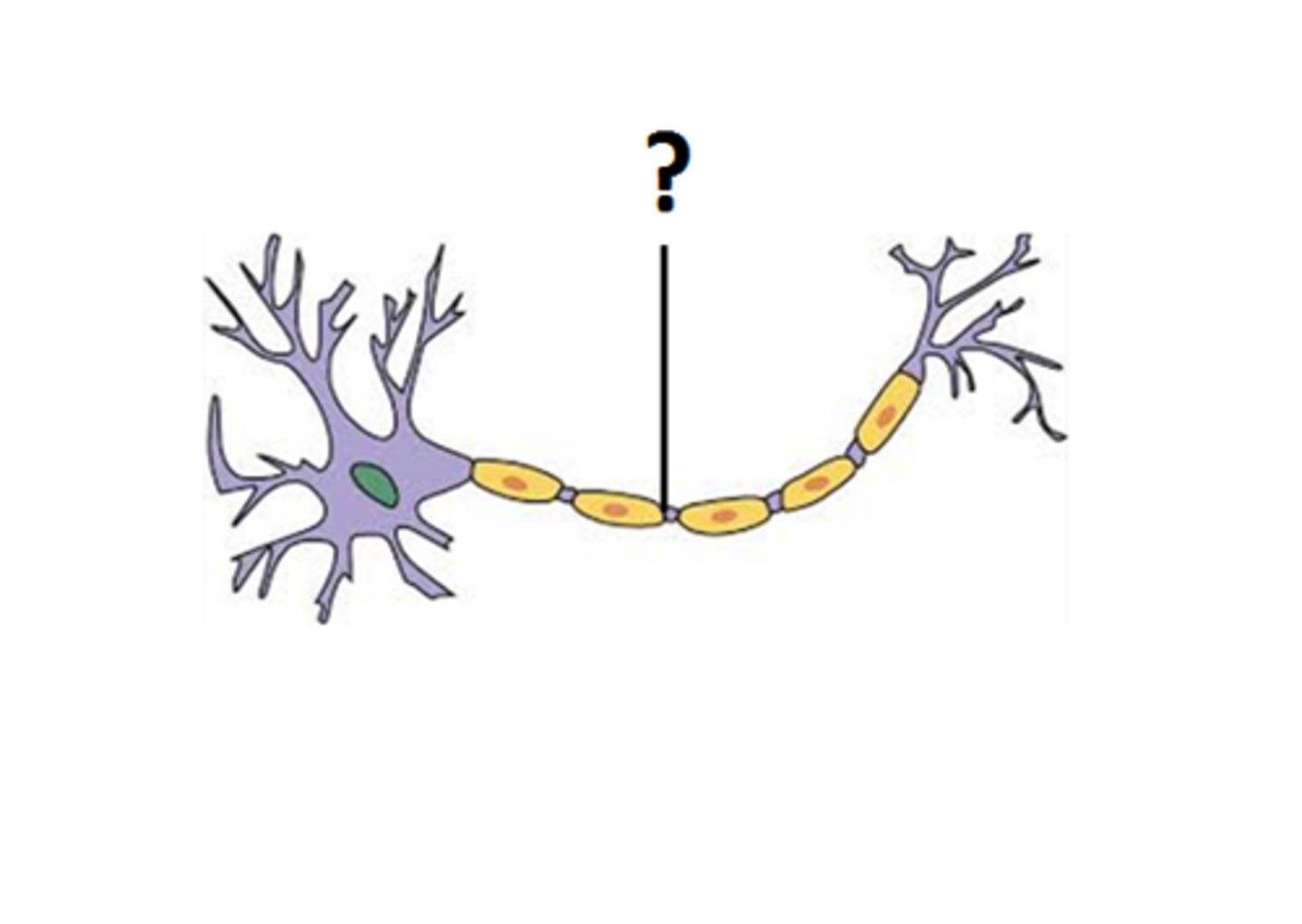
axon
muscle cells
specialized cells to contract
types of contraction
voluntary and involuntary
muscle types
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
skeletal is under control of
somatic nervous system
smooth and cardiac are under the control of
autonomic nervous system
epithelium
layer of cell which separates internal from external environment
when epithelium lines hollow organs or vessels it is called:
endothelium
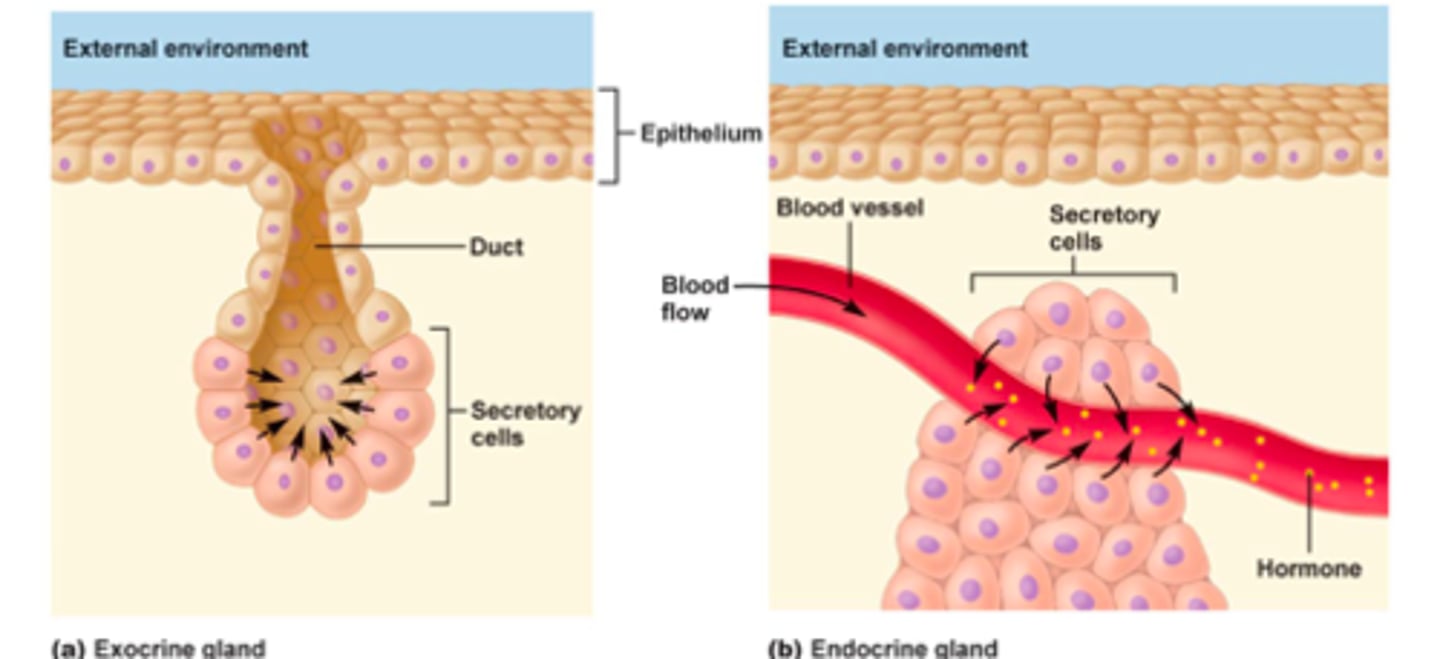
glands are formed by
epithelium
function of glands
to produce a product; exocrine: secrete things outside, endocrine: secrete product into blood.
connective tissue
characcterized by extracellular matrix, anchored or support things
interstitial fluid
surrounds all types of cell except blood cells
plasma
surrounds the blood cells
membranes are semipermeable
Allow some things to pass through when restricting others
what percent of your body weight is TBW?
60%
TBW (total body water) is consisted of
40% ICF, 20% ECF which is (80% interstitial fluid, 20% plasma)
homeostasis
maintaining a constant internal environment with a variable external environment. (ex. eat a dessert, BS high, your beta cells in the pancreas will secrete insulin which takes BS from blood and stores in cells, BS back to normal)
4 structures enabling homeostasis
receptors, integrating centers, effectors, signals
pathophysiology
when you disrupt homeostasis
regulated variable
aspect which is maintained (ex. blood glucose concentration)
Set point
most normal number (blood glucose is 100 mg, although this varies person to person)
error signal
difference between acceptable value and what it actually is
negative feedback
Stopping process because we reached baseline number (Ex. BS high, send info to pancreas, release insulin, insulin will store BS in cells, lower blood sugar, normal, tell STOP WE HAVE REACHED NORMAL)
Receptors
sensors that detect stimuli
thermoreceptors
temperature
chemoreceptors
ph of blood
baroreceptors
blood pressure
mechanoreceptors
vibration or movement
osmoreceptors
concentration
photoreceptors
light
integrating center
orchestrate an appropriate response
effector cells
responsible for body responses (Ex. muscles or glands)
signals
allows cells to communicate; afferent (going to the integrating sensor) and efferent (coming out of)
positive feedback
the change in the variable is reinforced, goes to completion. (ex. pituitary gland will secrete luitinizing hormone that will reach ovaries, increasing estrogen secretion. Release LH - increase estrogen. Release LH - increase estrogen. until egg is mature enough.)
All cells in the human body are derived from
fertilized ovum
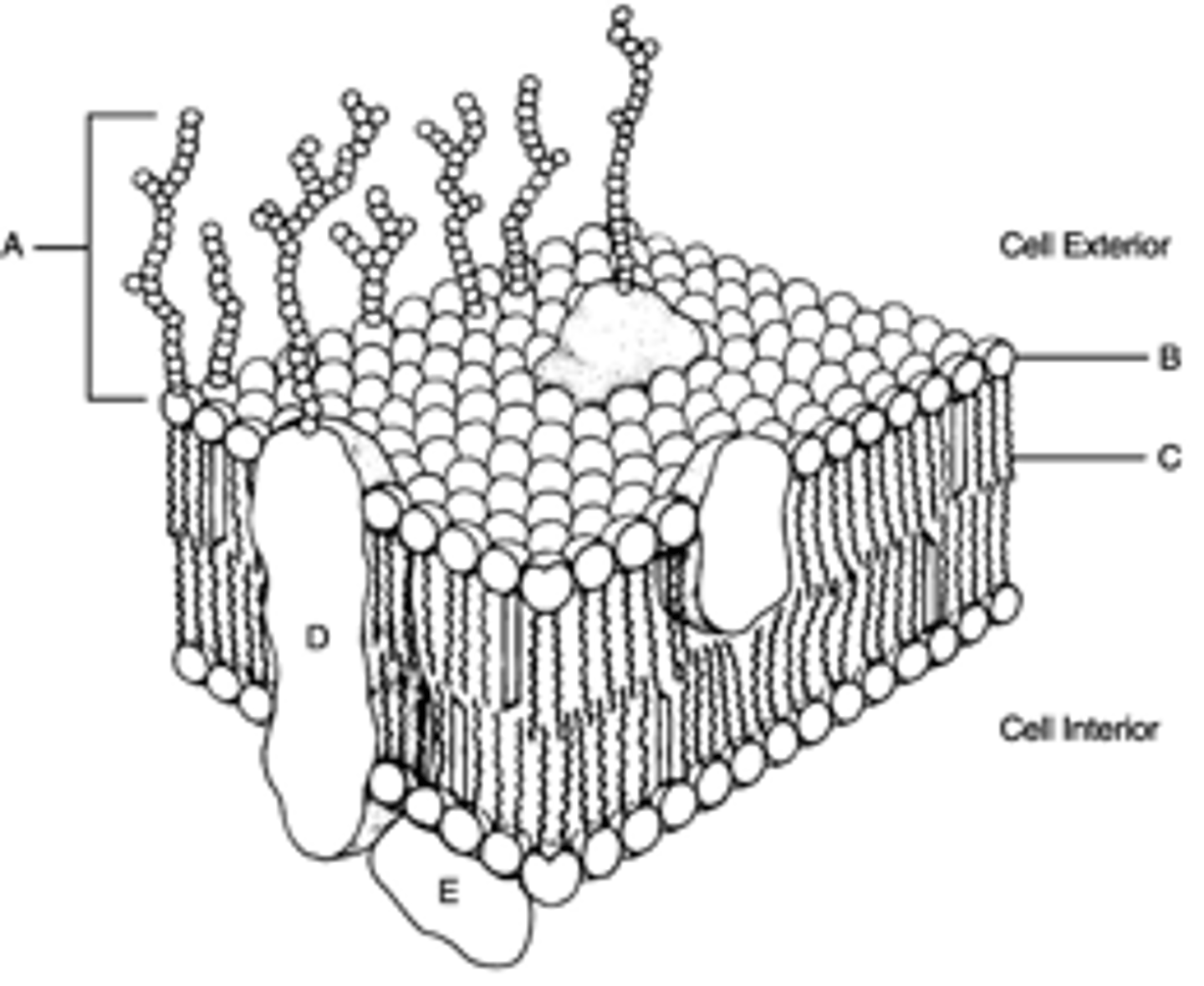
Plasma membrane
barrier between the cell and external environment. ECF: fluid outside cell, ICF: fluid inside cell
Plasma membrane fluid mosaic model includes
phospholipid bilayer, cholesterol, membrane proteins, and membrane carbohydrates.
amphipathic
Having both a hydrophilic side and a hydrophobic side
Lipid soluable =
nonpolar, lipophilic, and hydrophobic
easily move accross lipid bilayer
water soluable =
polar, lipophobic, hydrophilic
If a membrane is hydrophobic __ can pass through the membrane easily
lipids
covalently bound to membrane lipids or proteines are
glycoproteins and glycolipids, function cell recognition
Nucleus
transmission and expression of genetic information
Cytosol
Fluid portion of cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
fluid and organelles
Rough ER
ribosomes on surface; synthesis of proteins to be packaged into vesicles
Smooth ER
lipid synthesis, storage of calcium, detoxification through enzymes
___ of the rough and the smooth ER are connected
lumens
where are ribosomes made
nucleolus
golgi
packaging of proteins and direct them to their destination, post translational processing of proteins.
mitochondria
generates ATP
lysosomes
An organelle containing digestive enzymes, degrade extracellular debris through endocytosis and exocytosis.
peroxisomes
degrade certain waste molecules; contain enzyme called catalase. H2O2 -> H2O + O2
-ase
enzyme
ribosomes
rRNA and proteins, made up of two subunits, necessary for protein synthesis.
vaults
barrel-shaped organelles, may function in the transport of molecules between nucleus and cytoplasm. Important in apoptosis. possess vault RNA (vRNA).
centrioles
pared cylindrical structures, perpendicular to each other. Function in development of the mitotic spindle.
cytoskeleton
support and structure, transport of materials, suspension of organelles, formation of adhesions with other cells, contraction, and movement.
to be able to contract you must have
actin and myosin
microfilaments
7 nm diameter, common type is actin
intermediate filaments
10 nm diameter, common types myosin and keratin
microtubules
25 nm diameter, function as mitotic spindle and major component of cilia and flagella.
protein synthesis
Theres no ___ in RNA
thiamine. RNA has uracil but not thiamine.
transcription
DNA to pre mRNA, occurs in the nucleus
translation
mRNA to protein, occurs in the cytoplasm
Gene
portion of dna holding the genetic code
Triplet
a nucleotide sequence that codes for a specific amino acid, has 3 bases
a triplet is transcripted into a
codon, has 3 bases
initiation codon
for translation!!! not transcription. Where you START translation
-promotor sequence
splicing
the process of removing introns and reconnecting exons in a pre-mRNA (think introns=trash, want exons)
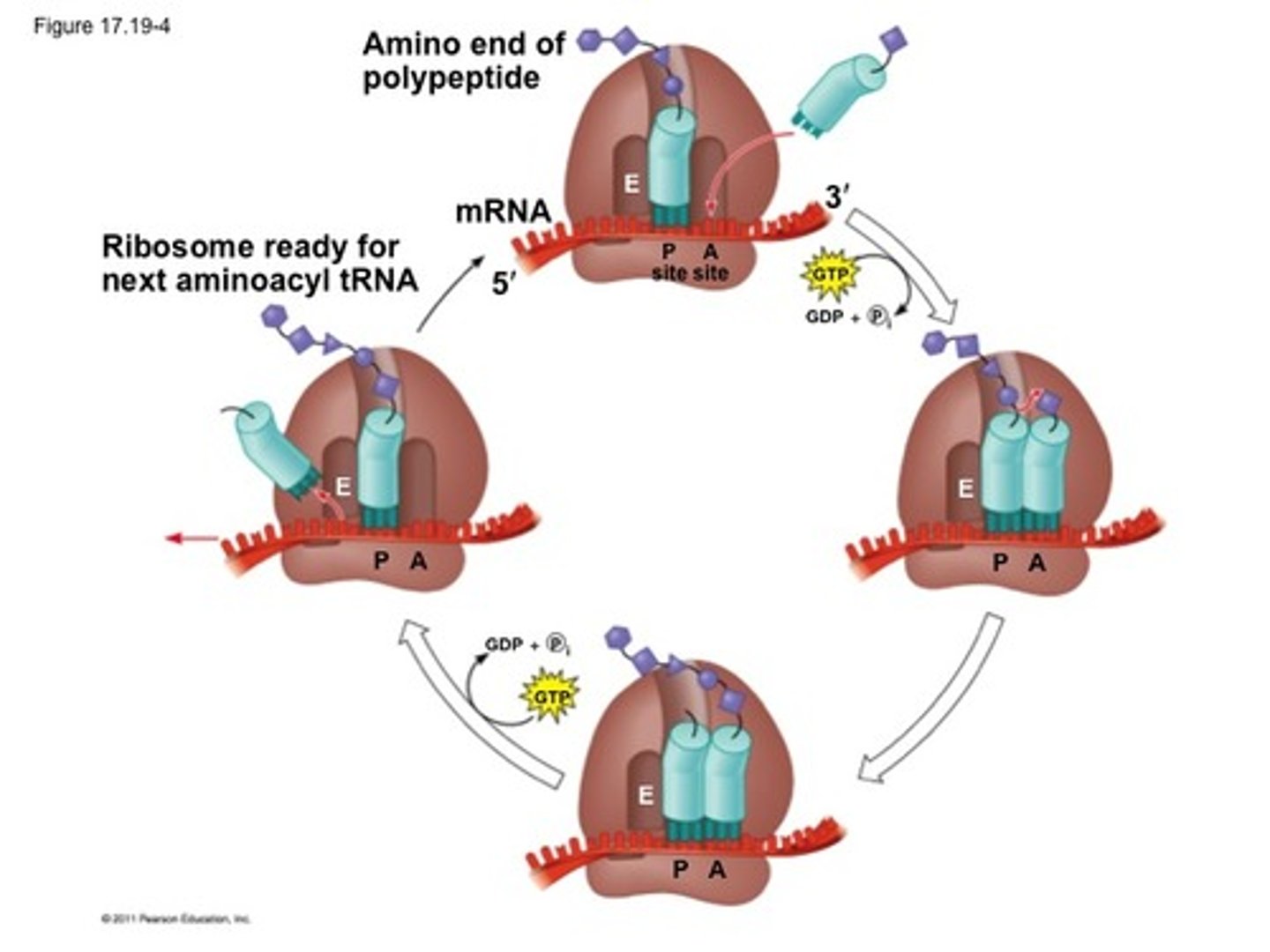
elongation
addition of amino acids to the polypeptide chain; continues until it reaches a stop codon
termination codon
One of the three codons (UAA, UAG, UGA) that signal the termination of translation of a polypeptide.
-terminator sequence
RNA polymerase
Enzyme similar to DNA polymerase that binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands during transcription
capping and poly a tail
protect from degrading, support
what codon starts translation
AUG (think "Are You Good?")
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
-Charged: amino acid bound
-Free: no amino acid bound
-two binding sites: P site, A site
P site
holds the tRNA with the LAST amino acid added to the polypeptide chain
A site
holds tRNA with the NEXT amino acid to be added to the polypeptide chain
post translational modification
changes made to polypeptides following translation
-folding
-cleavage
leader sequence
Leads the protein to where it should be then is removed. Can lead to the nucleus, peroxisome, or mitochondria.
post transcriptional modification
-splicing, removing introns
alternative splicing
Some exons are removed or joined in various combinations. (ex: 1-3-2, 2-1-3, 3-2-1)
protease
enzyme that degrades proteins
Proteasomes contain proteases
ubiquitin
Marks proteins for degradation, a chemical tag.
metabolism
the sum of all chemical reactions occurring in a cell
catabolic reactions
break down molecules
Anabolic reactions
build molecules
Is hydrolysis catabolic or anabolic?
Ex) sucrose + H20 -> glucose + fructose
Catabolic
is condensation anabolic or catabolic?
Ex) glucose + fructose -> sucrose + H2O
anabolic
Is this reaction phosphorylation or dephosphorylation? Anabolic or catabolic?
ADP + Pi -> ATP + H2O
phosphorylation, anabolic
Is this reaction phosphorylation or dephosphorylation? Anabolic or catabolic?
ATP + H2O -> ADP + Pi
dephosphorylation, catabolic