oral exam high yield stuff
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
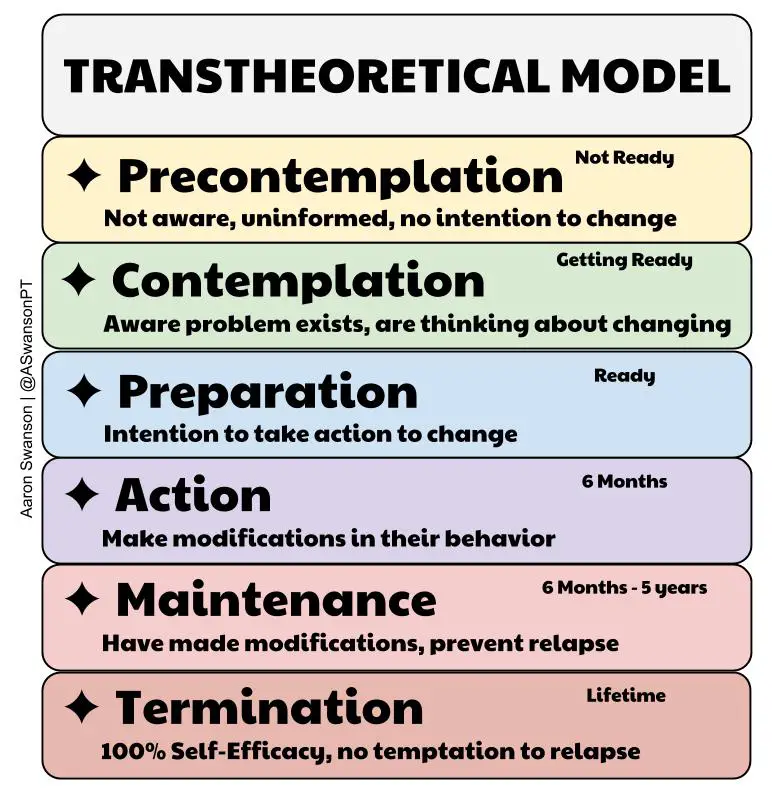
What is the trans-theoretical model?
"stages of change"- individuals move through a series of predictable stages when changing a behavior (i.e quitting smoking)
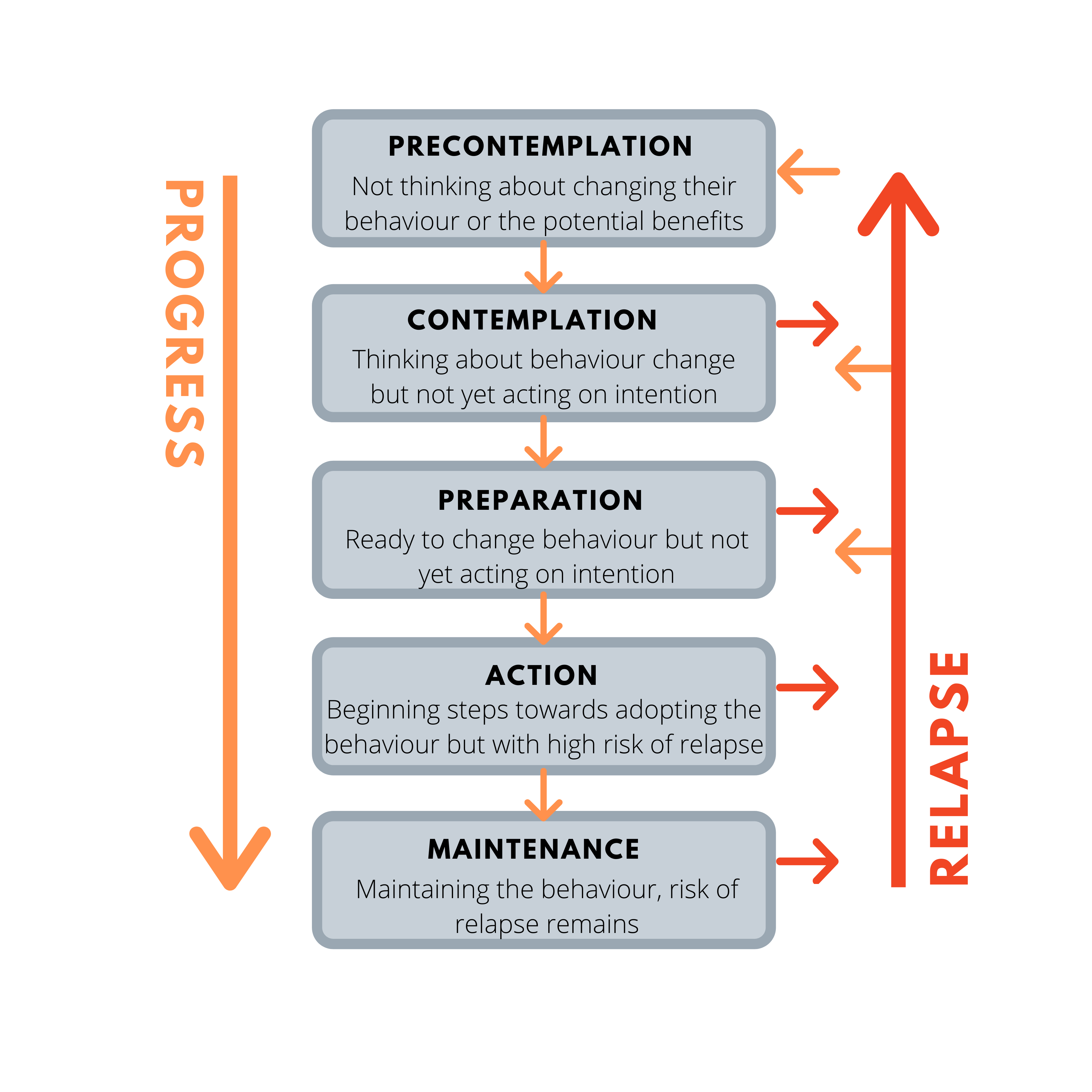
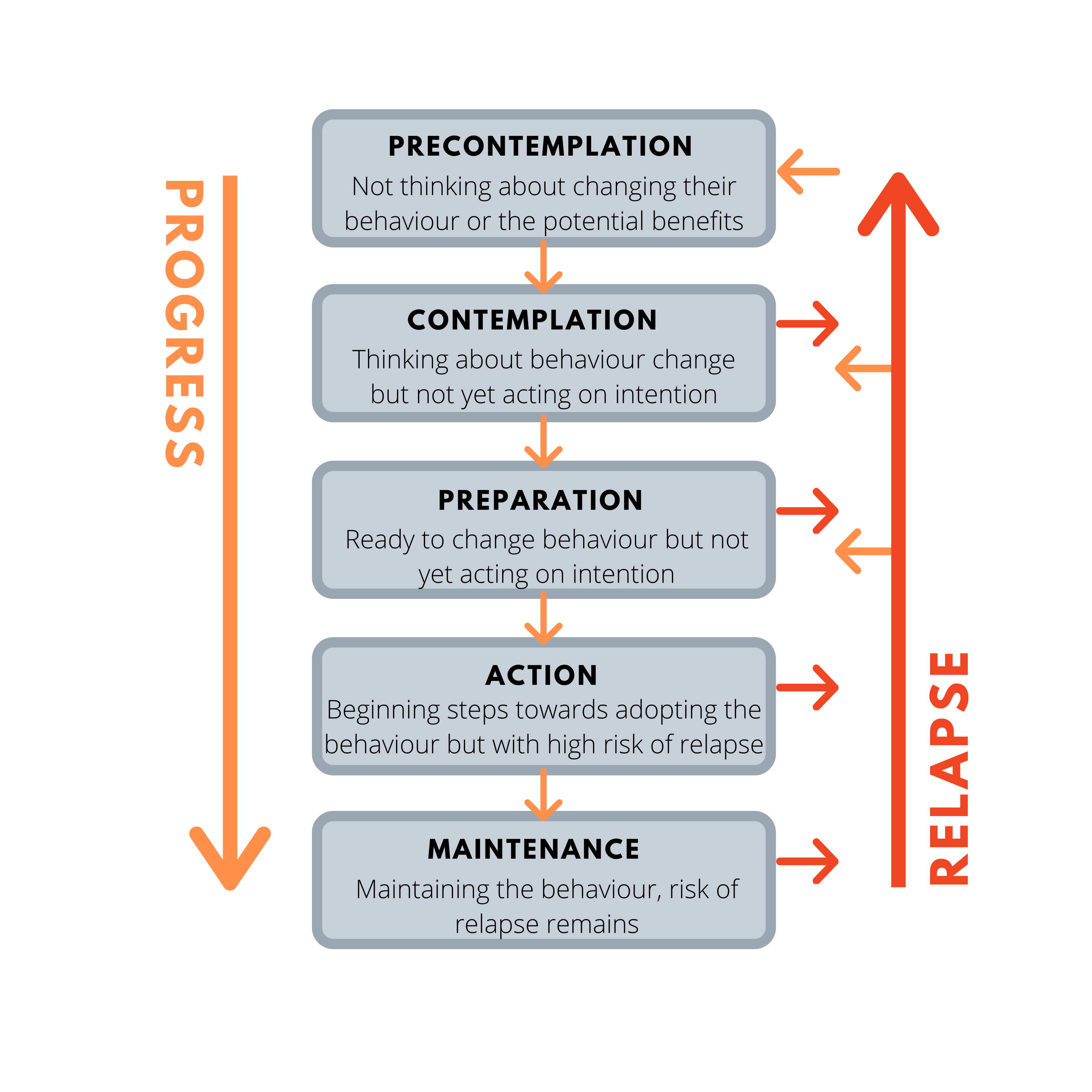
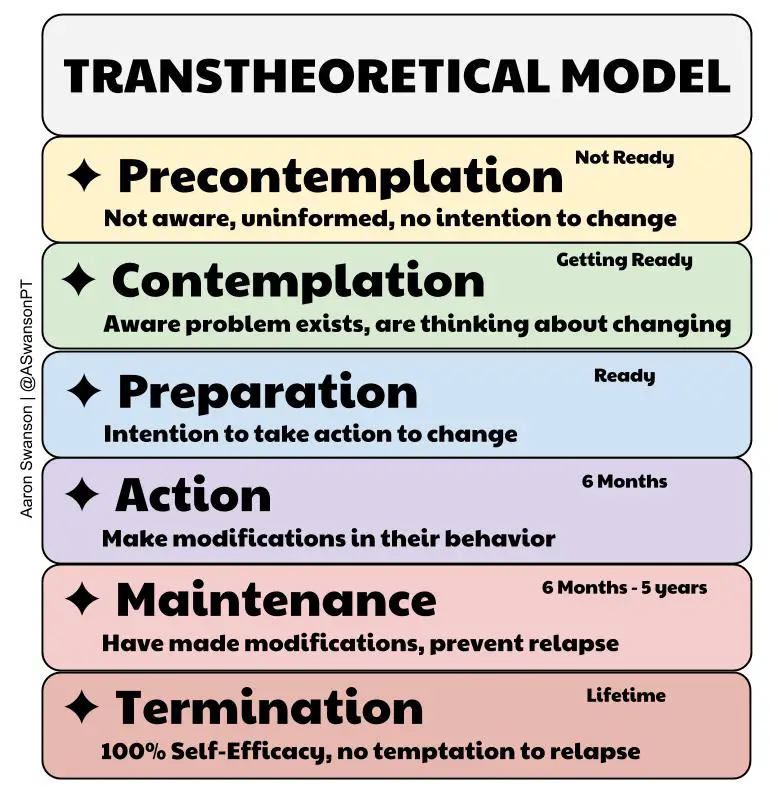
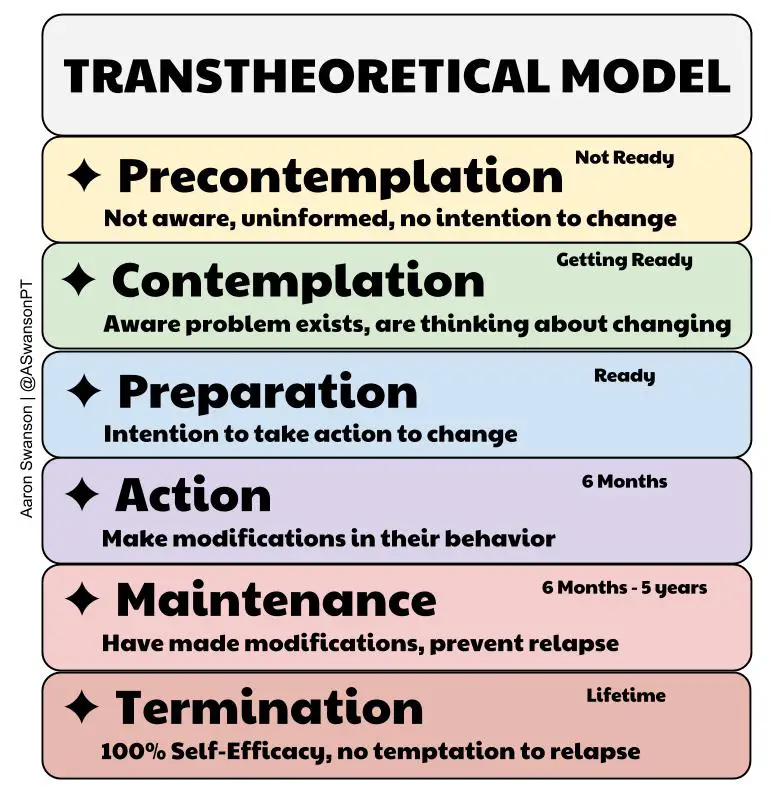
What are the stages of change seen in the trans-theoretical model?
1, pre-contemplative
2. contemplative
3. preparation
4. action
5. maintenance of change
6. relapse
What is the pre-contemplative stage?
consider change or unaware of how behavior affects health; not intending on taking action in foreseeable future
ex/ not aware smoking is a problem
What is the contemplative stage?
more aware; starting to think about initial change
ex/ know smoker's a problem and want to change
What is the preparation stage?
seriously thinking about the change; date is set
ex/ making plans and changing things to prepare to stop smoking
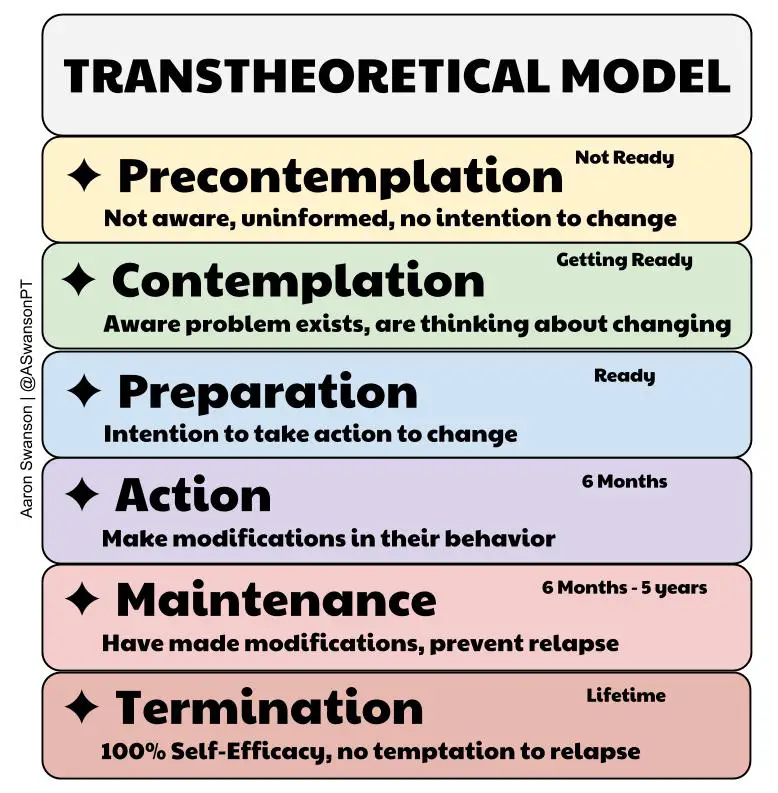
What is the action stage?
making change in or stopping the target behavior within a given time period and intending to continue with change
ex/ stopping smokers
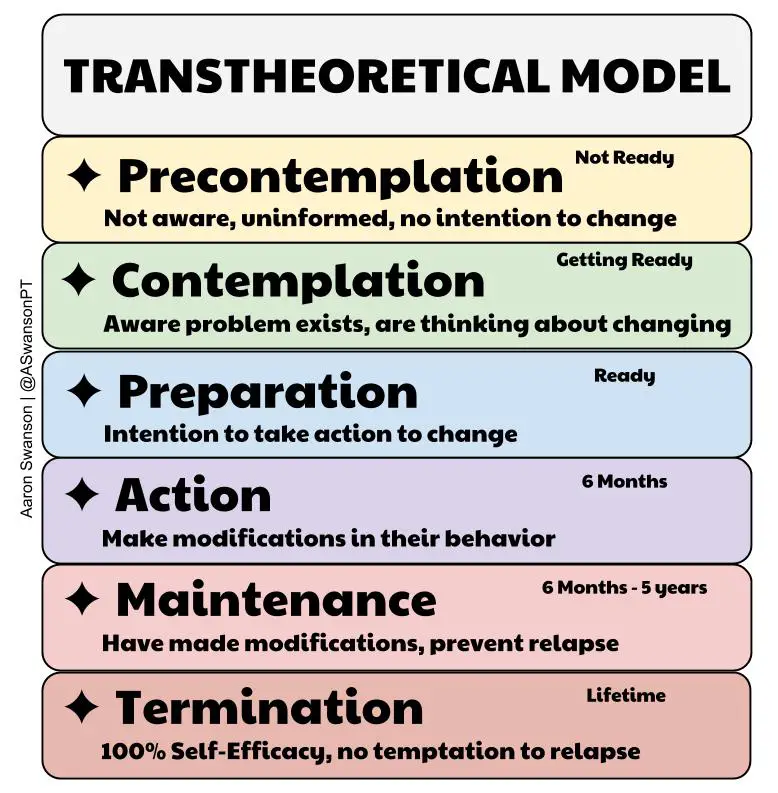
What is the maintenance of change stage?
maintaining target behavior change for more than given time period
ex/ continuing to not smoke
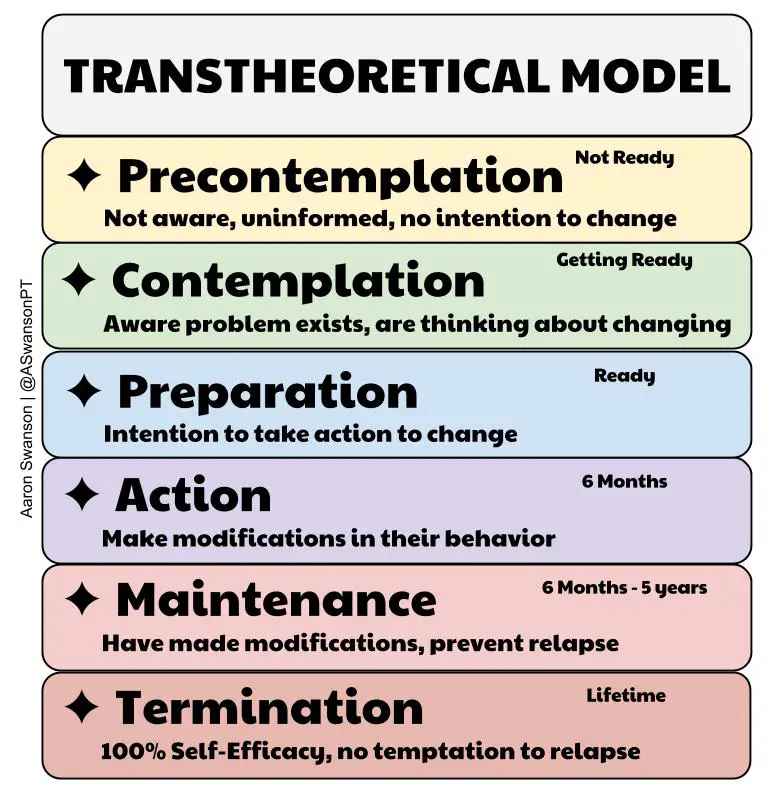
What is the relapse phase?
cessation of behavioral changes; patient reverts to old behavior
An individual will adopt healthy behaviors if they believe what 3 things?
1. the behavior creates a serious health problem
2. they are personally susceptible to the health harm
3. changing their behaviors would help and face no significant barriers to doing so
What is the social cognitive theory?
- emphasized importance of intervening thought processes and the importance of self control for the performance of behavior
- modeling (observational learning)
self efficacy: both outcome and efficacy expectations are critical to behavior change (empower the patient)
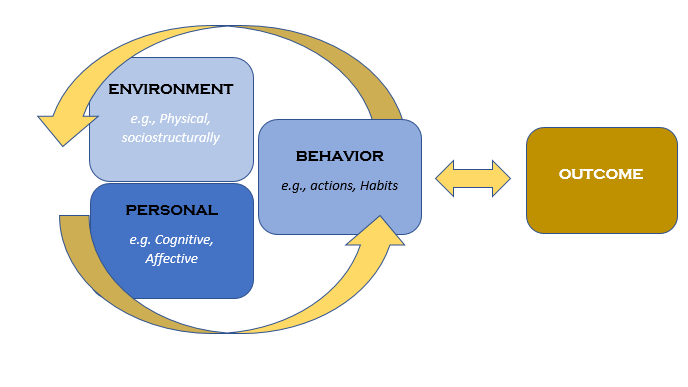
What are the 5 A's of health behavior counseling (ex/ smoking cessation)?
1. Ask (about tobacco use)
2. Advise (to quit)
3. Assess (if they are willing to make an attempt to quit)
4. Assist (based on where they are at)
5. Arrange follow up
What is motivational interviewing?
patient centered communication that empower change by utilizing language that motivates patients to change their unhealthy behaviors and habits for better outcomes
What are the 5 principles of motivational interviewing?
1. resist "righting reflex"
2. express empathy
3. develop discrepancy
4. roll with resistance
5. support self-efficacy

What is change talk? What are the components of it?
patient uses language that is an argument for change
Desire
Ability
Reason
Need
Commitment
Activation
Taking steps

What is OARS? What does it stand for?
4 core motivational interviewing skills!
open ended questions
affirmations
reflective listening
summaries

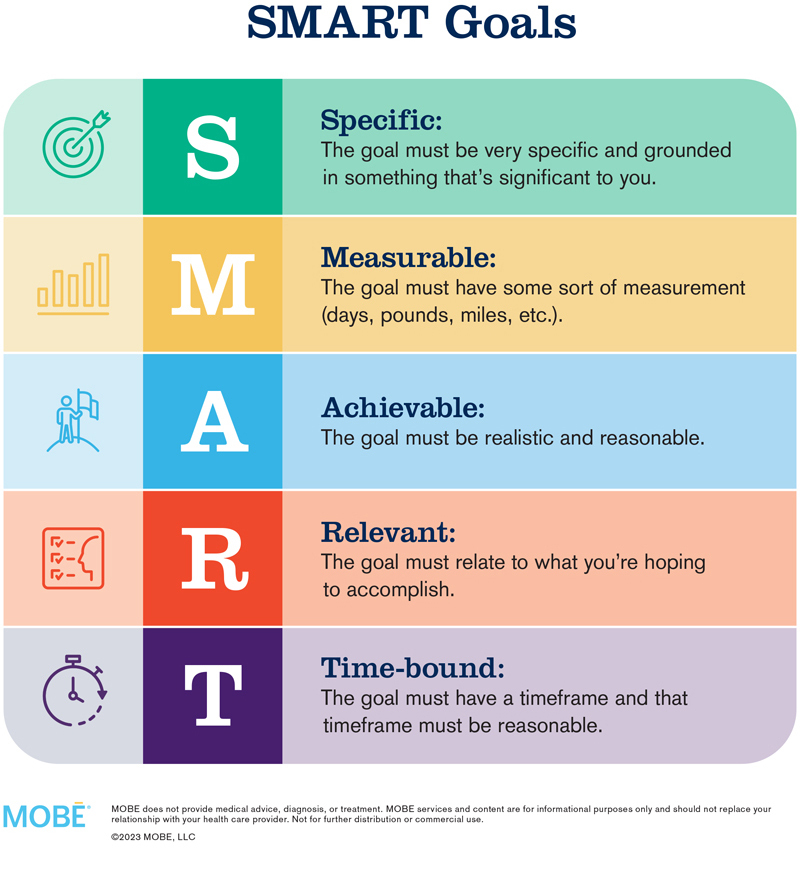
What are SMART goals?
Specific
Measurable
Attainable
Realistic
Timely
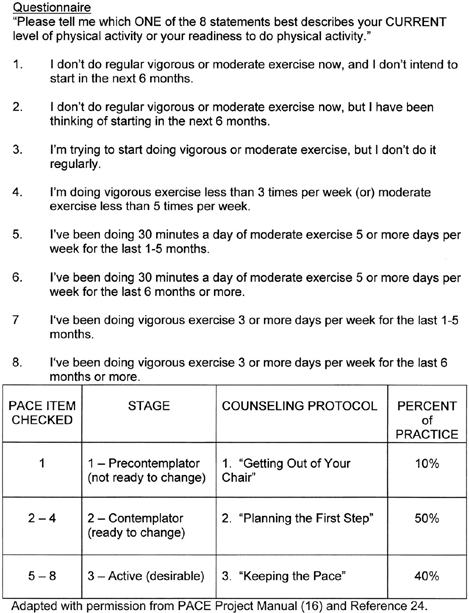
What is PACE? What does it stand for?
questionnaire for patients to help physicians understand how to counsel patients on increasing physical activity...meet them where they're at!
Patient centered
Assessment and..
Counseling for...
Exercise
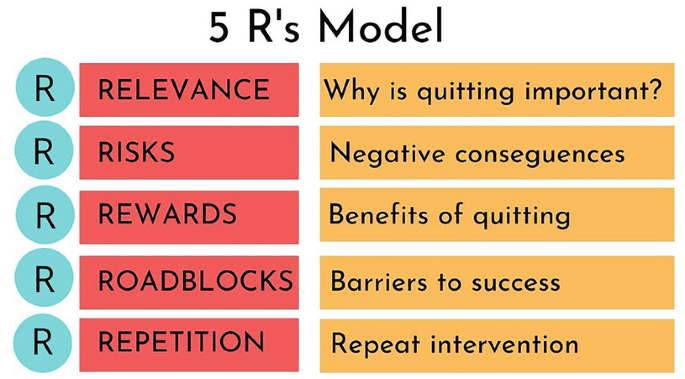
What are the 5 R's designed to motivate smokers to consider attempting to quit?
1. Relevance (why is quitting personally relevant)
2. Risk (identify potential negative consequences of not quitting)
3. Rewards (identify potential positives of quitting)
4. Roadblocks (identify barriers or impediments to quitting and brainstorm how to address)
5. Rate- how important is it to quit? How confident are you that you can quit?
What is CAGE (hint used in the situation of alcohol/drug abuse)?
1. Cut down: have you ever felt you should cut down on your drinking?
2. Annoyed: have people annoyed you by criticizing your drinking or drug use?
3. Guilty: have you ever felt bad or guilty about your drinking?
4. Eye opener: have you ever had a drink first thing in the morning to steady your nerves or get rid of a hangover (eye opener as in as soon as you open your eyes in the morning)
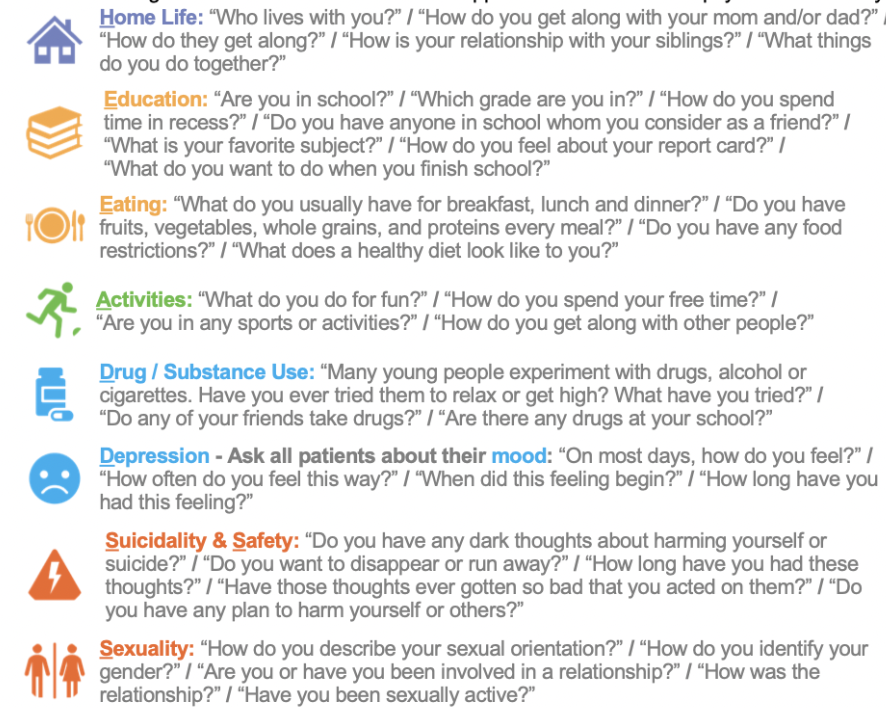
What is HEADSS?
1. Home: safety, own room, relationships, who you live with
2. Education/Employment: fav. subject, detention, future plans
3. Activities: sports, TV, hangout with friends, couch potato
4. Drugs: friends, do you know what they are, parents use
5. Sexuality: orientation, crushes, any past experiences
6. Suicide/Depression: how are you sleeping, appetite, feelings of boredom or sadness
***RF for suicide: death of caregiver, divorce, family hx, abuse, mobility geographically, etc. (SADPERSONS)
What is the SAFE model screening tool for intimate partner violence?
S: stress and safety
A: afraid or abused
F: friend or family awareness
E: emergency escape plan
The principles of biomedical ethic includes having respect for what 4 things?
1. autonomy: self determination and a right to control one's own body, requires being informed and free of coercion
2. non-maleficence: refrain from causing harm (a negative duty)
3. beneficence: promote and contribute to a person's welfare (positive duty)
4. justice: fair, equitable, and appropriate distribution of benefits and norms
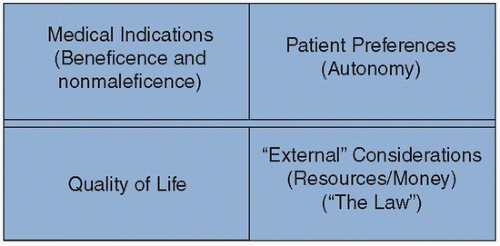
What are the components of the 4 box method of ethical analysis?
1. medical indications
- beneficence and nonmaleficence
- noting specific clinical findings, diagnoses, prognoses, and clinical questions that need to be addressed
2. patient preferences
- respect for autonomy
- capacity, oral and written advance directives
3. quality of life
- honoring beneficence, nonmaleficence, and respect for autonomy
- how will the clinical decision impact the function and quality of the patient's life
4. contextual features of the case
- honoring justice
- i.e. religious, cultural, legal, and financial issues
What is virtue ethics?
what a virtuous person would do in the situation
Who do you want to be? What does it mean to be a good person?
What are the 4 divides between clinicians and patients?
1. relation to mortality
- everyone only experiences death once
- death can only be apprehended
- providers encounter death more (more sensitized to death than the general public)
2. context of illness
- clinicians view illnesses through the lens of disease and biological processes
- patients view illnesses through lens of their full life stories
3. beliefs about disease causality
- patient ideas about what illness can differ widely (sometimes do not know what is relevant to their situation)
- providers focus upon pathophysiology that patients may not understand
4. shame, blame, and fear
- embarrassment leads to details being withheld
- patients blame themselves and providers
- providers blame themselves and patients
- patients fear death, providers fear being wrong/sued
What are the 4 R's of an effective apology?
1. recognition: acknowledge the error
2. responsibility: accept responsibility
3. regret: offer with sincerity
4. remedy: commit to doing better in the future
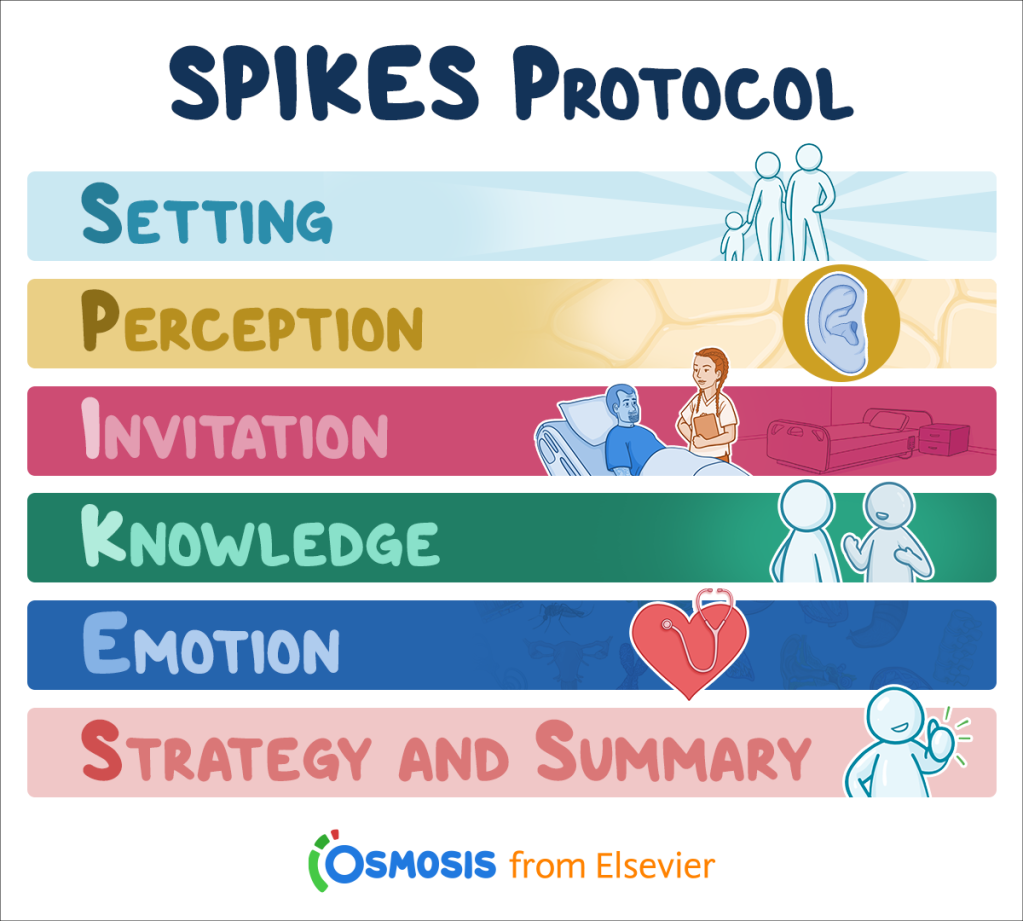
What is the SPIKES protocol?
1. Setting: choose a comfortable setting
2. Perception: asses how much they know/understand about their condition
3. Invitation: obtain the patient's permission to talk about the topic
4. Knowledge: give information to the patient, avoid jargon, and confirm understanding
5. Explore emotions: identify emotion being expresses and empathize
6. Summarize: summarize the information given and received; outline next steps and set time to follow up
When do you use the SPIKES protocol?
- sharing difficult test results
- life changing diagnosis
- introducing transitions in care
- cancer recurrence
- times you are concerned the new info will elicit strong emotions
What is an advanced directive? What is the importance of it?
legal document prepared by a living, competent adult to provide guidance to the healthcare team if the individual should become unable to make decision regarding his or her medical care
Importance: empowers the patient to exercise their goals of care
What is a medical power of attorney?
legal document signed by a person who is giving another individual the power to make healthcare decisions for the first person if he or she becomes incompetent, unconscious, or unable to make decisions for himself or herself
What is a living will?
designate choices in case of terminal or irreversible condition
doesn't account for contingencies
What are the 4 C's of culture?
1. What do you CALL your problem?
2. What do you think CAUSED your problem?
-this gets to the source of the problem
3. How do you COPE with your condition?
4. What are your CONCERNS about the condition/tx?
-it is important to understand the patient's perception, fears, and you can address concerns and correct misconceptions
What is the method for countering microaggressions as a recipient?
Recipient= ACTION
A= ask a clarifying question to assist with understanding intentions
C= come from curiosity not judgment
T= tell what you observed as problematic in a factual manner
I= impact exploration (discuss the impact of the statement on you and others)
O= own thoughts and feelings around the situation
N= next steps
What is the method for countering microaggressions as a bystander?
Bystander= ARISE
A= awareness of microaggressions
R= respond with empathy
I= injury of facts
S= Statements that start with "I"
E= educate and engage
What is the method for countering microaggressions as a source?
Source= ASSIST
A= acknowledge your bias
S= seek feedback
S= say you are sorry
I= impact, not intent
S= say...
T= thank you
What is redlining?
refusing someone because they live in an area deemed to be poor
ex/ after WWII banks excluded communities from mortgage lending because they were considered "financially risky" communities
What is reverse redlining?
offering unjust credit terms to a certain neighborhood/ racial group
ex/ targeting black and brown communities with subprime mortgages
What is gerrymandering?
redrawing of electoral district boundaries to favor the political party in power
What is the tool used to take charge of mitigating your own bias?
CHARGE^2
C: change your context- is there another perspective that is possible?
H: be honest- with yourself, acknowledge and be aware
A: avoid blaming yourself- know that you can do something about it
R: realize when you need to slow down
G: get to know people you perceive as different from you
E: engage- remember why you are doing this
E: empower- your patients and peers
What is the FICA spiritual assessment tool?
- Faith and belief: Do you have spiritual beliefs that help you cope with stress? If no, ask what gives your life meaning?
- Importance: Have your beliefs influenced how you take care of yourselves and others?
- Community: Are you part of a spiritual or religious community?
- Address in care: How would you like me to address these issues in your health care?
What is the HOPE spiritual assessment tool?
H- sources of hope:
+ What are your sources of hope, strength, comfort, and peace?
O- organized religion:
+ Are you part of a religious or spiritual community?
+ Does it help you? How?
P- personal spirituality and practices:
+ Do you have personal spiritual beliefs?
+ What aspects of your spirituality or spiritual practices do you find most helpful?
E- effects on medical care and end of life issues:
+ Does your current situation affect your ability to do things that usually help you spiritually?
+ As a doctor, is there anything that I can do to help you access the resources that usually help you?
+ Are there any specific practices or restrictions I should know about in providing your medical care?
+ If the patient is dying: How do you beliefs affect the kind of medical care you would like me to provide over the next few days/weeks/months?