Nutrition Final - All Units
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
Define “health”
State of complete physical, social, and mental wellbeing. Not merely the absence of disease.
Define “nutrients”
Essential substances your body needs in order to grow and stay healthy
Six categories of nutrients
Carbs
Protein
Minerals
Vitamins
Lipids/fats
Water
Define the functions of nutrients
Energetic - Provide energy (carbs/lipids)
Plastic - Form and maintain structures within the body (protein)
Regulatory - Regulate metabolic processes (minerals and vitamins, hormones/enzymes)
Define “metabolism”
Set of chemical reactions that take place in the different cells of living beings and from which they obtain energy and synthesize the substances they need.
Four components of diet
Availability
Selection
Appetite
Nutritional Needs
What are essential nutrients?
These cannot be synthesized internally/in sufficient quantities, so we must get them through our diet.
Ex: Macronutrients and micronutrients needed to survive. Vitamin C, A, etc.
What are non essential nutrients?
These can be generated by the body, and also absorbed through food.
Ex: Vitamin D, biotin.
What factors influence when we eat?
Hunger (physiological factor)
Appetite (psychological factor)
Meal time (sociological factor)
Factors to when we stop eating
Satiation - Psychological and physiological factors. Perception of food as well as stomach volume.
Satiety - The feeling of fullness that continues after eating
Factors that influence why we eat what we eat
Personal preference
Habit
Tradition
Social interactions
Availability, convenience, economy
Positive and negative associations with food
Emotional comfort
Values
Body weight and image
Nutrition and health benefits
Organs that influence eating behavior?
Hypothalamus - Maintain homeostasis. Hunger and thirst, body temp both controlled by this organ.
Pituitary gland - Controls growth hormone, consumption of nutrients impacts the effectiveness of this gland
Pancreas - Secretes insulin and inhibits hunger
Upper small bowel - inhibit hugner
Colon - Peptide 5, this organ stimulates hunger
Lower small bowel - Inhibit hunger
Fat cells - Inhibits hunger
Stomach - Ghrelin, stimulates hunger
Define “nutrients” (unit 3)
Substances with a defined chemical structure contained in food/beverages that are essential for the health and activity of the body since they provide energy, form and maintain structures, and regulate metabolic processes of the organism.
Function and sources of carbohydrates
Carbs used for energy. Found in cereals, potatoes and other starchy root vegetables.
Function and sources of protein
Protein helps build and maintain structures within the body. Protein is found through meats, plant based sources such as legumes, eggs, etc.
Digestive process of carbohydrates
Mouth - Amylase found in saliva starts breaking carbs into small polysaccharides
Stomach - Stomach acid inactivates amylase
Small intestine - Continue breaking down polysaccharides
Digestion of fiber
Mouth - Fiber crushed
Stomach - Fiber delays gastric emptying
Small intestine - Fiber not digested, delays absorption of other nutrients
Large intestine - Bacteria ferments certain fibers, fiber attracts water, binds to cholesterol and bile to carry it out of the body
Protein digestion
Stomach - Pepsin breaks down protein into smaller polypeptides
Small intestine - Enzymes from pancreas break down proteins further. Enzymes from epithelium break down small polypeptides into amino acids.
Fat/lipids digestion
Small intestine - Lipase from pancreas breaks down lipids into glycerol, fatty acids, and monoglycerides
Definition of fibers
Indigestible carbohydrates from plants that regulate digestive health, nutrient absorption, promote feeling of fullness, lower cholesterol, etc.
Insoluble fiber is found in cereals with fiber, whole grain, brussel sprouts, legumes.
Soluble fiber found in oats, barley, fruits like strawberries/raspberries, carrots, etc.
Define “vitamins”
Organic compounds essential for the maintenance of normal metabolic functions and growth. Classified into water soluble and fat soluble groups. The human organism is unable to synthesize them.
Fat soluble vitamins
Vitamins:
A - Retinol
D2/D3
E
K1
Must be ingested with fats, held in fatty tissues and liver until needed.
Vitamin A functions
Vision process
Protein synthesis and cell differentiation in epithelial tissue
Reproduction
Growth of bones
Deficiency increases risk of infectious disease
Orange, squash, carrots, pumpkin, spinach, liver
Vitamin D
Non essential, synthesized in the presence of sunlight
Bone growth
Immunity, CNS, skin, muscle and reproductive organs
Deficiency in children causes bone malformations, in adults leads to osteoporosis and osteomalacia
Excess leads to kidney stones and hardening of blood vessels
Fish, eggs, liver, mushrooms
Vitamin E
Formation of erythrocytes, muscles, and other tissues
Main function as an antioxidant
Needed to form male sex cells
Deficiency leads to destruction of red blood cells (anemia), muscle degeneration, and reproductive disorders
Many fruits and vegetables
Vitamin K
Essential for blood clotting
Non essential vitamin
Bone building
Very rare to have a deficiency, usually caused by drugs
Found in egg yolks, liver, leafy green vegetables
Water soluble vitamins
Vitamin C
B1
B2
B3
B5
B6
B8
B9
B12
Vitamin C
Antioxidant
Growth and maintenance of gums, blood vessels, bones, and teeth
Role in immunity
Deficiency leads to scurvy
Found in many fruits and vegetable s
Vitamin B
These work together in energy metabolism. Several form part of the coenzymes that assist enzymes in release of energy from macronutrients.
Define “slow carbs”
Better for blood sugar control than simple carbs
Low glycemic index
Complex carbs
Examples include whole grain products, legumes, fruits, starchy vegetables including squash and sweet potatoe
Define “fast carbs”
Simple carbs
White flour products
Flavored yoghurts
Fruit juices, sodas, snacks etc
Define “minerals”
Inorganic elements that always retain their chemical structure. Cannot be destroyed by heat or acid. In some cases the presence of minerals effect the absorption/metabolism/excretion of another one.
Health effects of starch and fibers on diabetes?
Whole grains reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. Soluble fibers trap nutrients and delay their transit through the GI tract so glucose absorption is slowed.
Relevance of GI index to diabetics?
Diabetics need to pay attention to their blood sugar, when the glycemic index spikes so does the blood sugar. Fast carbs raise blood sugar, slow carbs prevent these spikes.
Define “glycemic index”
Value that indicates the rate of elevation of blood glucose after the consumption of a food containing carbohydrates, and expressed as a percentage.
Importance of omega 3
These are essential fats that the body cannot make on its own. They have an antioxidant effect and lower cardiovascular risk.
What is the “biological value” of a protein?
Biological value depends on digestibility and essential amino acid component. Digestibility depends on the source of protein and other foods eaten with it. Animal proteins are the highest. Essential amino acid content, the dietary protein must supply 9 essential amino acids. For protein synthesis to take place essential amino acids have to be present at the same time in sufficient quantities.
How to create a “complex protein”?
To create complex protein nutrition, combine "incomplete" plant-based proteins (grains, legumes, nuts, seeds) to get all essential amino acids, like pairing beans with rice, nut butter on whole-grain bread, or hummus with pita; or simply eat a varied diet of animal sources (meat, dairy, eggs) and plants, as your body naturally combines amino acids over the day.
What does basal metabolism depend on?
Varies on age, sex, weight/height, (metabolic stress) and body composition. In adults, the recommended intake decreases with age.
Energy balance calculation
EB = income - expenses
*Balance controlled by hypothalamus, efficiency of energy production, and endocrine balance
Total energy expenditure - determined by metabolic rate and physical activity
Formula - TEE = ( BMR x PAEE ) + TEF
(TEF - Thermic effect of food, PAEE - physical activity energy expenditure)
BMR: Basal metabolic rate
Harris Benedict Formula
PAEE - Physical Activity Energy Expenditure
Easiest to change
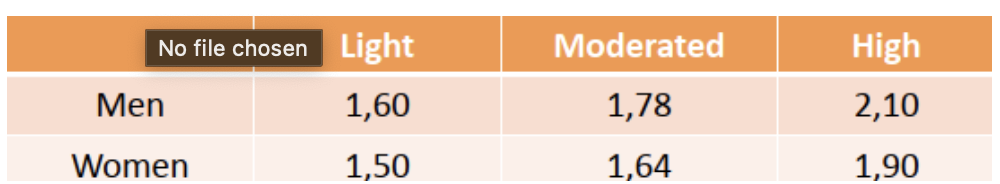
Thermic effect of food
Energy body uses to digest food
10% of BMR
Dietary Reference Intake (DRI)
Nutrient reference values in a healthy population
Indicators of good health and prevention chronic disease, adverse effects of excess intakes of nutrients
Based on 4 reference values
4 reference values DRI
Estimated average requirement - estimated to meet the requirements for a specific criterion of adequacy of half of the healthy individuals of a specific age, sex, and life-stage
Recommended dietary allowance - daily dietary intake level that is sufficient to meet the nutrient requirement of nearly all (97 to 98 percent) healthy individuals in a particular life-stage and gender group
Adequate intake - recommended average daily nutrient intake level based on observed or experimentally determined approximations or estimates of nutrient intake by a group (or groups) of apparently healthy people who are assumed to be maintaining an adequate nutritional state.
Tolerable upper intake level - highest level of continuing daily nutrient intake that is likely to pose no risk of adverse health effects
How to use DRIs
They apply to healthy people. Need to be adjusted for malnourished people or with medical problems. 2. Recommendations are not minimum requirements. They target most of the people and do not account for individual variation in nutrient needs (registered dietitian can help determine if recommendations should be adjusted. 3. Variety of food (mixtures of nutriens) : excess intakes are unlikely. 4. Recommendations apply to average daily intakes. Depending on the nutrient, deficiency develops more rapidly ( Ex. Thiamin and vit C : days or weeks) or more slowly (vit. A and Vt B12 : months or years) 5. Each DRI category serves a unique purpose - EAR: develop and evaluate nutrition programs for certain groups - RDA: goals for individuals - UIL: serve as reminder specially upon supplements
Nutrition science definition
relationship between the body’s physiological functioning and the essential elements from the food we eat.
Bromatology definition
Combines the science of biology, physics and chemistry to study the nature of food
Dietetics definition
Connects food to nutrition and health
Processed food
Loss of valuable nutrients and the gain of sugar, fats, and salt
Their value in the diet depends on the starting food and how it was processed.
Sometimes processed foods are fortified (nutrients that were not present originally are added) to improve their nutrient contents
New food
Food which has been designed using genetic engineering techniques
Gm food
Functional food
Pro/prebiotics
Nutraceuticals
Super food
Genetically modified food
Biodiversity can decrease
Non target organisms can be harmed
Probiotics
Live microorganisms
Produces certain vitamins
Improve the immune response
Protects against pathogens
Reduce symptoms of poor lactose absorption
Prebiotics
Food ingredients that the body cannot digest and therefore stimulate growth intestinal microbiota
Ex: soluble fiber
Functional food
Natural or processed, enriched component that provides significant health property regardless of its nutritional value
Beneficial effect reached with usual amounts consumed in diet
Consumed daily, reduce risk of chronic diseases, provide nutrients
Nutraceuticals
Isolated from food products, sold as drug
Beneficial physiological effects and protect against chronic diseases
Ex: capsules with flavonoids
Dietary supplement in non food form
Super food
Foods whose nutrient content confers a health benefit over and above that or other foods.
Ex:
Blueberries
Pomegranate
Chia seeds
Ginger
Turmeric
Green tea
Nutritional characteristics of cereals
Most abundant protein gluten
High iron, K+, phosphorus, Ca
Vitamins B, no vit. C
Fiber and vitamins when consumed in whole grain form
Potatoes
Low protein, fat free, starch
High fiber and folic acid
Acrylamide
Caused by maillard reaction
Golden brown color on food, linked to cancer
Nutritional characteristics of sugar
Absorbed quickly in intestine, high glucose in blood after consumption
Honey composed rapidly absorbed carbs, B/C vitamins
Antimicrobial and fungicidal
Royal jelly higher nutritional value
Nutritional components of lipids
Oil, butter, margarine
Higher saturated fatty acids
Butter high vitamin A
Fat same in butter/marg
Nutritional components of milk
Calcium, vit D/lactose, little iron
Dairy proteins high biological value
Yoghurts contain probiotics, fats and protein easier to digest than in milk
Cheese high protein, Ca, Vit A/D
Nutritional components of proteins
Contains all essential amino acids
B vitamins
Low Vit A/C/folic acid
Fish good for B vitamins and omega 3
Eggs high bio value, A/B vitamins
Nutritional components of legumes
compliment cereals rich in methionine and low in lysine
Meals that combine legumes and cereals achieve a good nutritional balance: lentils with rice, chickpeas with noodles, legumes with bread or beans with corn
High protein high fiber
K+
Nutritional components of nuts
Low carbs, high protein
Easily absorbed minerals
Nutritional components of vegetables
Low cal
Carbs
High water content
Rich in fiber, low in fat
No cholesterol
Vit A/C/B/folic acid
Nutritional components of fruits
High carbs, high sugar
Many vitamins
Fiber and pectins
High water content
Antioxidants
How to calculate BMI
Weight in kg/height² (M)
Below 18.5 underweight, over 25 overweight
Waist to height ratio
assesses the accumulation of central fat and results from the division of the perimeter of the waist in cm between the height in cm.
It is considered that there is abdominal obesity when the value of WHR is > 0.5
DIVIDE WAIST BY HEIGHT
Waist to hip ratio
Results from the division of the perimeter of the waist in cm between the perimeter of the hips in cm
Skin folds
Lipocalibrators
Triceps fold
Abdominal fold
Subscapular fold
Suprailiac fold
Estimate total BF
Electrical bioimpedance
Body composition based on conduction properties of the human body
The fat mass has high impedance/resistance due to the lack of fluids.
24 hr recall
Nutritional reference values
Carbs 55-60%
Proteins 10-15%
Fats 30%
Fiber 30-50g per day
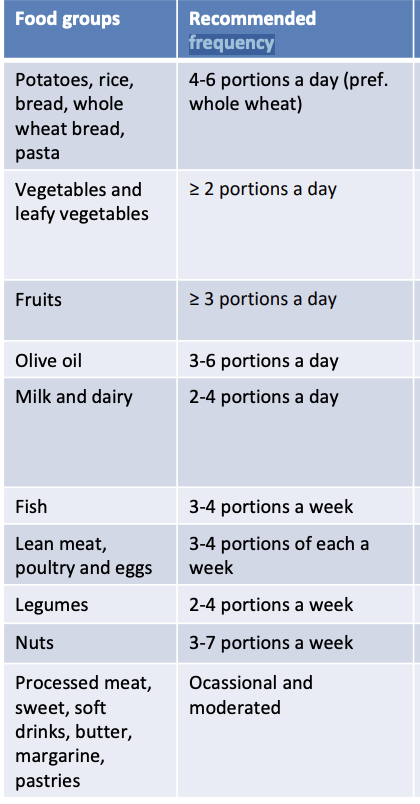
Recommended frequency food groups
Lactic period
Breast milk only recommended food until 6 months as single source of energy
Artificial breast feeding every 3 hours
Beikost period when introduction of non-dairy foods from the 4th-6th month
Diet in puberty
Family loses influence on eating behavior, friends fashion and media take over
High biological value proteins needed
Ca, Zinc, iron recommended
Regular meal times without skipping any
Wholegrain bread and cereals
Fish, legumes, cereals
Reduce processed foods
Drinking water with meals
Diet in older age
Osteoarthritis, back pain, hypertension and vision problems
It is necessary to avoid the associated CALORIC-PROTEIN MALNUTRITION, as it is an indicator of FRAGILITY
Omega 3 needed
More proteins
Food sources with Ca+
Cheeses
Oregano
Cinnamon
Milk
Marasmus
Due to energy supply deficit or poor use of nutrients. Slow evolution
Protein malnutrition/kwashiorkor
Due to protein intake deficit. Rapid evolution
Mixed malnutrition/cachexia
Energy supply deficit + protein hypercatabolism that increases needs. Rapid evolution
Anorexia
Self induced weight loss
Distorted body image
Restrictive/purgative
Mainly effect women 12-25
Refusal to gain weight
Amenorrhoea
Bulimia
Suffers episodes of binge eating, followed by a great feeling of guilt and a sense of loss of control.
Fasting episodes
Inappropriate compensatory behaviours at least twice a week for a period of at least 3 months
Self-evaluation is exaggeratedly influenced by body weight and body shape
Vigorexia
Obsessed with having muscular body
Addiction to physical activity
Excessive exercise to achieve larger muscles
Orthorexia
Obsession with eating healthy food
Elimination of some food groups that are not nutritionally replaced by others
Permarexia
People constantly on a diet, worried about weight and calories
Diuretics, vitamins, fibre
High levels of exercise to control weight gain
Think they know a lot about nutrition
Obesity definition
Problem in which an individual accumulates an excessive level of fat for their age and sex, which exceeds the levels of overweight
Excess fat mass under skin and around organs
Overweight definition
Treated as if they have central obesity, hypertension, type II diabetes. Not as large as obesity.
Bariatric surgery
Treatment morbid obesity
For Pi who have a BMI greater than 40 kg / m2 or 35 kg / m
Most common is reduction of stomach volume, others reduce the length of the intestine
Obesity risks
Risk of metabolic syndrome - develops a set of symptoms that increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus which may compromise health
Hypertension
Dyslipidemia
Type 2 diabetes
Obesity treatment
Achieve WL behavior
Self control
Physical exerciser
Goal to lose 5-10% of initial weight maintained over time
Decrease 500 calories per day
Psychological support behaviors
Distributions of fat tissue
Homogeneous or generalized distribution
Abdominal or android distribution: the accumulation of fat is in the abdominal region
Gluteal-femoral or gynoid distribution: fat accumulates in the hip and gluteal-femoral region
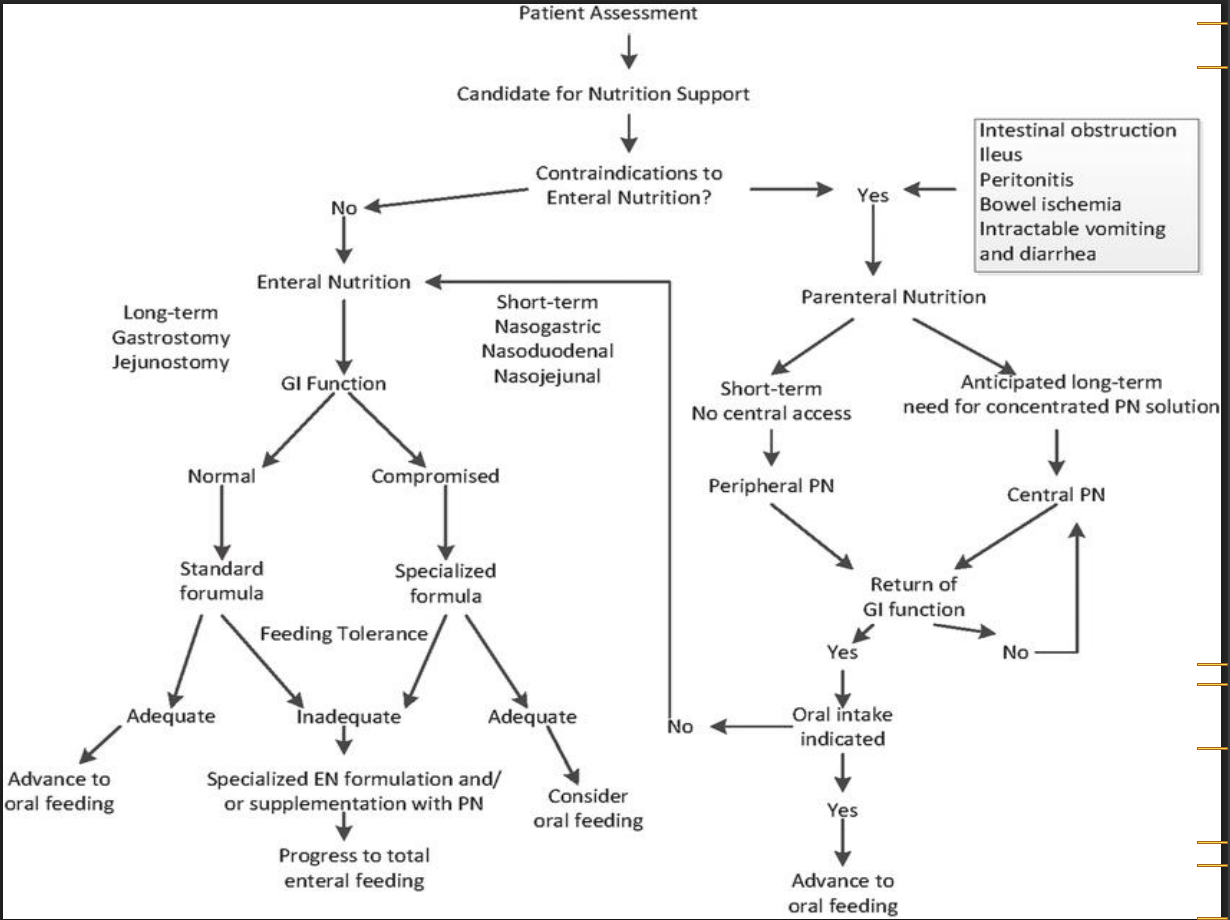
Types of artificial nutrition
Enteral
Parenteral
Enteral
Nutrients given directly to digestive system by means of implanted tubes
Used for unconscious patient, swallowing disorders, intestinal failure, CNS disorders, stroke
Nasogastric for short term, ostomy for long term
Postpyloric if there is aspiration risk
Gastric if no risk
Parenteral nutrition
Intravenous supply of all nutrients
Go directly into bloodstream, bypassing digestive process and the liver filter
Parentral vs. Enteral Diagram
Diet plan for diabetics
Increase fiber intake
Cooking increases GI, al dente
Fresh fruit and natural juices
No alcohol, avoid sweeteners
Normal lipids
Nephropathy present restrict protein
regular exercise
Avoid tobacco, alcohol, other drugs
Fast absorbing carbs when hypoglycemic