Putting a business idea into practice - Topic 1.3
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What are aims?
Overall goals that they want to achieve
What are financial aims?
Aims based on the amount of money or the number of sales a business wants to use
What are examples of financial aims?
Survival
Enough money to stay open
Maximise profit
Increase market share
The percentage of a markets total sales a particular product or company has made
Having a part of the market share means the business establishes itself, takes sales away from competitors and persuades customers to buy its products
Maximise sales
Increases the sales eg by reducing products price
Not the same as wanting more profit
Achieve financial security
Depend on its own revenue and not external sources
What are examples of non-financial aims?
Accomplishing a personal challange
Achieving personal satisfaction
Follow personal interest
Gaining independence and control
Independence of being their own boss
Doing whats right for society
Moral goals
What are objectives?
Steps that help business achieve their aims
What factors effect a businesses objectives and aims?
The size and age of the business
Small and new businesses are likely to aim for survival or growth
Established businesses may concentrate on achieving finiancial security and a increase in sales
Larger business may have social aims as they have publics attention
Who owns the business
Shareholders may have pressure to have aims on maximising profit
Soletraders may aim for non-financial aims as they are young
The level of competition the business faces
If a business as a competitive market they may aim for survival
Firms that dont have that many competitors may aim for increasing market share and maximising profit
What is revenue? What is the calculation?
The income earned by a business
Revenue = quanity sold x price
What are the costs? What is the equation?
The expenses paid out to run the business
Total costs = total varible costs + total fixed costs
What are fixed cost?
Cost that dont vary with output and must be paid even if the business produces nothing
What are variable cost? What is the equation?
Costs that will increase as the firm expands output
Total varible cost = quantity sold x variable cost per unit
What is interest?
A charge for borrowing money so the business can pay back more then what was borrowed
What is the equation for interest?
Interest (on loans) = total repayment - borrowed amount / borrowed money x 100
What is profit? What is the equation?
The different between revenue and costs over a period of time
Profit = revenue - cost
What is the break-even point?
The level of sales a firm needs in order to just cover its costs
What can break-even be measured in?
The number of units that has to be sold to meet it
The revenue the firms needs to cover its costs
What is the equation for break even in units?
Break-even point in units= fixed costs / sales price - variable cost per unit
What is the equation for the break-even point for revenue (or costs) ?
Break-even point for revenue (or cost) = break-even point in units x sales price
What is a loss?
When a firm sells less then its break-even point
Break-even diagrams
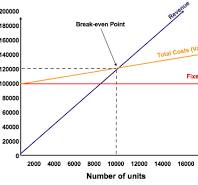
What is the margin of safety?
The gap between the current level of output and the break even output (how many units are currently being sold vs what needs to be sold)
What is the equation for the margin of safety?
Margin of safety = actual sales (or budgeted sales) - break-even slaes
What is cash?
The money a company can spend immediately
Why do businesses need cash?
To pay:
Employees
Suppliers
Overheads (on going expenses)
What is cash flow?
The flow of money in and out the business
What is the equation for net cash flow?
Net cash flow = cash inflows - cash outflows for a given period of time
What is positive cash flow?
When there is more cash inflow than cash outflow for a particular period of time
What is the advantage and disadvantage of positive cash flow?
Advantage
No problem making payments
Disadvantage
Losing opportunities to invest in ways that might improve eg new equipment
What is a cash flow forecast?
Lists all the inflows and ouflows of cash that appear in the budget (a forecast of all of the firms likely expenses and revenue)
What is the equation for closing balance?
Closing balance = opening balance + net cash flow
What are credit terms?
Tells you how long after agreeing to buy a product the customer has to pay
Why do firms need finance?
New firms need start-up capital (they money or assets needed to set up a business)
New firms often have poor initial cash flow - means they find it hard to cover their cost
Sometimes customers delay payment so fianances need to cover the shortfall of cash flow
If a business is struggling, it may need additional finance to meet its day-to day running cost
Need finances in order to expand
What is trade credit?
A short-term source
Gives a firm a month or two to pay for certain purchases
Gives them time to earn money to pay it off
However a large fee may be charged if money cant be payed back in time
What is overdraft?
Short-term source
Allows firms to take more money out of their account than it has paid into it
Allow businesses to may payments on times even if they cant afford it
However, they usually have a high interest rate than other loans and the bank can cancle the overdraft at any time
If it hasnt been paid off the bank can take some of the business’ assests
What is a loan?
Long-term source
Bank loans are quick and easy to take out
Repaid with interest
If not paid, the bank can repossess the firms assets
However, the interest rate is usually lower then overdrafts
May pay their bank back in monthly instalments which will increase their fixed costs
Businesses check they can still reach their break-even with this extra cost
What are personal savings?
A business owners own money into the business to get it started or if it is having cash flow problems
Risky as individual could loose their money if the business fails
What is share capital?
Individauls can buy shares in the businss
This means they have part ownership
The business can gain the money through issuing shares
What is venture capital?
Money raised through selling shares to individuals or businesses who specialises in giving finance to new or expanding firms
Venture capitals usually buy shares that are risky but have potential to grow quickly
They will take a stake in the business and may expect returns more quickly than other shareholders would
What is retained profit?
These are profits that are owners have decided to plough back into the business after theyve paid themselves a dividend
What is crown funding?
When a large number of people contribute money towards starting up a business or funding a business idea