APHG 2.10-2.12 Migration (tprosk)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
mobility
All types of movement from one location to another.
Circulation
Short-term, repetitive, or cyclical movements of people that recur on a regular basis.

Migration
A permanent move to a new location.

Net Migration
the difference between the number of immigrants and the number of emigrants (determines whether migration raises or lowers your population)

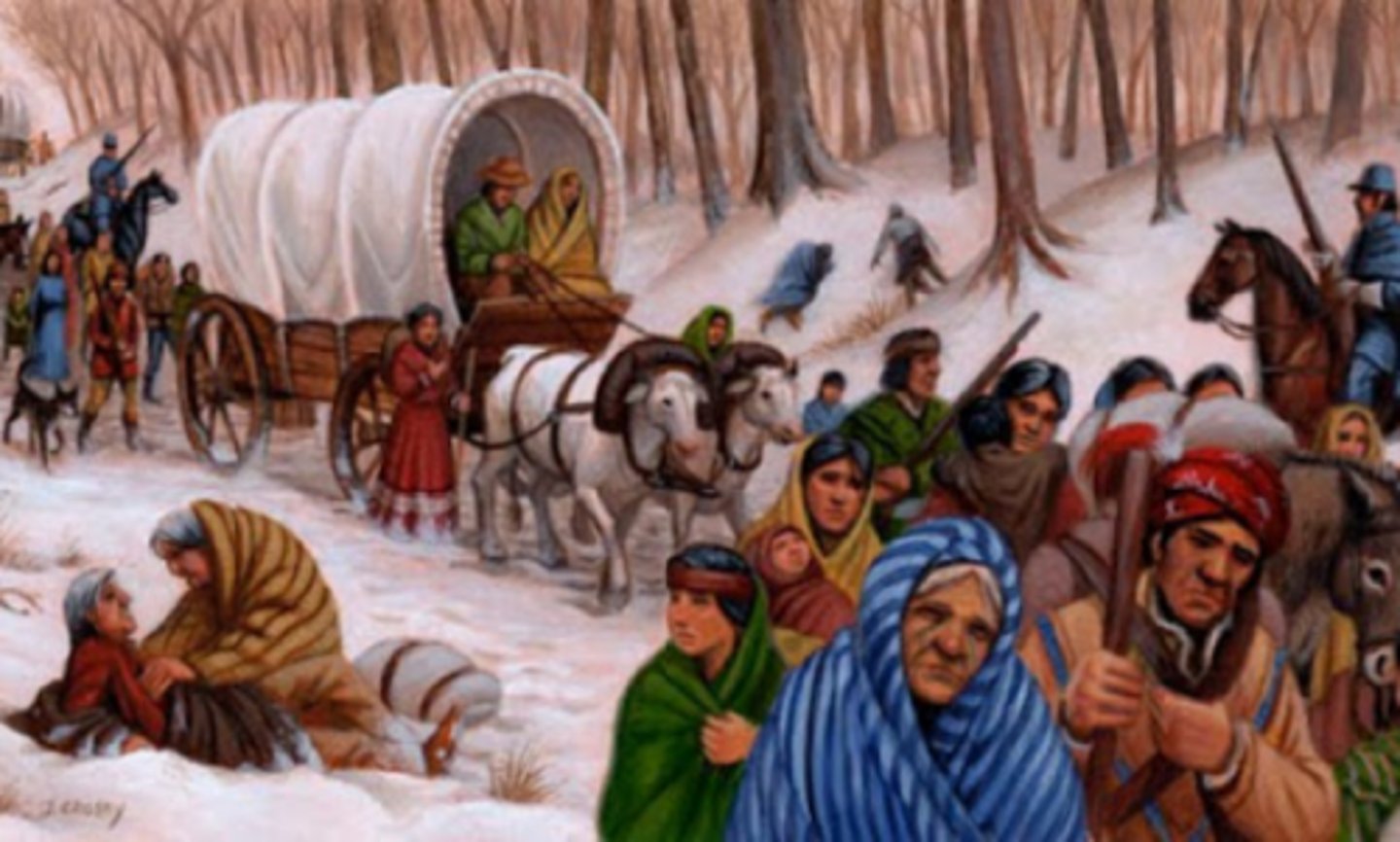
Forced Migration
Human migration flows in which the movers have no choice but to relocate.

Voluntary Migration
movement in which people relocate in response to perceived opportunity; not forced.

Emigration
movement of individuals out of an area

Immigration
Movement of individuals into a population
Internal Migration
Permanent movement within a particular country.
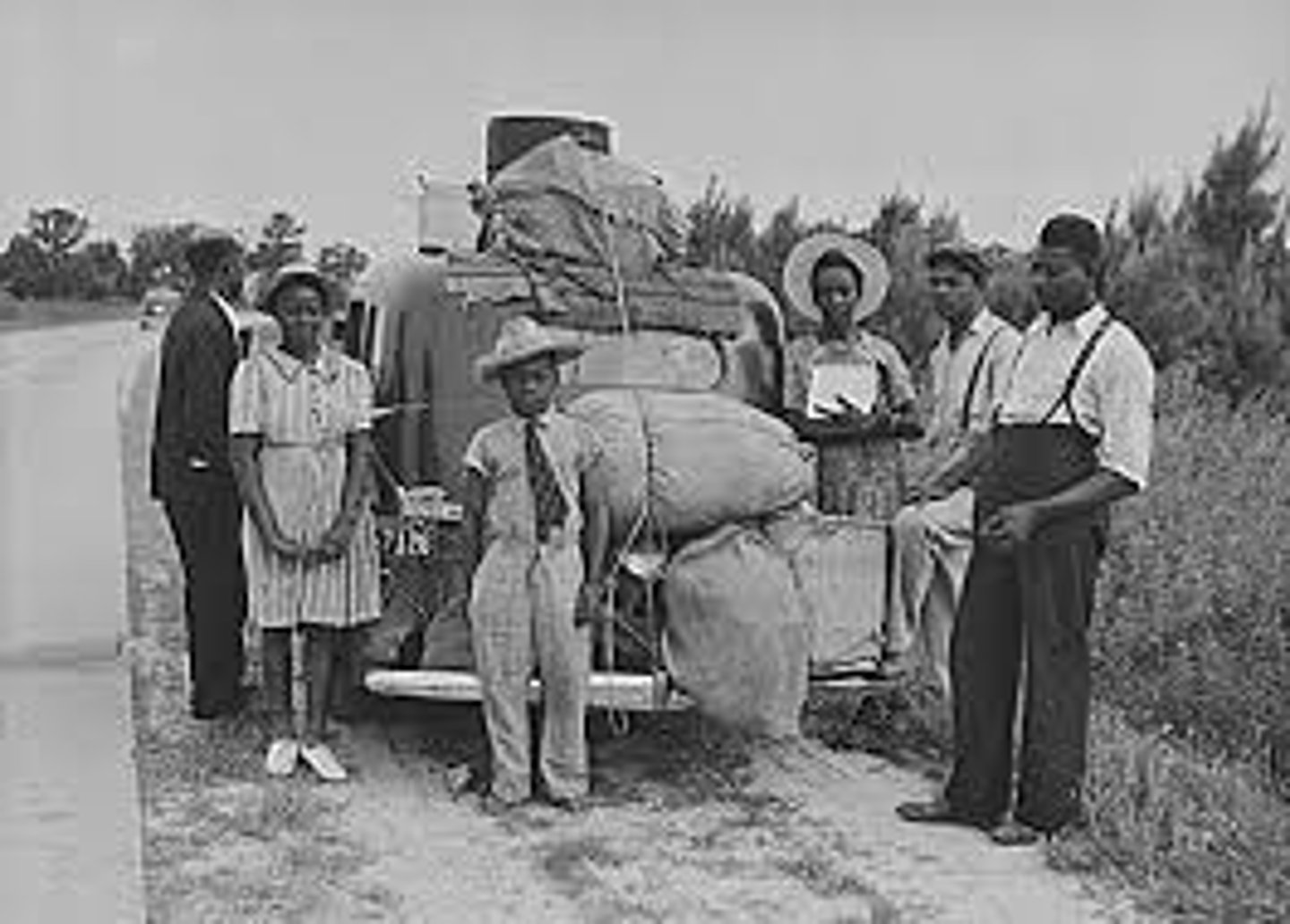

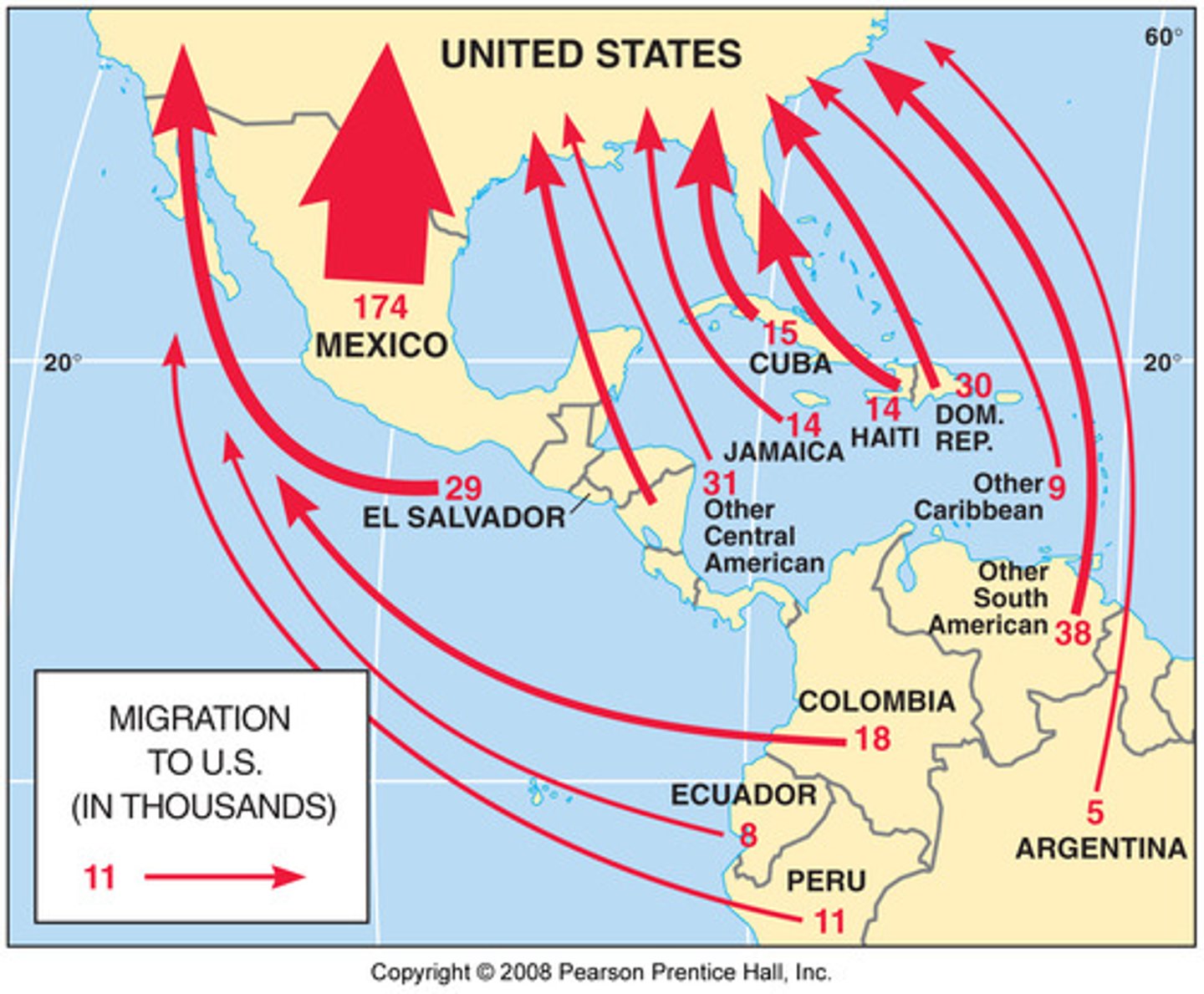
International Migration
Permanent movement from one country to another.
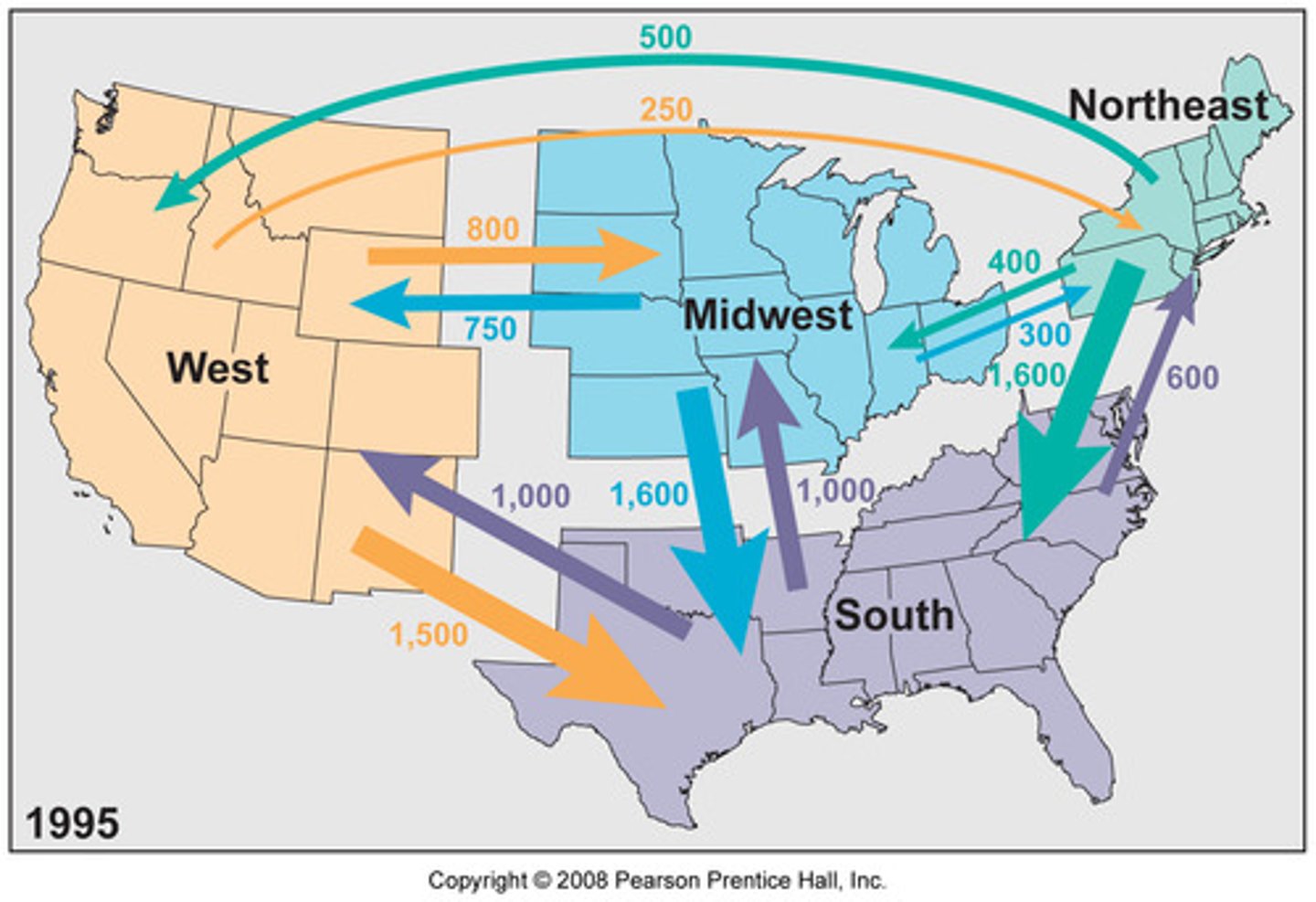
Interregional Migration
Permanent movement from one region of a country to another.
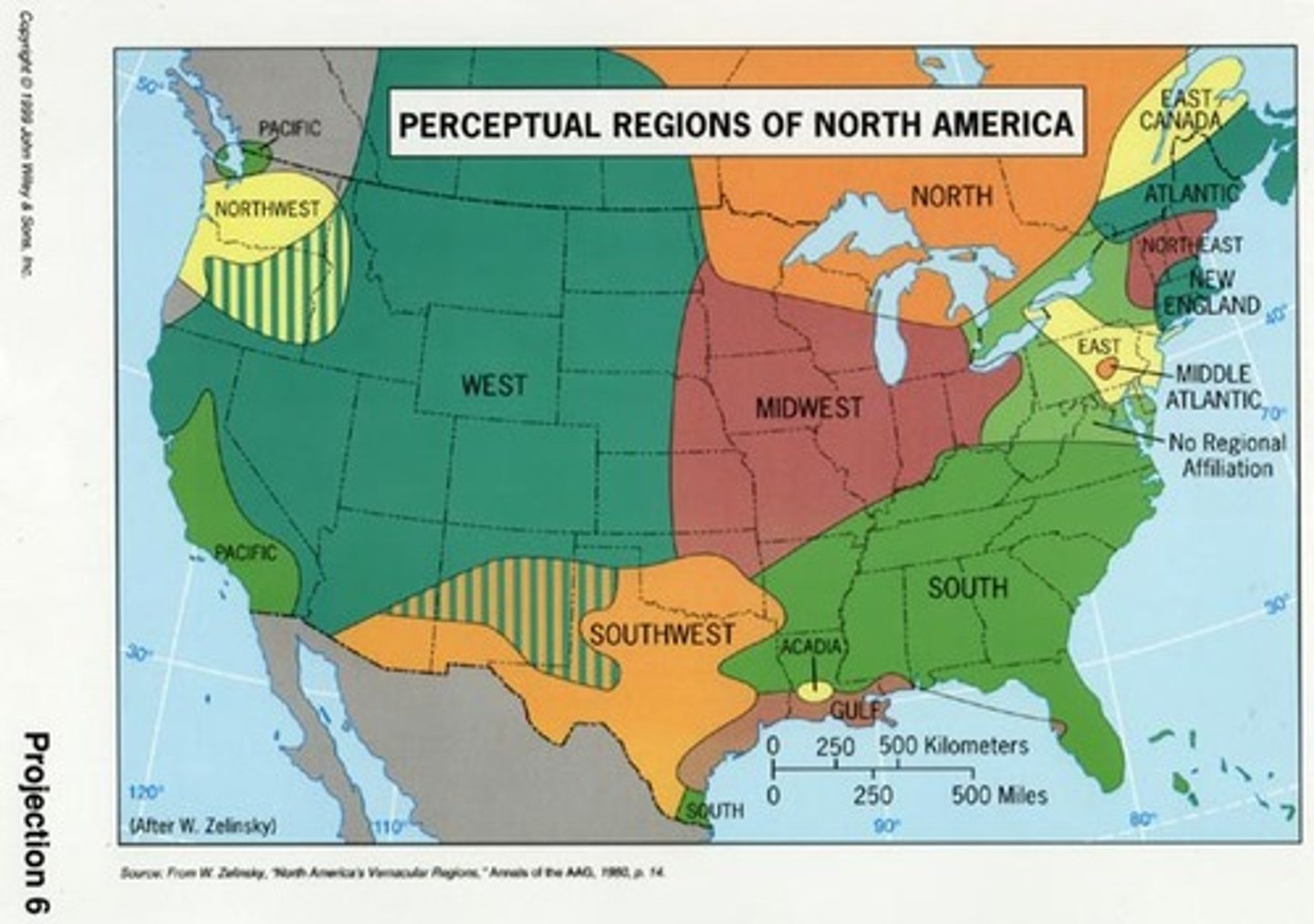
Intraregional migration
Permanent movement within one region of a country.
Migration Transition
Change in the migration pattern in a society that results from industrialization, population growth, and other social and economic changes that also produce the demographic transition.
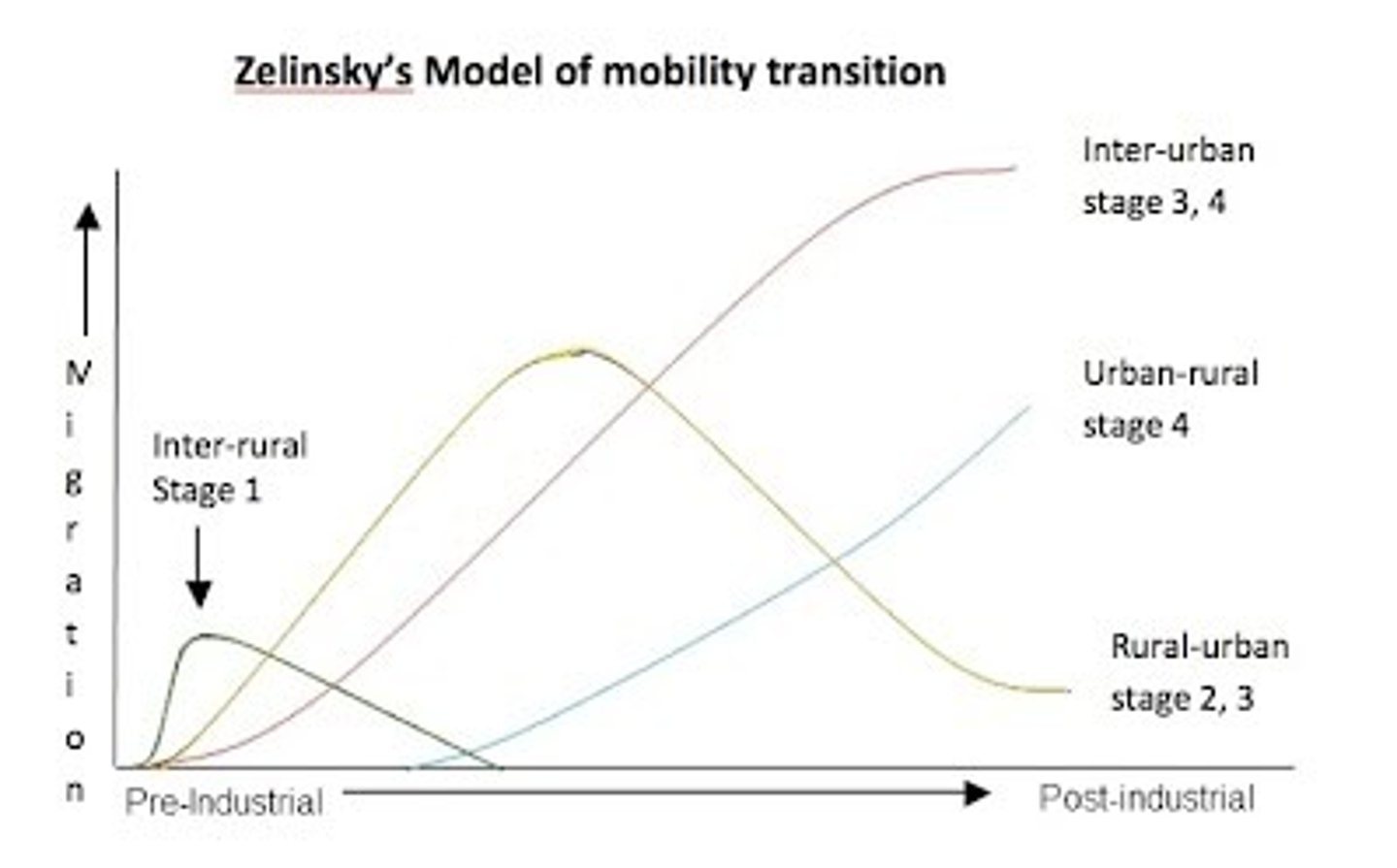
Ravenstein's Law
11 principles that describe most common patterns in migration. For example: 1) Most migrants move only a short distance. 2) females are more migratory than males within the areas of their birth, but males more frequently venture beyond; 3) most migrants are young adults; families rarely migrate out of their country of birth
Counterurbanization
Net migration from urban to rural areas in more developed countries.
Asylum Seeker
a person who has left their home country as a political refugee and is seeking asylum in another.

Guest Worker
a foreign laborer living and working temporarily in another country

Internally Displaced Person (IDP)
someone who is forced to flee his or her home but who remains within his or her country's borders

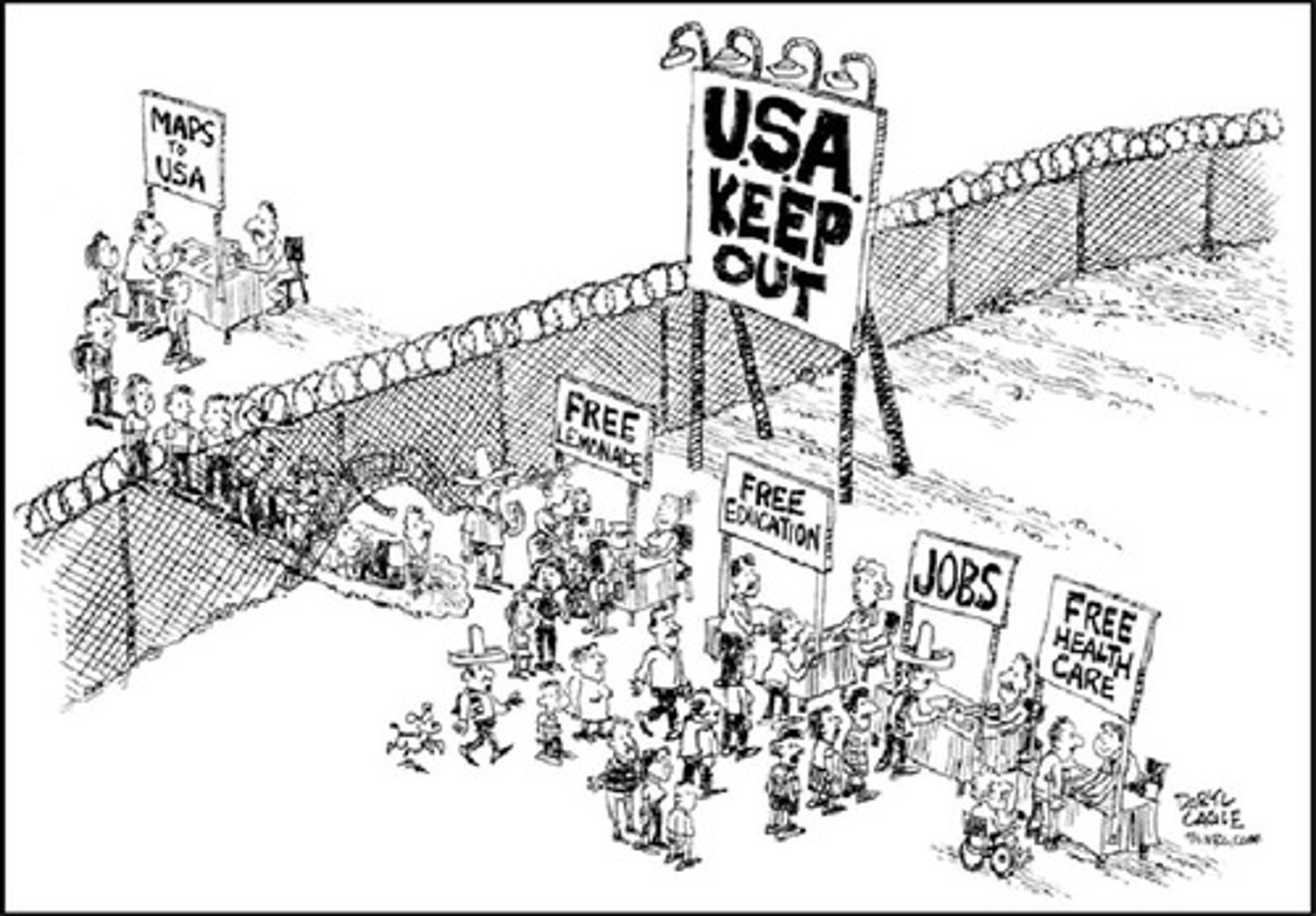
Pull Factor
A positive factor that draws or attracts people to another location
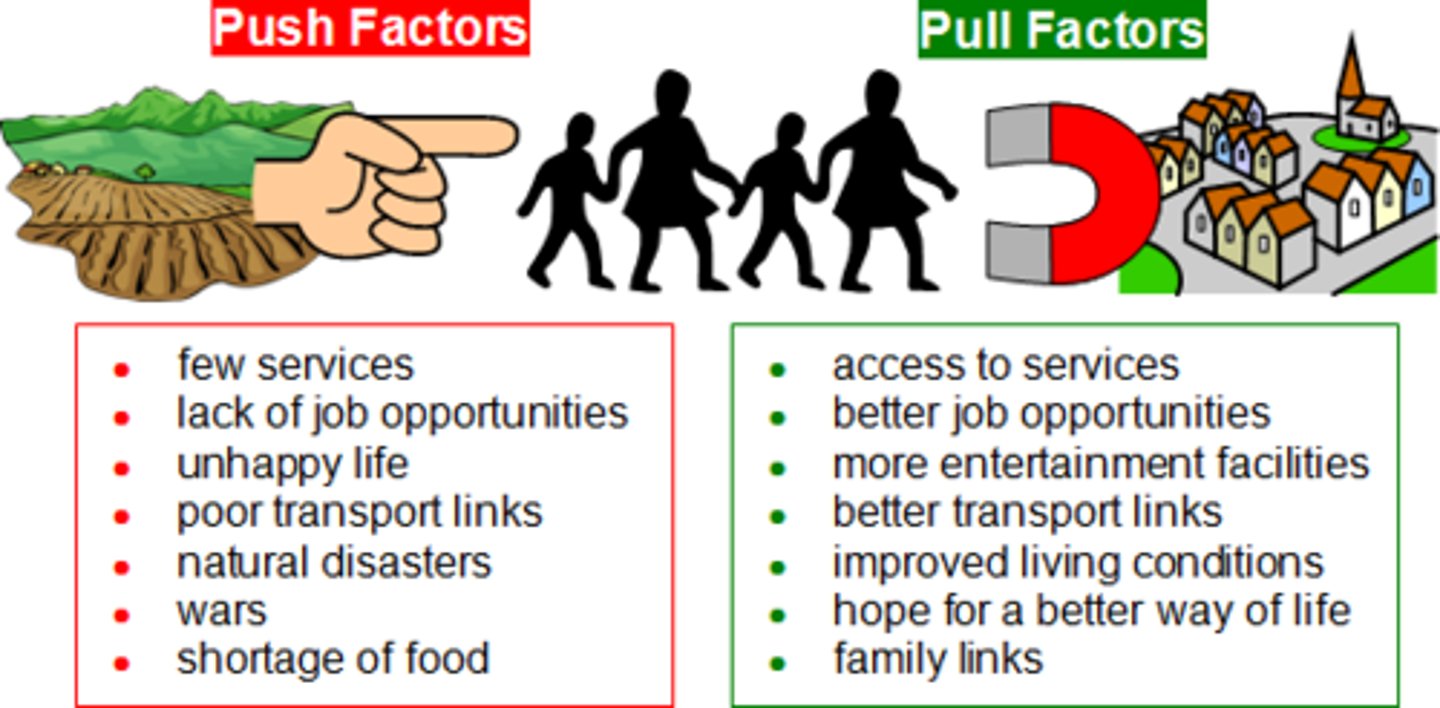
Push Factor
negative home conditions that encourage the decision to migrate

Refugee
A person who has been forced to leave their country in order to escape war, persecution, or natural disaster

Step Migration
Migration to a distant destination that occurs in stages, for example, from farm to nearby village and later to a town and city

Brain Drain
the emigration of highly trained or intelligent people from a particular country.

Chain Migration
migration of people to a specific location because relatives or members of the same nationality previously migrated there

Intervening Obstacle
An environmental or cultural feature of the landscape that hinders migration.

intervening opportunity
The presence of a nearer opportunity that greatly diminishes the attractiveness of sites farther away.

Quotas
In reference to migration, laws that place maximum limits on the number of people who can immigrate to a country each year.

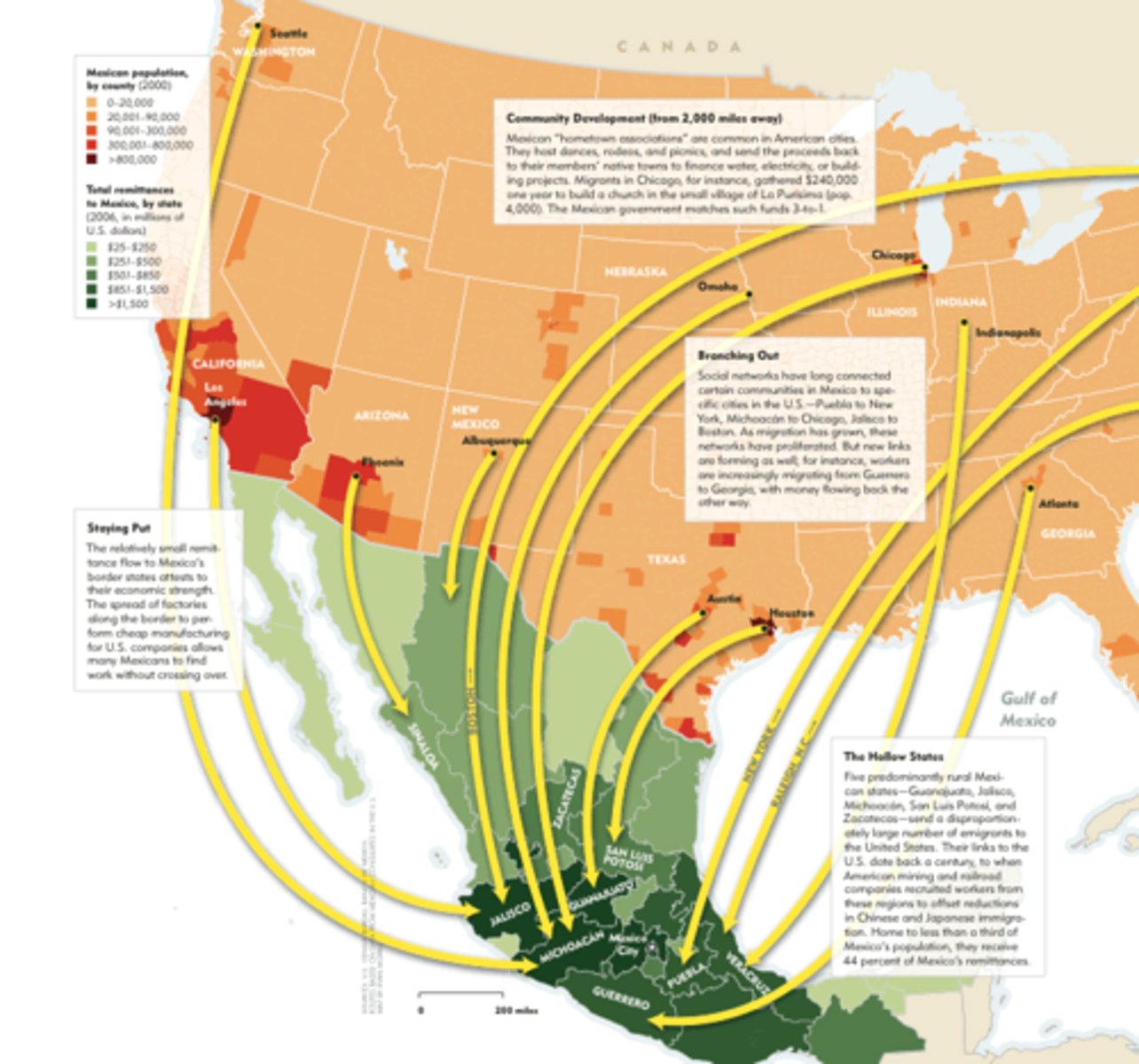
Remittances
Money migrants send back to family and friends in their home countries, often in cash, forming an important part of the economy in many poorer countries
Unauthorized Immigration
People who enter a country without proper documents to do so
transnational migration
regular movement of a person between two or more countries resulting in a new cultural identity (i.e. nuyorrican)

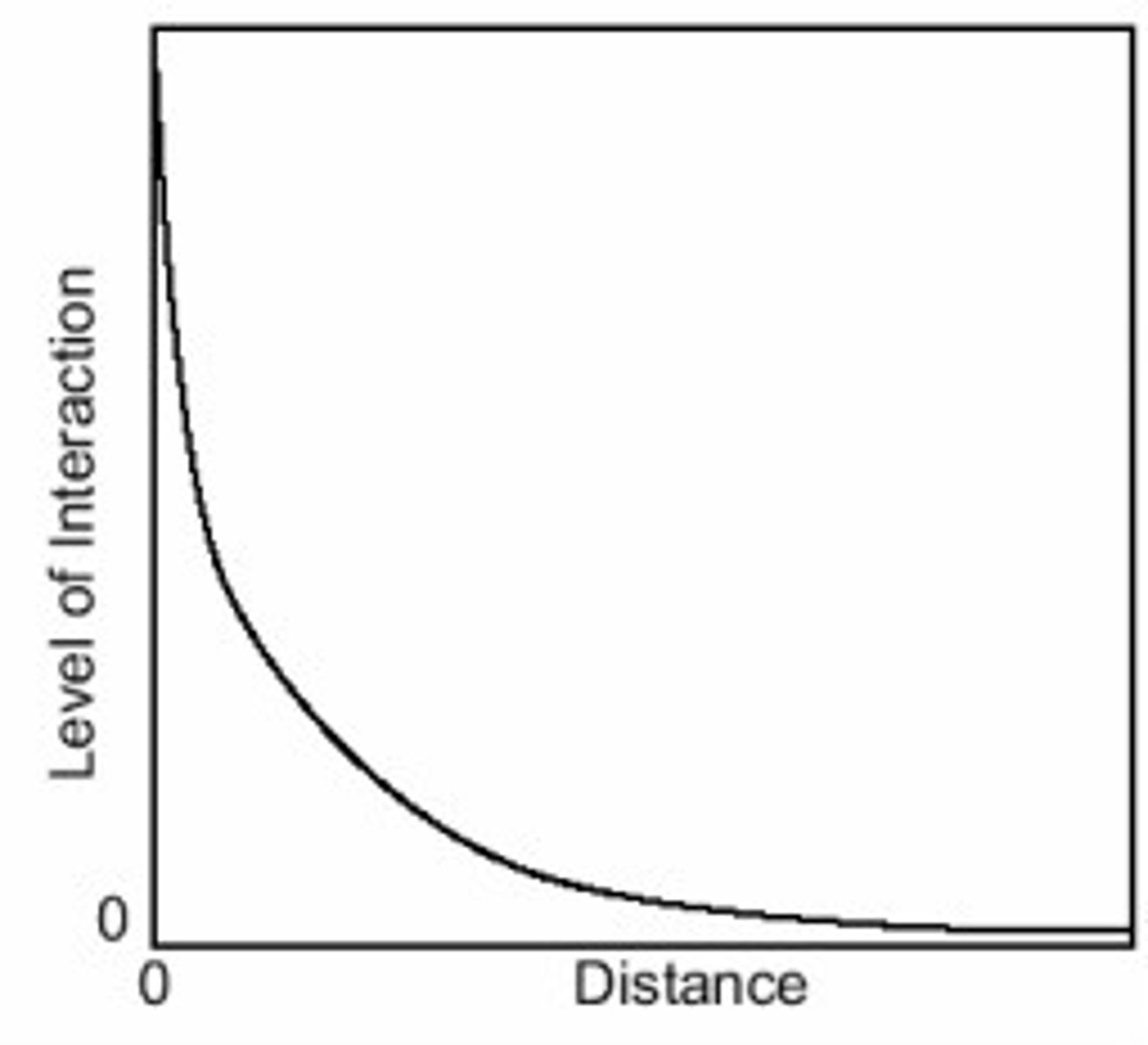
friction of distance
A measure of how much the distance affects the interaction between two places.
repatriate
send (someone) back to their own country

human trafficking
the illegal movement of people, typically for the purposes of forced labor or commercial sexual exploitation

circular migration
repeated movement between two or more places, either within or between countries

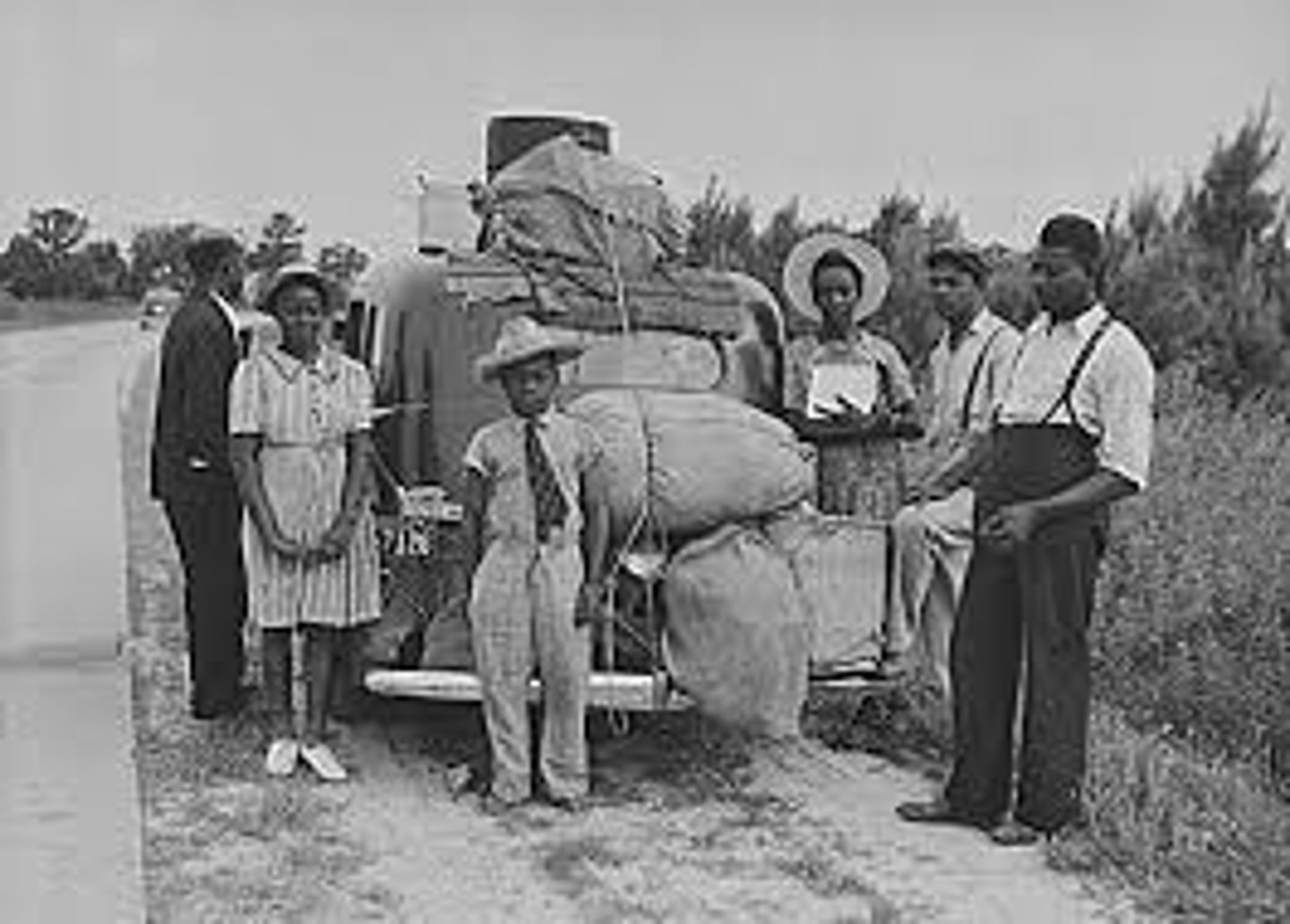
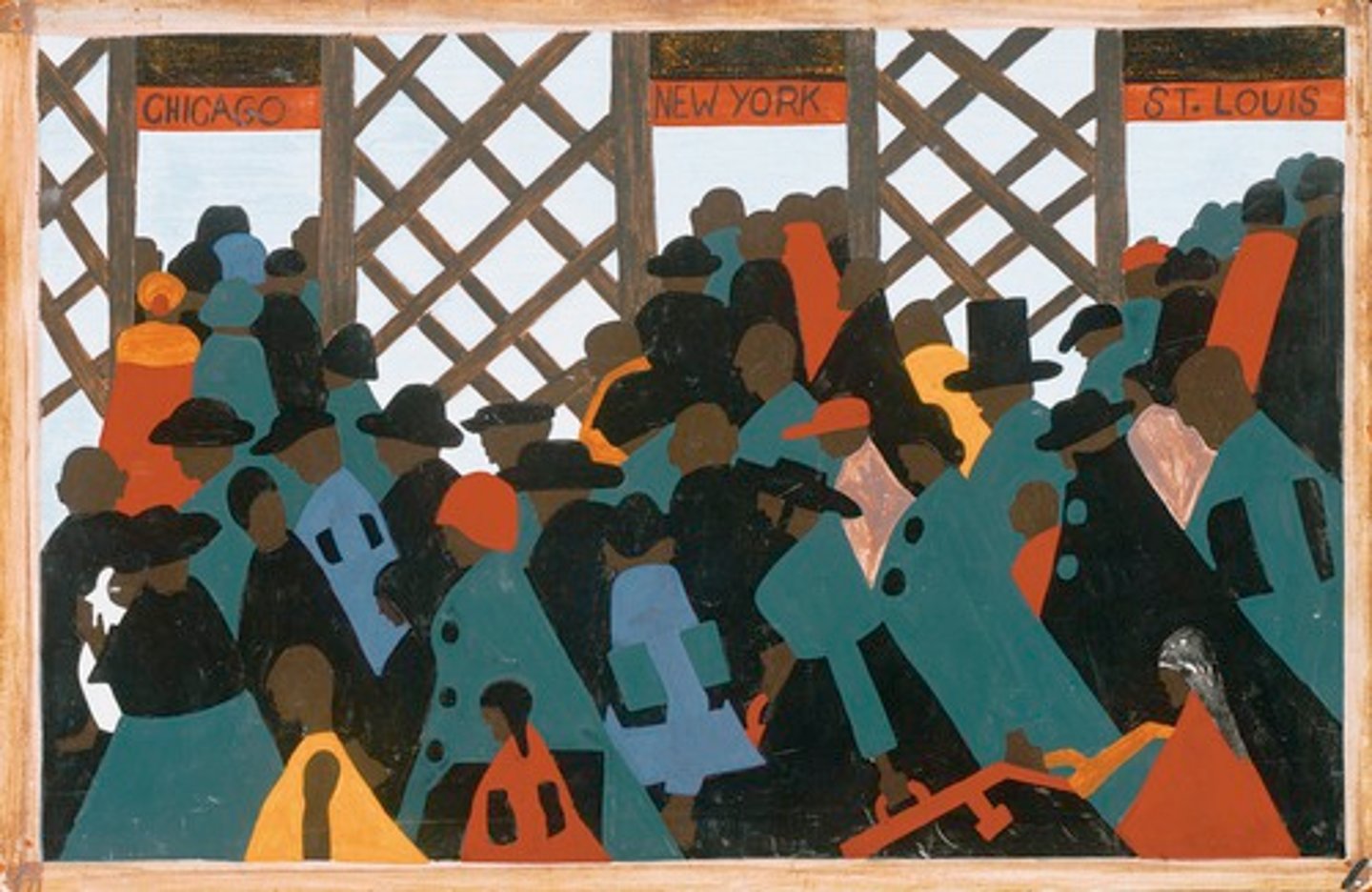
Great Migration
Movement of African Americans from the rural South to the North in the first half of the 1900s for jobs and increased freedom
