OCR GCSE Computer Science - Paper 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is a flashcard set for OCR GCSE Computer Science - Paper 2, but it does not include programming-related flashcards except definitions.
Last updated 10:41 PM on 11/9/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
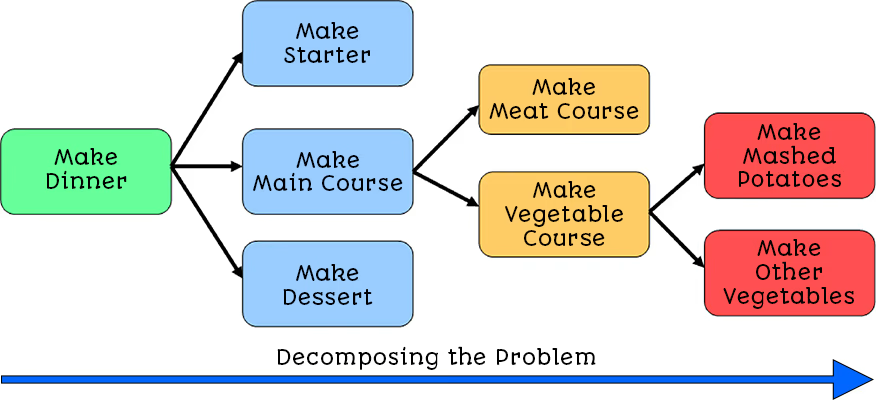
Breaking a problem down into smaller sub-problems. Once each sub-problem is small and simple enough it can be tackled individually.
Decomposition is...
2
New cards
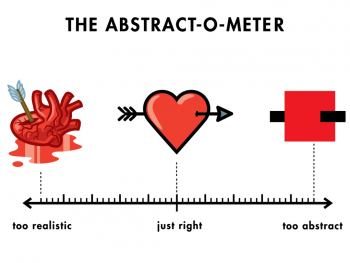
Removing or hiding unnecessary details from a problem so that the important details can be focused on or more easily understood.
Abstraction is...
3
New cards

Looking for similarities among and within problems.
Pattern recognition is...
4
New cards
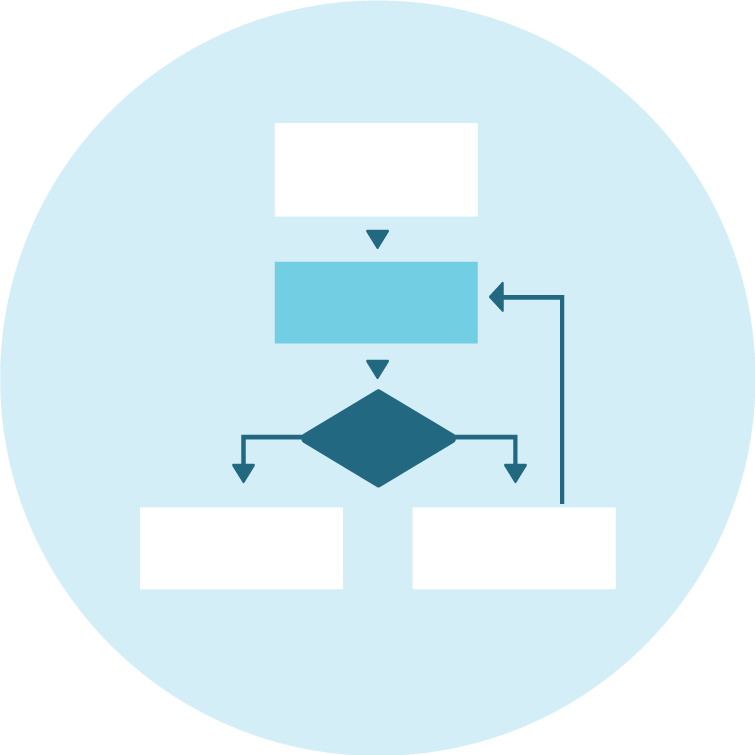
Deciding on the order that instructions are carried out and identifying decisions that need to be made by the computer.
Algorithmic thinking is...
5
New cards
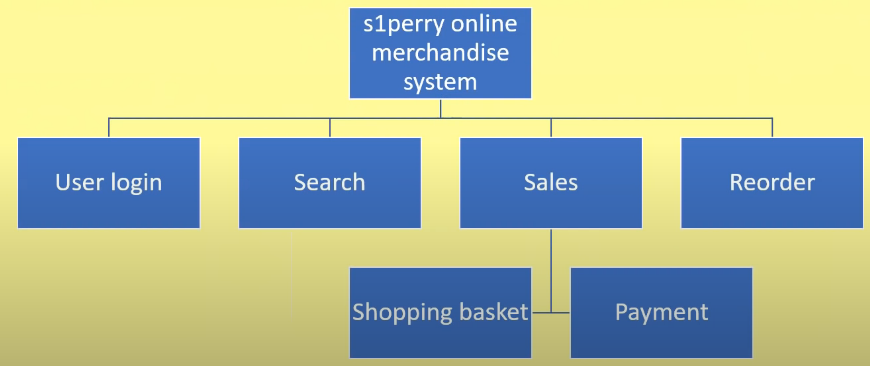
A graphical method of decomposing a problem, with each layer breaking down the layer above it into smaller and smaller sub-problems.
A structure diagram is...
6
New cards
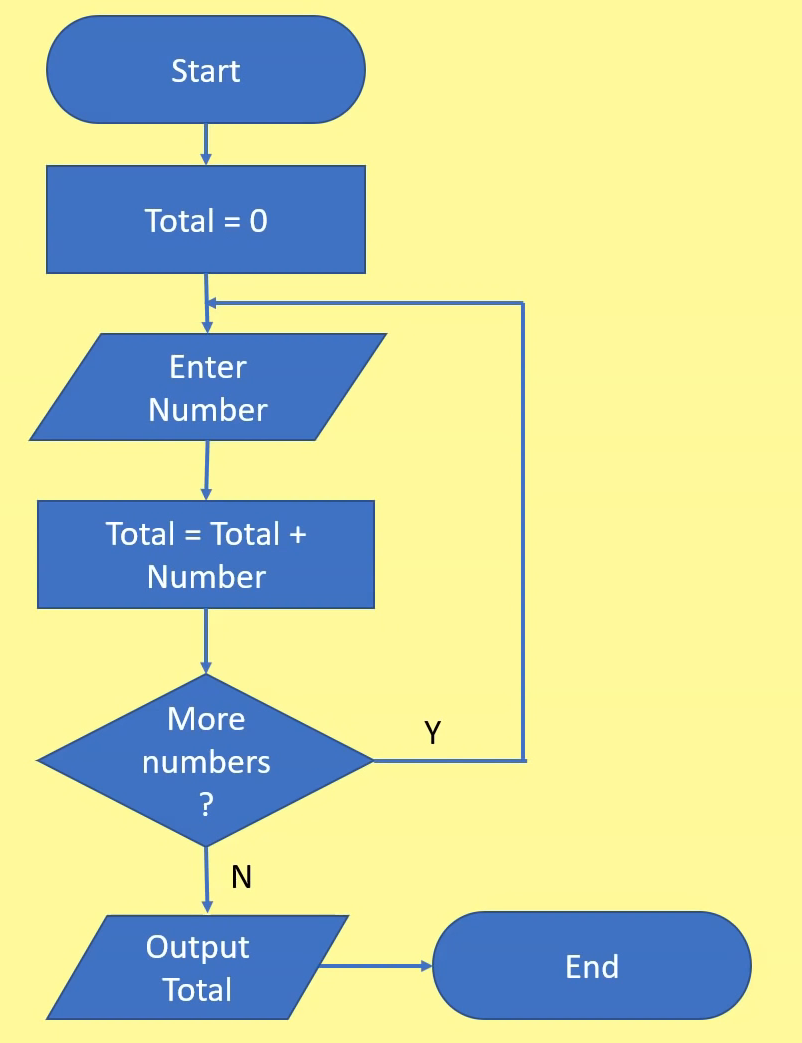
A graphical representation of an algorithm and uses symbols to denote each step, with arrows showing how to move between each step.
A flowchart is...
7
New cards

A textual representation of an algorithm. It is very closely related to high-level languages, although it does not require the same precise syntax. It also enables programmers to communicate algorithms to other programmers without worrying about which language they know.
Pseudocode is...
8
New cards
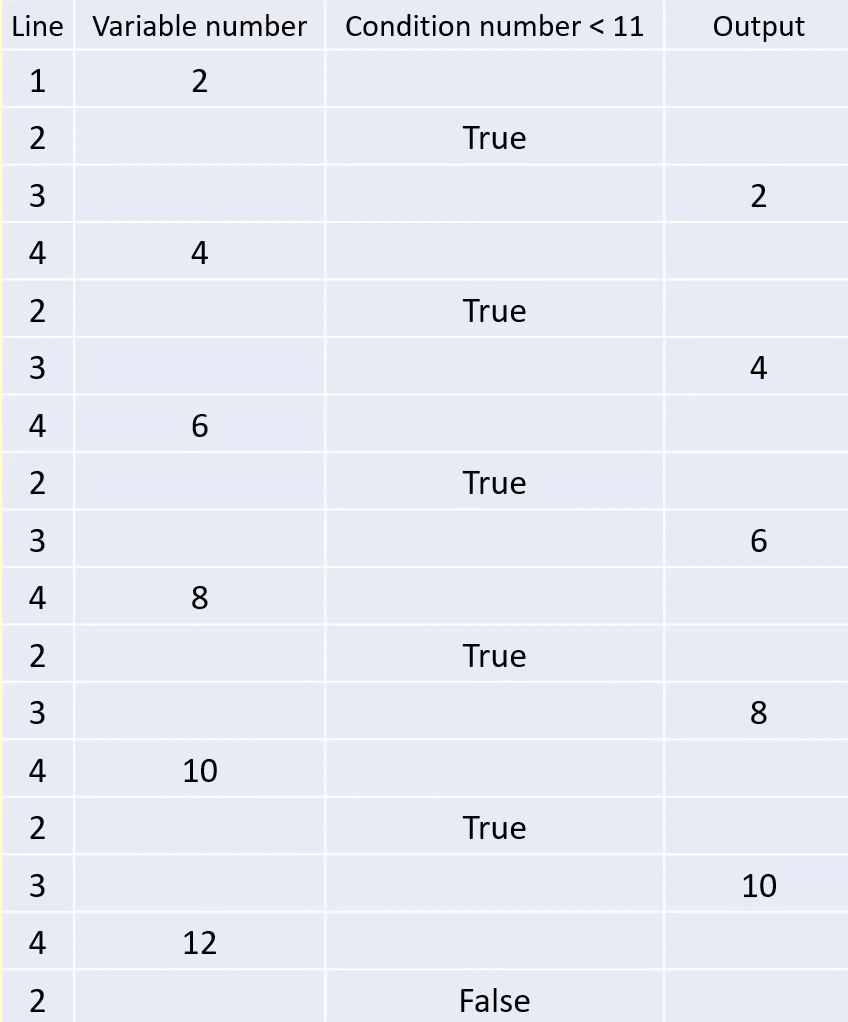
A tool that can be used to follow each line
of an algorithm through, step by step. A trace table will show the contents of each variable after each line has been carried out and will also show any output.
of an algorithm through, step by step. A trace table will show the contents of each variable after each line has been carried out and will also show any output.
A trace table is...
9
New cards
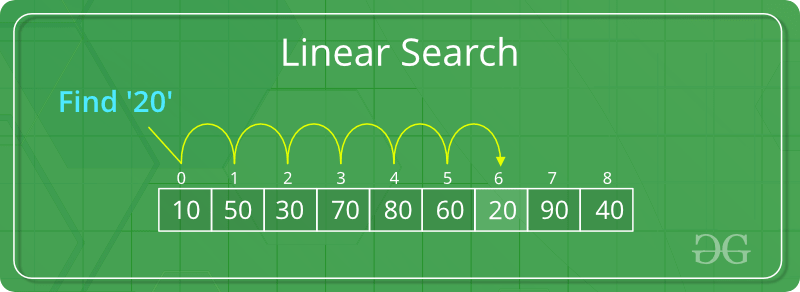
Compares each item one by one until the target is found. There is no need for the list to be in order.
A linear search...
10
New cards
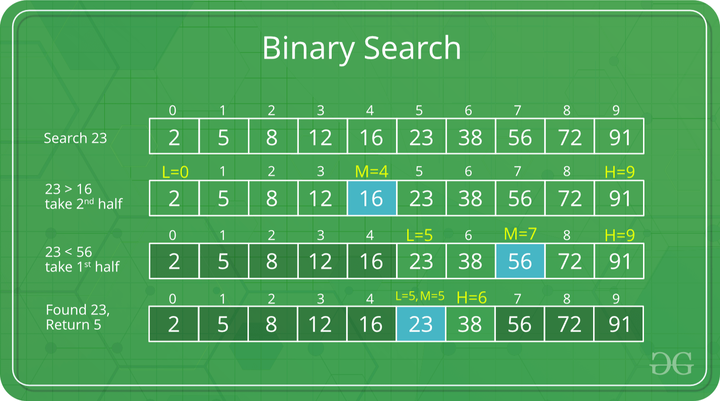
Compares the middle item to the target then discards half of the list which the target can't be in. It then finds the next middle item, and repeats until the target is found.
A binary search...
11
New cards
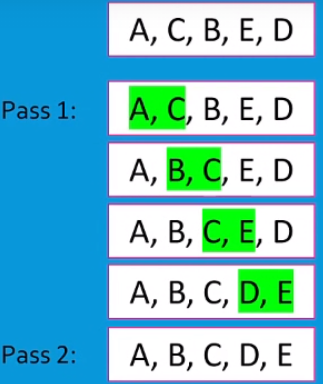
Goes through each pair, swapping if needed, in one pass. I then repeats the passes until a pass happens with no swaps.
A bubble sort...
12
New cards
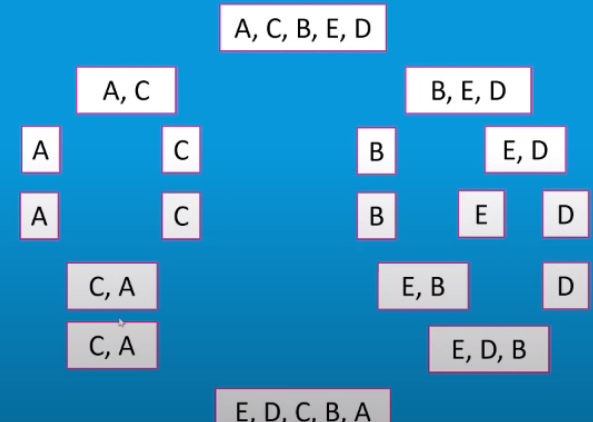
Divides the list continuously by two until each list has 1 item. It then combines two lists at a time, which keeps the items in order.
A merge sort...
13
New cards

Starts with 1 item in the 'sorted part' and moves items one by one from the 'unsorted part' to the 'sorted part'.
An insertion sort...
14
New cards
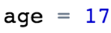
Used to temporarily store information to be referenced and used by programs.
A variable is...
15
New cards

Typically just contains items of the same data type and is of a fixed length. Assume that indexing starts at 0 unless told otherwise.
An array...
16
New cards
The testing of modules throughout development. Any issues found will be fixed and then the module should be retested.
Iterative testing is...
17
New cards
The testing of the whole program at the end of the development.
Terminal testing is...
18
New cards

Code doesn't follow the rules of the programming language.
A syntax error occurs when...
19
New cards
Code does not do as you intend.
A logic error occurs when...
20
New cards
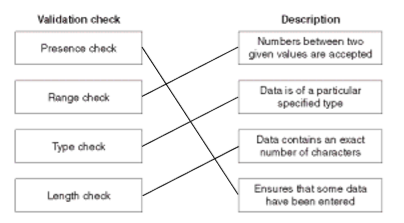
Enforcing a rule around user input.
A validation check is...
21
New cards
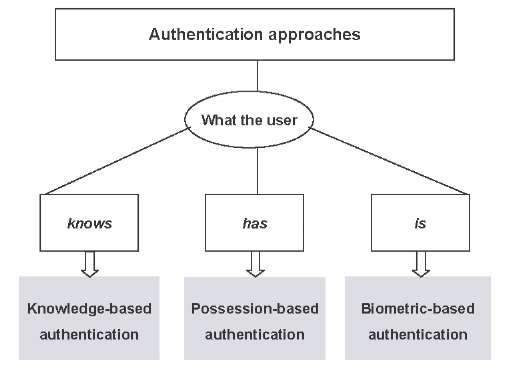
Checking the identity of a user e.g using password checkers.
Authentication is...
22
New cards
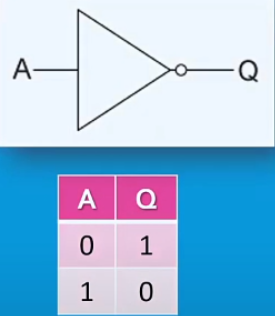
Negation - Inverts the input and outputs it e.g TRUE = FALSE.
NOT gate:
23
New cards
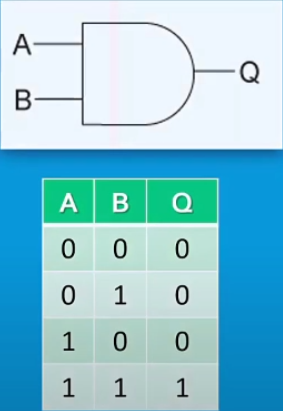
Conjunction - Both inputs need to be true for a true output e.g TRUE & TRUE = TRUE, TRUE & FALSE = FALSE.
AND gate:
24
New cards
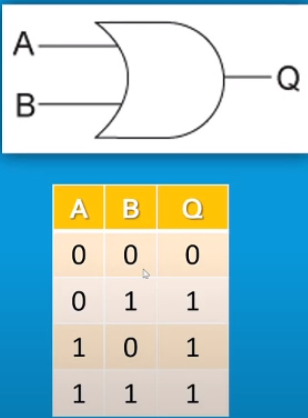
Disjunction - One input out of two needs to be true for a true output e.g TRUE & TRUE = TRUE, TRUE & FALSE = TRUE.
OR gate:
25
New cards

Are like written English, more readable, portable (can run on many CPUs), but are slower to execute.
High-level languages...
26
New cards

The two types of low-level languages are assembly and machine code. They are also easier to optimise but are specific to particular CPUs.
Low-level languages are...
27
New cards
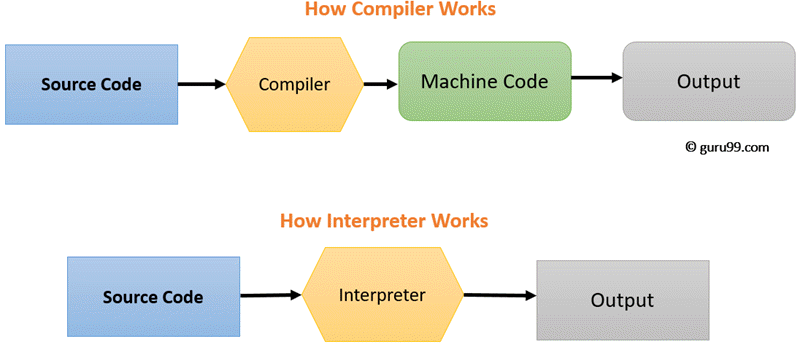
Convert one programming language to another. Only machine code doesn't need to be translated to run.
Translators are programs which...
28
New cards

Produce an executable file and no source code is needed after this. They are fast to execute but errors are only shown right at the end.
Compilers...
29
New cards

Translate an instruction, then execute it. Errors are discovered straight away as code is ran line-by-line, checking for errors on each line but the source code is needed to run and it is slower to execute.
Interpreters...
30
New cards
Providing an editor, providing error diagnostic tools, having a run-time environment and using a translator so it is able to run.
IDEs support programming by...