3.3.1 structural isomerism
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is an isomer?
2.Answer the image?
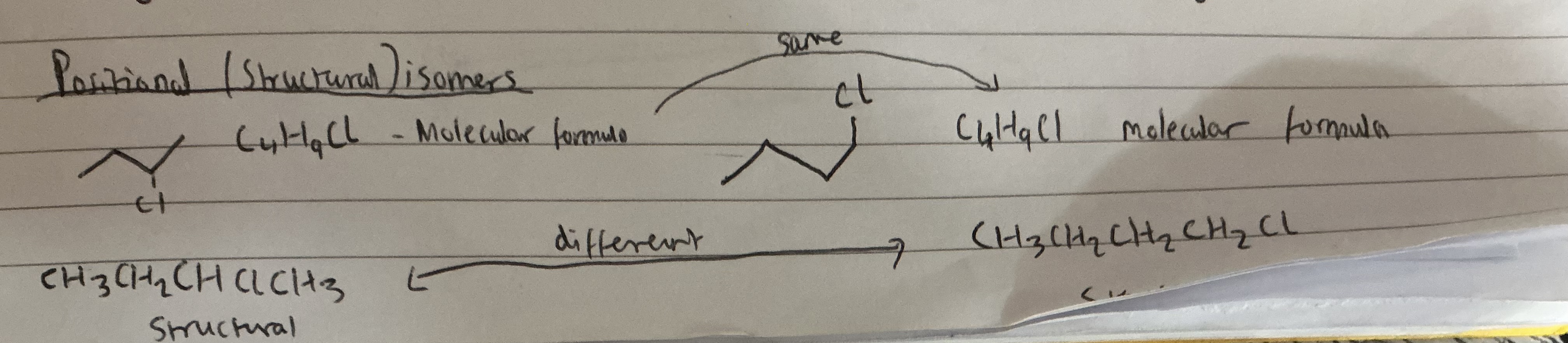
Organic compounds with the same molecular formula(e.g.C4H10) but different arrangement of atoms
A and B

Info:
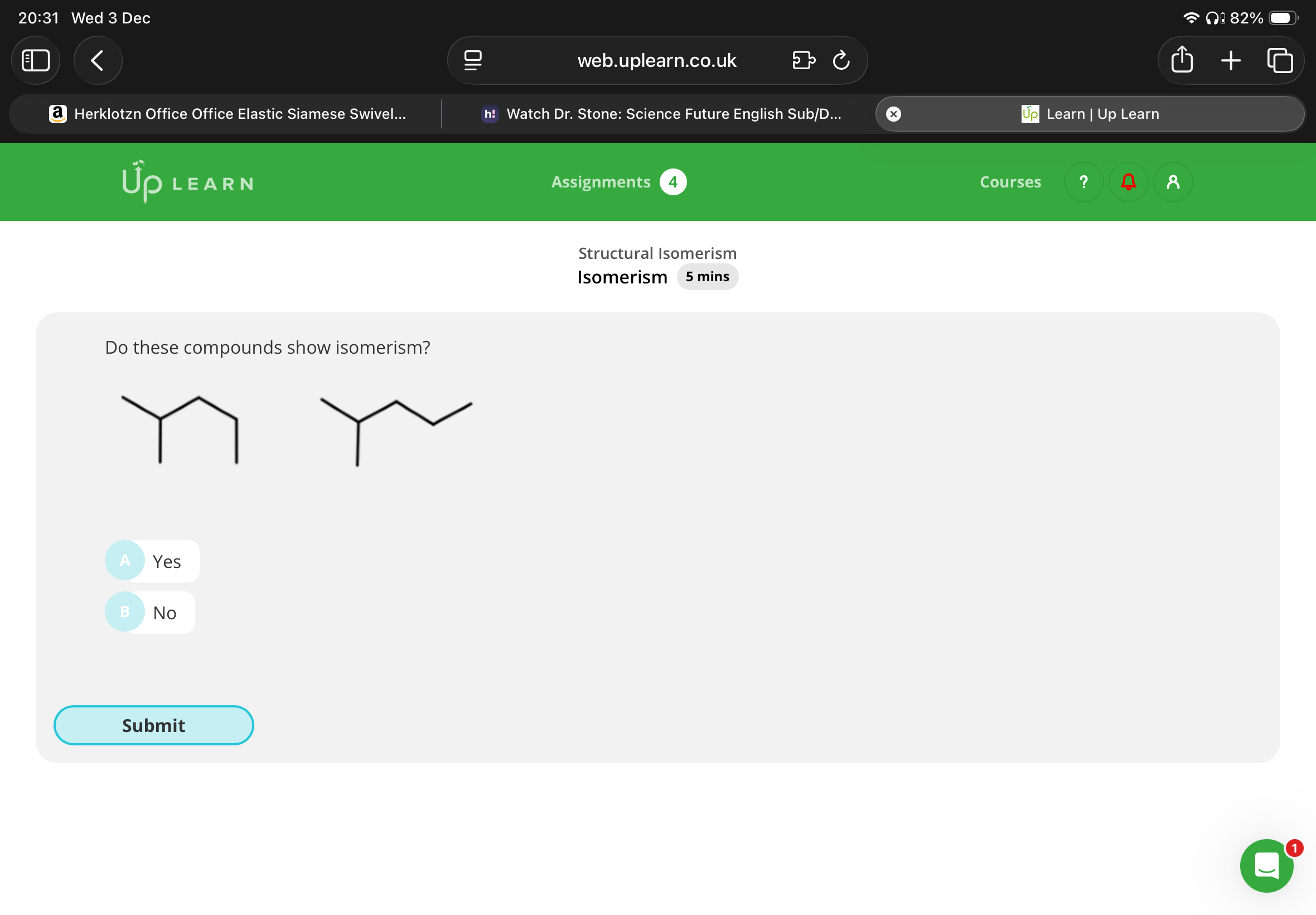
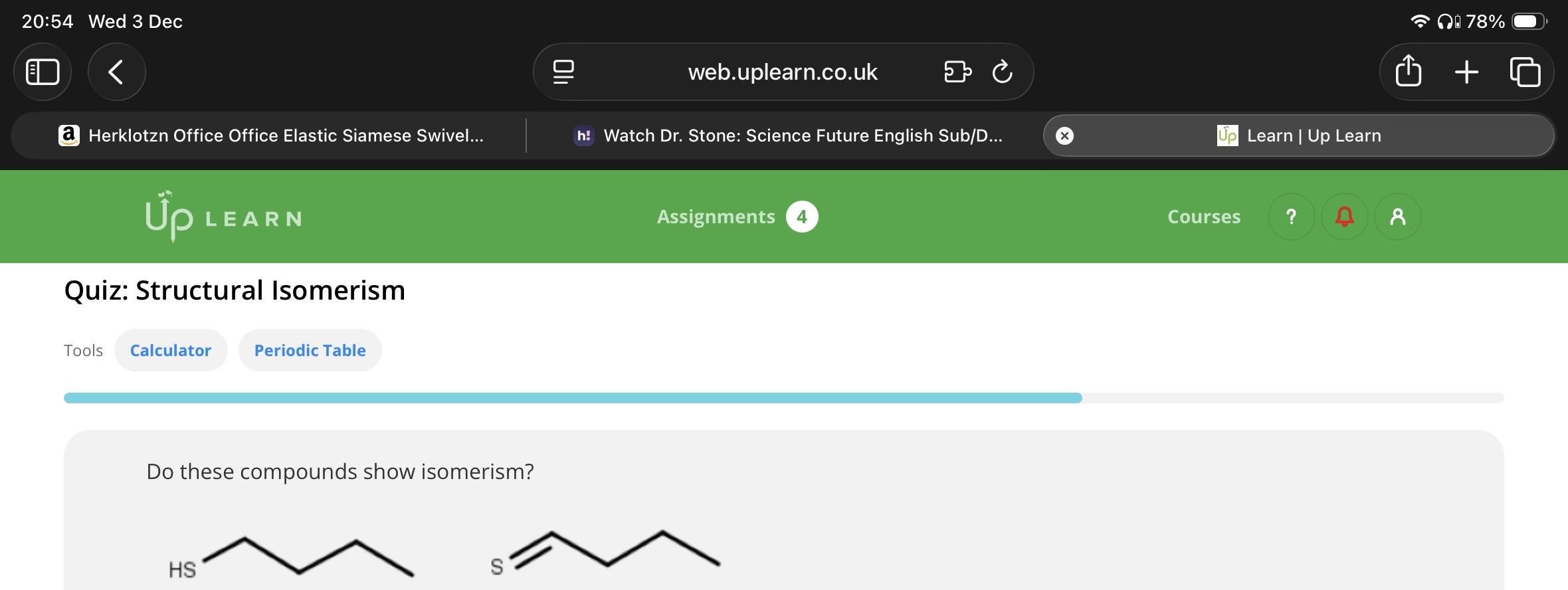
Do these compounds show isomerism(are they isomers )?
No(one of them is drawn in a straight line and the other one is wonky so they have the same structural formula but they are just drawn differently)
(You can also check by naming them and since both are 2-methylpentane, they are not isomers)
Explain your answer
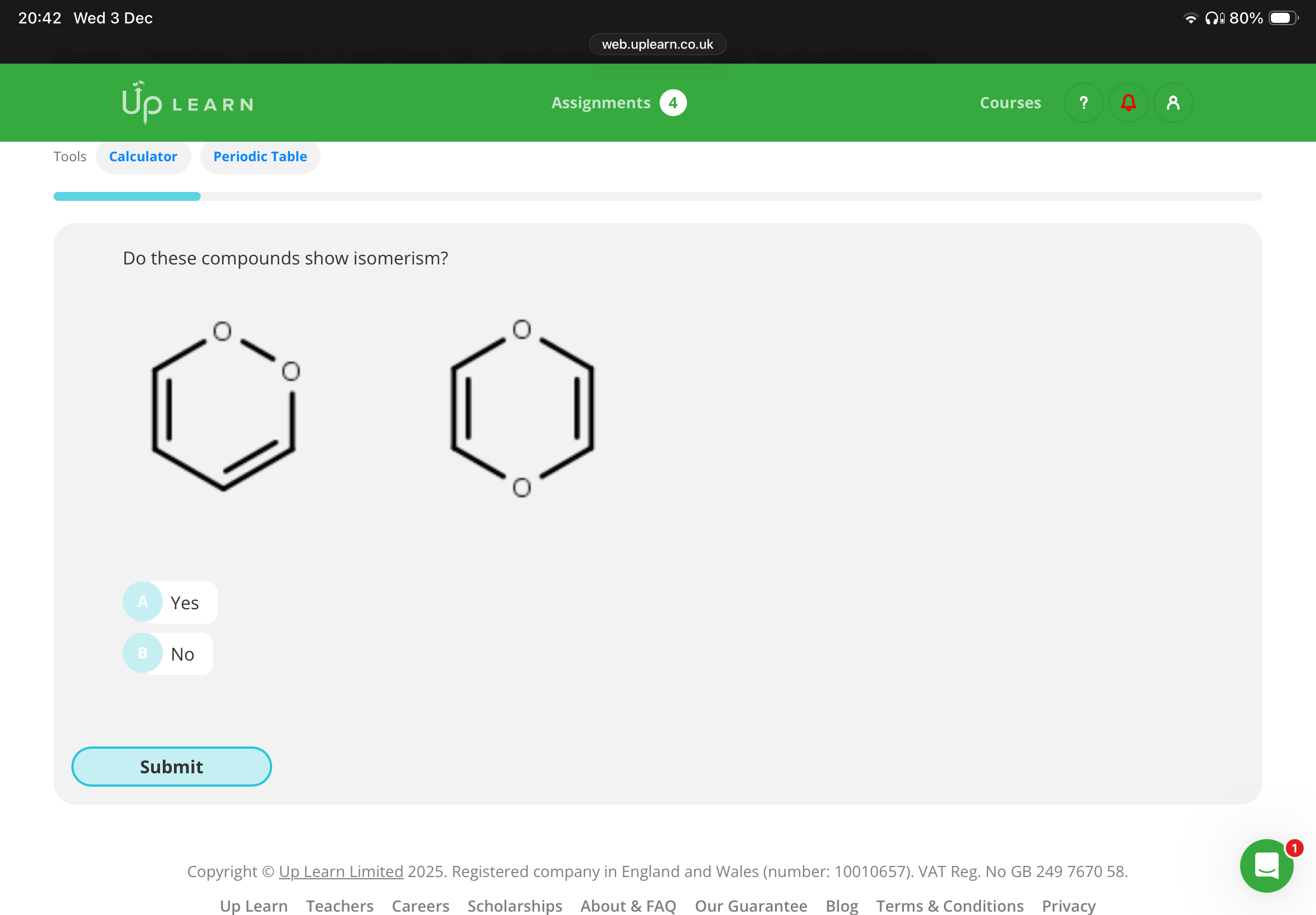
A:These compounds are isomers because they both have the same molecular formula and a different arrangement of atoms.
The molecular formula of both molecules is C4H4O2. In the first molecule, the oxygen atoms are connected directly through a single bond in the carbon ring. In the second molecule, these two oxygen atoms are on opposite sides of the carbon ring.
Info:
No(These compounds are not isomers because they don’t have the same molecular formula.
For the first molecule, the molecular formula is C4H10S. For the second molecule, the molecular formula is C4H8S)
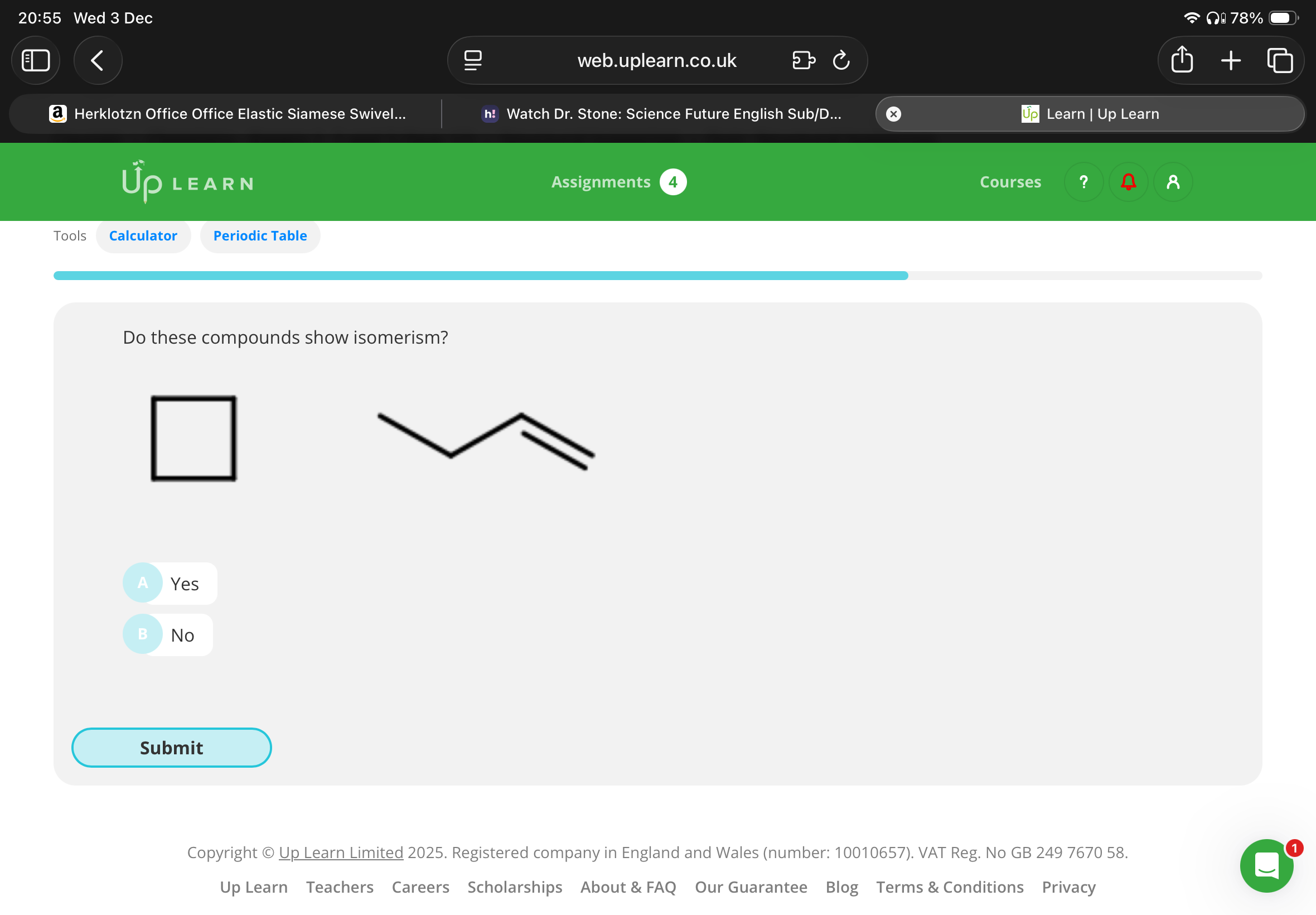
Yes:These compounds are isomers because they both have the same molecular formula and a different arrangement of atoms.
The molecular formula of both molecules is C4H8. In the first molecule, the carbons are connected by single bonds. In the second molecule, the third and fourth carbon have a double bond between them.
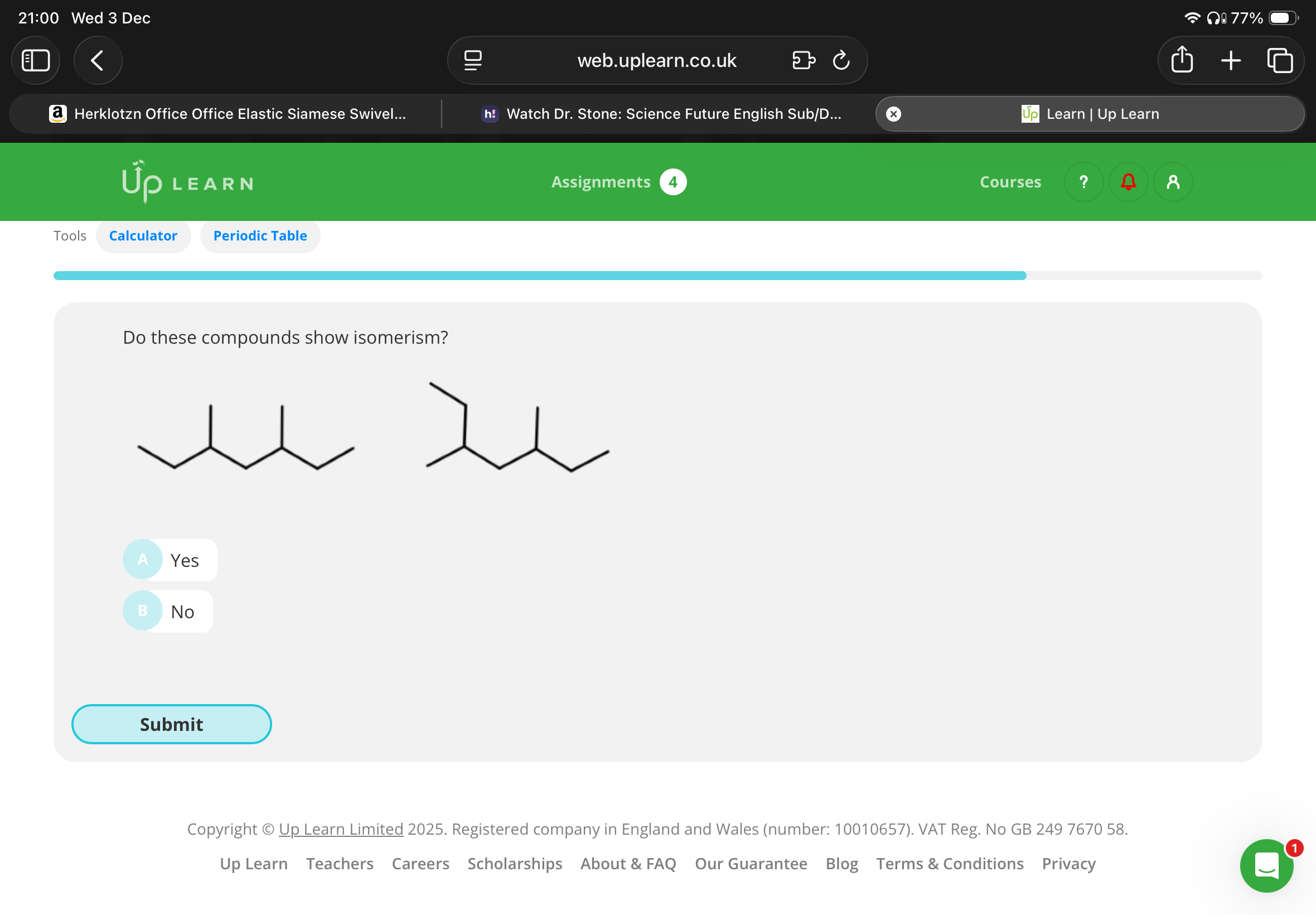
No:These compounds are not isomers because they both have the same molecular formula (C9H20) and the same arrangement of atoms.
In both molecules, the methyl side chains are on the third and fifth carbon of the longest chain. The molecules are the same molecule, just rotated differently!
What is structural isomerism?
What are the 3 types of structural isomers?
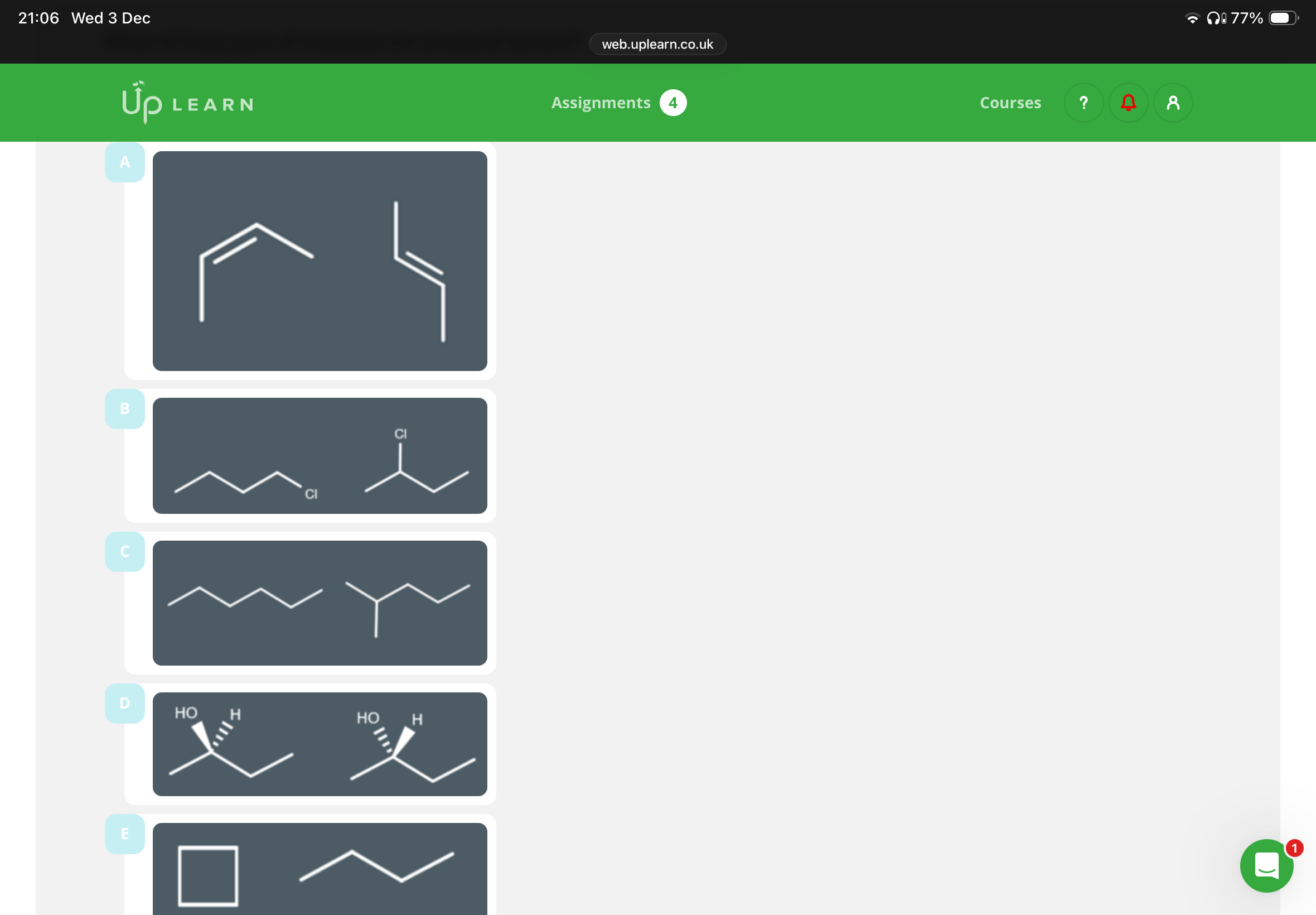
Answer the image and explain why E is or is not a structural isomers?
Organic compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formula
positional,chain,functional
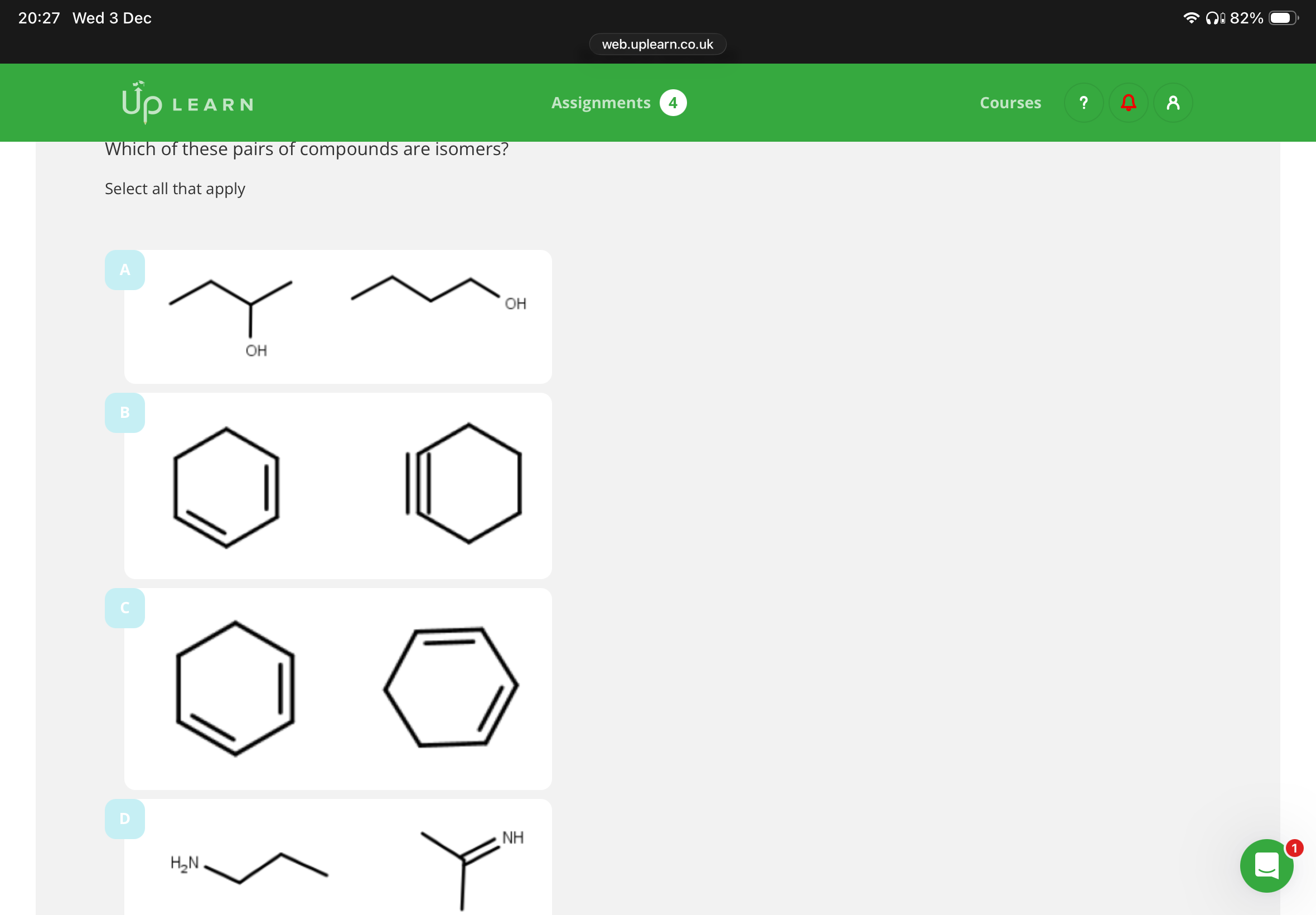
3.B,C,D E isn’t because it has a different molecular formula
Image is info:
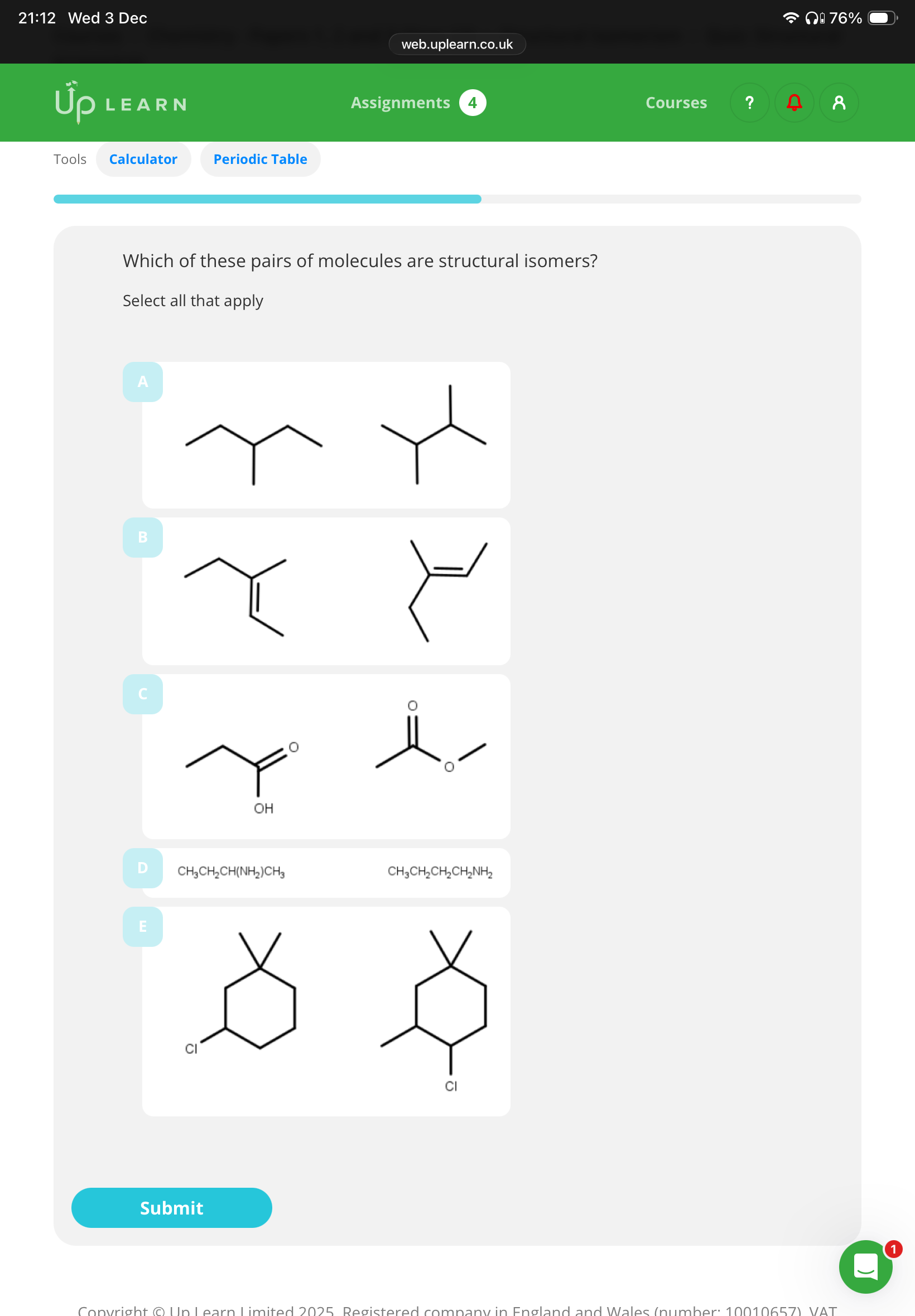
A,D(idk why C ain’t functional)
A,D,E
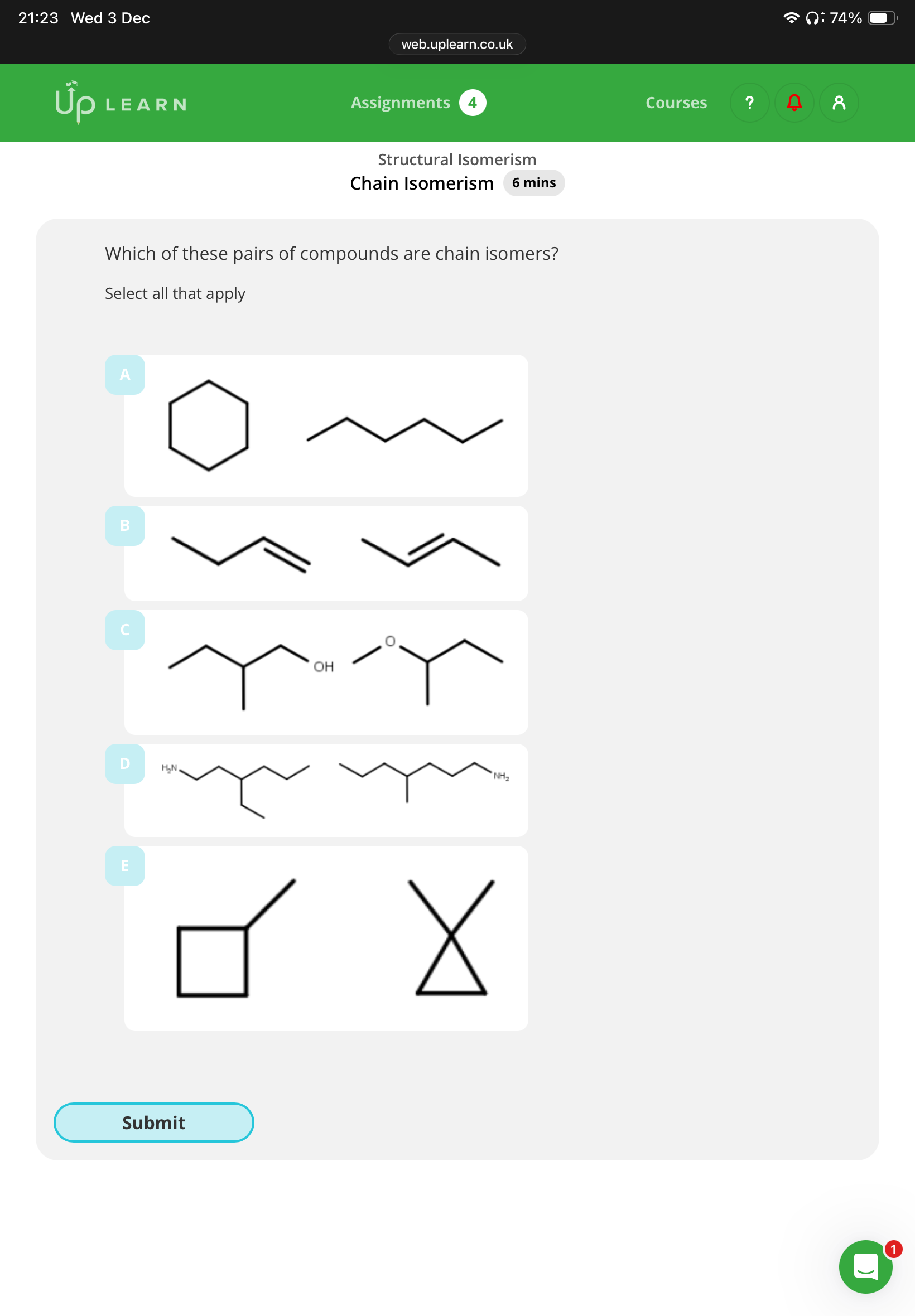
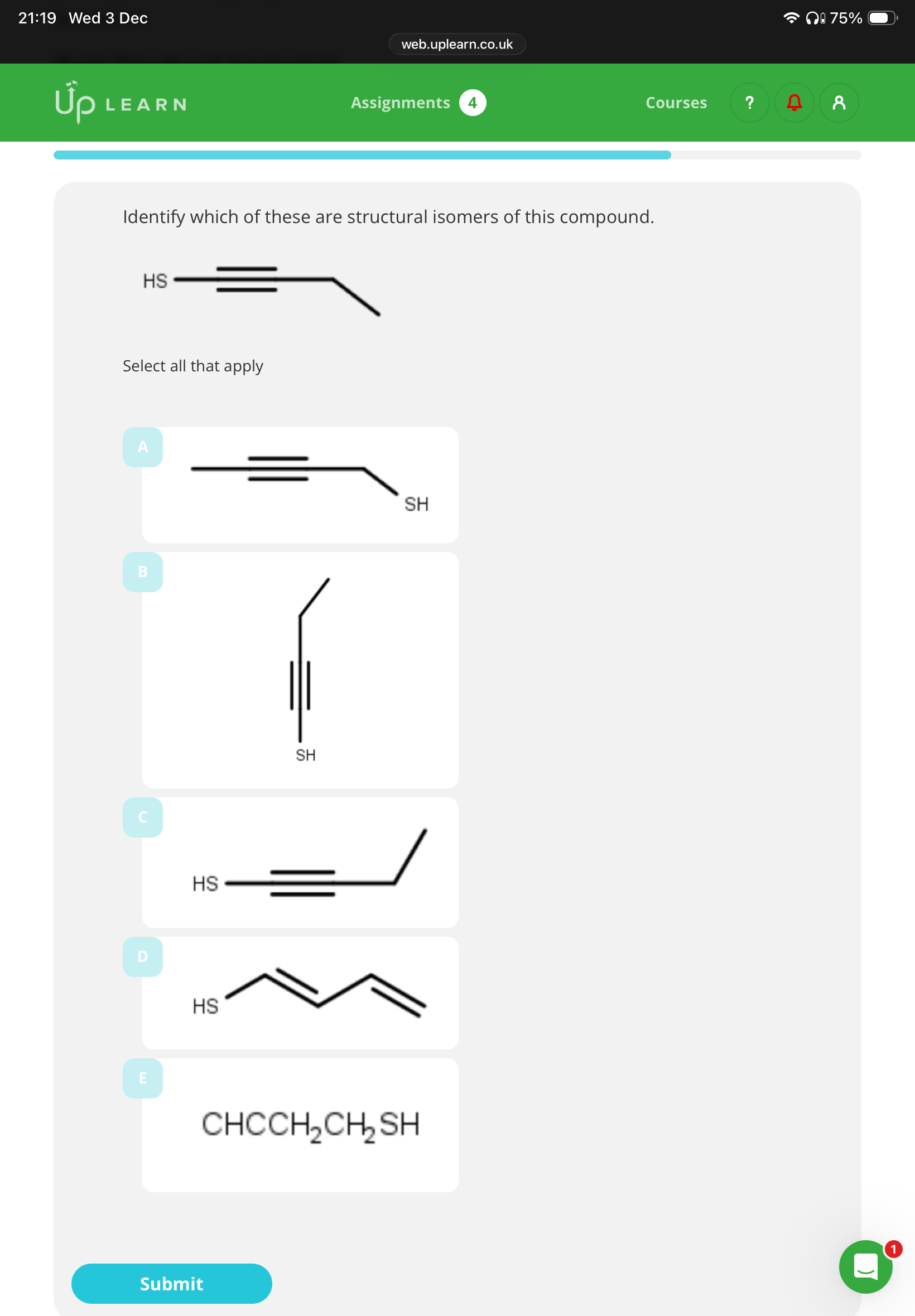
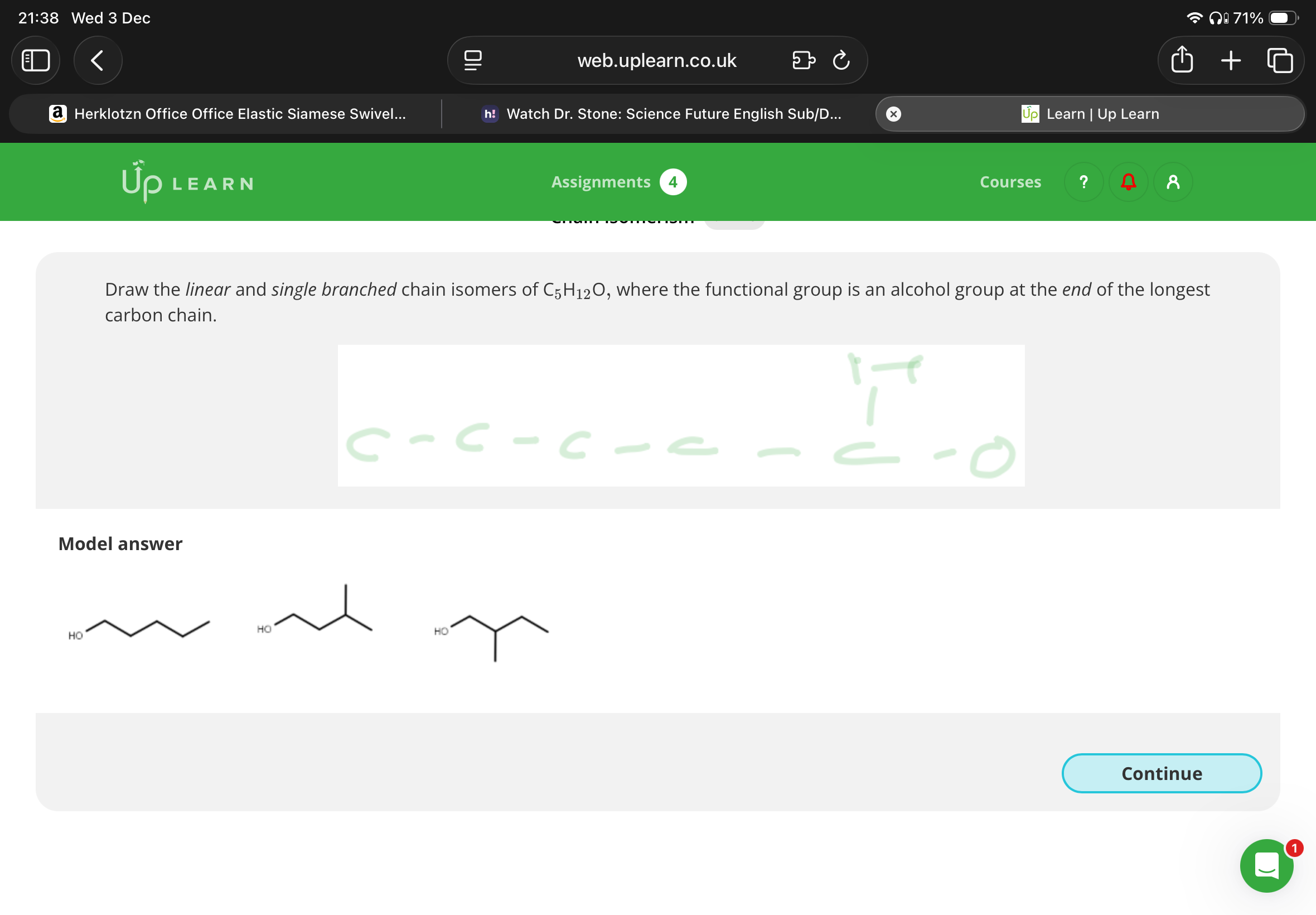
1.What are chain isomers?
2 answer the image:
1.compounds with the Same molecular formula but have a different carbon chain
D and E(B is functional)
Image has info:
1.If a molecule has the general formula CnH2n+2, which homologous series does it belong to?
Note:You can work out the general formula of a compound by looking at the number of hydrogens and carbons and this will tell u whether it is an alkane or alkene that you are drawing
2.What is the general formula of cycloalkanes?
Answer the image
1.Alkane
2.CnH2n
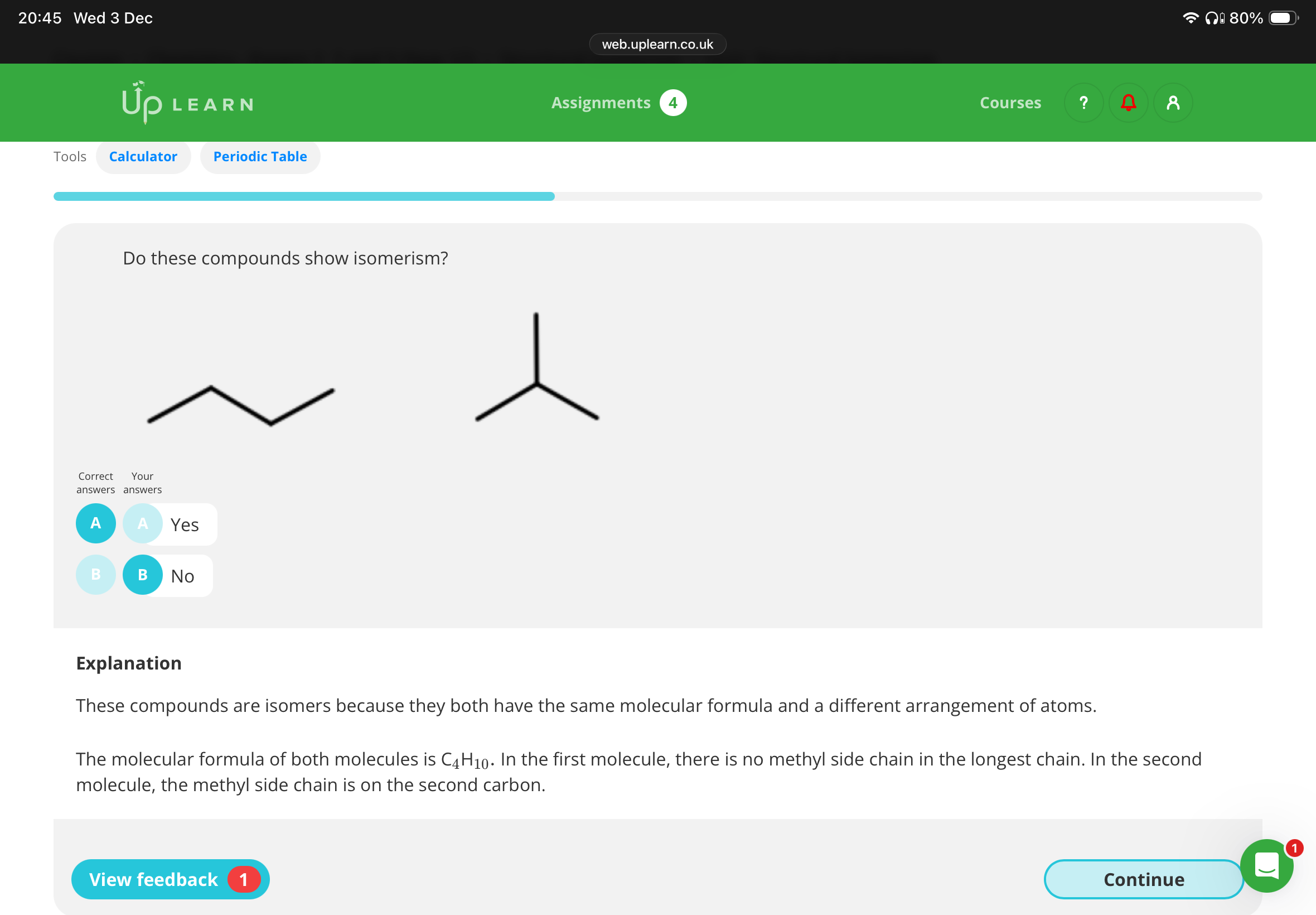
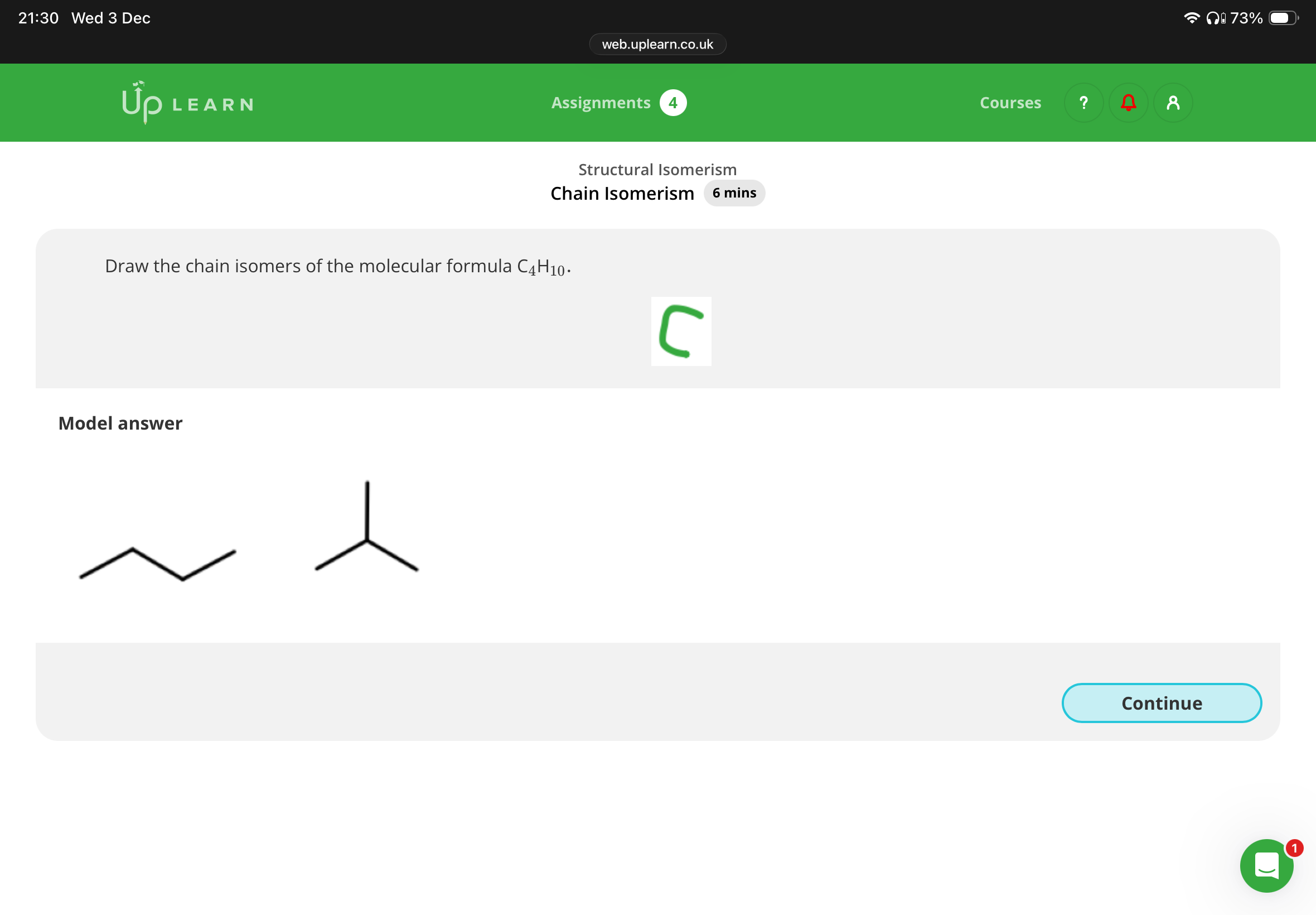
Info:If you put the branch on the end of the chain for C4H10, it actually gives you the same structure as butane, just drawn differently. The branch has to be attached to the second carbon to create a different isomer (2-methylpropane).
So, putting the branch on the end doesn’t create a new isomer—it’s just the straight-chain butane again.
That’s why there are only two chain isomers for C4H10: butane and 2-methylpropane.
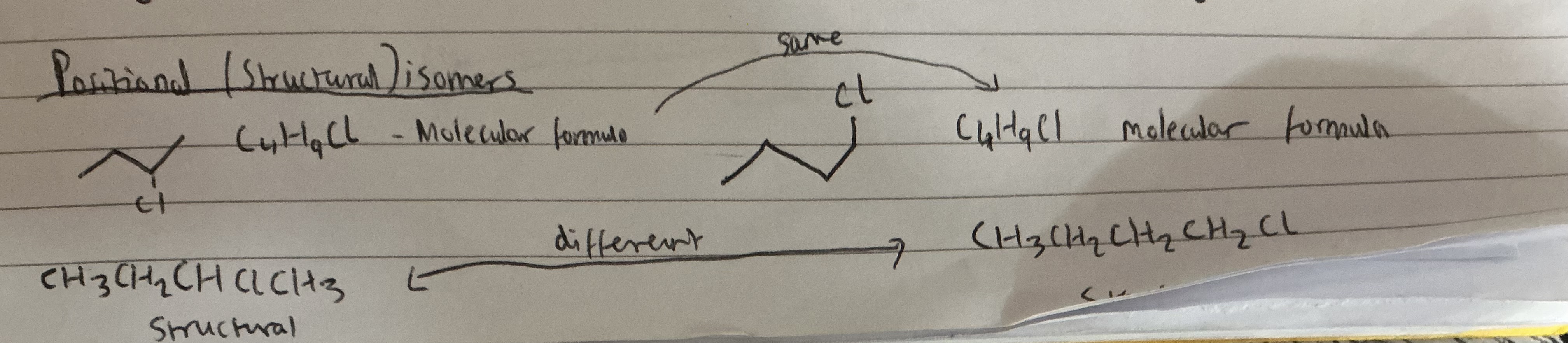
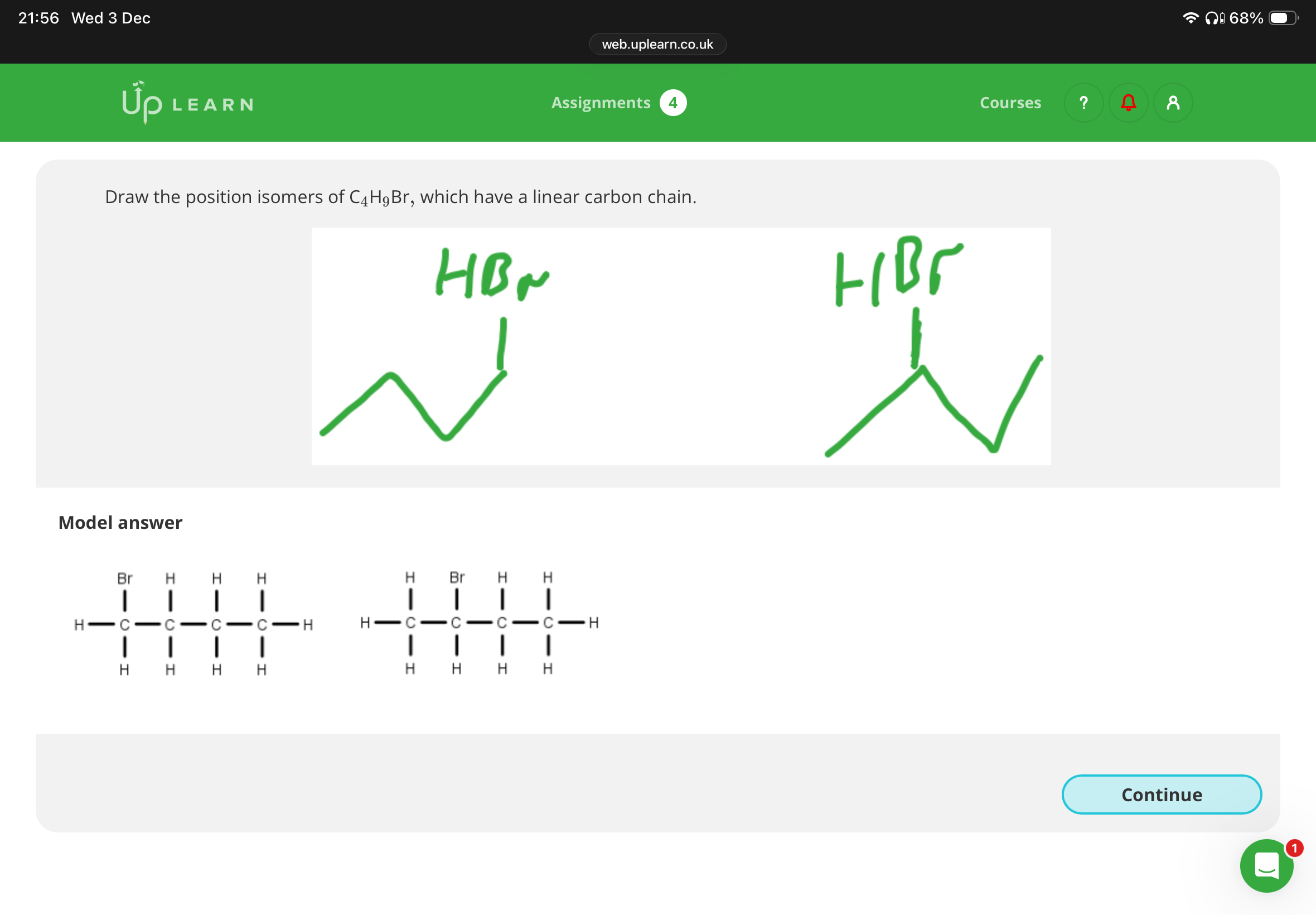
1.What are positional isomers?
Answer the image:
Organic compounds with the same molecular formula but the same functional groups are arranged in a different positions in the compound.
Band E

Draw the positional isomers of C4H9Br, which has a linear carbon chain
Note:It’s possible for compounds to be positional and chain isomers
Note:Image has info
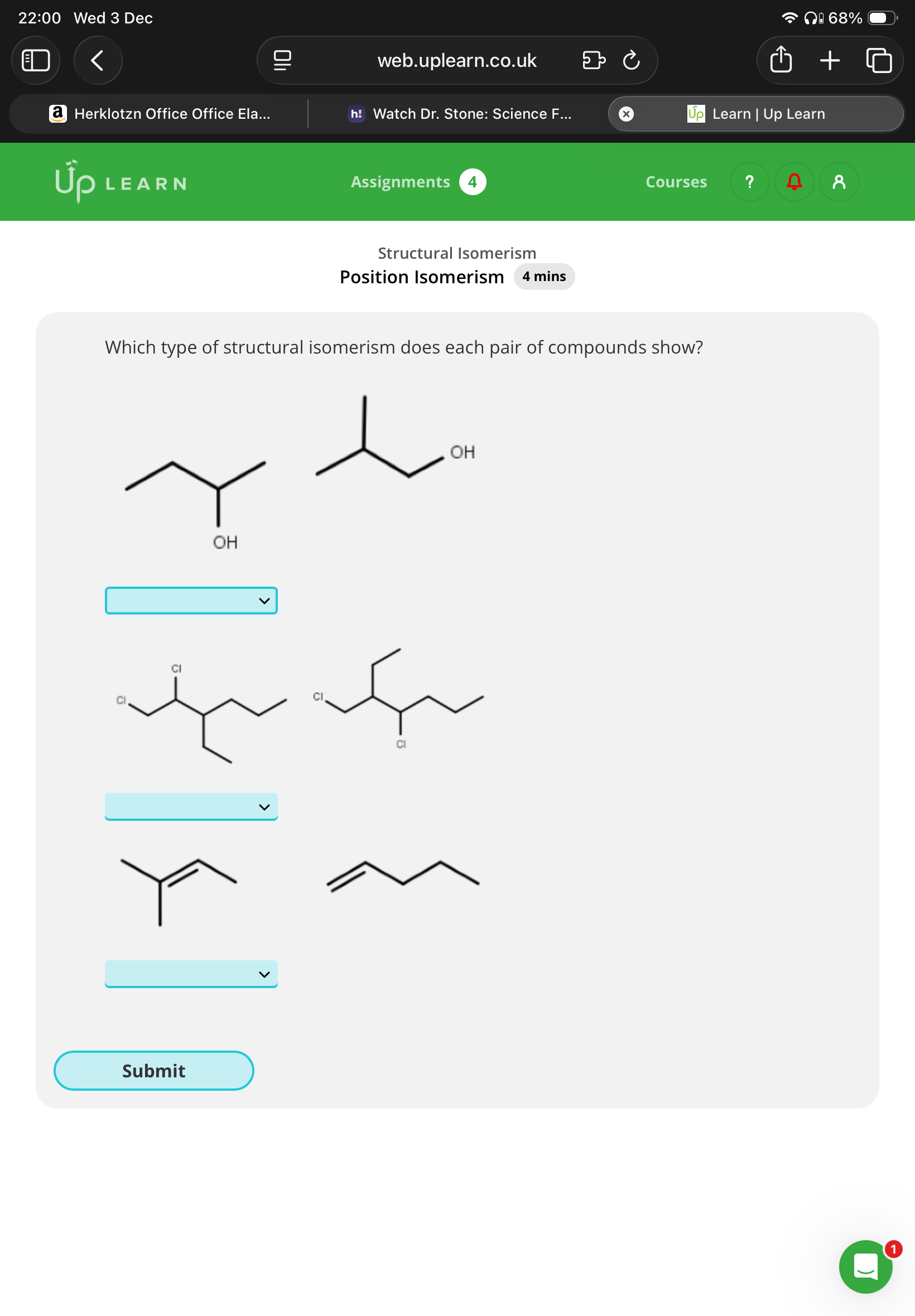
Hint:It’s either,positional,chain,both or neither
Both for all
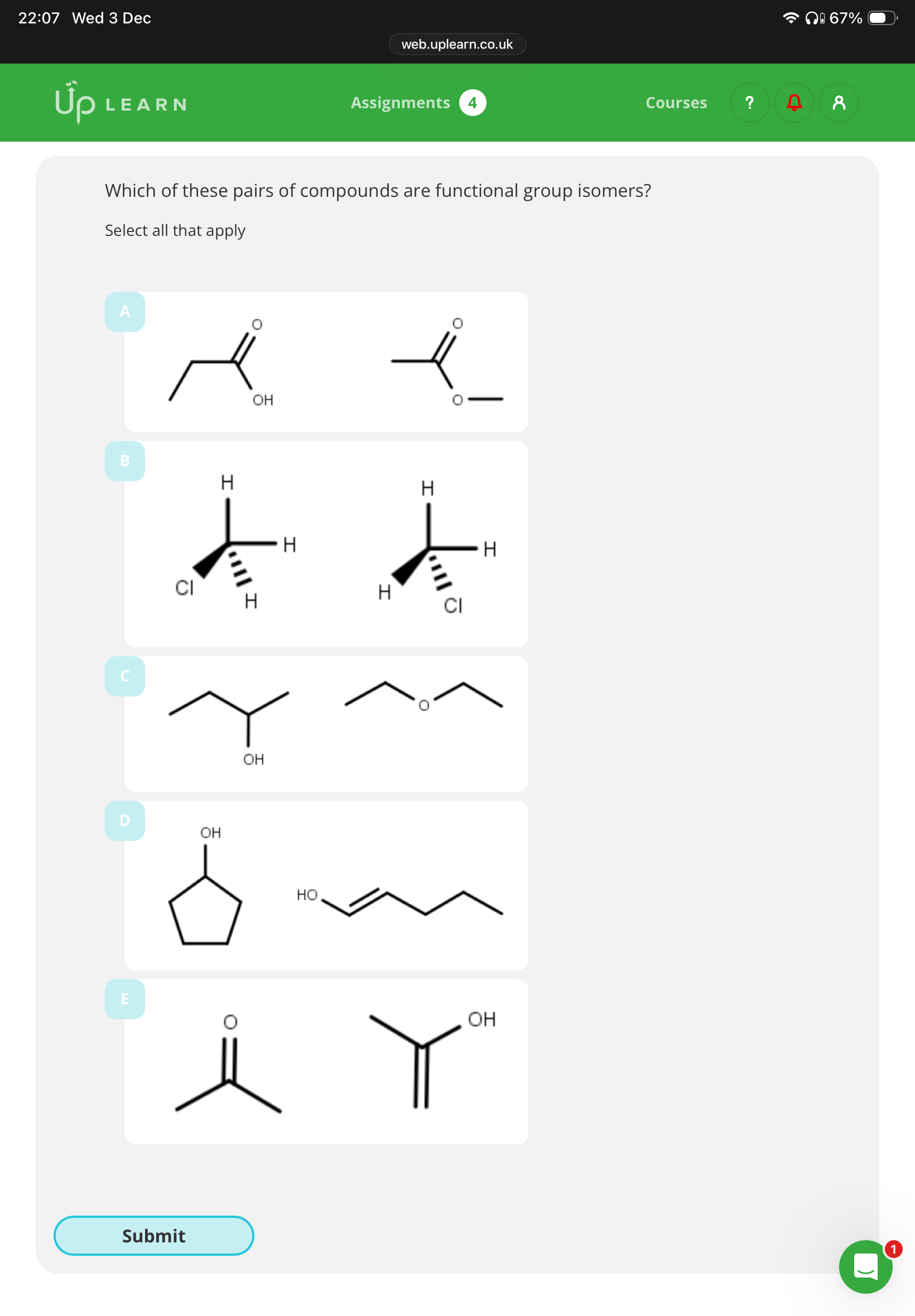
1.What are functional groups isomers?
Answer the question
1.Compounds with the same molecular formula but different functional groups in the compound.
2.A,C,D,E
Note:image has info

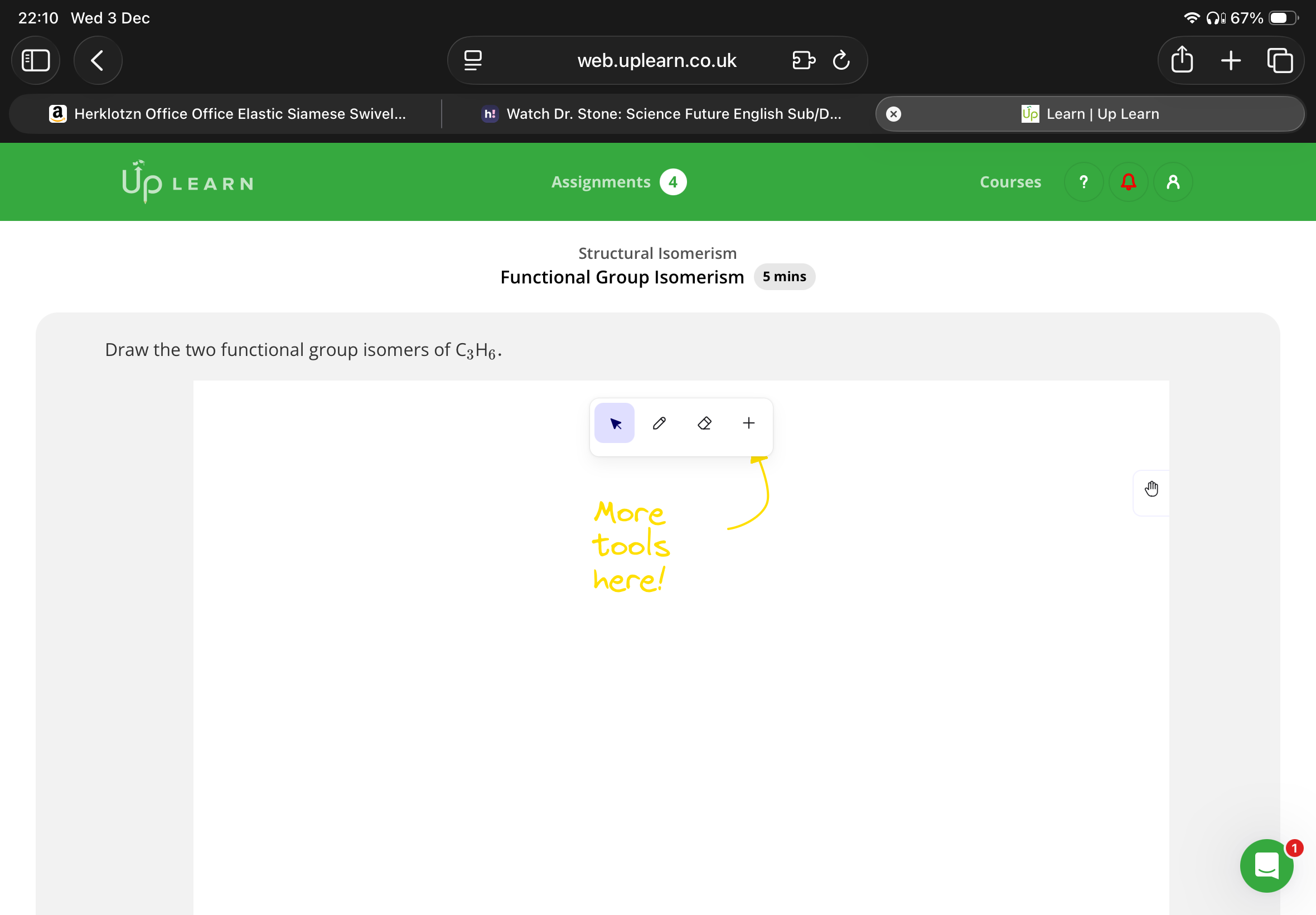
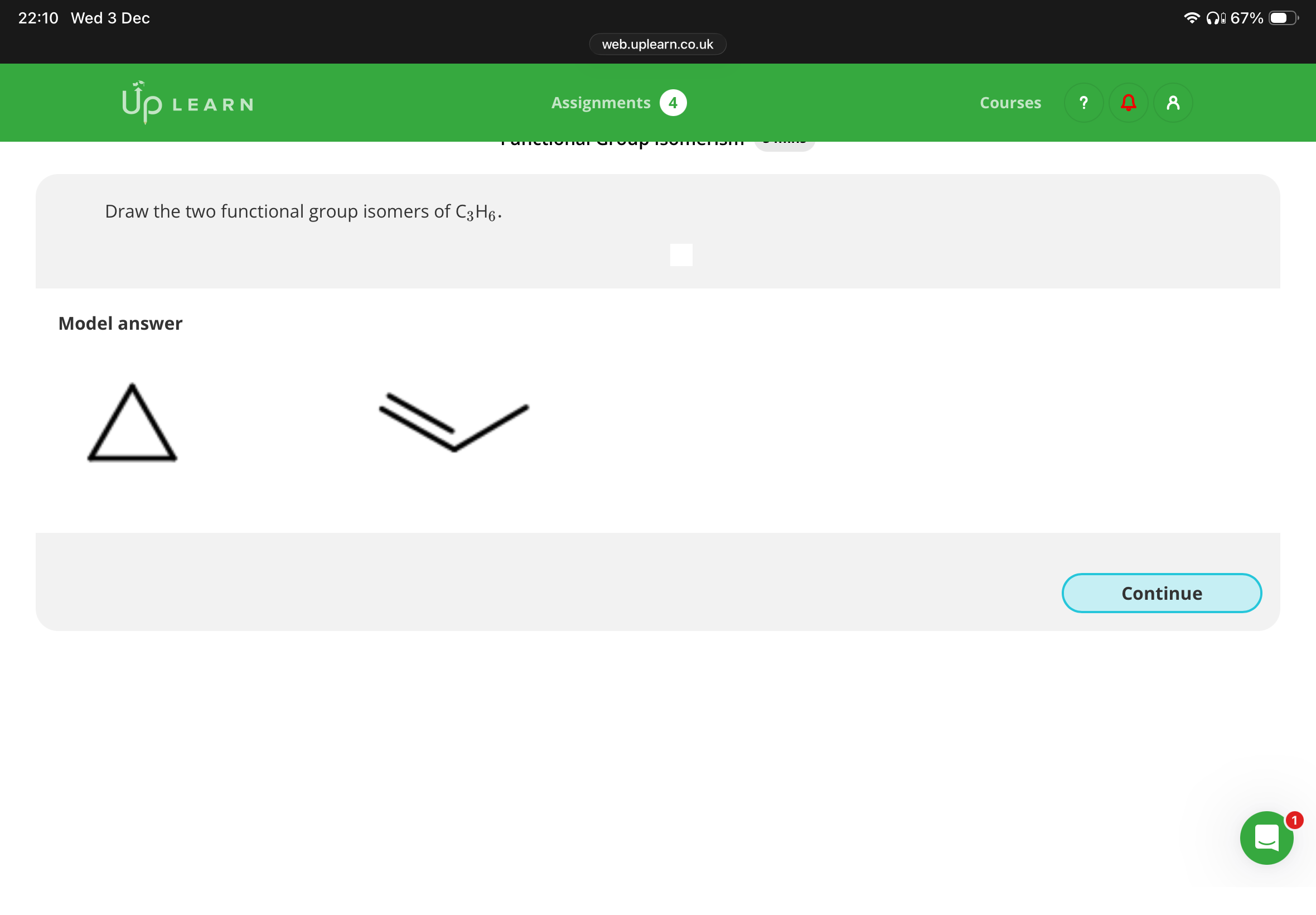
If a molecule has the general formula CnH2n, which homologous series does it belong to?
Note: U can work out the general formula by looking at the amount of carbons and hydrogens so you know whether it’s an alkane or alkene you are drawing.
Alkene or cycloalkane
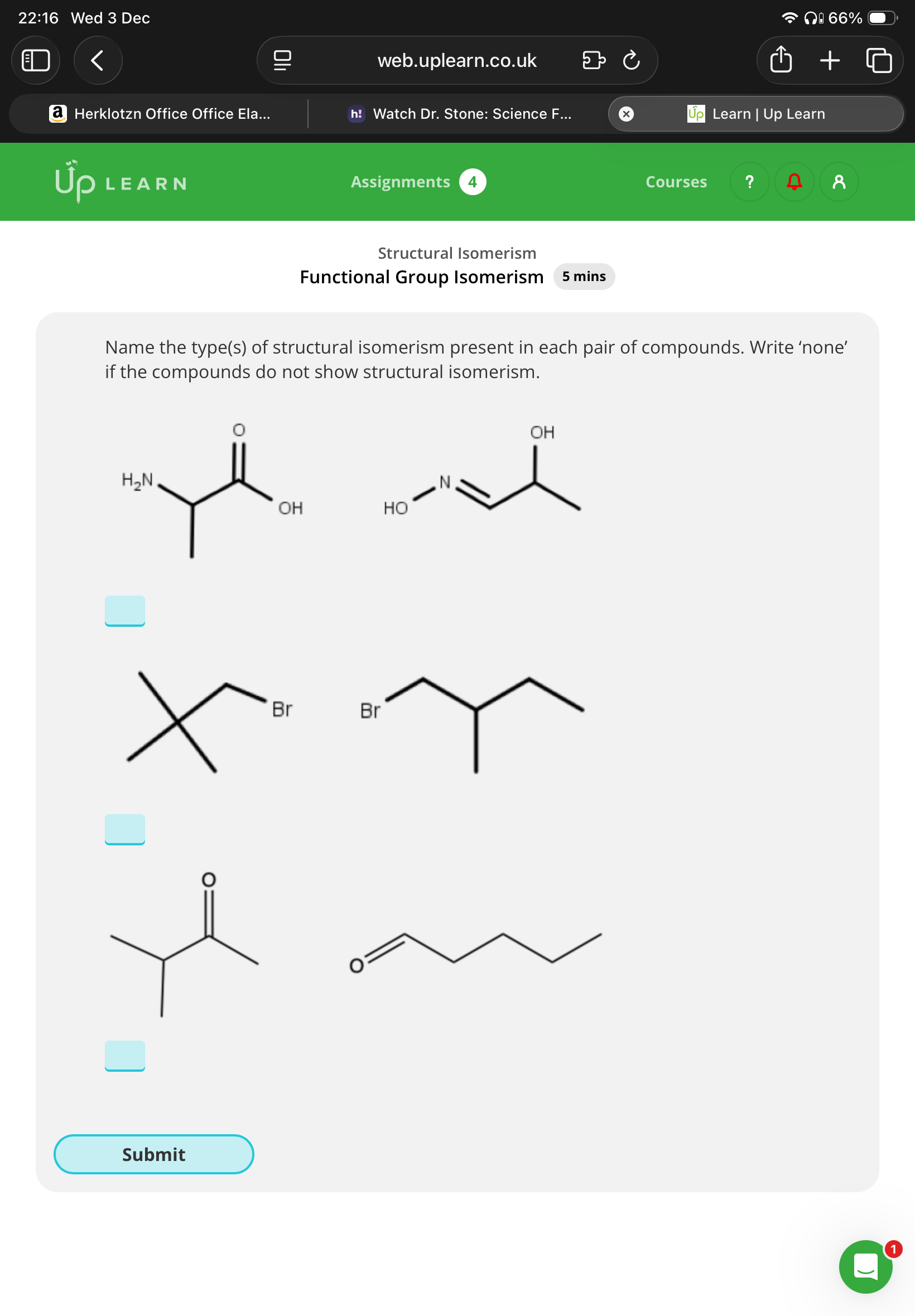
1.functional
2.Chain
3.functional(methyl),chain