Immunology Chapter 8 T Cell-Mediated Immunity
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
T-cell Activation
the stimulation of mature naive T cells by antigen presented to them by professional antigen-presenting cells. It leads to their proliferation and differentiation into effector T cells. Also called T-cell priming.
The immune system __________ initiate adaptive immune responses at the innumerable sites in the body where infections can occur. Instead, the strategy is to _________________________________________, an environment dedicated to the generation of an adaptive immune response.
DOES NOT; capture some of the pathogen and sequester it in secondary lymphoid tissue
___________ of dendritic cells changes their form and function. They focus on activating __________.
Maturation; naive t cells
MHC class II stained _____
Lysosomal protein stained _____
Shows how peptide-loaded ____________ out of the endocytic vesicles and onto the ___________.
red; green; MHC class II is moving; cell surface
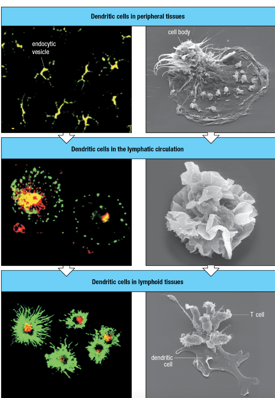
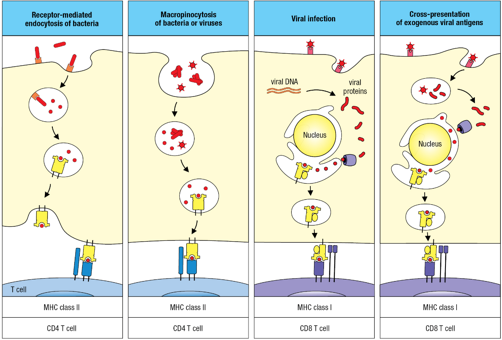
Dendritic cells use _____________ to process and present protein antigen.
several pathways
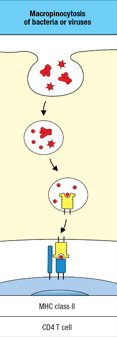
Macropinocytos
The nonspecific uptakes of large amounts of extracellular fluid and molecules by endocytosis, a characteristic of dendritic cells.
T cells that encounter specific antigen (blue) on the antigen-presenting (dendritic cell or macrophage) cells are activated to ____________________________________________.
proliferate and differentiate into effector cells
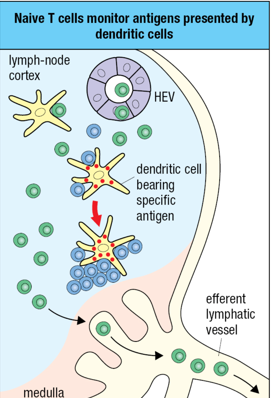
T cells that _____ to find specific antigen leave the ___________ and reenter the ____________.
fail; lymph node; blood stream
During most of its visits to the lymph node, a naive T cell does not find its specific antigen and leaves the afferent lymph and continue _________. Circulating T cells live for __________.
Circulating; many years
Diapedesis
The process where white blood cells (leukocytes) squeeze through the walls of intact blood vessels to move into surrounding tissues.
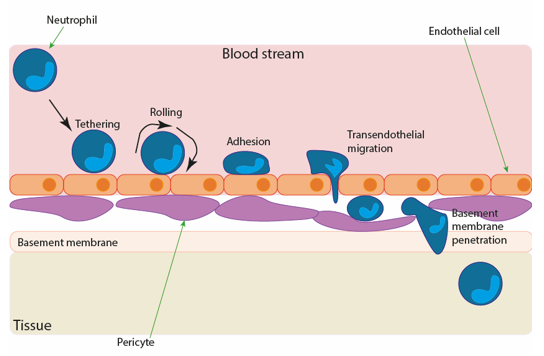
Important adhesion molecules that slow leukocytes down for processes like diapedesis and antigen recognition. ______ on the T cell. ______ on the other cell.
LFA-1; ICAM-1
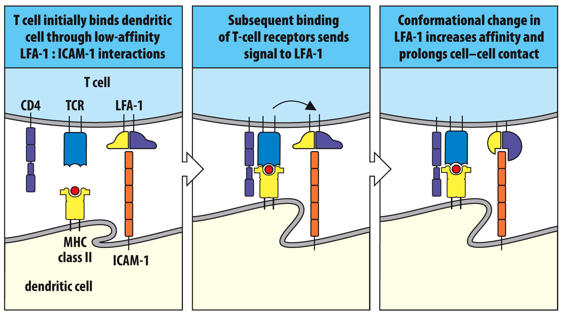
Transient adhesive interaction between a naive T cell and a dendritic cell is stabilized by the recognition of ______________.
specific antigen
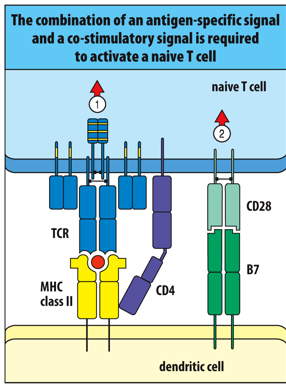
Activation and clonal expansion of the antigen-specific naive T cell occurs only if the ___________ and _________ signals are delivered together. This goes for both to ____________________ . _______ is the co-stimulator receptor and ____ is a co-stimulator.
antigen-specific; co-stimulatory; naive CD8 and naive CD4 T cells; CD28; B7
Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM)
Conserved sequence of four amino acids that is repeated twice in the cytoplasmic tails.
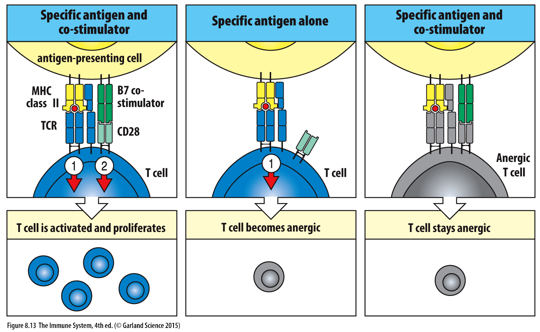
____________ is a state of functional inactivation where a T cell is unable to respond to an antigen because it _____________________________________________. This process is a crucial part of immune system’s self tolerance mechanism, preventing diseases by stopping self reactive T cells from becoming fully activated.
T-cell anergy; did not receive the necessary co-stimulatory signals during its activation
Proliferation and differentiation of activated T cells is driven by the cytokine _______________.
Internlukin-2 (IL-2)
Master Regulator
transcription factor that controls the differentiation of a cell
TH1 Cells
Defining Transcription Factor
Function
T-bet
Activate macrophages
Help macrophages to suppress intracellular infections
TH17 Cells
Defining Transcription Factor
Function
RORγT
Enhance neutrophil response
Enhance the neutrophil response to fungal and extracellular bacterial infections
TH2 Cells
Defining Transcription Factor
Function
GATA3
Activate cellular and antibody response to parasites
Help basophils, mast cells, eosinophils, and B cells respond to parasite infections
TFH Cells
Defining Transcription Factor
Function
Bcl6
Activate B cells maturation of antibody response
Help B cells become activated, switch isotype, and increase antibody affinity
T regulatory cells (Treg)
Defining Transcription Factor
Function
FoxP3
Suppress other effector T cells
Suppress the activities of other effector T-cell populations
In people with a polarized _________________, the cytokines made by TH1 cells help the infected macrophages to suppress the growth and dissemination of the bacteria. The _____________ damages skin and peripheral nerves, but the disease progresses slowly, and people ___________________.
TH1 response (tuberculoid leprosy); chronic state of inflammation; do not usually die from it.
For people making a polarized _______________, the outcome is different. Pathogen specific ___________________ in quantity, but they are __________ against bacteria hidden in macrophages.
TH2 response (Lepromatous leprosy); antibodies are made; ineffective
Polarized T-cell response
TH1 and TH2 cells, the cytokine driving their differentiation— ______ for TH1, and ____ for TH2— is central to their effector function and is secreted in quantity. This situation facilitates ___________________, whereby the functional effector T cells drive further differentiation of the same effector T-cell type. This can cause rapid expansion of a population of pathogen-specific CD4 T cells, with either TH1 or TH2 cells becoming dominant.
IFN-γ; IL-4; positive reinforcement
TH1-cell mediated immunity
Effector T cells dominate adaptive immune response
TH2-humoral immunity
Mediated by antibodies
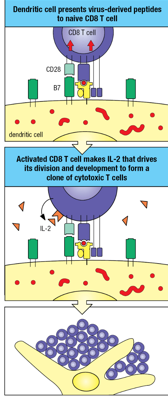
Direct Activation of CD8 T-cells
Dendritic cell presents virus-derived peptides to naive CD8 T cells
Activated CD8 T cell makes IL-2 that drives its division and development to form a clone of cytotoxic T cells
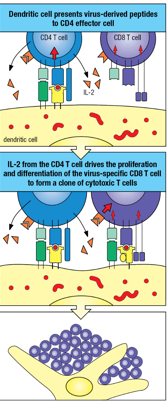
Indirect activation of CD8 T-cells
Dendritic cell presents virus-derived peptides to CD4 effector cells
IL-2 from the CD4 T cell drives the proliferation and differentiation of the virus-specific CD8 T cell to form a clone of cytotoxic T cells
Activation of T cells changes the expression of several __________________________.
cell-surface molecules
_________________express VLA-4, enabling them to enter infected tissue.
Effector T cells
VCAM-1, which is selectively expressed on the endothelium of blood vessels in inflamed tissue, __________________________ from the blood into the infected tissue.
recruits effector T cells
Co-stimulatory signals are required for _______________ but NOT for activating effector T cells.
activating naive T cells
Neither _________________________ require co-stimulatory signals for activation
CD4 nor CD8 effector T cells
Cytotoxic CD8 T cells
Kills virus-infected cells
CD8 T cells kill infected cells by secretion of ______________ and focused delivery of cytotoxins onto the target cell surface
lytic granules (LG)