Biochem 501 Exam 1 UW Madison MASTERY : 74 Expert-Verified Q&A on Metabolic Pathways, Enzyme Kinetics & Molecular Mechanisms (Latest Updates)
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Glycine (Gly/G)
Nonpolar, aliphatic R Groups
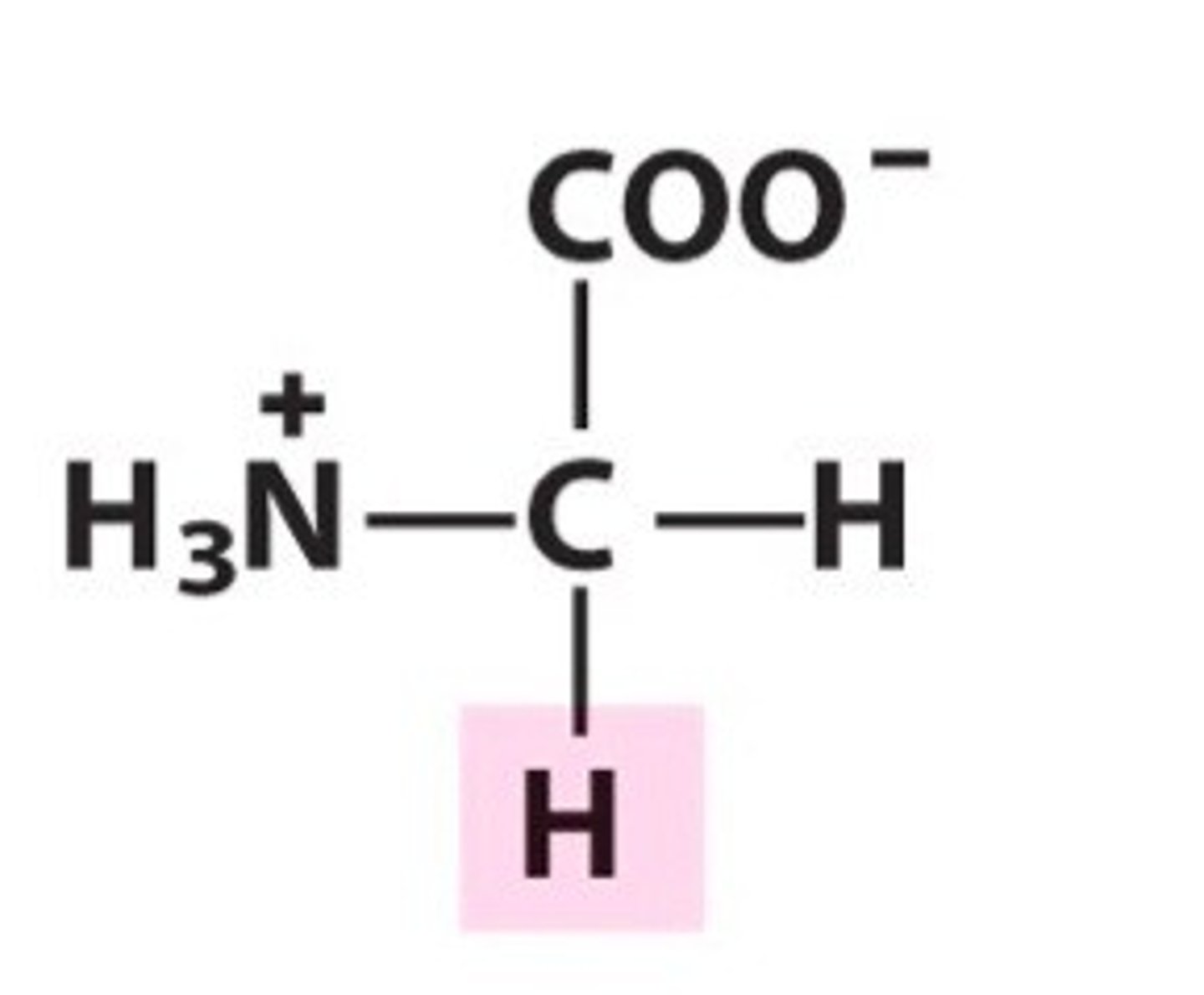
Alanine (Ala/A)
Nonpolar, aliphatic R Groups
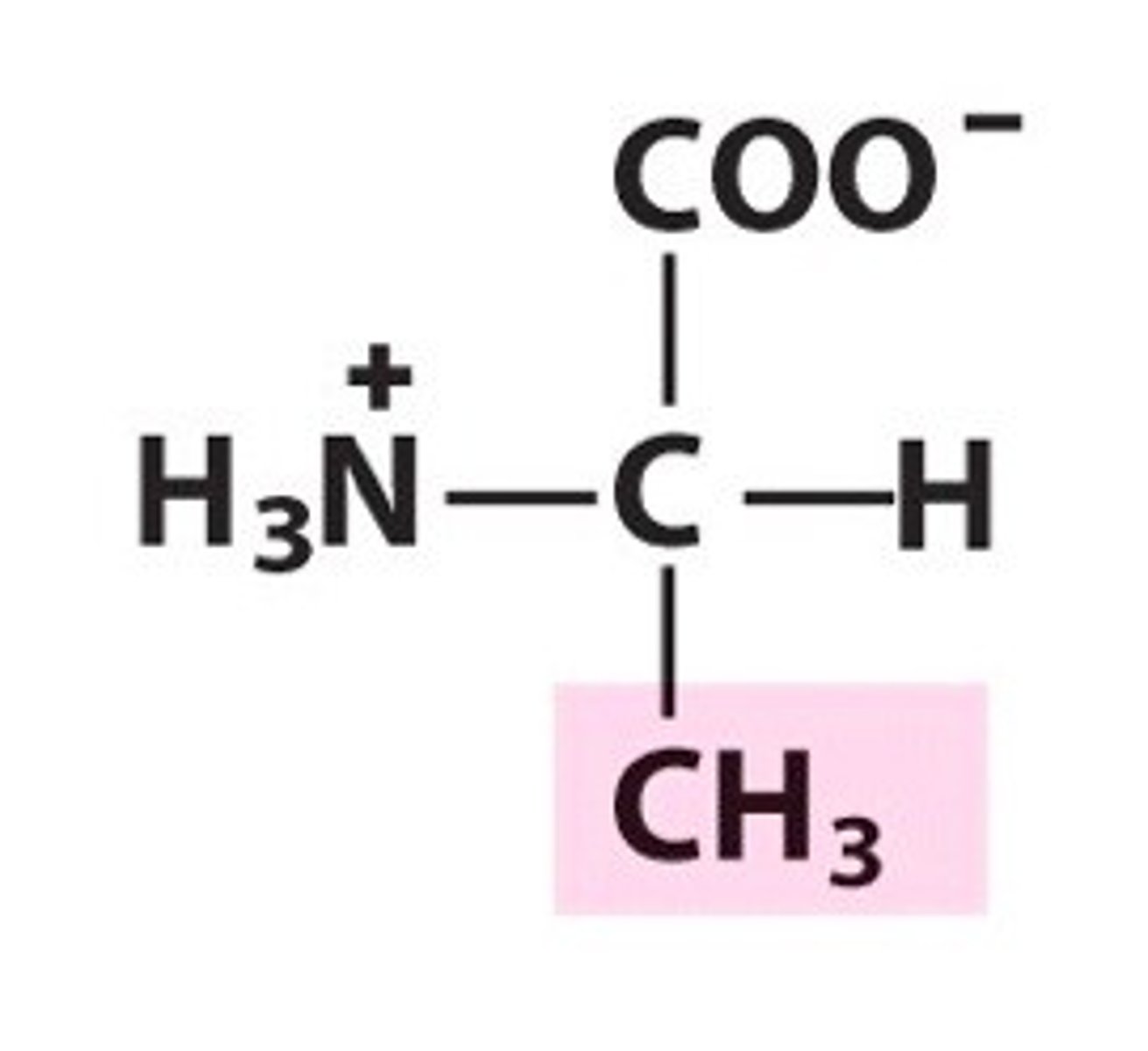
Proline (Pro/P)
Nonpolar, aliphatic R Groups
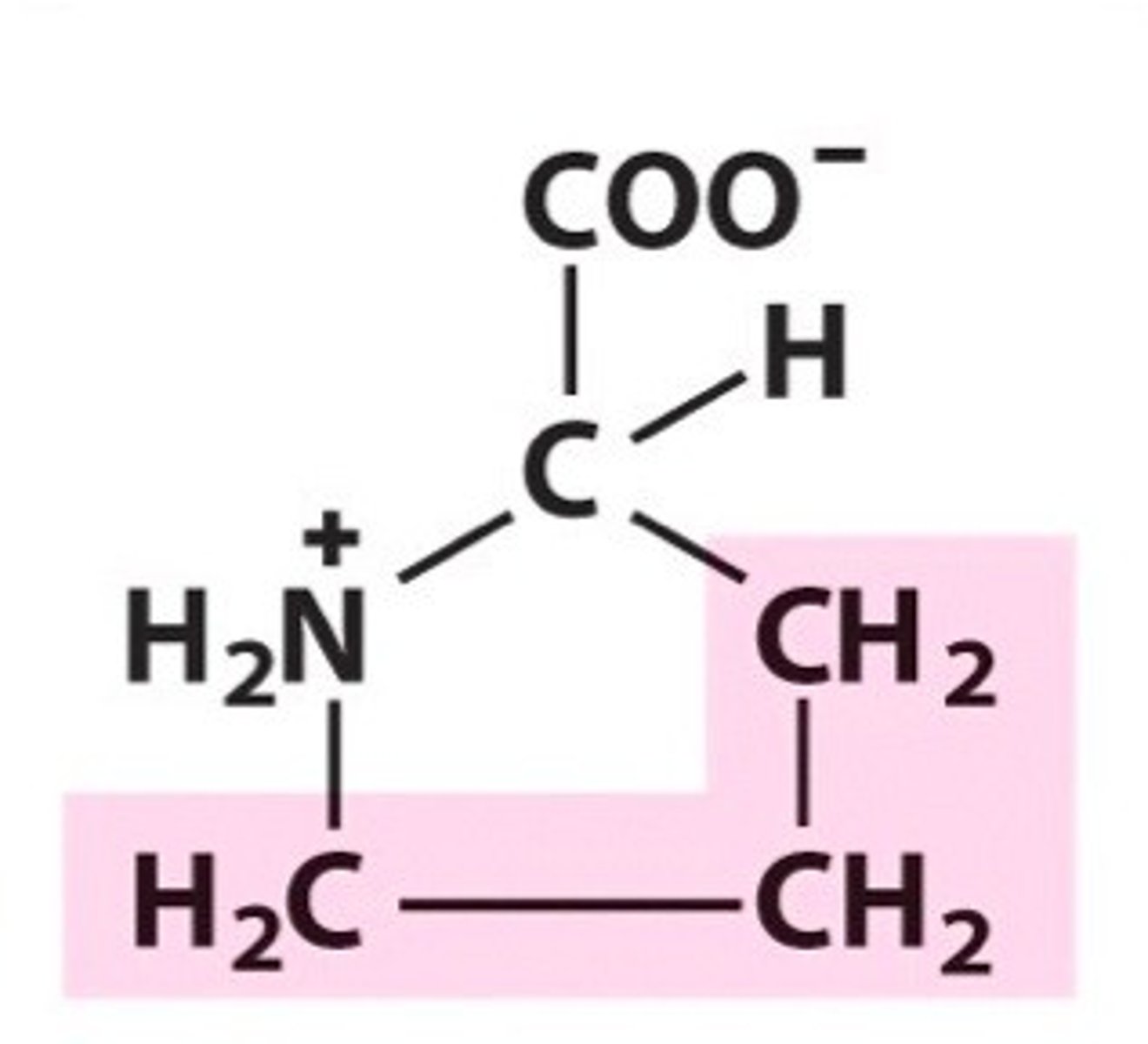
Valine (Val/V)
Nonpolar, aliphatic R Groups
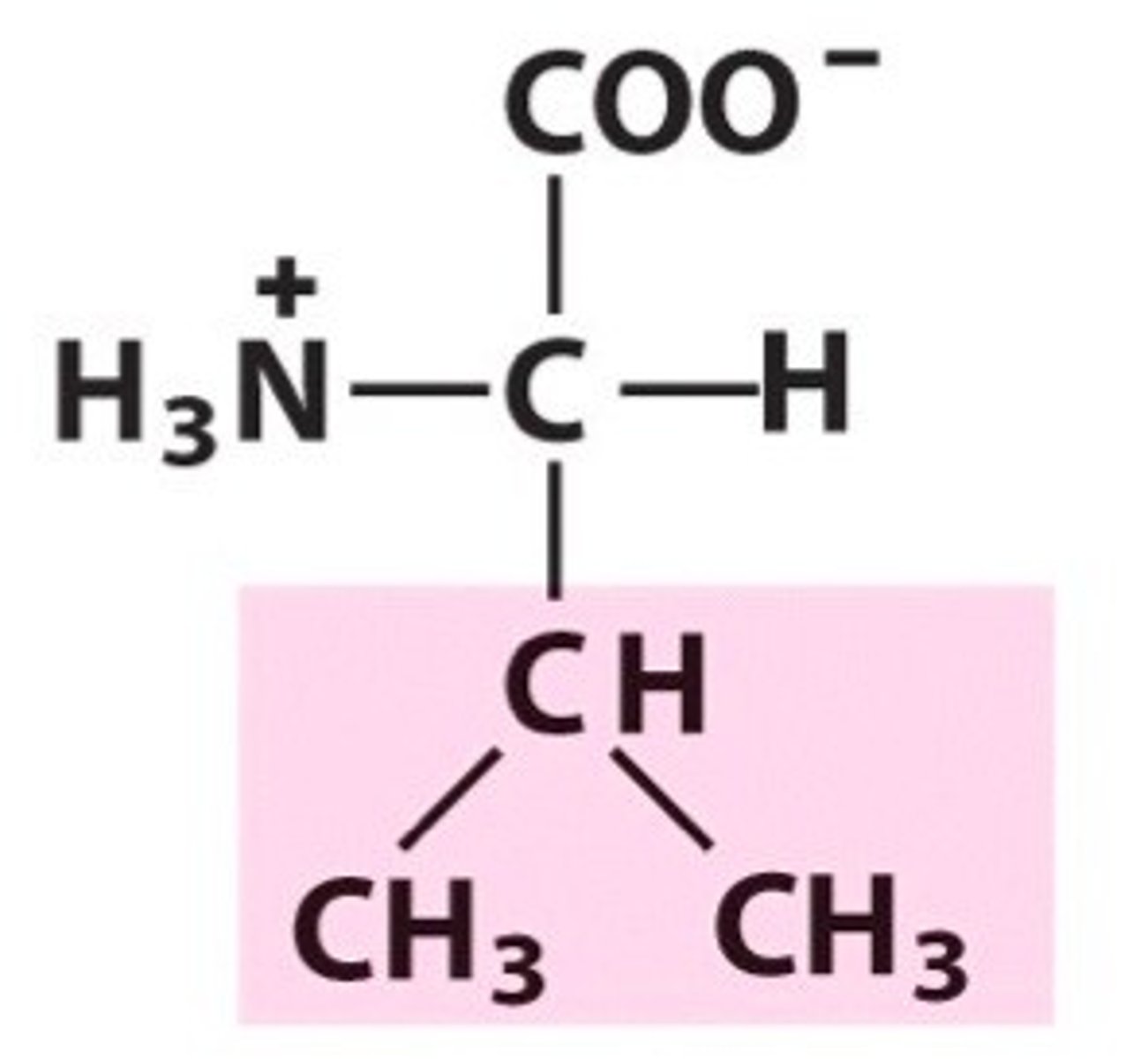
Leucine (Leu/L)
Nonpolar, aliphatic R Groups
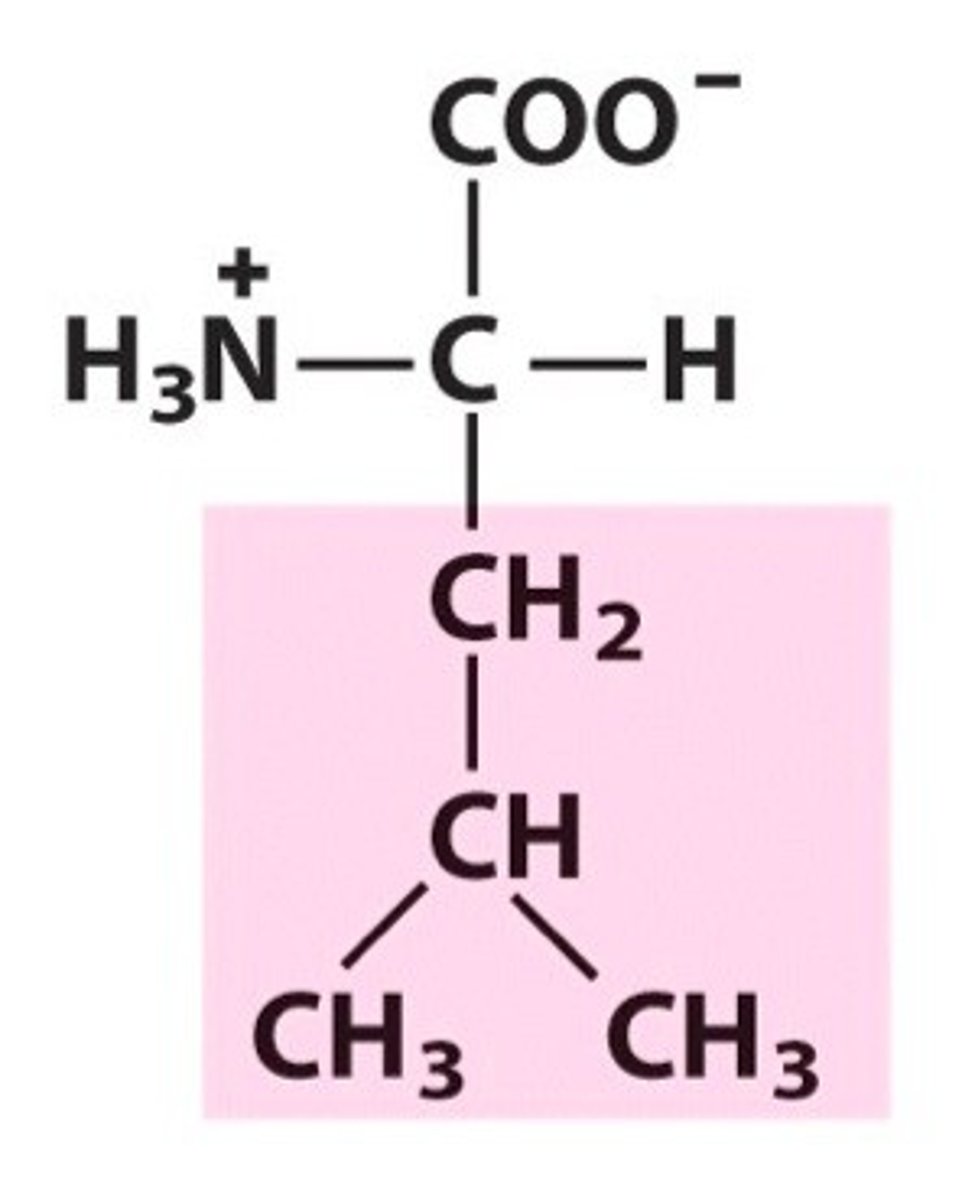
Isoleucine (Ile/I)
Nonpolar, aliphatic R Groups
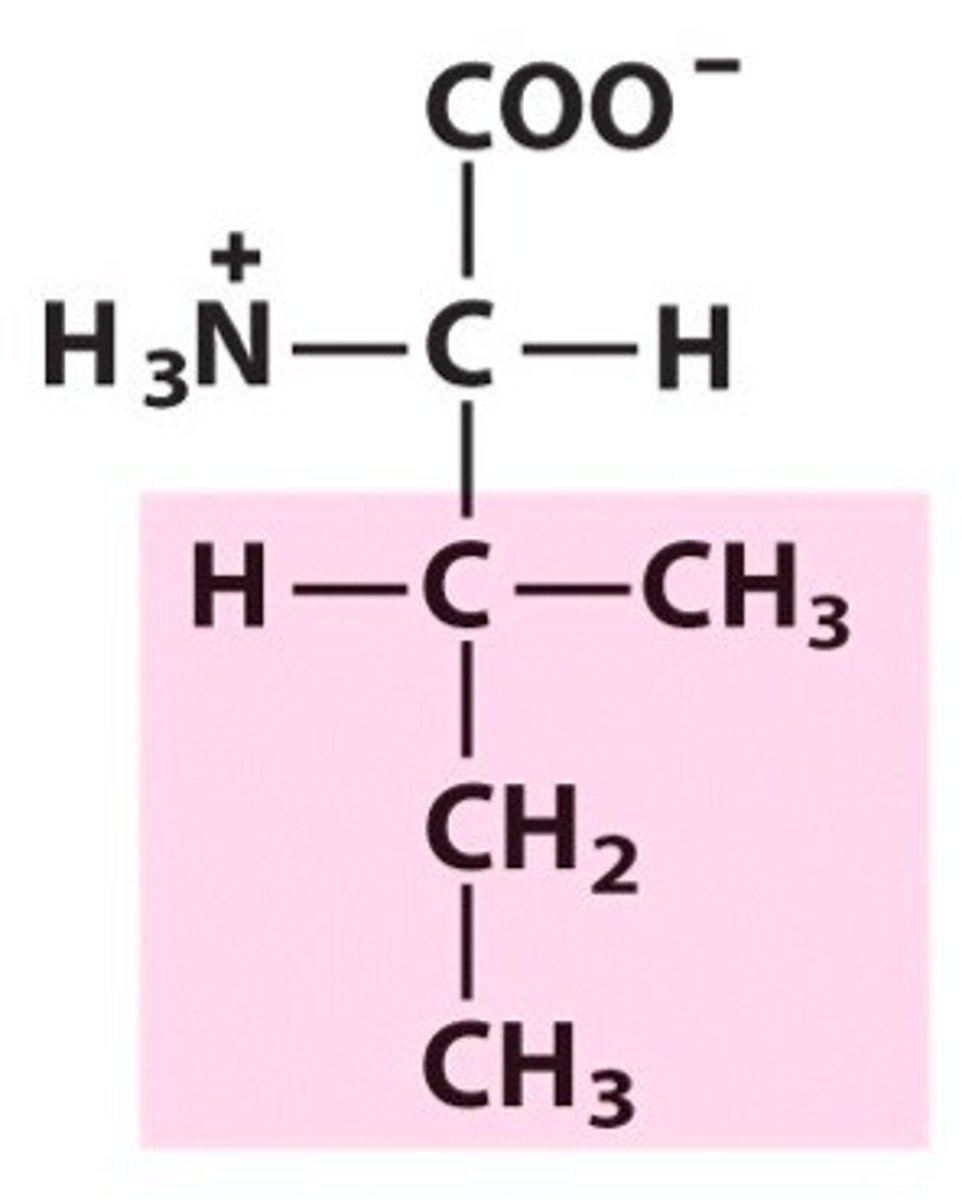
Methionine (Met/M)
Nonpolar, aliphatic R Groups
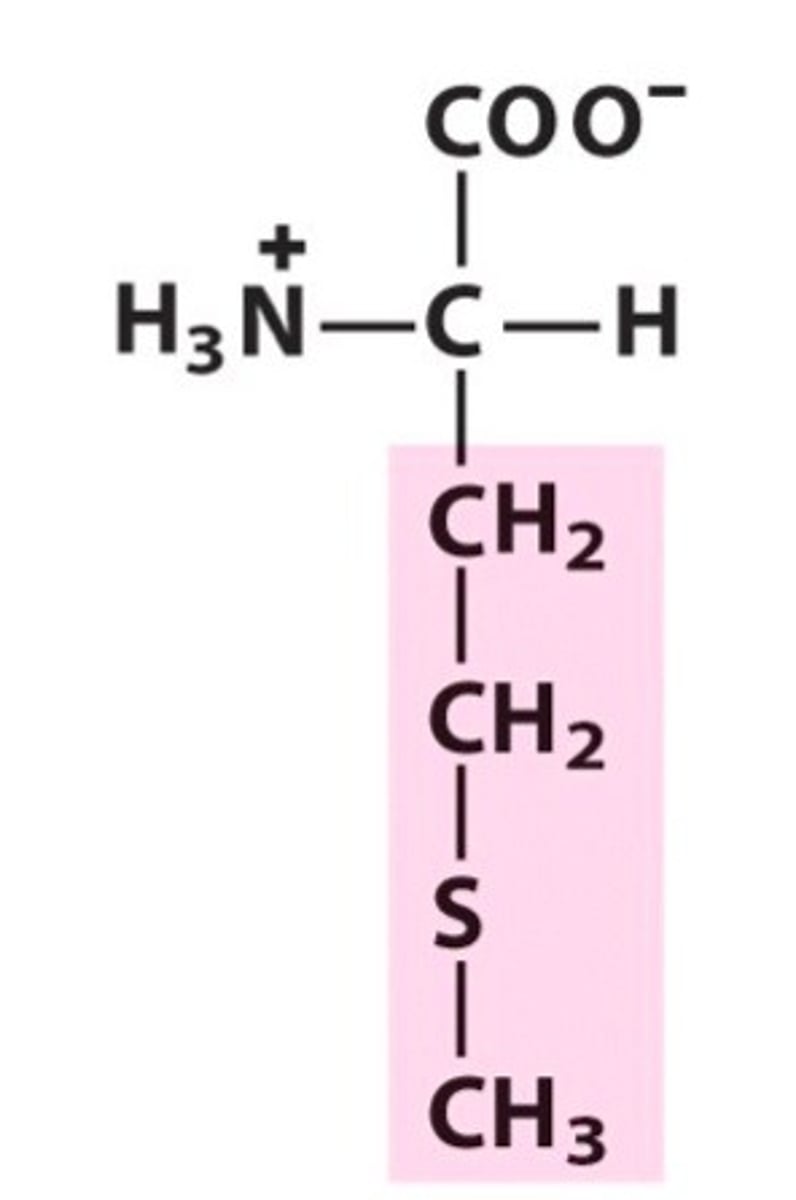
Phenylalanine (Phe/F)
Aromatic R groups
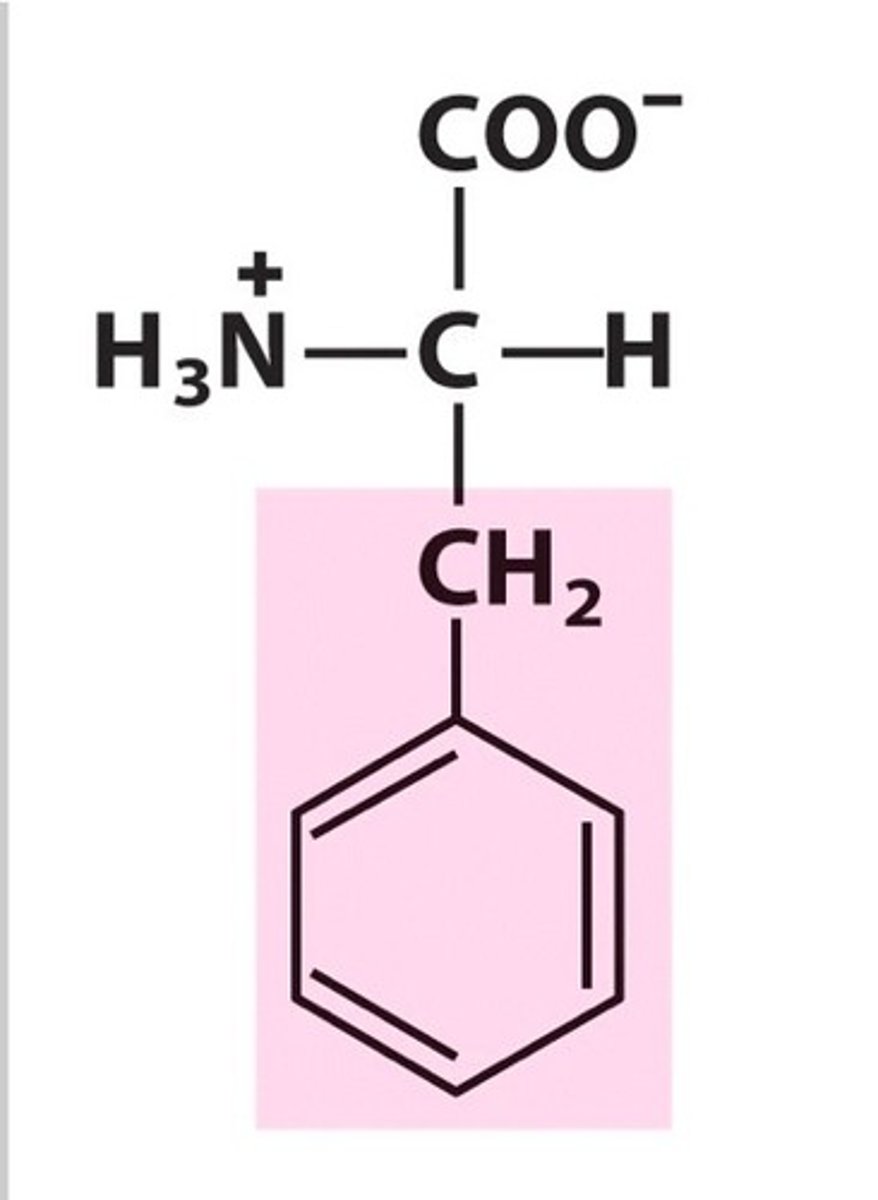
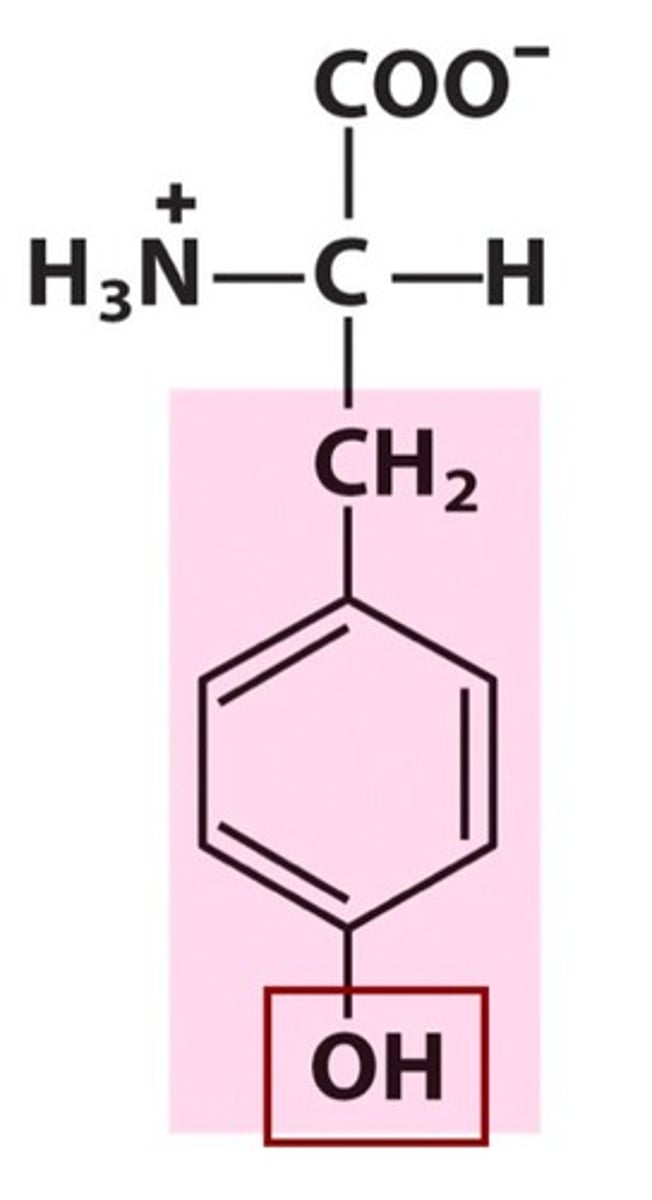
Tyrosine (Tyr/Y)
Aromatic R groups
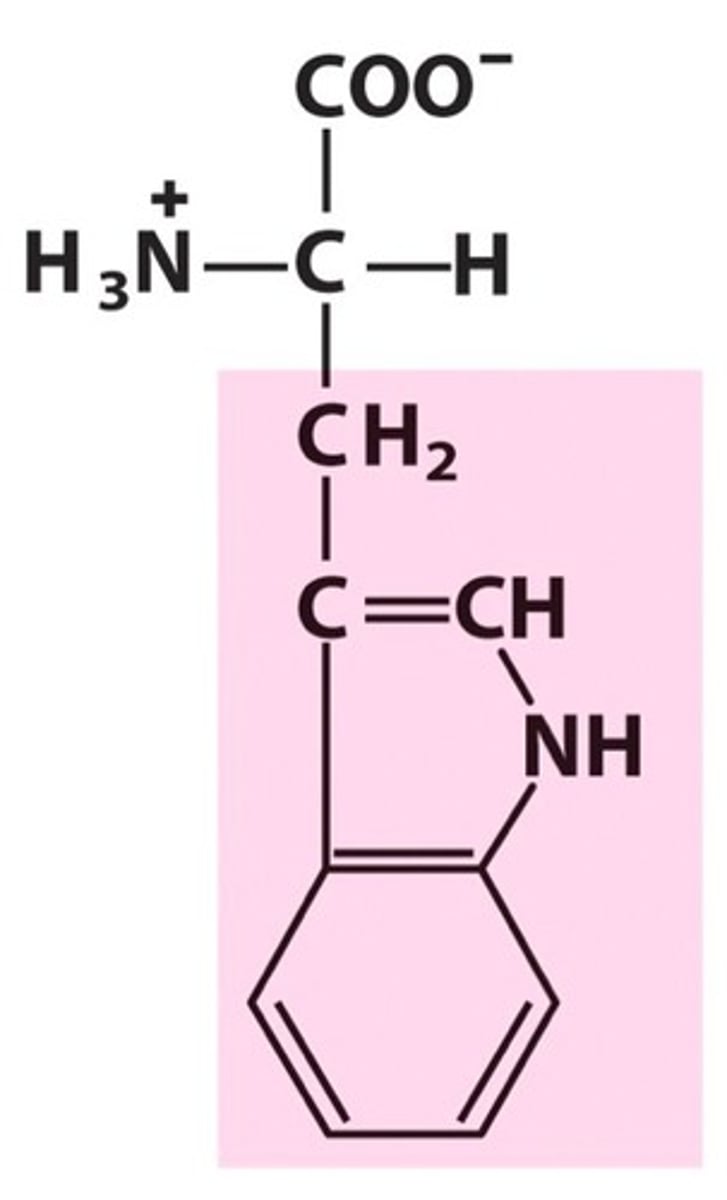
Tryptophan (Trp/W)
Aromatic R groups
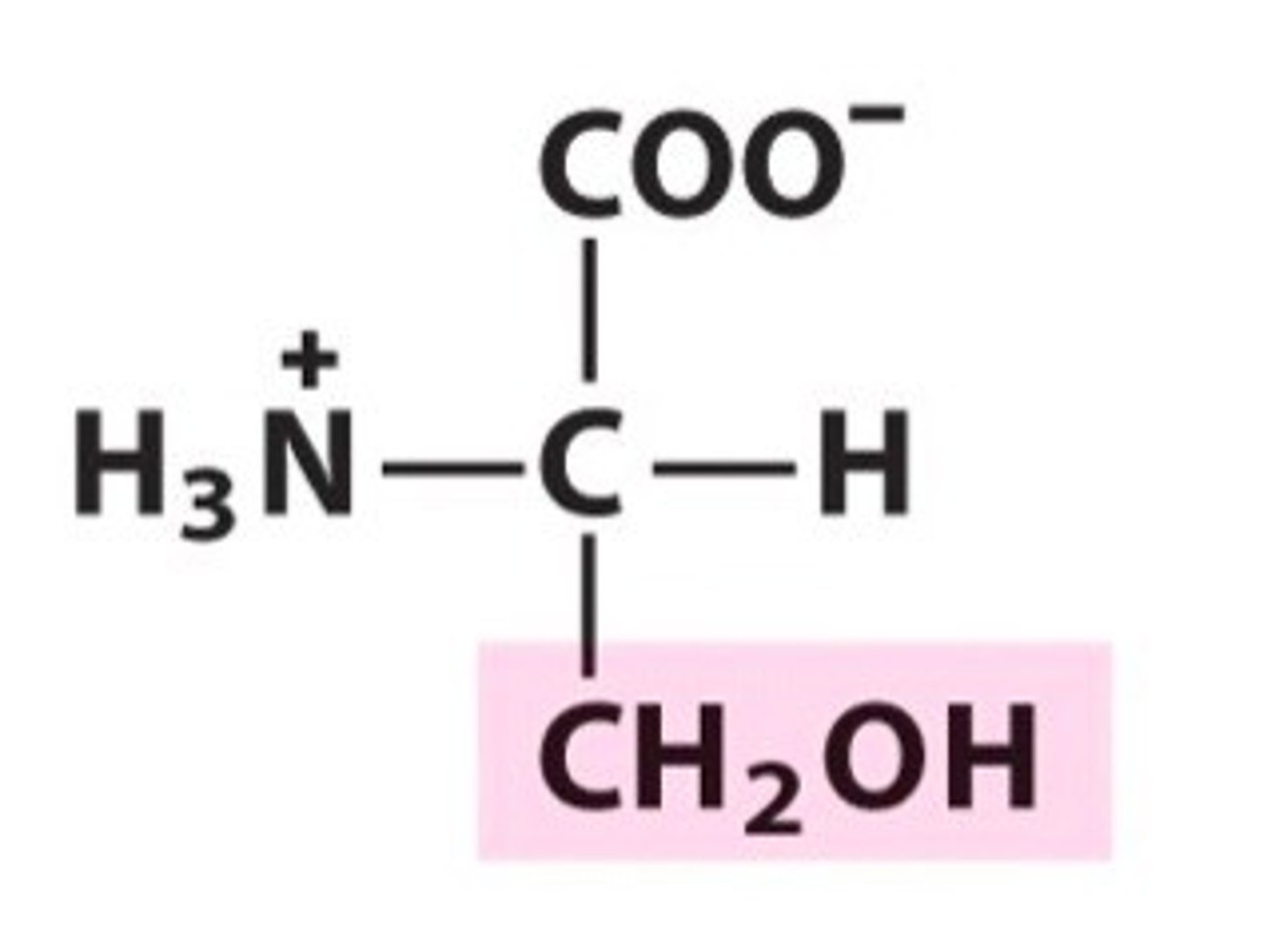
Serine (Ser/S)
Polar, uncharged R groups
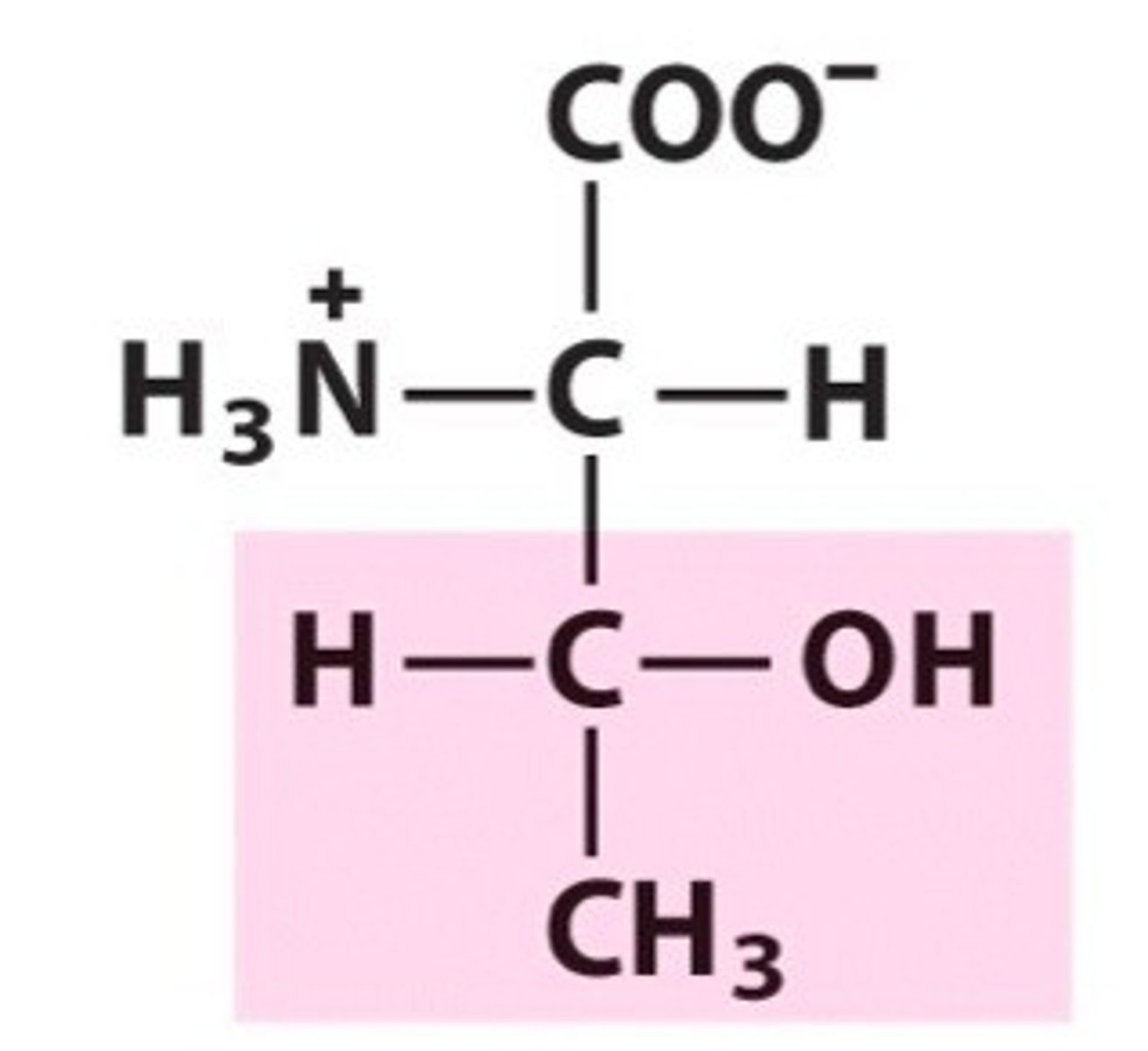
Threonine (Thr/T)
Polar, uncharged R groups
Cysteine (Cys/C)
Polar, uncharged R groups
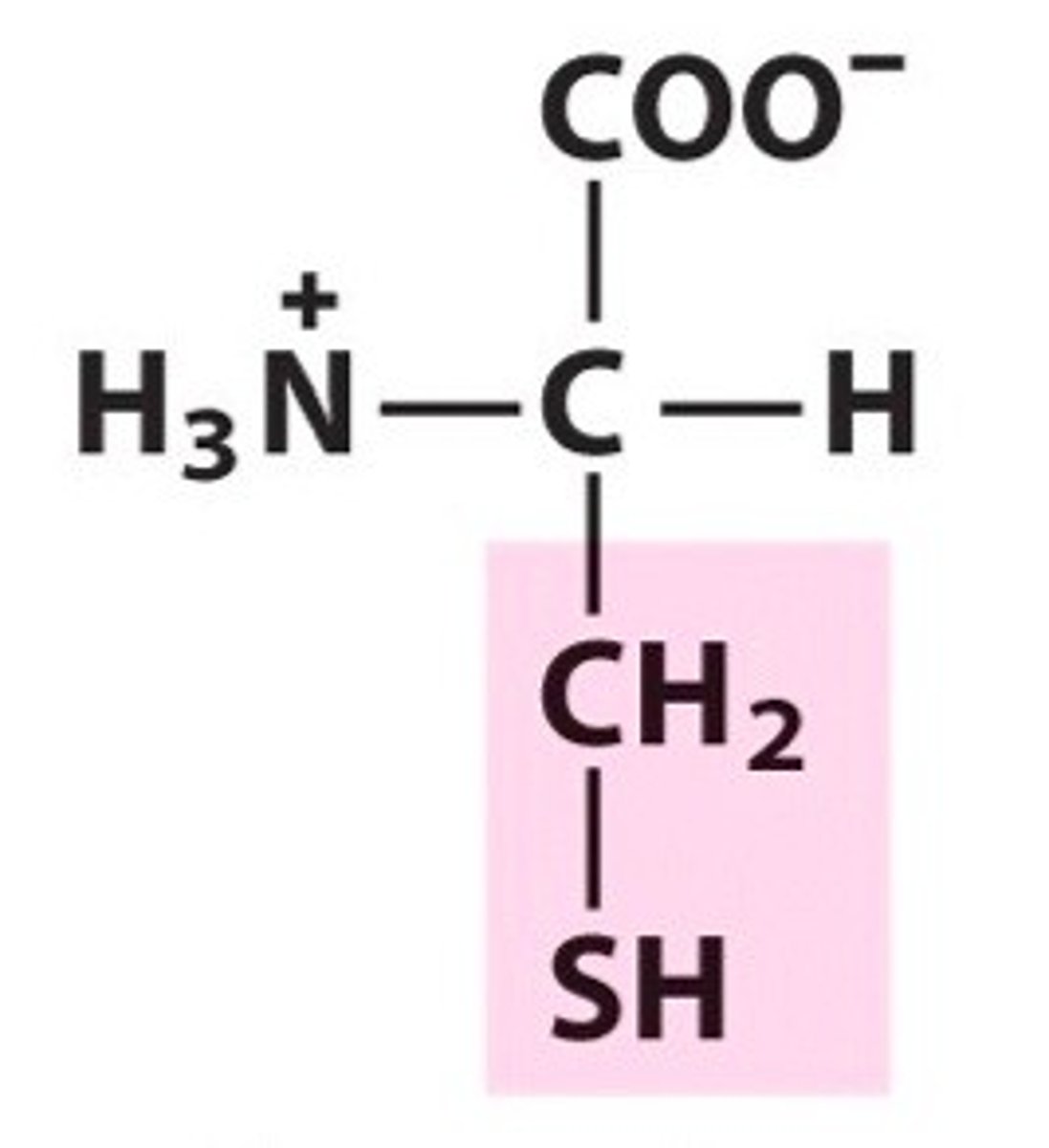
Asparagine (Asn/N)
Polar, uncharged R groups
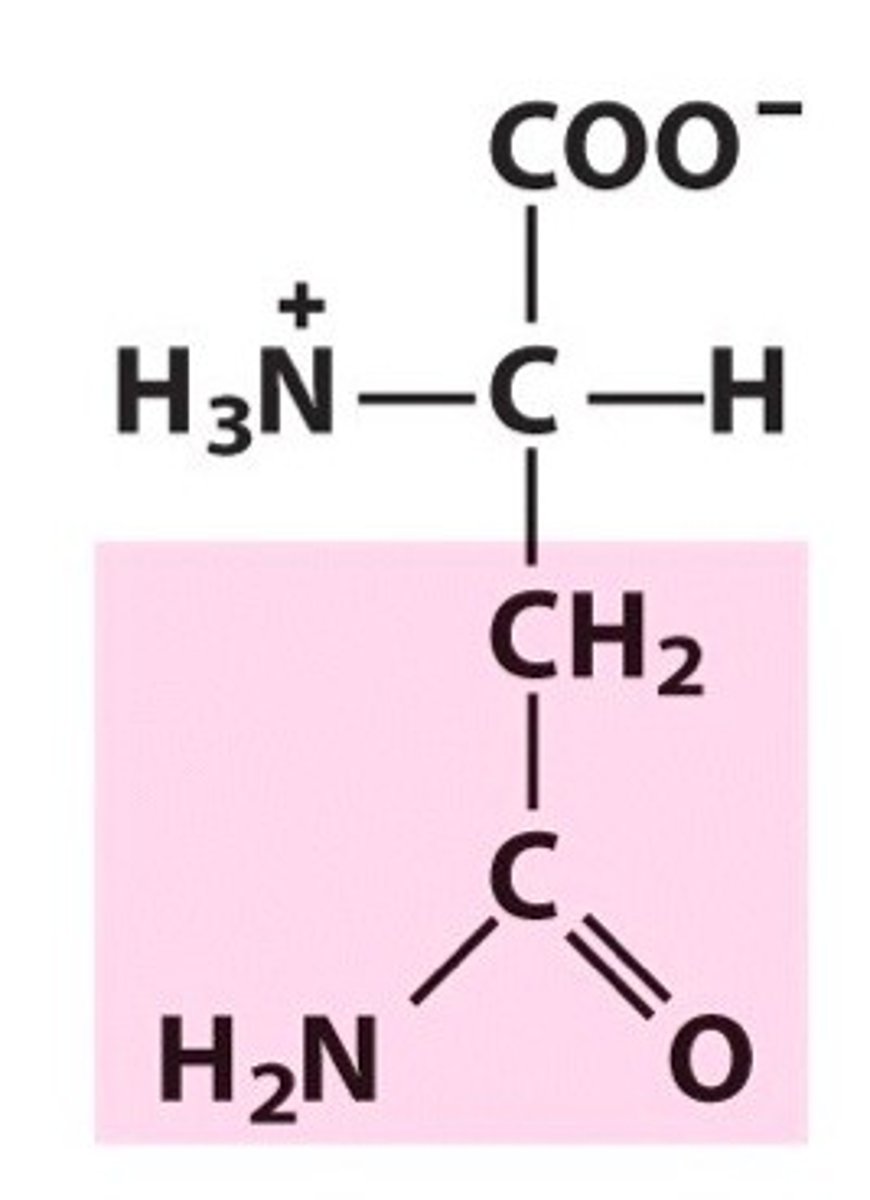
Glutamine (Gln/Q)
Polar, uncharged R groups
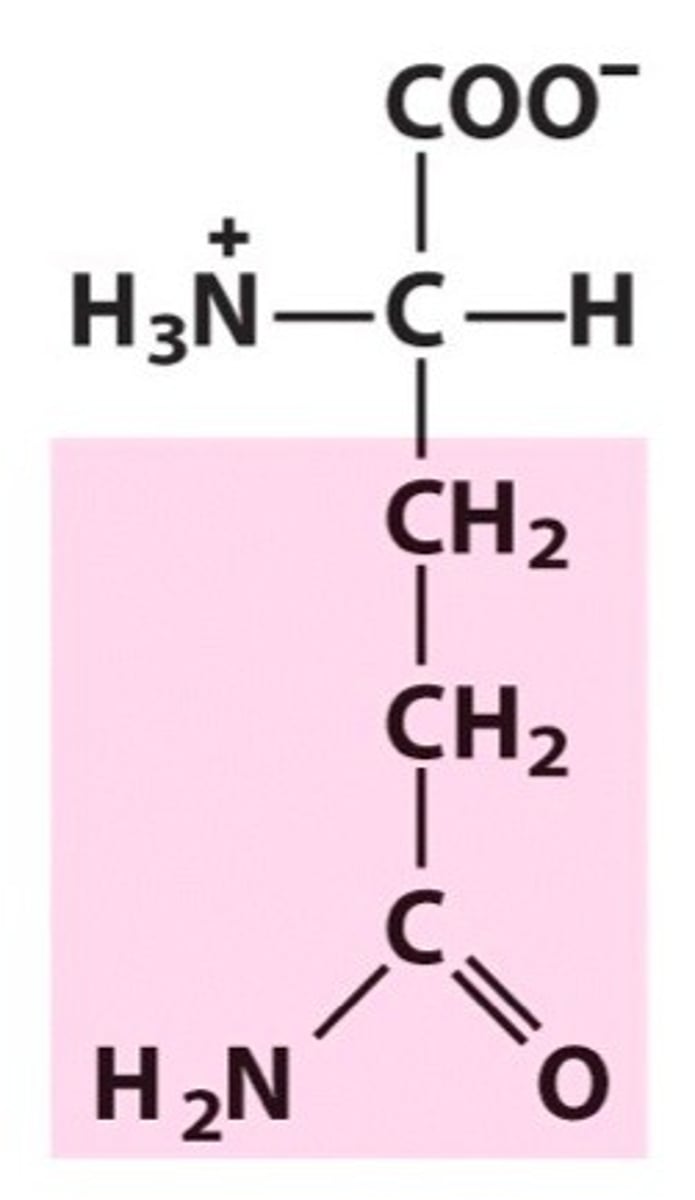
Lysine (Lys/K)
Positively charged R groups
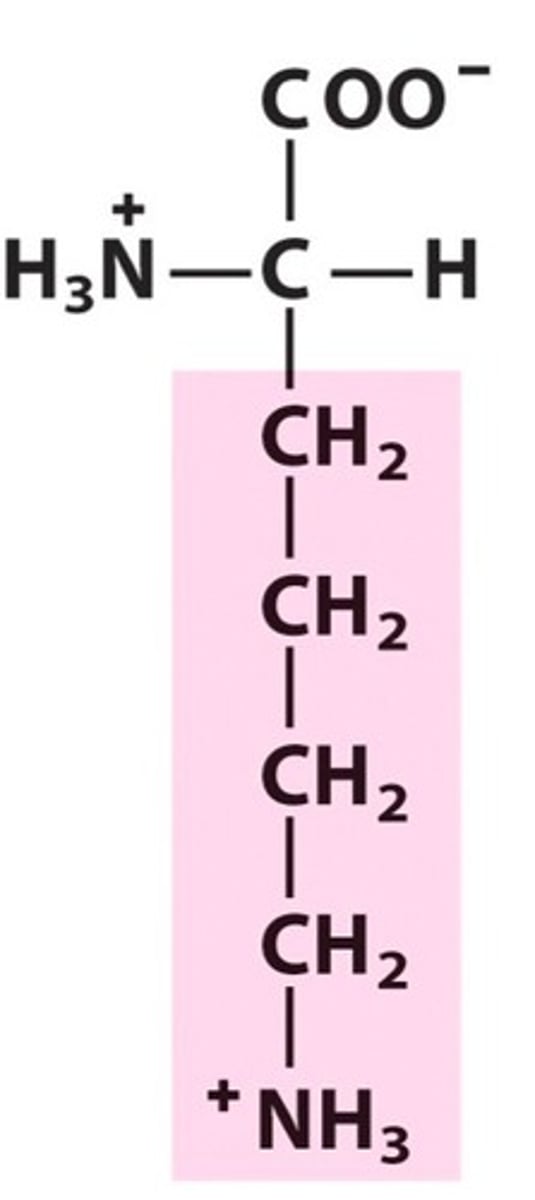
Arginine (Arg/R)
Positively charged R groups
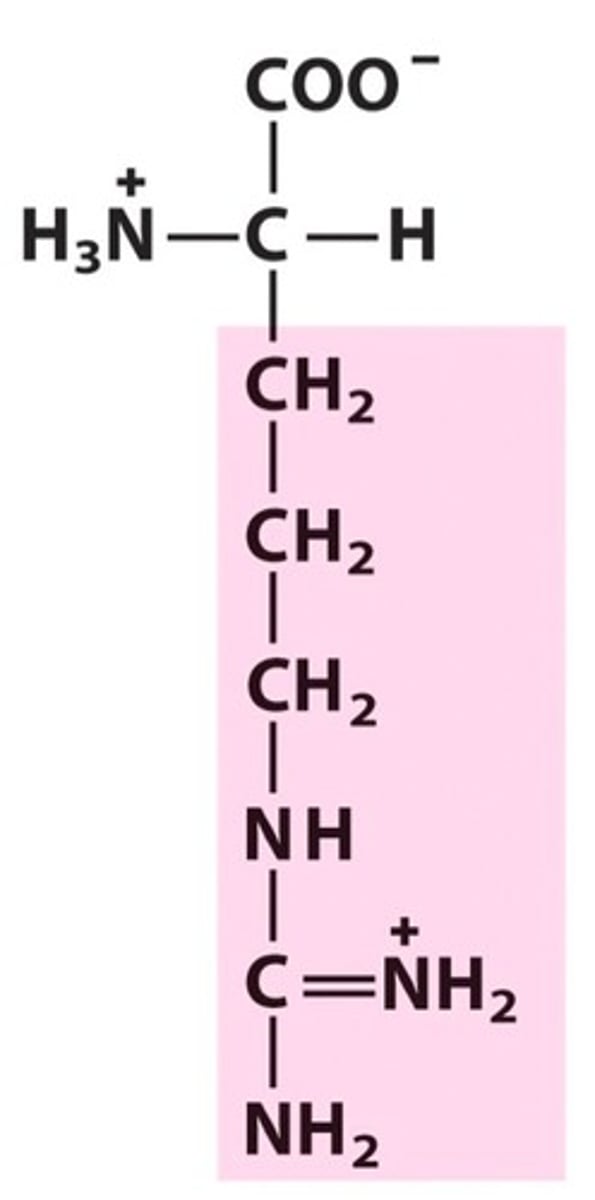
Histidine (His/H)
Positively charged R groups
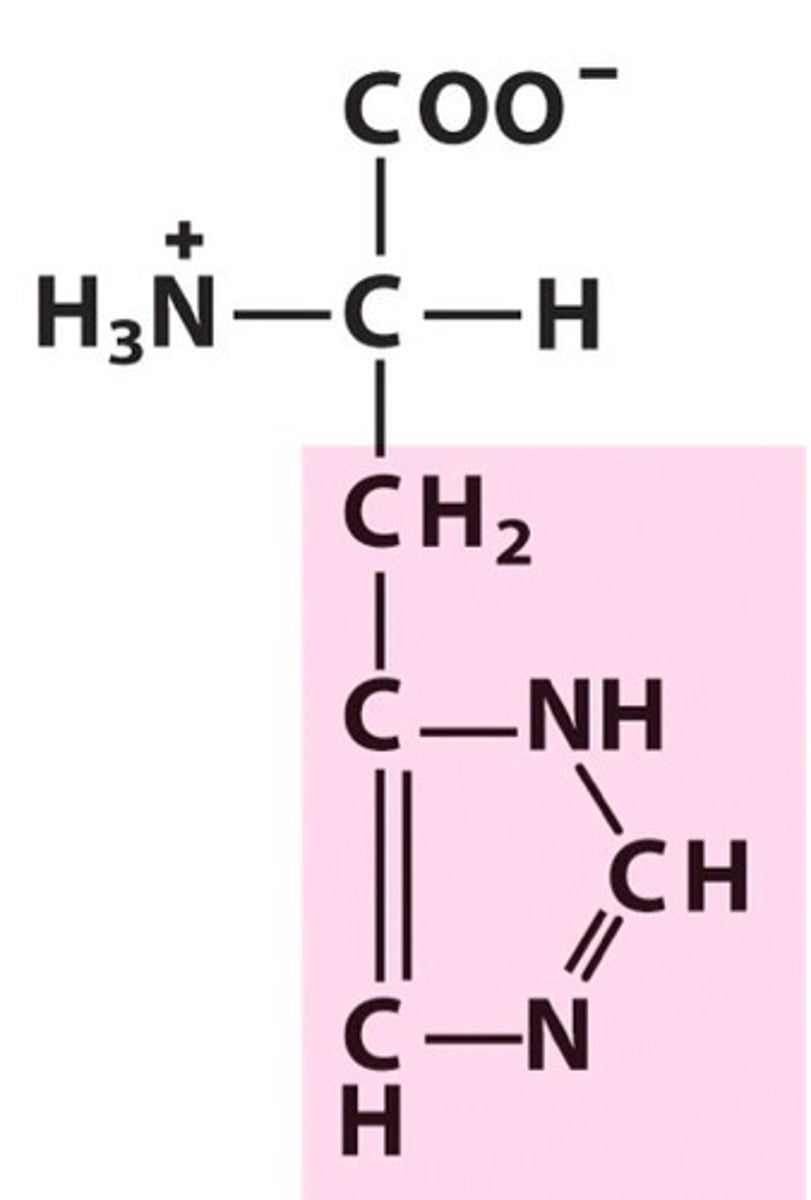
Aspartate (Asp/D)
Negatively charged R groups
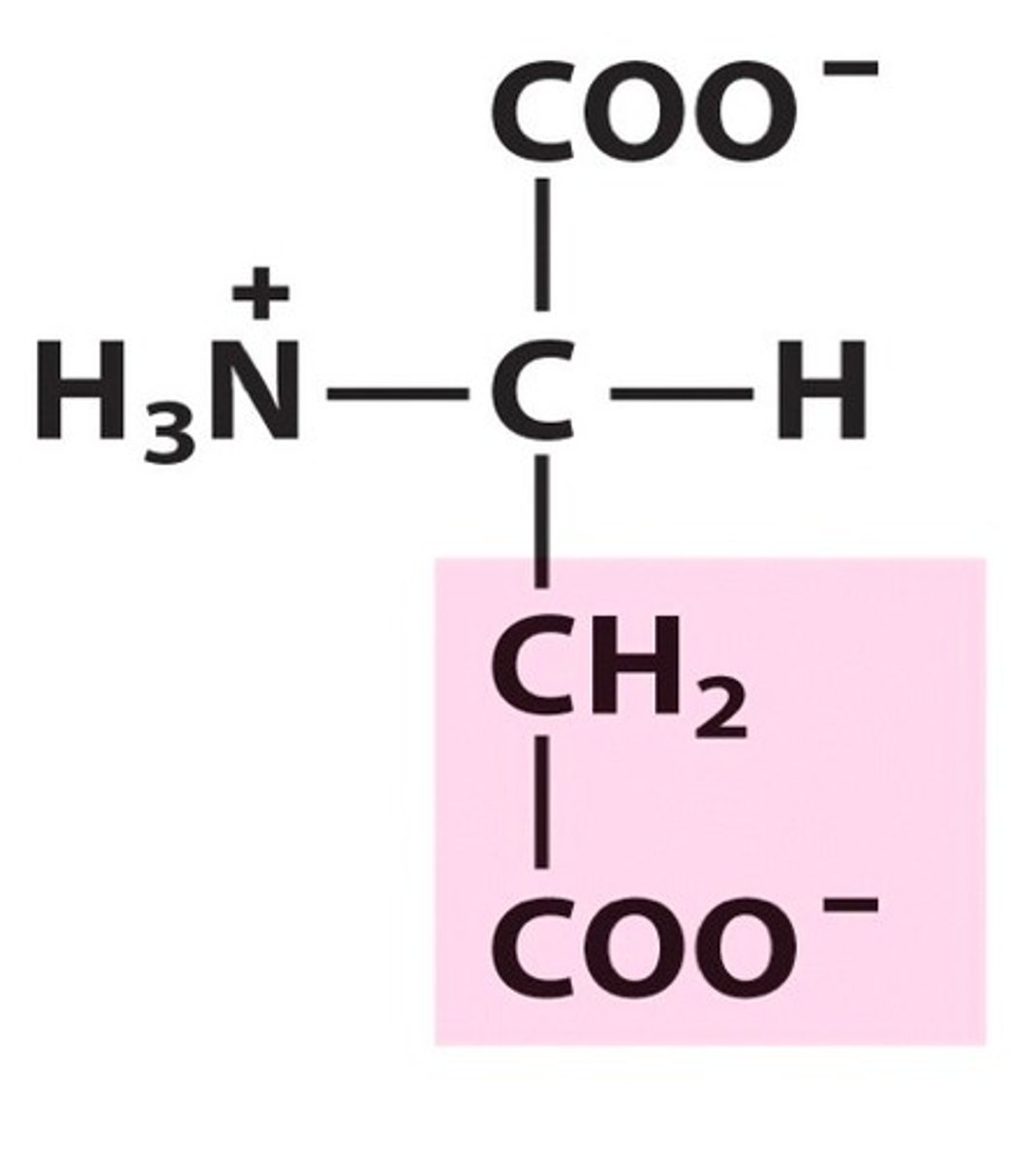
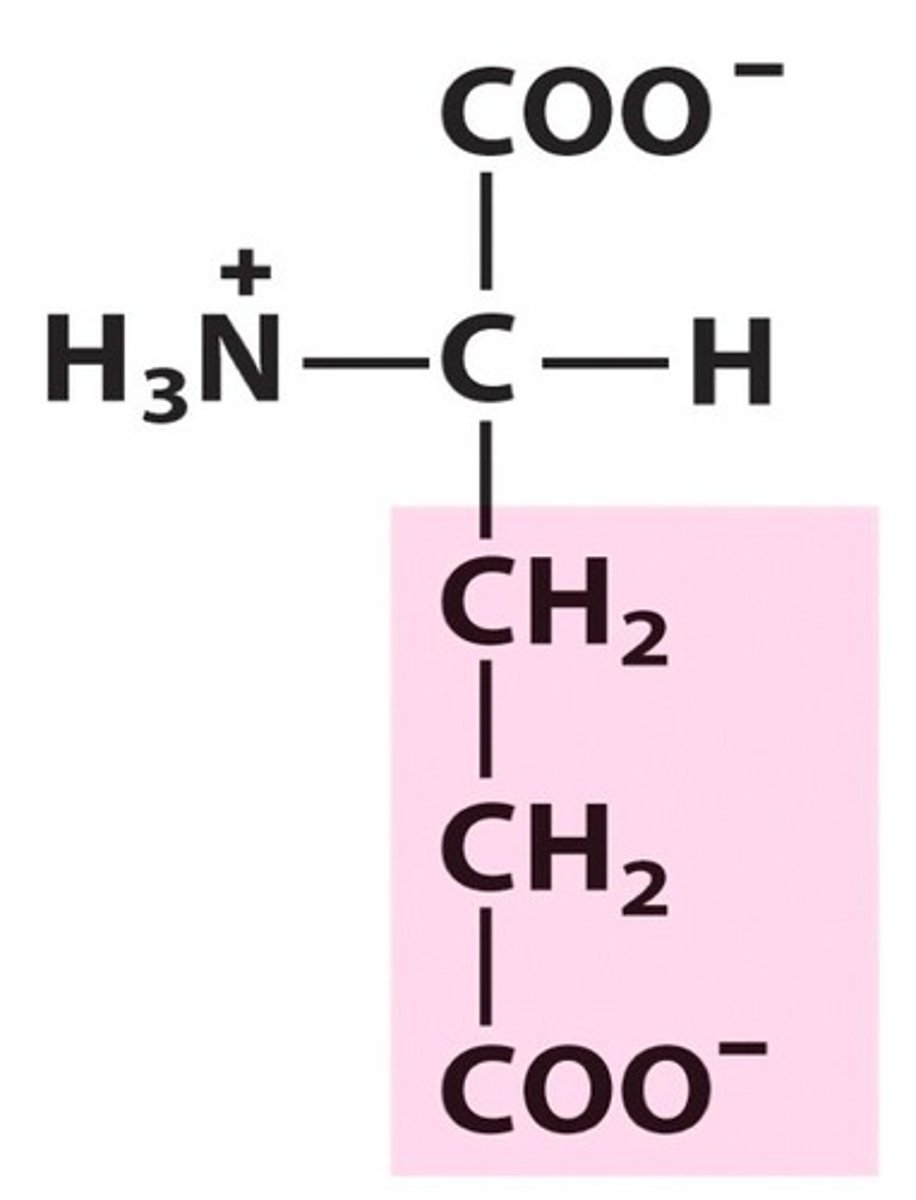
Glutamate (Glu/E)
Negatively charged R groups
What is the maximum number of hydrogen bonds that water can form?
4
The strongest hydrogen bonds have angles of ________.
180 degrees
The spontaneous clustering of lipids is driven by an energetically favorable increase in the _______ of water.
Entropy
Phosphoric acid has a pKa of 2.1. At what pH will 75% of phosphoric acid be in the conjugate base form?
math hints: log 3 = 0.5 and log 0.33 = -0.5
2.6
All of the amino acids are chiral except:
Glycine
Which amino acids are negatively charged at a neutral pH?
Glutamate, aspartate
The pKa values of most carboxylic acid groups is about _____. At pH 7, the majority of these groups will have a ________ charge.
about 2
negative
The pKa values of most amino groups is about _____. Above pH 9, the majority of these groups will have a ________ charge.
about 9
neutral
What amino acids have positive ionizable groups?
Lysine, Arginine, Histidine
What amino acids have negative ionizable groups?
Aspartate, Glutamate
What amino acids are nonpolar?
Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine, Proline, Phenylalanine, Valine, Alanine, Glycine
What amino acids are aromatic?
Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan
What amino acids are polar, uncharged?
Serine, Threonine, Cysteine, asparagine, glutamine
What technique separates proteins based on size?
Gel filtration chromatography
Which technique is generally used for protein analysis but not protein purification?
SDS-PAGE
How do you elute a peptide from an ion exchange chromatography column?
Change salt conditions
In a size exclusion chromatography column, which proteins come out first?
Largest
In a size exclusion chromatography column, is the protein denatured first?
No, SDS-PAGE does
In an SDS-PAGE gel, which proteins travel farthest?
Smallest
In an SDS-PAGE gel, is the protein denatured first?
Yes, by an anionic detergent. So for example, if a protein has 4 subunits, you have to divide the mass by 4 in order to determine order.
Which amino acids absorb UV light?
Tryptophan and tyrosine
Which technique is used to sequence a protein?
Edman degradation
Which of the following bonds in a protein does not rotate? Psi, Phi, or peptide?
Peptide
How many hydrogen bonds will be found in an alpha helix that is n amino acids long?
n-4
T/F: Beta sheets are flat.
False, they are pleated
What kind of bonds for between beta sheets?
Hydrogen bonds
What interaction contributes to the most protein stability?
Hydrophobic effect
T/F: Myoglobin does not have a quaternary structure.
True
What hemoglobin state is stabilized by oxygen binding?
R state
Where does oxygen bind to hemoglobin?
Heme group in the center
Where does CO2 bind to hemoglobin?
N terminal of each tertiary structure
Where do hydrogen ions in a low pH environment bond to hemoglobin?
Amino acid side chains that can accept H's
What hemoglobin state is stabilized by CO2 binding?
T state
What amino acids in hemoglobin are carbamylated at low pH?
The first amino acids of each subunit
What shape is the oxygen-binding curve for hemoglobin in the absence of BPG?
Hyperbolic
What is Km?
Concentration of the substrate required to achieve 1/2 Vmax
What does BPG do?
decreases the binding affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen. Without BPG the binding curve is hyperbolic, there is no cooperativity.
BPG stabilizes ______ state.
T
Enzymes may increase the rate of a reaction by _______ fold.
10^5 - 10^17
Enzymes (raise/lower) the activation energy of a reaction.
Lower
Enzymes have evolved to bind most tightly to the _______ state.
Transition
What is a cofactor?
a substance (other than the substrate) whose presence is essential for the activity of an enzyme.
Some enzymes are comprised of _____ instead of protein.
RNA
What is the best measure of catalytic efficiency?
kcat/Km
What is located in the active site of the enzyme chymotrypsin and participates in covalent catalysis?
The side chain of serine
What is located in the active site of the enzyme chymotrypsin and acts as both a general base and general acid?
Histidine
What stabilizes the transition star oxyanion that forms during chymotrypsin catalysis?
Hydrogen bonds from N-H groups
A series of enzymes perform a multiple-step reaction pathway to produce the nucleotide cytidine triphosphate (CTP). CTP allosterically inhibits the first enzyme in the pathway. This is an example of:
Feedback inhibition
List the following lipids in order of decreasing melting point: 13:0, 15:0, 17:1, 17:2
15:0, 13:0, 17:1, 17:2
Long, saturated lipids have the highest melting point. They are able to pack more tightly due to the hydrophobic effect.
Triacylglycerides have _______ fatty acids and a _______ backbone.
3, glycerol
Glycerophospholipids have ______ fatty acids and a ______ backbone.
2, glycerol
Sphingolipis have ______ fatty acids and a ______ backbone.
1, Sphingosine
What did Anfinsen's RNase and protein folding experiment demonstrate?
That the primary sequence of a polypeptide is sufficient for proper protein folding and
activity.
What does the Bohr Effect state?
An increase in hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen with increasing pH