Chapter 17 Interpreting Clinical and Laboratory Data
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Clinical Laboratory Tests
Tests to evaluate a patient’s general health and identify organ dysfunction.
Laboratory Medicine
The study of tissue and fluid specimens from patients.
Reference Range
The range of values that a laboratory test result is expected to fall within for it to be considered normal.
Critical Test Value
A laboratory result significantly outside the reference range indicating a pathophysiologic condition.
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
A test that measures the number of white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets.
White Blood Cell Count (WBC)
Measures the total number of white blood cells in the blood.
Leukocytosis
Significant elevation in the WBC count, often indicating infection.
Leukopenia
A below-normal WBC count, indicating a compromised immune system.
Neutrophilia
An absolute elevation in neutrophils, often associated with bacterial infection.
Neutropenia
A reduction in the number of circulating neutrophils.
Red Blood Cell (RBC) Count
Helps determine the blood's ability to carry oxygen to tissues.
Hemoglobin (Hb)
The protein in red blood cells that binds to oxygen.
Hematocrit (Hct)
The ratio of the volume of red blood cells to the total volume of blood.
Electrolyte Tests
Tests that measure electrolyte levels to assess fluid and acid-base balance.
Anion Gap
A method for evaluating acid-base disorders in the blood.
Creatinine
A key marker of kidney function.
Bilirubin
A substance produced by the liver that indicates liver function.
Troponin
A protein used to assess cardiac muscle damage.
BNP (B-type natriuretic peptide)
A hormone secreted by the heart in response to increased cardiac muscle strength.
Prothrombin Time (PT)
A test measuring the time required for blood to clot.
Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT)
A test evaluating abnormalities in blood clotting.
D-dimer
A protein fragment indicating clot dissolution used to diagnose DVT and PE.
Thrombocytopenia
A condition characterized by low platelets causing excessive bleeding.
Thrombocytosis
A condition marked by an excess of platelets, leading to excessive clotting.
Glucose
A simple sugar that is an important energy source for cells.
Hyperglycemia
Elevated blood glucose levels, often associated with diabetes.
Hypoglycemia
Reduced glucose levels in the blood, associated with various conditions.
Liver Function Tests
Tests that assess the health and function of the liver.
Transfusions
The process of receiving blood or blood products into one's circulation.
Electrolytes
Minerals in the body that carry an electric charge essential for various bodily functions.
Hematology
The branch of medicine concerned with the study of blood.
Immunology
The study of the immune system and immune responses.
Clinical Microbiology
The study of microorganisms and their effects on human health.
Anatomical Pathology
The study of disease through the examination of tissues and cells.
C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
A protein that rises in response to inflammation and infection.
Lactic Acid
A byproduct of anaerobic metabolism, often elevated in tissue hypoxia.
Sweat Chloride Test
A test used to diagnose cystic fibrosis based on chloride concentration in sweat.
Sputum Culture
A test to identify infectious agents causing lung infections.
Gram Stain
A laboratory technique used to classify bacteria based on their cell wall properties.
Electrolyte Imbalance
Disruption in the levels of electrolytes in the body, affecting physiological functions.
Acidosis
A condition characterized by an excess of acid in the body.
Alkalosis
A condition characterized by an excess of base in the body.
Oxygen Carrying Capacity
The ability of blood to transport oxygen to tissues.
Vascular Endothelium
The layer of cells lining blood vessels, involved in clotting.
Procalcitonin (PCT)
A protein that increases in response to bacterial infections, used as a marker for sepsis.
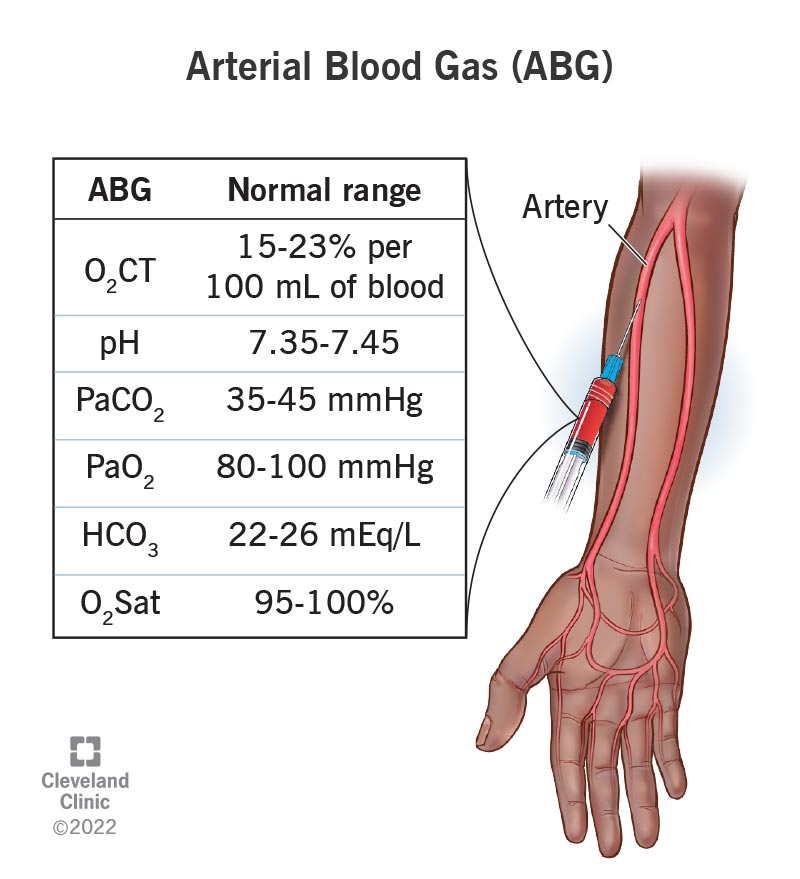
ABG Testing
Arterial blood gas testing used to assess lung function and gas exchange.
Bronchoscopy
A procedure that allows examination of the airways using a bronchoscope.
Nasotracheal Suctioning
A procedure used to clear secretions from the airway.