ECON 11 1ST LE
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
Economics 1
explores the behavior of the financial markets, including interest rates, exchange rates, and stock prices.
Economics 2
The subject examines the reasons why some people or countries have high incomes while others are poor; it goes on to analyze ways that poverty can be reduced without harming the economy.
Economics 3
It studies business cycles—the fluctuations in credit, unemployment, and infl ation—along with policies to moderate them.
Economics 4
Studies international trade and fi nance and the impacts of globalization, and it particularly examines the thorny issues involved in opening up borders to free trade.
Economics 5
It asks how government policies can be used to pursue important goals such as rapid economic growth, efficient use of resources, full employment, price stability, and a fair distribution of income.
Economics 6
The study of how societies use scarce resources to produce valuable goods and services and distribute them among different individuals.
goods are scarce and that society must use its resources efficiently
Two ideas that run through all economics
Fact of scarcity and the desire for efficiency
Why will the concerns of economics will not go away
One in which goods are limited relative to desires
Situation of scarcity
Efficiency
The most effective use of a society’s resources in satisfying people’s wants and needs
Economic efficiency
Requires that an economy produce the highest combination of quantity and quality of goods and services given its technology and scarce resources
When no individual’s economic welfare can be improved unless someone else is made worse off
When an economy is producing efficiently
Essence of economics
To acknowledge the reality of scarcity and then figure out how to organize society in a wat shich produces the most efficient use of resources
microeconomics and macroeconomics
Two major subfields of economics
Adam smith
Founder of microeconomics
Microeconomics
Concerned with the behavior of individual entities such as markets, firms, and hourseholds
Adam Smith
He identified the remarkable efficiency properties of markets nd explained how the self-interest of individuals working thorugh the competitive market can produce a societal economic benefit
Microeconomics 1
moved beyond the early concerns to include the study of monopoly, the role of international trade, finance, and many other vital subjects
Macroeconomics 1
Concerned with the overall performance of the economy
1936
is when macroeconomics exist in its modern form
John Maynard Keynes
Published his revolutionary General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money that made macroeconomics exist in its modern form
Macroeconomics 2
Examines a wide variety of areas, such as how total investment and consumption are determined
Macroeconomics 3
How central banks manage money and interest rates, what causes international financial crises, and why sone nations grow rapidly while others stagnate
Scientific approach
Economist use this approach to understand economic life
Scientific approach
Observing economics affairs and drawing upon statistics and the historical record
analyses and theories
This is where economics often relies on
Theoretical approach
Allows economist to make broad generalization, such as those concerning advantages of international trade and specialization or the disadvantages of tariffs and quotas
Econometrics
A specialized technique developed by economists which applies the tools of statistics to economics problems
Econometrics 2
With the use of this, economist can sift through mountains of data to extract simple relationship
Post hoc fallacy 1
Involves the interference of causality
Post hoc fallacy
Occurs when we assume that, because one event occurred before another event, the first event caused the second event
Post hoc, ergo propter hoc
This means “after this, therefore necessarily because of this”
Failure to hold other things constant
The argument assumes that other things were constant
Fallacy of composition
When you assume what is true for the part is also true for the whole
Positive economics 1
Describes the fact so of an economy
Normative economics 2
Involves value judgement
Positive economics 2
deals with the questions that can all be resolved by reference to analysis and empirical evidence
Normative economics 2
Involved ethical precepts and norms of fairness
Normative economics 2
There are no right or wrong answers to the question because it involve ethics and values rather than facts
Normative economics 3
can be resolved only by discussions and debates over society’s fundamental values
Ultimate goal of economics science
To improve the living conditions of people in their everyday lives
what, how, for whom
The three fundamental questions of economic organization
What
What commodities are produced and in what quantities?
How
Determines who will do the production, with what resources, and what production techniques they will use
For whom
Who gets to eat the fruit of economic activity?
Alternative economic systems
Is where different societies are organized, and economics studies various mechanisms that a society can use to allocate the resources.
command economy 1
Government makes most economics decisions, with those in top of the hierarchy giving economics commands to those further down the ladder.
Market economy 1
Decisions are made in markets, where individuals or ent enterprises voluntarily agree to exchange goods and services
Market economy 2
it is one in which individuals and private firms make the major decisions about production and consumption
Firms
They produce commodities that yield the highest profits by the techiniques of production that are least costly.
Consumption
It is determined by individual’s decisions about how to apend the wages and property incomes generated by their lenor and property ownership
Laissez-faire
The extreme case of a market economy in which the government keeps its hands off economic decisions
Command economics 2
The government makes all important decisions about production and distribution
Command economy 3
The government owns most of the means of production. It also owns and directs the operations of enterprises in most industries
Command economy 4
The government is the employer of most workers and tells them how to do their jobs and it decides how the output of the society is to be divided among different goods and services
Command economy 5
The government answers the major economics questions thorough its ownership of resources and its power to enforce decisions
Government
It plays an important role in overseeing the functioning of the market. It pass laws that regulate economic life, produce educational and police services, and control pollution
Inputs
These are commodities or services that are used to produce goods and services
Outputs
These are the various useful goods or services that result from the production process and are either consumed or employed in further production
factors production
It is the other term for inputs
Labor
It consists of the human time spent in production
Capital resources
It is a form of durable goods of an economy, produced in order to produce yet other goods
Capital goods
It includes machines, roads, computers, software, trucks, steel mills, automobiles, washing machines, and building
What 2
Outputs to produce and in what quantity
How 2
With what inputs and techniques, to produce the desired outputs
For whom 2
The outputs should be produced and distributed
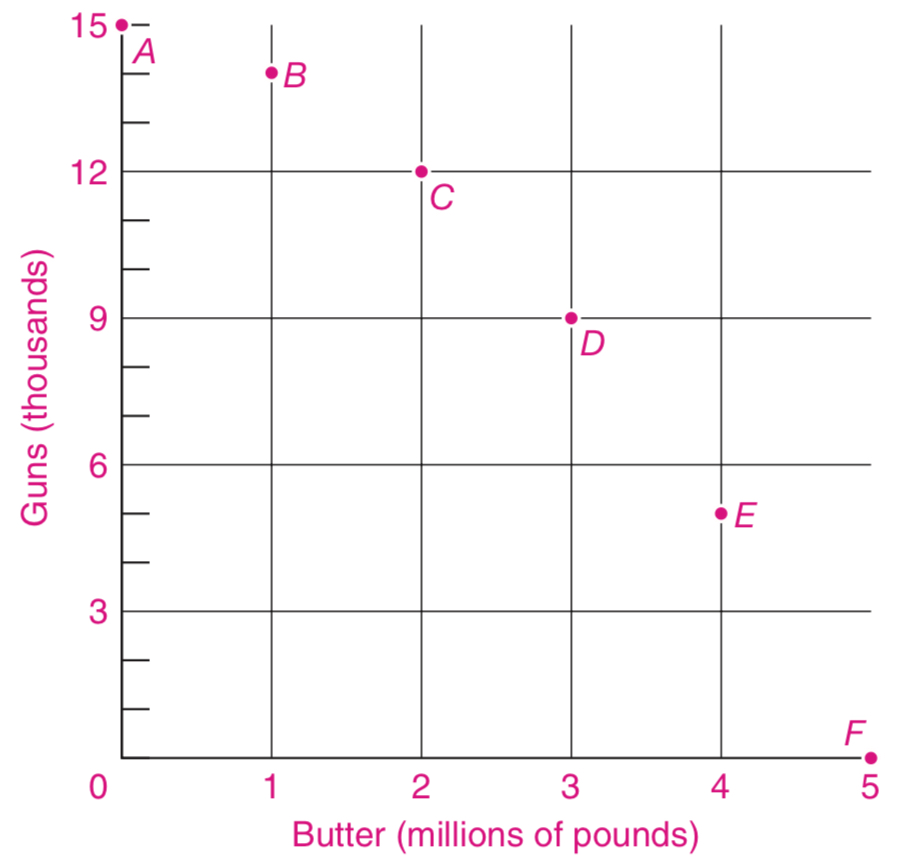
Production Possibility Frontier
It shows the maximum quantity of goods that can be efficiently produced by an economy, given its technological knowledge and the quantity of available inputs
The maximal amount of good
This depends on the quantity and quality of the economy’s resources and productive efficiency with which they are used
production possibility frontier graph
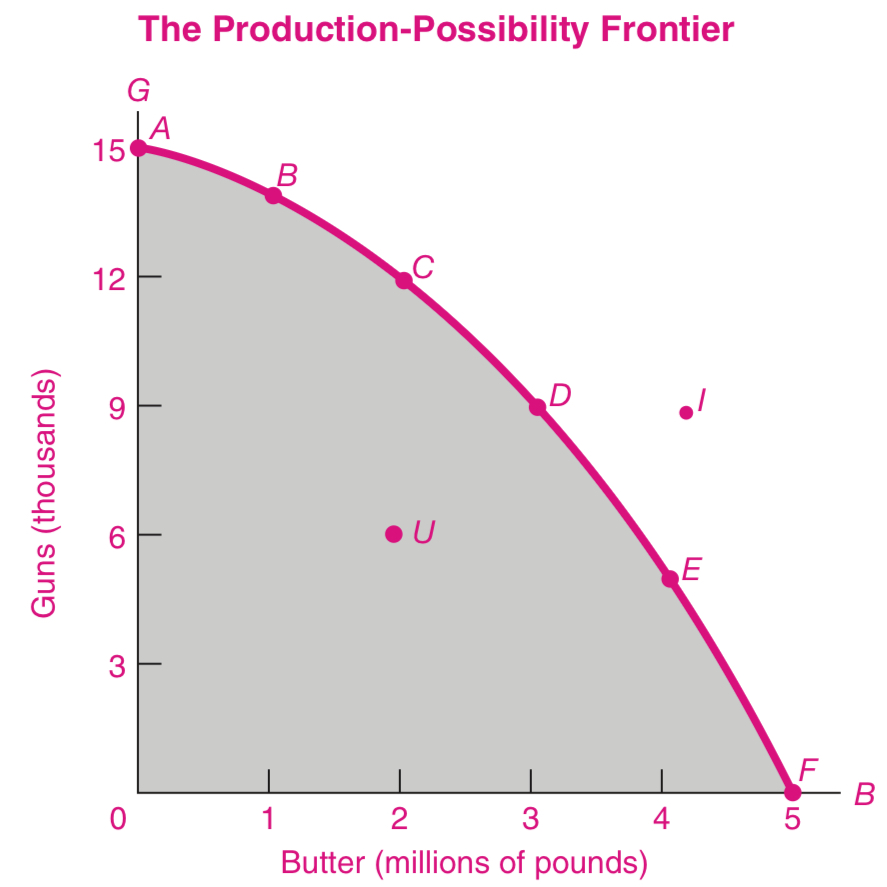
Inefficient
Point U
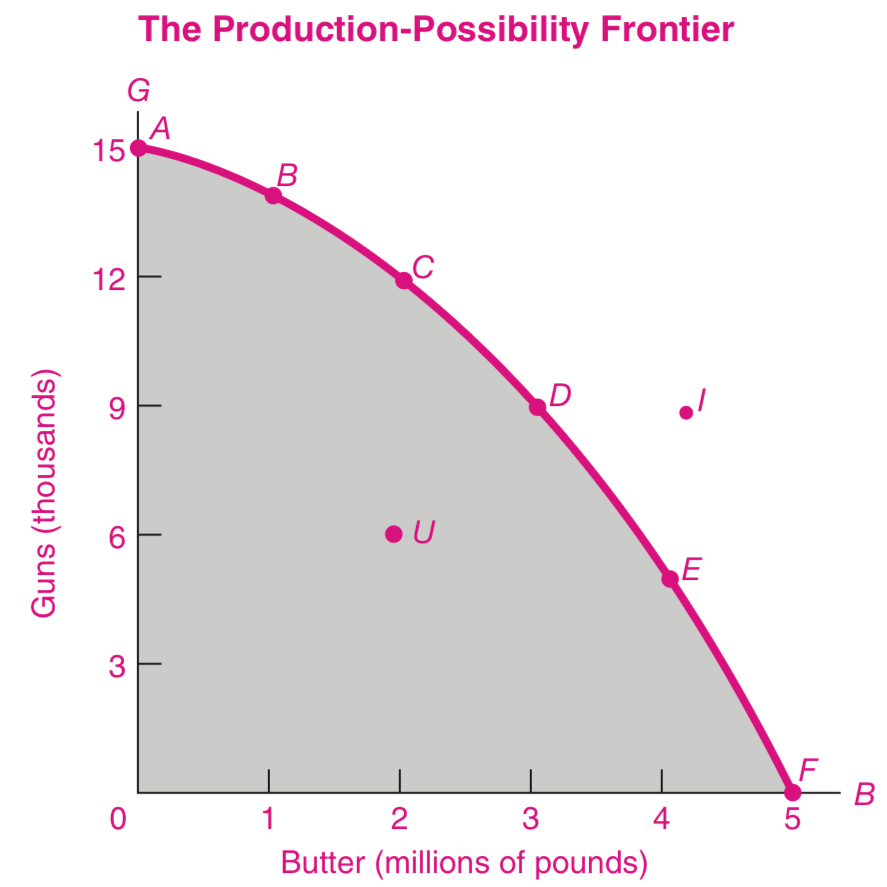
Infeasible
Point I
Same PPF
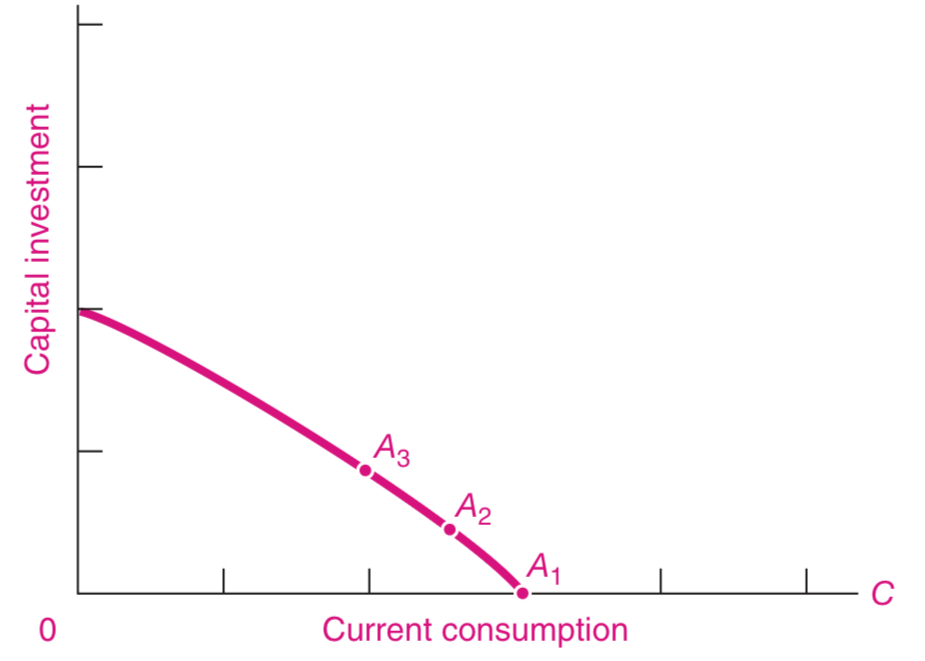
Point A1
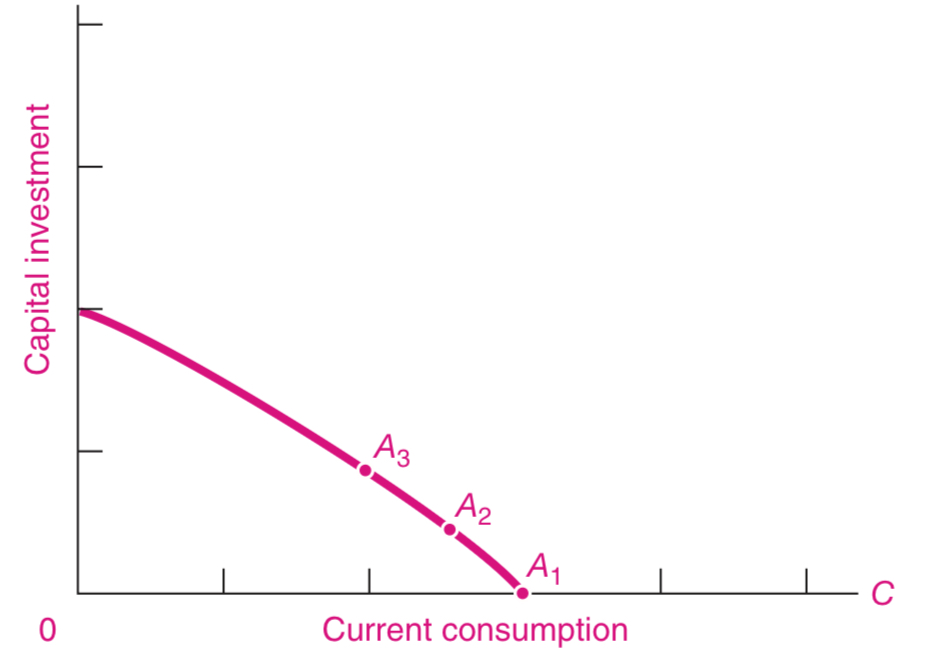
The PPF will move outward
Point A2 and A3
Poor countries
Country that can afford little of public goods like public health and primary education
By sacrificing current consumption and producing more capital goods
With this, a nation’s economy can grow more rapidly, making possible more of both goods (consumption and investment) in the future
Time
Coin of your life. It is the only coin you have, and only you can determine how it will be spent
Opportunity cost
The next-best good that is forgone
Pierce the veil
We need to do this in economics to examine the real impacts of alternative decisions.
Productive efficiency
It occurs when an economy cannot produce more of one good without producing less of another good
Substitution
It is the law of life in a full-employment economy, and the production-possiblity frontier depicts the menu of society’s choices
Variable
It is an item of interest that can be defined and measured and that takes on different values at different times or places
Slope
Represents the change in one variable that occurs when another variable changes