3.3.8 - 3.3.9 The Carbonyl Group
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Suggest why the carbonyl group undergoes nucleophilic addition.
The high electron density in the double bond leads to addition reactions and the polar bond means the delta positive carbon is susceptible to attack by nucleophiles.
Suggest why aldehydes and ketones have higher boiling points than alkanes, but lower boiling points than alcohols.
Aldehydes and ketones have a carbonyl group, which is polar, so have dipole-dipole forces between molecules, which require more energy to break than the weak van der Walls' forces alone in alkanes.
Alcohols, however, have strong hydrogen bonding between the hydroxyl group of molecules; hydrogen bonding is the strongest intermolecular force of attraction and so requires more energy to break.
Suggest why ketones tend to have a slightly higher boiling point than aldehydes.
Aldehydes have the carbonyl group at the end of the chain, leading to a longer non-polar section and so less permanent dipole-dipole forces.
Do short chain aldehydes and ketones dissolve in water?
Yes; hydrogen bonding occurs between the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen of the polar carbonyl group and the delta positive hydrogen of the water molecules.
Aldehydes are readily oxidised to ________ ________.
carboxylic acids
What are the conditions for the oxidation of an aldehyde?
State any observations.
What is used to represent the oxidising agent in equations?
Warm, acidified potassium dichromate.
Orange solution changes to green.
[O]
Describe two chemical tests to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones.
Tollens' reagent: silver mirror formed with aldehyde, no visible change with ketone.
Fehling's solution: blue to red with aldehyde, no visible change with ketone.
What reducing agent can be used to reduce aldehydes and ketones to alcohols?
sodium tetrahydridoborate(III)
(also known as sodium borohydride)
NaBH₄
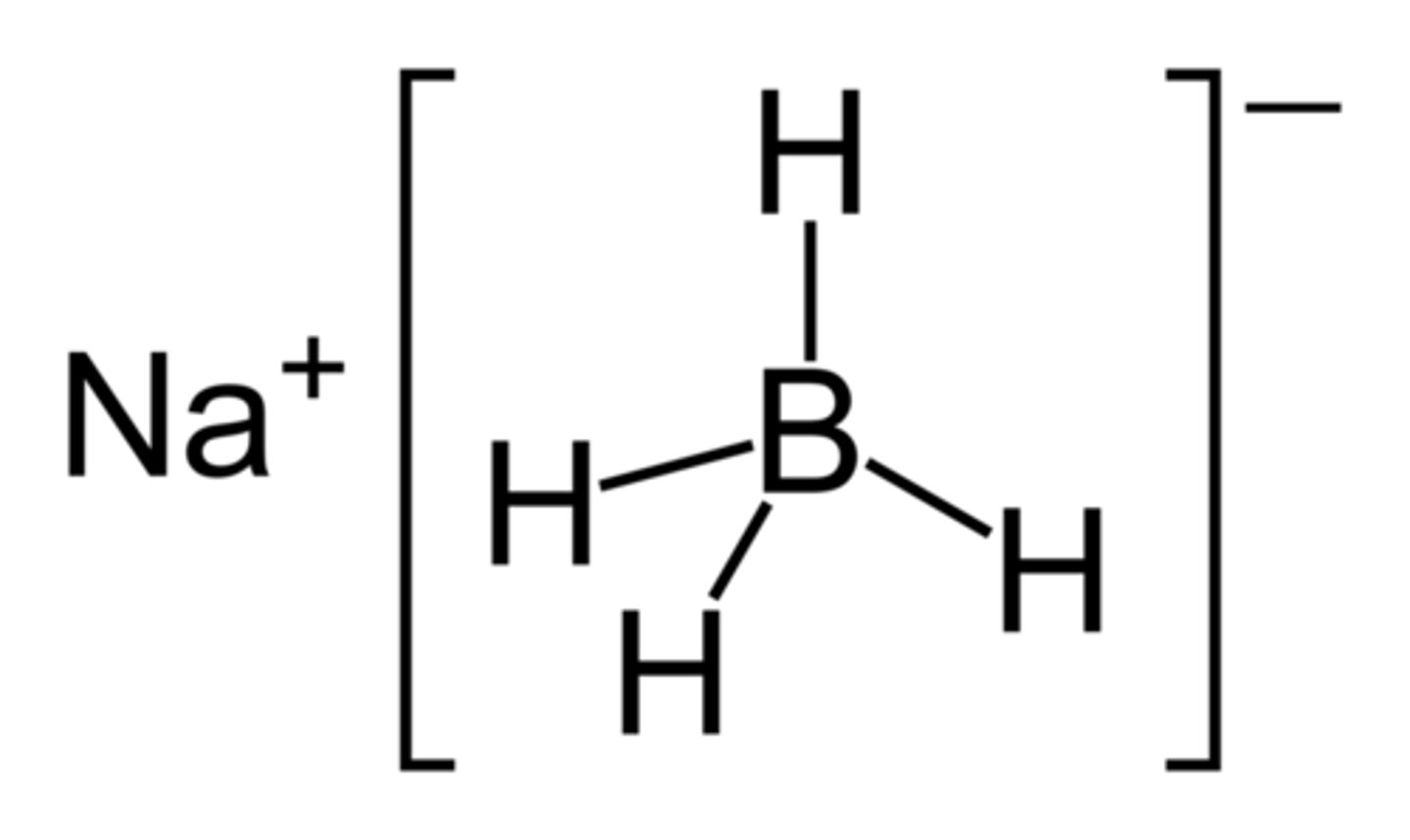
What is a reducing agent represented as in an equation?
[H]
Write an equation for the reduction of propanal.
What conditions are required?
CH₃CH₂CHO + 2[H] → CH₃CH₂CH₂OH
Heat under reflux with sodium tetrahydridoborate in aqueous ethanol followed by acidification with dilute sulphuric acid.
Write an equation for the reduction of propanone.
What conditions are required?
CH₃COCH₃ + 2[H] → CH₃CHOHCH₃
Heat under reflux with sodium tetrahydridoborate in aqueous solution followed by acidification with dilute sulphuric acid.
The reduction of aldehydes to primary alcohols and ketones to secondary alcohols are examples of what mechanism?
Nucleophilic addition
Suggest why NaBH₄ is used in reduction reactions.
It is a less reactive reducing agent than many others, so can selectively reduce the carbonyl group.
Name the product formed when ethanal reacts with hydrogen cyanide.
2-hydroxypropanenitrile
Name the product formed when propanone reacts with hydrogen cyanide.
2-hydoxy-2-methylpropanenitrile
Explain the dangers of using HCN. What is used instead?
Hydrogen cyanide is an extremely toxic and flammable gas.
HCN is generated in the reaction mixture by adding dilute acid to an aqueous solution of potassium cyanide instead.
KCN is toxic when ingested and forms hydrogen cyanide when in contact with acid.
Define a nucleophile.
Electron pair donor.
What is a hydride ion?
A negatively charged hydrogen ion with a lone pair of electrons.
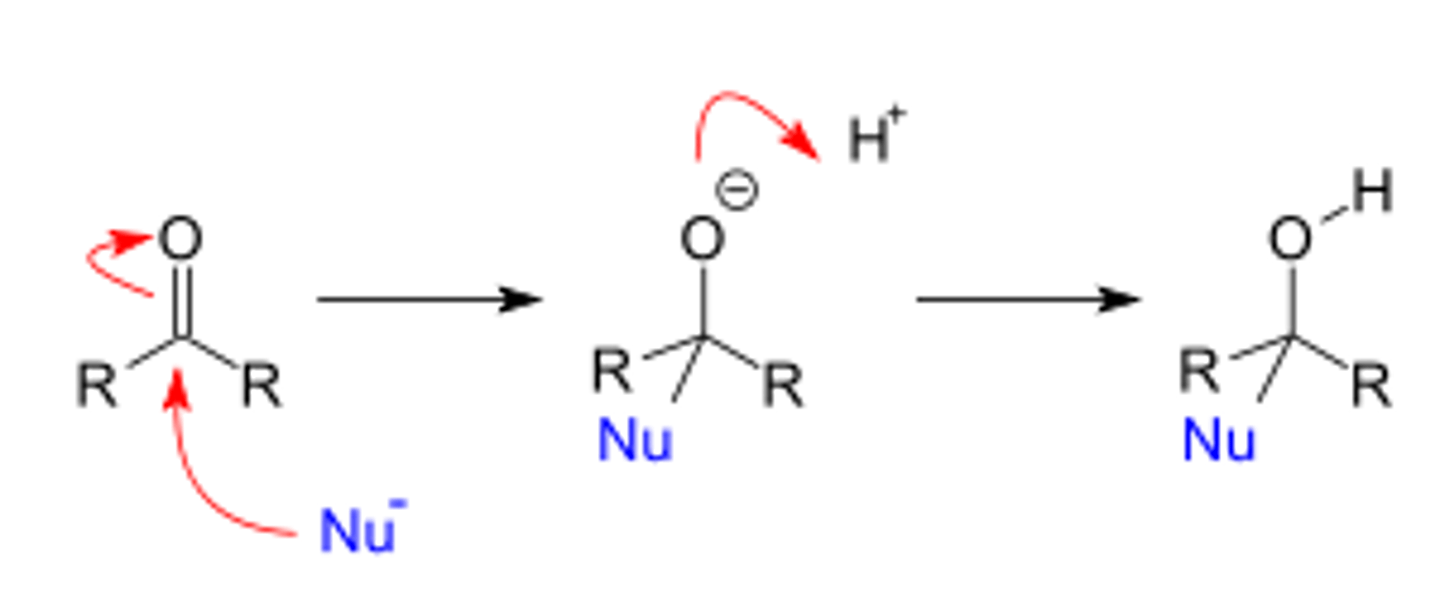
Describe what happens in the nucleophilic addition reaction of ethanal.
Outline the mechanism and name the final product.
The hydride ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks the δ+ carbon.
The lone pair of electrons on the hydride ion is donated and forms a bond with the carbon; the higher energy pi electrons in the carbonyl group move to the oxygen, giving it a negative charge.
When acid is added, the lone pair on the negative ion forms a covalent bond with H⁺ from the acid, producing an alcohol.
Ethanol is formed.
(Replace Nu with :H⁻, one R replace with CH₃ and other R replaced with H)
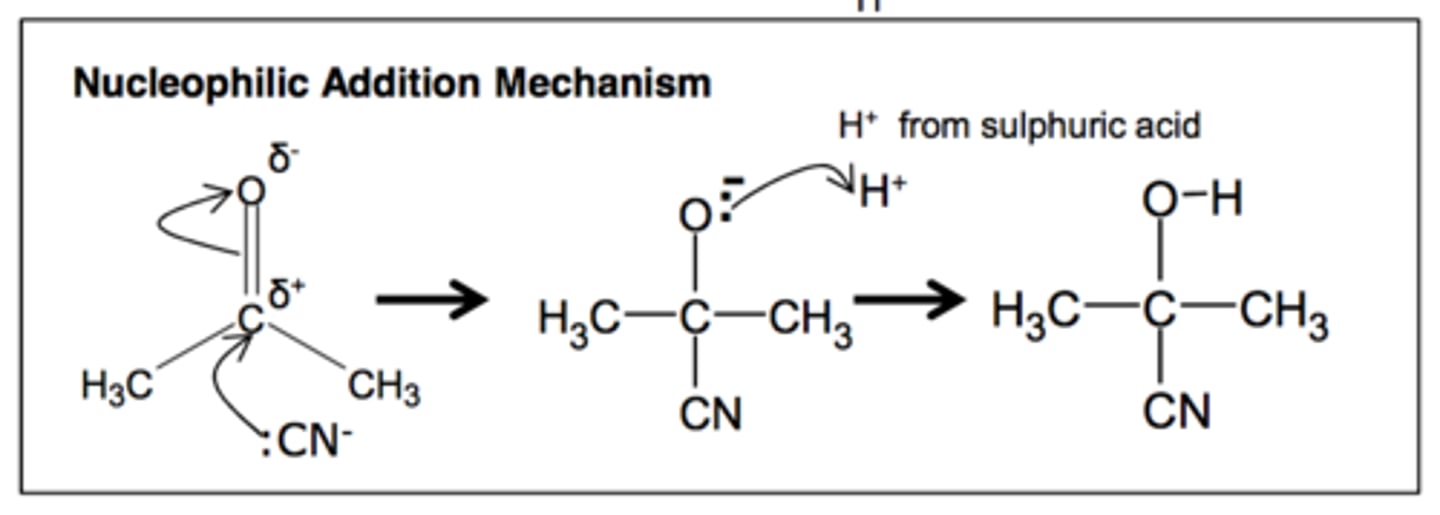
Outline the mechanism for the nucleophilic addition of ethanal with KCN and dilute acid, and name the final product.
2-hydroxypropanenitrile
Explain how the nucleophilic addition of KCN followed by dilute acid could result in a racemate.
The nitrile produced from any aldehyde (except methanal) exhibits optical isomerism, since it has an asymmetric chiral carbon centre with four different groups attached.
However, the product is optically inactive because a racemic mixture is formed. The carbonyl group is planar and the cyanide ion could attack the carbon atom equally from either side. The formation of each enantiomer is equally likely.
Unsymmetrical ketones can also form optical isomers in a racemate, due to having an asymmetrical carbon.
Carboxylic acids are ________ acids but will liberate ________ from ________.
weak, carbon dioxide, carbonates.
Explain why short chain carboxylic acids are very soluble in water.
Suggest why increasing the chain length decreases its solubility.
The highly polar carbonyl and hydroxyl groups can form hydrogen bonds with water.
As the number of carbon atoms increases, there is a longer non-polar hydrocarbon chain that decreases solubility.
Explain why carboxylic acids have a higher boiling point than alcohols.
Hydrogen bonding occurs between two molecules of the acid to form a dimer; this doubles the size of the molecule, leading to greater van der Walls' forces between the dimer, resulting in a higher boiling point.
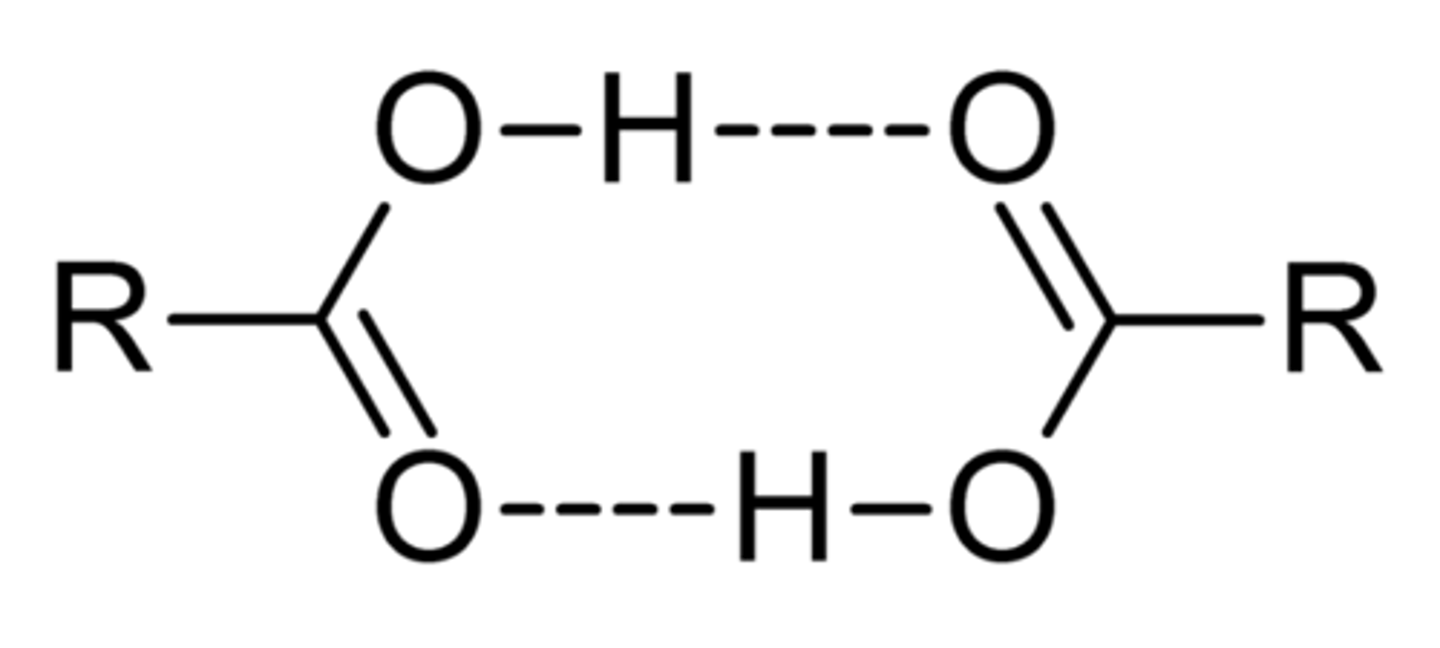
Name this moelcule: H₃O⁺
Hydroxonium ion / hydronium
How do you test for a carboxylic acid?
Add sodium (hydrogen)carbonate. Effervescence will occur if a carboxylic acid is present. The gas can be collected and bubbled into limewater which should turn cloudy, proving that the gas produced is carbon dioxide.
Write a word, symbol and displayed equation for the reaction of methanoic acid with sodium hydrogencarbonate.
Methanoic acid + sodium hydrogen carbonate → sodium methanoate + carbon dioxide + water
HCOOH + NaHCO₃ → HCOONa + CO₂ + H₂O
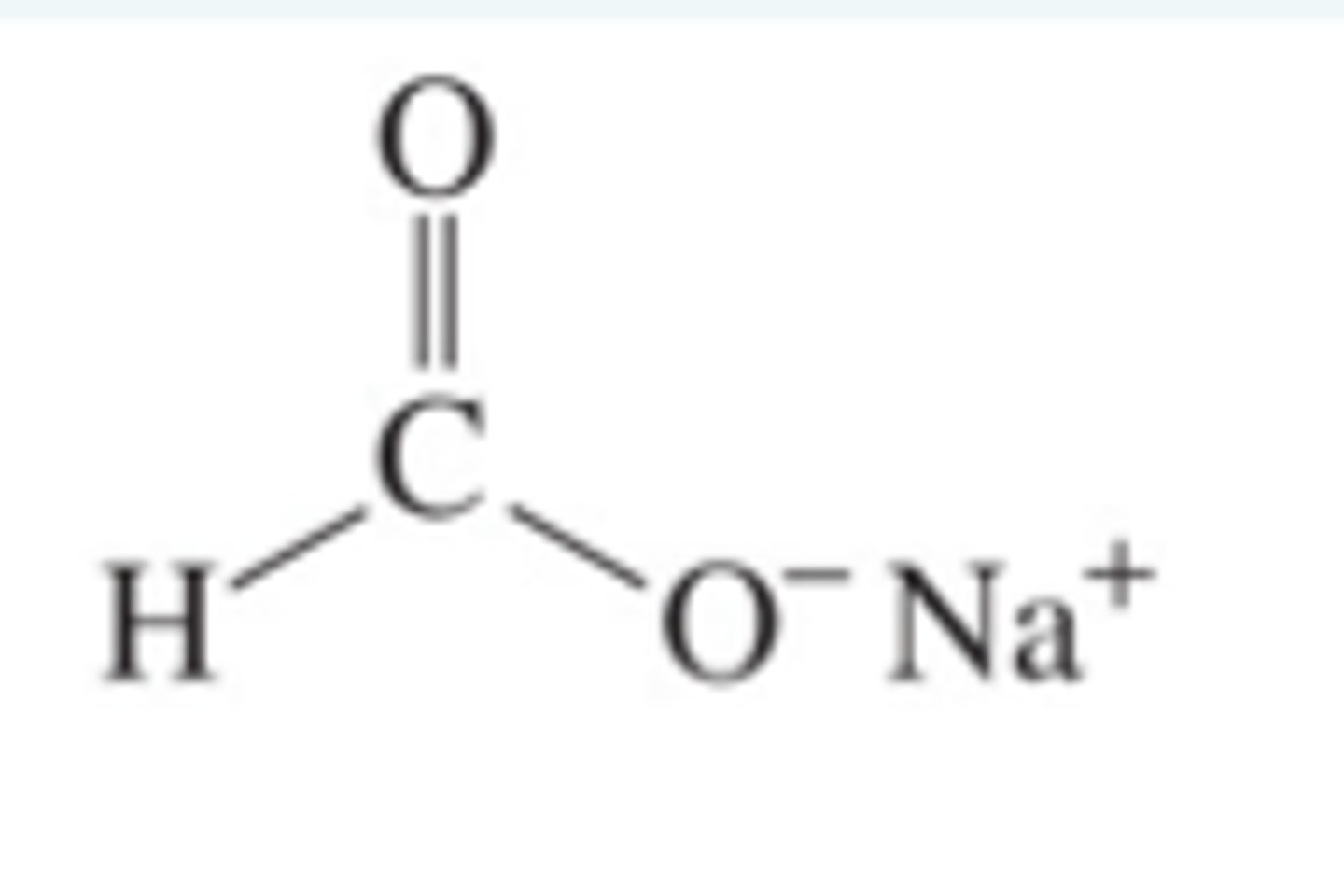
Write a symbol equation for the reaction between ethanoic acid and sodium hydroxide (base).
State an observation.
CH₃COOH + NaOH → CH₃COONa + H₂O
Heat released.
Write a symbol equation for the reaction between ethanoic acid and ammonia.
State the product formed. State an observation.
CH₃COOH + NH₃ → CH₃COONH₄
Ammonium ethanoate
Heat is released.
Carboxylic acids and ________ react, in the presence of a strong ________ ________, to produce ________.
Alcohols, acid catalyst, esters.
What is the -COO- group known as?
Ester group / ester linkage
Write the symbol equation for the reaction of methanoic acid with ethanol.
State the conditions required for this reaction.
HCOOH + CH₃CH₂OH → HCOOCH₂CH₃ + H₂O
Catalyst of concentrated sulphuric acid and mixture is heated.
Describe the uses of esters.
Used as plasticisers, which are additives mixed into polymers to improve their flexibility.
Used as solvents for organic compounds. They are volatile so are easily separated from the solute.
Used in perfumes due to their pleasant smells.
Used in food flavourings; many artificial fruit flavourings contain esters.
Used to make biofuels.
Give an example of an ester being used as a plasticiser.
PVC is rigid and used in drainpipes and window frames. If treated with up to 18% by mass of plasticiser (made form an ester), it becomes cling film, a much more flexible polymer used to wrap non-fatty foods.
Which ester is usually used as a solvent and why?
Ethyl ethanoate, due to its low cost and low toxicity. It is used in paints and nail varnish remover.
What is the opposite of an esterification reaction?
A hydrolysis reaction.
What are the required conditions for hydrolysis?
Heat, catalysed by a dilute mineral acid (e.g. HCl) or a solution of an alkali (e.g. sodium hydroxide).
Explain the difference between acid hydrolysis and alkaline hydrolysis, using equations.
Acid hydrolysis uses acidic conditions and esters are not completely hydrolysed. An equilibrium mixture is established where some ester is present.
ester + water ⇌ carboxylic acid + alcohol
Requires heat under reflux with dilute sulphuric or hydrochloric acid.
Alkaline hydrolysis uses sodium hydroxide in alkaline conditions. Esters undergo complete hydrolysis, forming the corresponding alcohol and the salt of the carboxylic acid (reaction is quicker than acid).
ester + base → carboxylic acid salt + alcohol
Requires heat under reflux with aqueous sodium hydroxide.
Write a symbol equation for the hydrolysis of ethyl ethanoate under acidic conditions.
CH₃COOC₂H₅ + H₂O ⇌ CH₃COOH + C₂H₅OH
Write a symbol equation for the hydrolysis of ethyl ethanoate under alkaline conditions.
What is another name for this reaction?
CH₃COOC₂H₅ + NaOH → CH₃COONa + C₂H₅OH
Saponification
How can the free acid in sodium ethanoate be released from its salt?
By the addition of a dilute mineral acid:
CH₃COONa + HCl → CH₃COOH + NaCl
Vegetable oils and animal fats are esters of propane-1,2,3-triol and 3 long carboxylic acid (fatty acid) chains.
State another name for propane-1,2,3-triol and draw its structure.
Glycerol
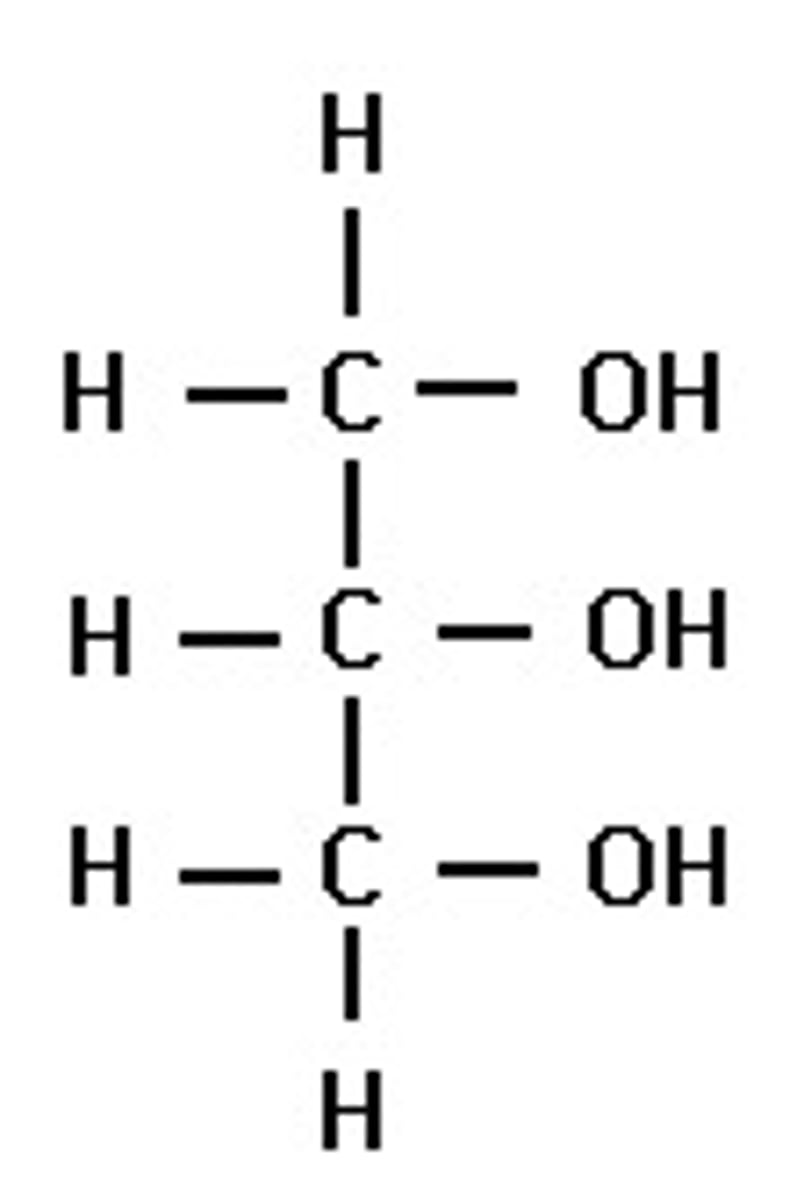
Define a triglyceride.
An ester of propane-1,2,3-triol and three fatty acid molecules.
What are fatty acids?
Naturally occurring long chain carboxylic acids.
State the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
Unsaturated contains at least one C=C in the hydrocarbon chain.
Define saponification.
The alkaline hydrolysis of fats into glycerol and soap (the salts of long-chain carboxylic acids).
Write an equation for the saponification of a fat, containing 3 fatty acid chains of equal length of 17 carbons.
Fat drawn, showing a triester (3 ester linkages).
(CH₂)₁₅-CH₃ used in fatty acid chain.
Addition of 3 NaOH
Produces glycerol and three salts of the carboxylic acid.
The sodium or potassium salts of the fatty acids are called soaps. How many carbons do they normally contain?
Generally 16 or 18
What is biodiesel? What does it consist of?
A renewable fuel produced by the heating of vegetable oil with methanol in the presence of an acid catalyst.
Consists of a mixture of methyl esters of long chain carboxylic acids.
What can biodiesel be used for?
It can be used in normal diesel engines to power cars and buses.
The process of heating vegetable oil and methanol to produce biodiesel can also be called a trans-esterification reaction. Explain what this means.
Reacting an ester with an alcohol to produce a different ester and a different alcohol.
The alkyl groups R₁, R₂ and R₃ may be the same of different.
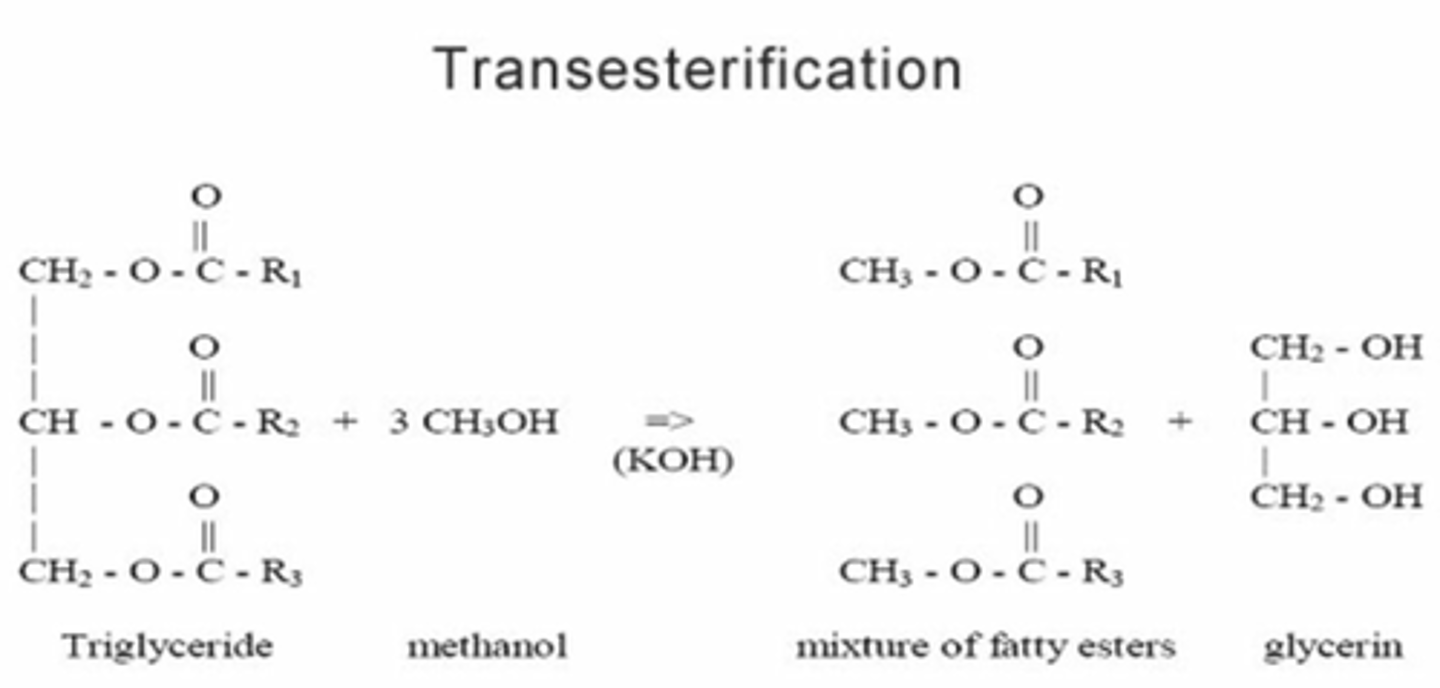
Glycerol is produced as a by-product in the production of biodiesel. Suggest what it can be used for.
It can be used in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. It has moisturising properties due to the three hydroxyl groups that can form hydrogen bonds with water, and so prevent its evaporation.
State a disadvantage of using biodiesel.
Using land for growing crops for biodiesel is in competition with land use for growing crops to produce food, which could lead to food shortages.
What are carboxylic acid derivatives?
Compounds that are related to carboxylic acids, but the OH group is replaced with another group.
Draw the functional group of an acyl chloride. What is the suffix when naming them?
-anoyl chloride
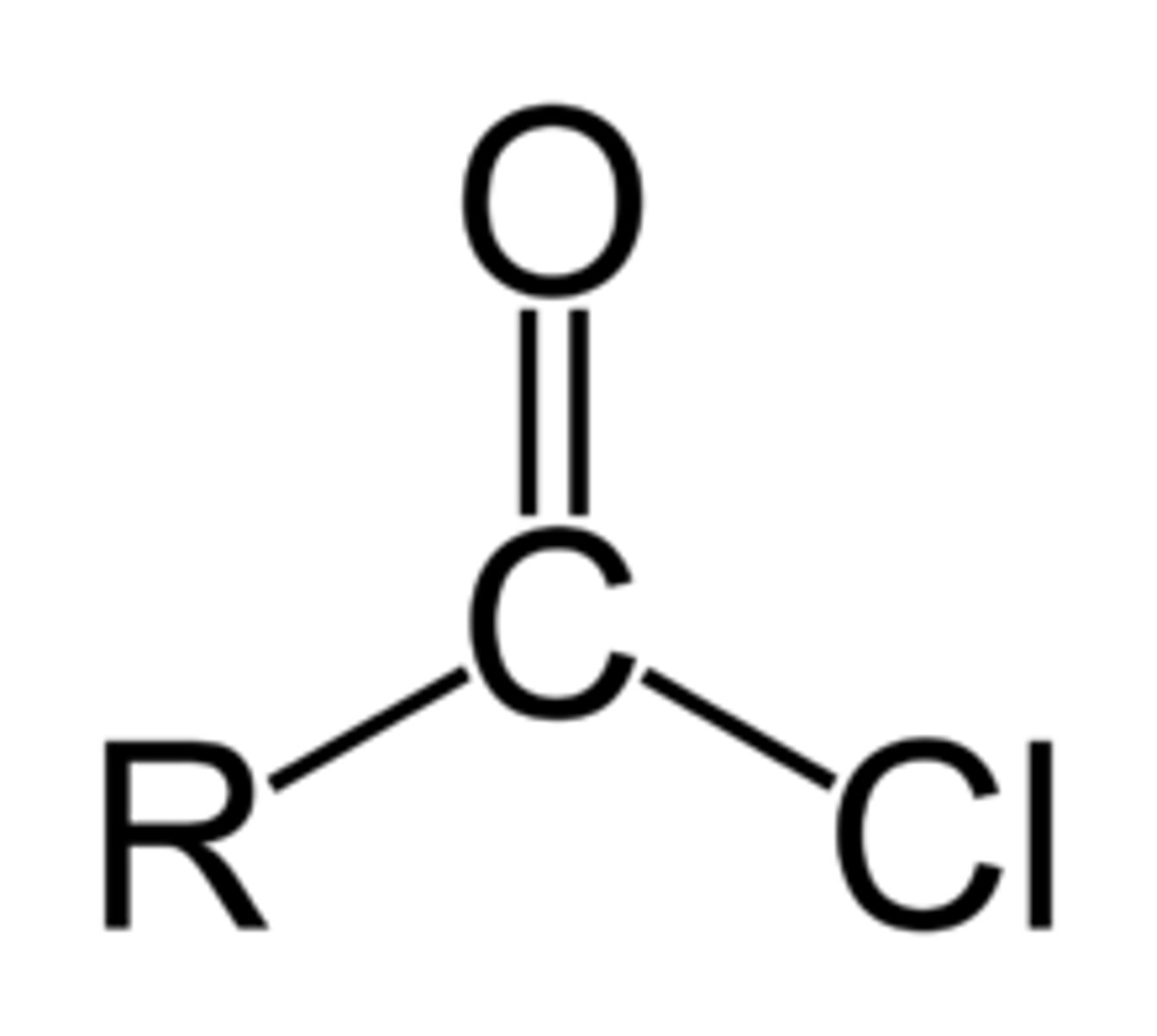
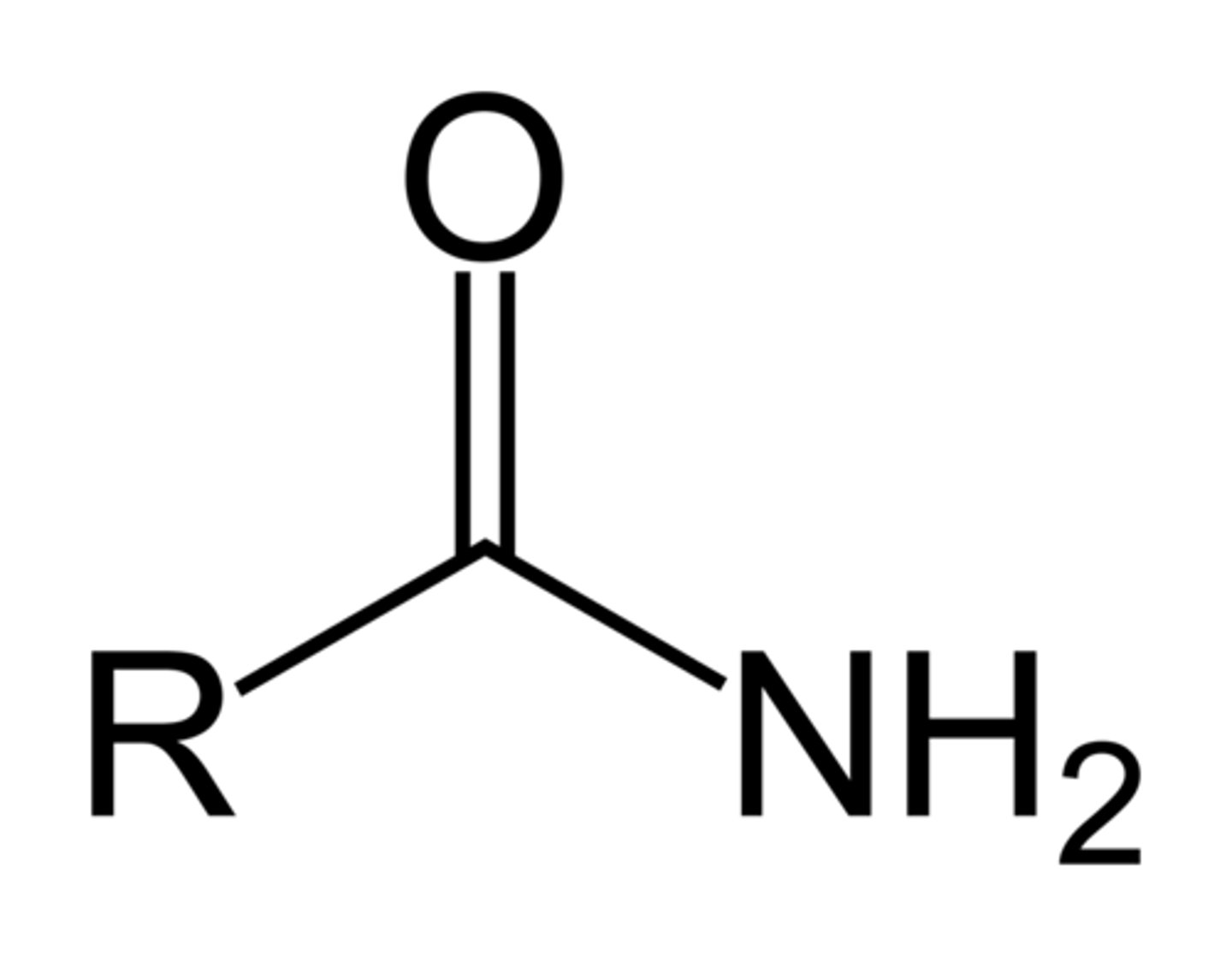
Draw the functional group of an amide. What is the suffix when naming them?
-anamide
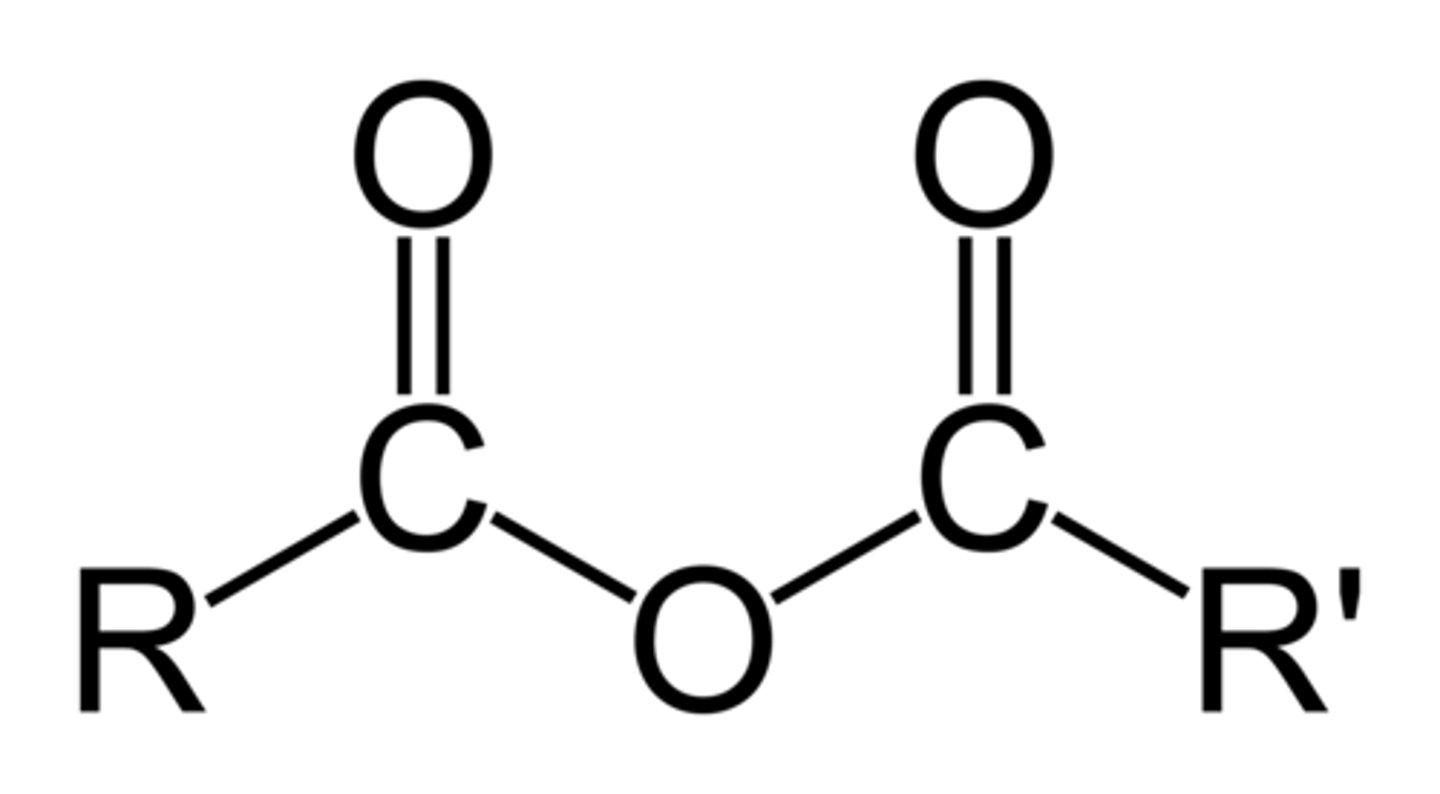
How are acid anhydrides formed?
When two molecules of a carboxylic acid join together and water is eliminated.
Draw the functional group of an acid anhydride.
What is the suffix when naming them?
-anoic anhydride
Write the structural formula of ethanoic anhydride.
(CH₃CO)₂O
What is an acyl functional group?
What is meant by acylation?
The process of replacing a hydrogen atom in certain molecules by an acyl group (RCO-).
Acylation can be carried out using acid derivatives (such as ________ ________ and ________ ________) which act as ________ ________.
Acyl chlorides, acid anhydrides, acylating agents.
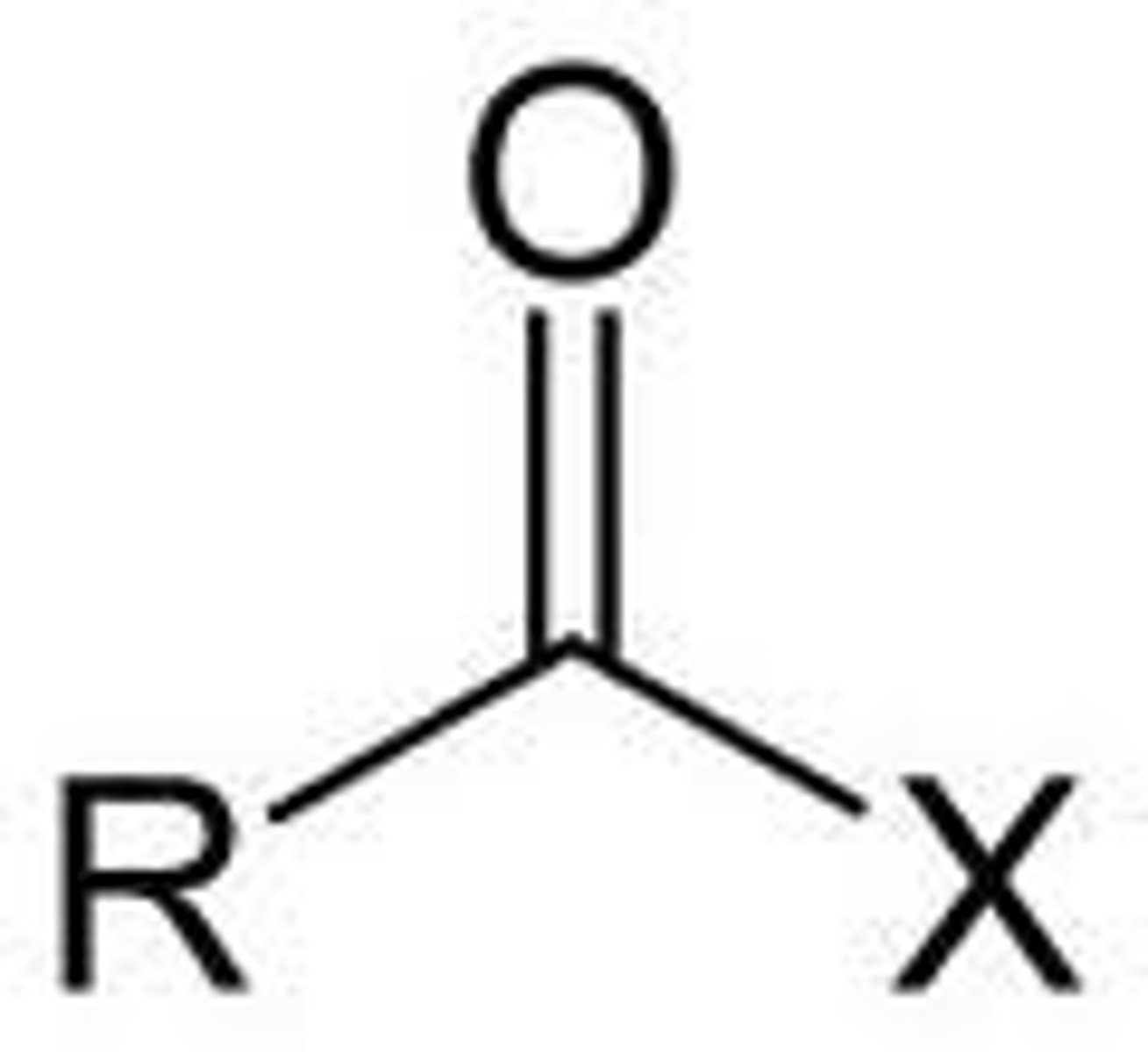
Draw the structure of an acylating agent.
Where X represents Cl in acyl chlorides, and OCOR in acid anhydrides.
Acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides show similar reactions with water, alcohol, ammonia and primary amines.
Describe the differences between the reactions of acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides.
Acyl chlorides react vigorously (with water), so anhydrous conditions must be used to prevent hydrolysis.
Acid anhydrides undergo slower reactions than acyl chlorides.
Write the equation for the reaction between ethanoyl chloride and ethanol.
Name the products formed.
State any observations.
CH₃COCl + CH₃CH₂OH → CH₃COOCH₂CH₃ + HCl
Ethyl ethanoate, hydrogen chloride
Steamy white fumes of HCl, heat produced.
Write the equation for the reaction between ethanoic anhydride and ethanol.
Name the products formed.
State any observations.
(CH₃CO)₂O + CH₃CH₂OH → CH₃COOCH₂CH₃ + CH₃COOH
Ethyl ethanoate, ethanoic acid
Slower and less vigorous than that of an acyl chloride.
Describe the advantages of using acyl chlorides and so the disadvantages of acid anhydrides to produce esters.
Advantages of acyl chloride:
- occurs at room temp
- irreversible reaction, high yield
- HCl is removed as a gas, forming pure ester.
Disadvantages of acid anhydride:
- needs heat
- is a reversible reaction
- requires a catalyst
- difficult to get a high yield of ester
- must be purified.
State the industrial advantages of ethanoic anhydride over ethanoyl chloride.
The reactions of acid anhydrides are easier to control.
Ethanoic anhydride is:
- less corrosive
- less vulnerable to hydrolysis
- less hazardous due to a less violent reaction
- cheaper than ethanoyl chloride
- does not produce corrosive fumes of HCl
Write the equations for the reaction between ethanoyl chloride, and then ethanoic anhydride, with water.
CH₃COCl + H₂O → CH₃COOH + HCl
(CH₃CO)₂O + H₂O → 2CH₃COOH
Write the equations for the reaction between ethanoyl chloride, and then ethanoic anhydride, with ammonia.
Name the products formed.
Describe differences between observations of these reactions.
CH₃COCl + 2NH₃ → CH₃CONH₂ + NH₄Cl
ethanamide, ammonium chloride
Violent reaction, produce white smoke.
(CH₃CO)₂O + 2NH₃ → CH₃CONH₂ + CH₃COONH₄
ethanamide, ammonium ethanoate
Slower reaction, heating may be required.
In the first part of the reaction between an acyl chloride and excess ammonia, hydrogen chloride is formed. Explain why the final product contains a salt but no HCl.
Ammonia is basic, so will react with the acidic HCl (in a neutralisation reaction) to form ammonium chloride.
In the first part of the reaction between an acid anhydride and excess ammonia, a carboxylic acid forms. Explain why the final product contains a salt of this carboxylic acid.
Ammonia is basic and so will react with the carboxylic acid to produce an ammonium salt.
What is an N-substituted amide?
When a hydrogen atom of the NH₂ group of an amide has been substituted for an alkyl group.
Write the equation for the reaction between ethyl chloride and ethylamine.
Name the products formed.
The reaction occurs in two steps, with HCl gas being released in the first. Explain what happens to the HCl.
CH₃COCl + 2CH₃CH₂NH₂ → CH₃CONHCH₂CH₃ + CH₃CH₂NH₃Cl
N-ethylethanamide, ethylammonium chloride
It reacts with the basic ammonia, forming a salt.
Draw N-propylbutanamide.
Carbon chain of 4, with carbonyl group and NH at one end. Propyl group attached to N.
Draw methylammonium chloride.
CH₃NH₃ drawn, with positive charge on N. Negative charge on Cl.
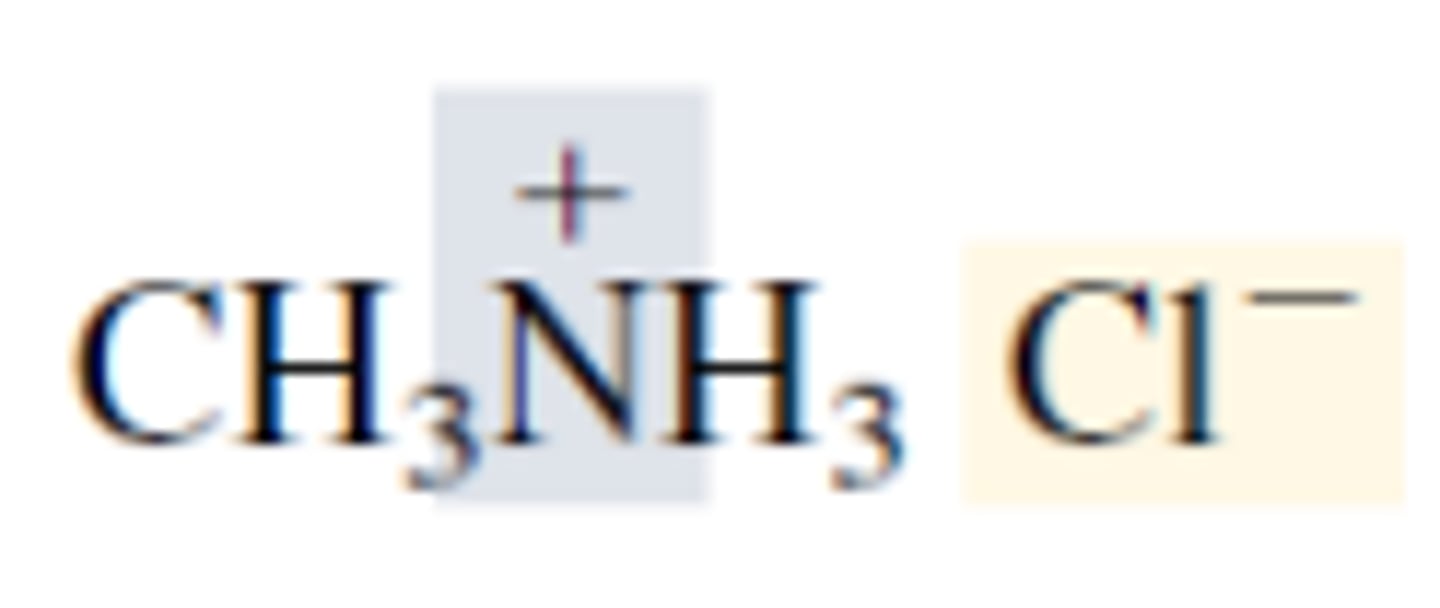
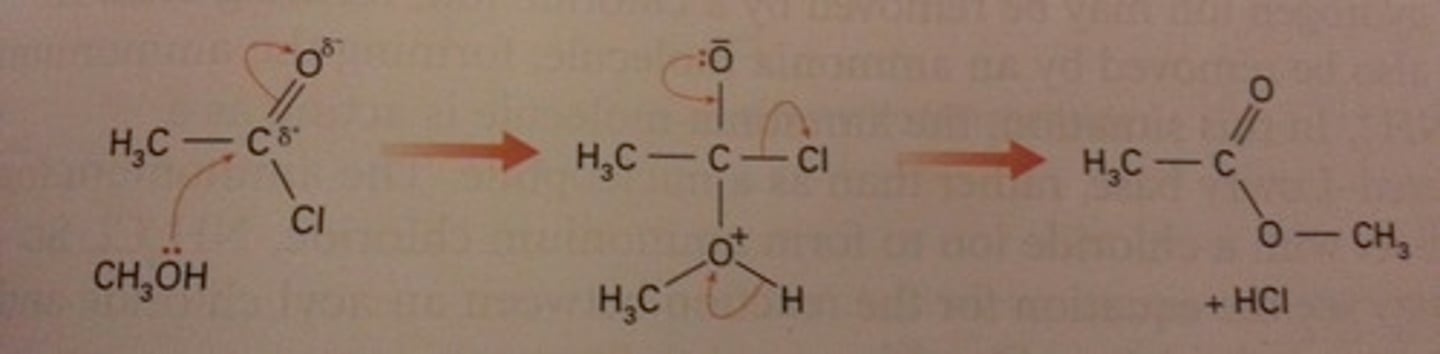
Write the equation for the reaction between ethanoic anhydride and methylamine.
Name the products formed.
(CH₃CO)₂O + 2CH₃NH₂ → CH₃CONHCH₃ + CH₃COONH₃CH₃
N-methylethanamide
methylammonium ethanoate
Outline the mechanism for ethanoyl chloride and water.
Name the mechanism.
Name the products formed.
Nucleophilic addition-elimination
ethanoic acid and hydrogen chloride
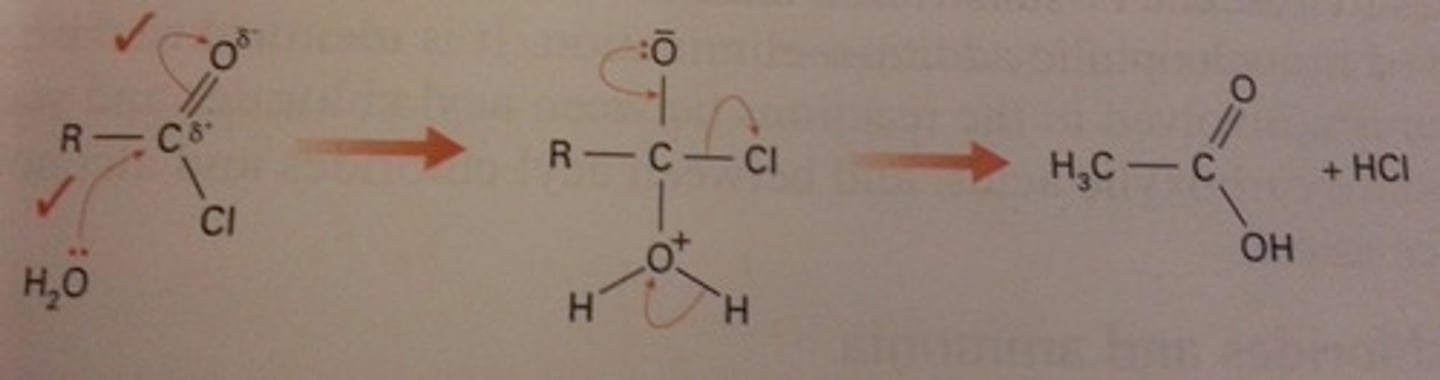
Outline the mechanism for ethanoyl chloride and methanol.
Name the products formed.
methyl ethanoate and hydrogen chloride
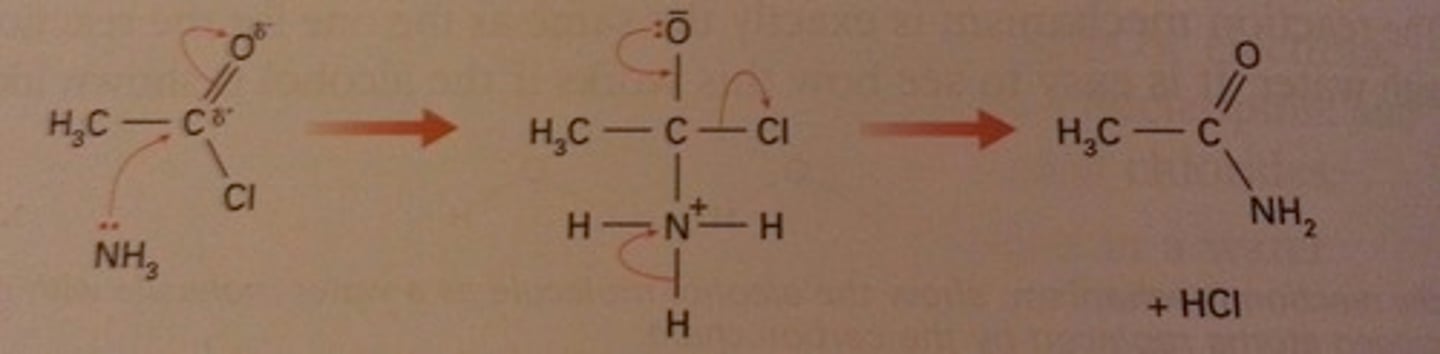
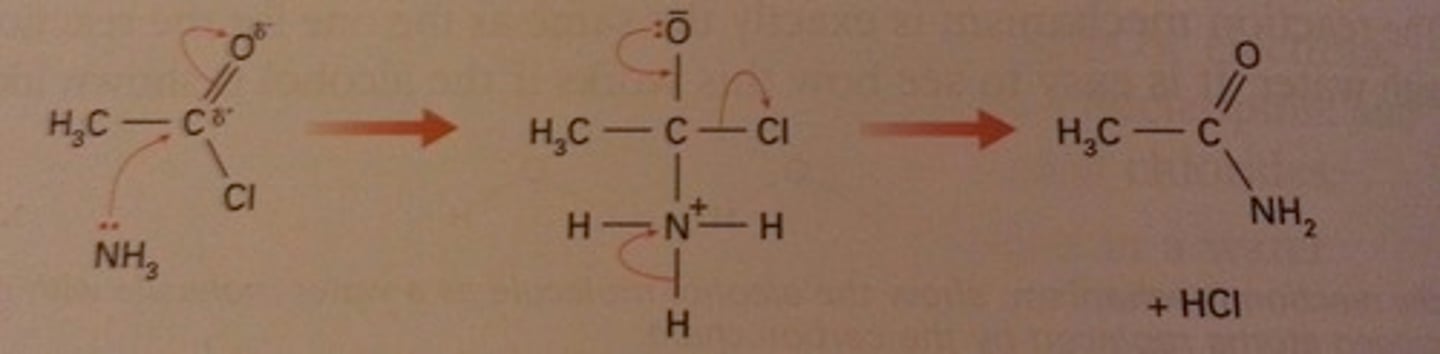
Outline the mechanism for ethanoyl chloride and ammonia.
Name the products formed.
ethanamide, hydrogen chloride
Outline the mechanism for ethanoyl chloride and methylamine.
Name the products formed.
One H on NH₃ replaced with CH₃.
Products formed are N-methylethanamide, hydrogen chloride.
Write the equation to show the production of aspirin.
Name the reactants and products.
This is an example of an ________ reaction.
Ethanoic anhydride, 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, aspirin, ethanoic acid.
Acylation.
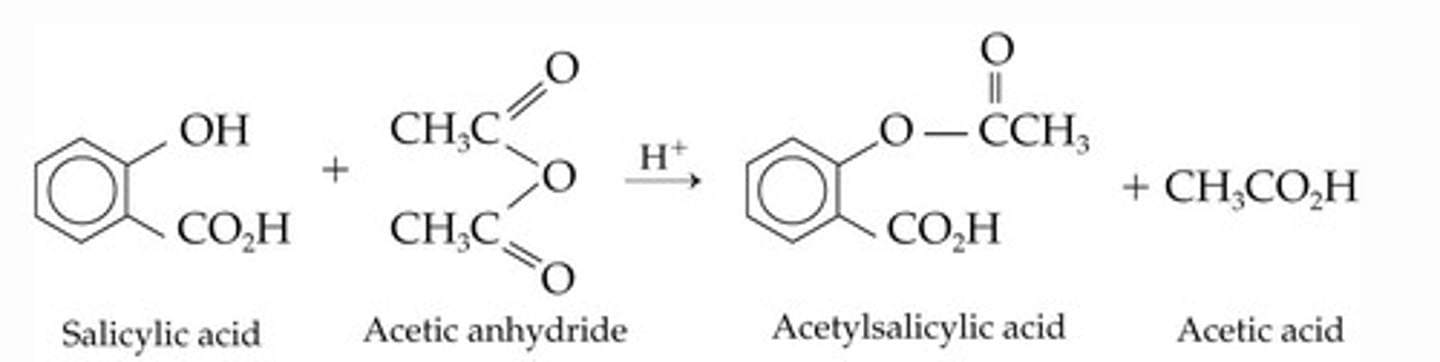
Which species is acting as the acylating agent in the production of aspirin?
Ethanoic anhydride
Suggest two reasons why impurities may form in a reaction.
Contamination with reactants due to incomplete reactions; presence of other compounds due to alternative competing reactions during the preparation.
What is the purpose of crystallisation?
Describe the practical steps for the process of recrystallisation.
In order to purify solids by removing unwanted by-products.
- Dissolve the impure crystals in the minimum volume of hot solvent.
- Filter the hot solution by gravity filtration, using a hot funnel and fluted filter paper, to remove any insoluble impurities.
- Allow the solution to cool and crystallise.
- Filter off the crystals using suction filtration.
- Dry between two sheets of filter paper.
Draw the apparatus for suction filtration.
Flask is called a side-arm conical flask.
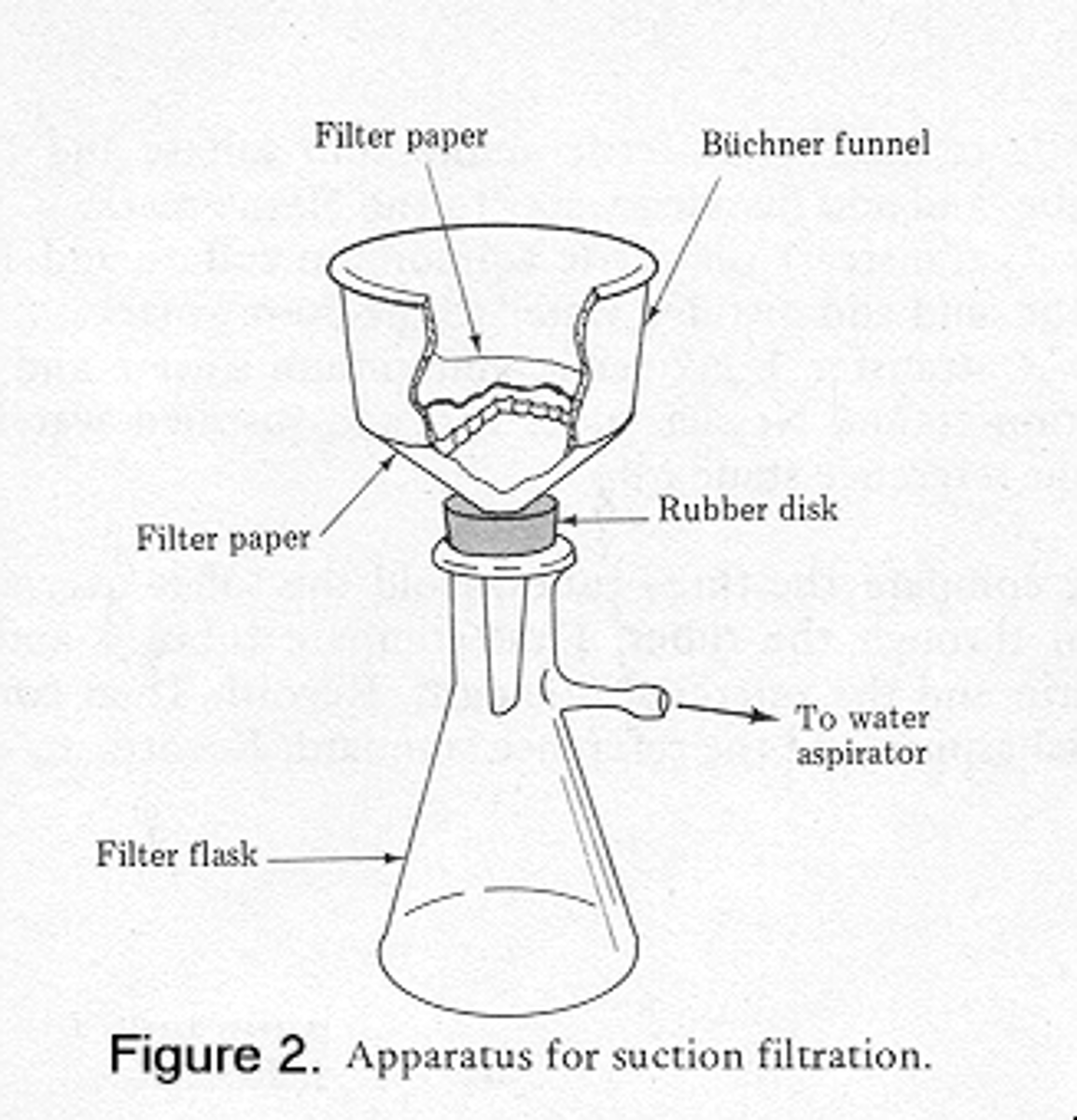
Explain the purpose of filtering twice.
In gravity filtration, which is slower, a hot funnel and fluted filter paper keeps the aspirin dissolved in solutions and prevents its precipitation. This removes insoluble impurities.
After the solution has cooled and crystallised, the insoluble crystals are aspirin. Faster suction filtration removes these crystals from the impure solution. This gives a drier solid than gravity filtration (by creating a vacuum).
Explain why a minimum volume of hot solvent is used.
In order to dissolve the solid, making a saturated solution. The solution is cooled and the solubility of the compound drops, causing it to recrystallise from solution. A minimum volume ensures that as much as the solute is obtained as possible.
Describe how to check the purity of an organic solid.
- Place some solid in a melting point tube.
- Place in melting point apparatus and heat slowly.
- Record the temperature at which the solid starts to melt and the temperature at which it finishes melting.
- Repeat and average the temperatures.
- Compare the melting points with known values in a data book.
The greater the range of temperatures in the melting point, the more ________ the substance. A range of less than ________ indicates a fairly ________ substance.
impure, 2⁰C, pure