Knee
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Define the Posterior Cruciate & Anterior Cruciate and role?
-Ligaments related to the knee joint that crisscross and stops movement from anterior to posterior
Define the Fibular (lateral) collateral & Tibial (medial) collateral and role?
-Ligaments related to the knee joint that are on the sides and help stop movement side to side
Define Meniscus and role?
There is a medial and lateral menisci located between the articular facets of the tibia, act as a shock absorber to reduce direct impact at the knee joint
Proximal Tibiofibular joint movement?
Gliding
Femorotibial joint movement?
Bicondylar/Hinge
Patellofemoral joint movement?
Saddle
Technical Considerations
Grid- if knee measures more than 10 cm
Nongrid = 65-75 kvp
Grid= 70-80 kvp
SID = 40 inches
Small FSS
AP knee
CR = ½ inch distal to apex of patella, parallel to tibial plateaus
Medial rotate leg 5 degrees to get true AP, condyles parallel to IR
Angle rules: 18 cm → 5 degrees caudal, 19-24 cm→ no angle, 25cm→ 5 degrees cephalic
Why angle? to get perpendicular to the tibial plateau/ femorotibial joint space
-Femorotibial joint space open
-Fibular head superimposed by the tibia
-Patella in middle of femur
-Intercondylar eminence in middle of condyles
AP Medial/Internal Oblique Knee
CR= ½ inch distal to apex of patella
No tube angle
45 degree medial rotation
-Tibia and fibula seperated
-Proximal tibiofibular joint seen
-Lateral condyles in profile
AP Lateral/External Oblique Knee
CR= ½ inch distal to apex of patella
No tube angle
45 degree lateral rotation
-Fibula superimposed by tibia
-Medial condyles in profile
Lateral knee
CR = 1 inch distal to medial epicondyle
Flex knee 20-30 degrees (not on cross table)
Angle 5-7 degree cephalad to compensate for medial condyle
-Femoral condyles superimposed
-Patella in profile
-Patellofemoral joint space open
-Tibial tuberosity in profile
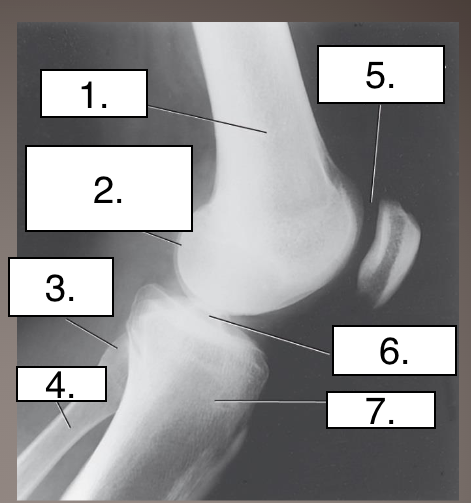
What projection?
Label?
Lateral knee
Femur
Superimposed medial and lateral condyles
Fibular head
Fibula
Femoropatellar joint
Intercondylar eminence
Tibia
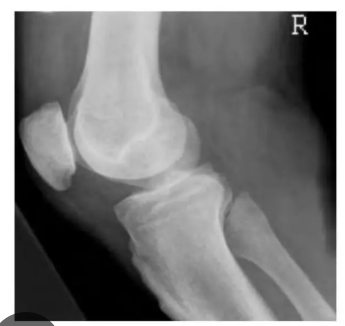
Is this under or over rotated?
How to correct it?
Over rotated - Fibula away from tibia, medial condyle more anterior
-Correction= roll patient knee away from IR

Is this under or over rotated?
How to correct it?
Under rotation = Fibula covered by tibia, medial condyle more posterior
Correction= Roll patient knee towards IR
Special - AP Weight Bearing
Special - PA Axial weight bearing = Rosenberg
Bilateral AP + Lateral
To evaluate joint space = Femorotibial joint space
No tube angle on lateral weight bearing
-Knee joints centered
-No rotation of knee
-Joint spaces open = Femortibial joint space
Camp Coventry method
Flex lower leg 40-50 degrees
CR= Perpendicular to lower leg (angle 40-50)
CR= popliteal crease
-Intercondylar fossa in profile
-Articular facets and intercondylar eminence well visualized
Holmblad Method
Lean forward 20-30 degree, leg forms 70 degree angle
CR= perpendicular to lower leg (no angle)
CR = popliteal crease
-Intercondylar fossa in profile
-Articular facets and intercondylar eminence well visualized
AP Axial - Beclere method
Knee flexed 40 to 50 degrees
CR = perpendicular to lower leg (angle)
CR= ½ inch distal to apex of patella
-Intercondylar fossa in profile
-Articular facets and intercondylar eminence well visualized
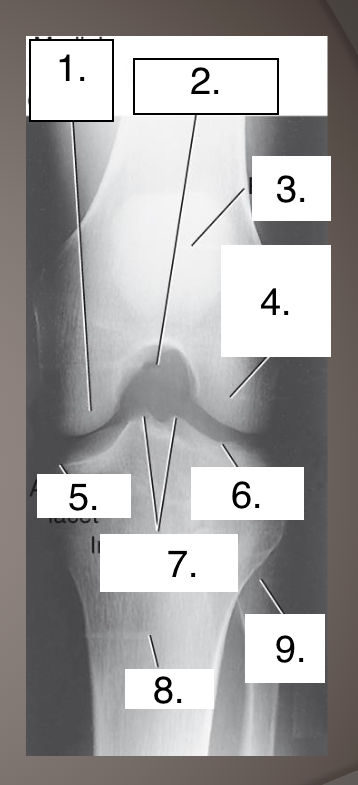
Projection?
Label?
Incondylar fossa
Medial femoral condyle
Intercondylar fossa
Patella
Lateral femoral condyle
Articular facet
Articular facets
Intercondylar eminence
Tibia
Fibular head
PA Patella
CR = Perpendicular to mid patella area (popliteal crease)
Rotate knee 5 degrees medial for true AP
-Patella centered to collimation field
Mediolateral Patella
CR= to patellofemoral joint space
Flex only 5-10 degrees
-Patella and knee joint in center of collimation field
-Patella in true lateral = in profile
Tangential (superior- inferior) merchant bilateral method
Knee flexed 40 degrees
CR angled 30 degree from horizontal
-Intercondylar sulcus and patella visualized
-Patellofemoral joint spaces open
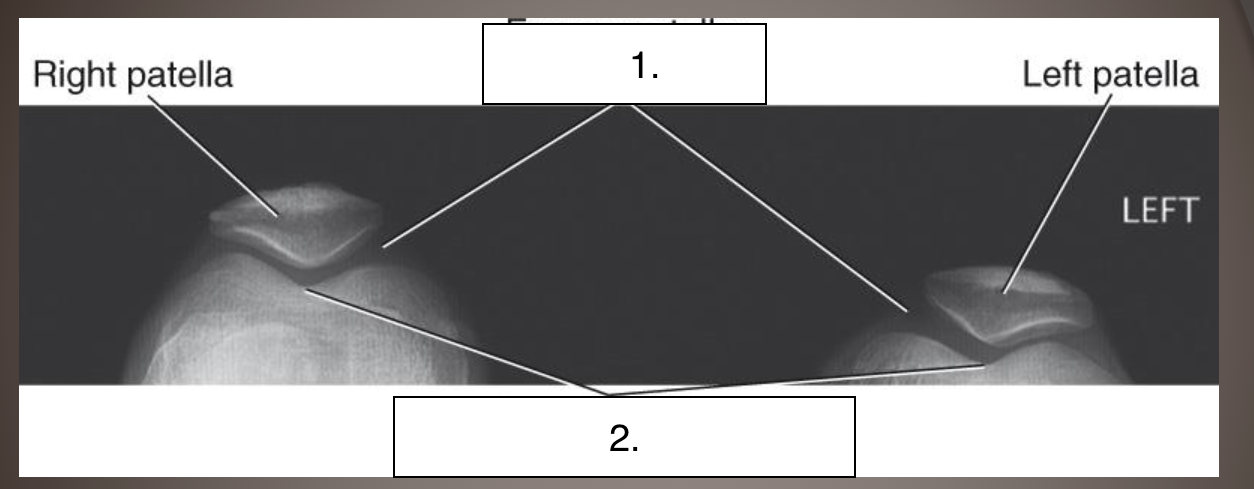
Projection?
Label?
Tangential patella - merchant method
Femoropatellar joint space
Intercondylar sulcus (trochlear groove)
Inferosuperior projection
40-45 degrees flexion of knees
CR - tangential to femoropatellar joint
Hughston method - Inferior to superior
Knee flexed 50- 60 degrees
CR - tangential to patellofemoral joint space
Looks at patella
Settegast Method (inferosuperior)
90 degree flexion (tangential to femoropatellar joint space)
CR- tangential to femoropatellar joint space
Looks at patella
Gout
a form of arthritis that may be hereditary in which uric acid appears in excessive quanities in the blood, very common in the first MTP of foot
Osteomyelitis
a bone infection that can result from bacteria or fungi spreading through the bloodstream or from an injury that directly exposes the bone to germs
Osteomalacia (Rickets)
Bone softening, disease caused by lack of bone mineralization. known as rickets in children and commonly results in bowing of the tibia
Osgood-Schlatter disease
Inflammation of the bone and cartilage of the anterior proximal tibia, most common in boys 10 -15, detaches part of the tibial tuberosity
Osteochondroma
Benign, neoplastic bone lesion that is caused by consolidated overproduction of the bone at a joint, usually the knee
Torn menisus/ACL
a common knee injury where the anterior cruciate ligament and the meniscus cartilage are both damaged
Flat foot
a common condition where the arches on the inside of your feet flatten, causing the entire sole to touch the ground when standing
-Reason why we do weightbearing foot