BIO extra credit 2
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
membrane proteins and lipids are able to move relative to one another within the plasma membrane according to the ___ ___
fluid-mosaic
One layer, or half of a phospholipid bilayer, is termed a ___
leaflet
The model used to explain the structure, organization and dynamics of biological membranes is the ___ ___ model
fluid mosaic
Within the plasma membrane, where are glycolipids normally found?
extracellular leaflet
What are the three main molecular components of cellular membranes?
proteins, carbs, lipids
a lipid bilayer is composed of ____ leaflets
2
The two leaflets of the plasma membrane have the same lipid composition. True or false
false
The cytosolic leaflet of the plasma membrane faces ___
the inside of the cell
Most transmembrane segments of integral membrane proteins are folded into what type of secondary structure?
alpha-helix
Transport of ions and large molecules into and out of the cell is mediated by membrane ___
proteins
Proteins that are non-covaently bound to the hydrophilic regions of integram proteins or to the polar head groups of lipids are called ___ membrane proteins
peripheral
Some proteins are found on the surface of the lipid bilayer of the membrane, and they are attached to it by hydrogen and/or ionic bonds. These are called ____ membrane proteins
peripheral
What types of interactions are typically involved in peripheral proteins binding to biological membranes?
ionic and hydrogen bonds
Movements that keep the phospholipid fatty acid tail within the ___ region of the bilayer are energetically favorable
hydrophobic
The transfer of phospholipids between leaflets requires the input of ___
ATP
What structural feature of a protein would suggest to a scientist that it is likely to be a transmembrane protein?
The presence of α helices
The movement of lipids between leaflets is catalyzed by the enzyme ___, which requires energy input in the form of ___
flipase, ATP
The transfer of phospholipids between leaflets requires the input of ___
ATP
Lipids with shorter tails ___ the fluidity of the plasma membrane
increase
Which of the following movements of a phospholipid are energetically favorable within the bilayer?
rotational and lateral movements
An unsaturated lipid contains ___ bonds
double
Phospholipids that have shorter tails are less likely to interact with each other, thus rendering the membranes more ___
fluid
The short, rigid molecule produced by animal cells that is involved in membrane fluidity is called ___
cholesterol
____ at low temperatures, makes the membrane more fluid and prevents freezing
cholesterol
The presence of a ___ ___ in a phospholipid tail makes the membrane more fluid because it prevents phospholipids from packing tightly
double bond
The Frye and Edidin experiment demonstrated that lateral protein movement within the membrane is affected by ___
temperature
Most membrane components of a eukaryotic cell are synthesized at the ___
ER
Some transmembrane proteins are restricted in their movement because they contain regions that projects into the cytosol and are anchored to components of the ____
cytoskelton
Because transmembrane proteins are much ___, than lipids, they diffuse within the membrane at a(n) ___ rate
bigger, slower
Transmembrane protein flip-flop does not occur spontaneously because it would be energetically ___
inefficient
A phospholipid consists of two ___ acids, one ___ molecule, and one phosphate attached to a polar head group
fatty, glycerol
In the process of phospholipid synthesis, the two ___ ___ molecules are activated by attachment to coenzymes A
fatty acid
In eukaryotic cells, lipids are produced by the ___ and ___ system working together
cytosol, endomembrane
Newly synthesized lipids are inserted into the cytosolic leaflet of the ___
ER membrane
The function of the enzyme called signal ___ is to remove the ER signal sequence from transmembrane proteins
peptidase
During phospholipid synthesis, fatty acids are activated by attachment to ___
coenzyme A
Most transmembrane proteins contain an ER ___ sequence that directs them to the ER membrane
signal
Some transmembrane proteins are restricted in their movement because they contain regions that project into the cytosol and are anchored to components of the ___
cytoskeleton
How are membrane proteins transferred from the ER to other regions of the cell?
vesicular transport
Which enzyme removes the ER signal sequence from transmembrane proteins?
signal peptidase
In the embryonic development of animals, the proper migration of cells relies on the recognition of cell types via the ___ on each cell’s surface
carbs
After being synthesized by ribosomes associated with the rough ER, membrane proteins are packaged into ___ which transport them to other regions of the cell
vesicles
Most transmembrane proteins contain an ER ___ sequence that directs them to the ER membrane
signal
Highly glycosylated proteins involved in the organization of the extracellular matrix are produced via what process?
o-linked glycosylation
Highly (O-linked) glycosylated proteins that are secreted from cells are called ___ One of their main biological functions is to organize the extracellular matrix surrounding cells.
proteoglycans
What types of protein glycosylation occur in eukaryotes?
O-linked, N-linked
The cell maintains a favorable internal environment due to the selective ___ of the plasma membrane
permeability
What is the target for N-linked glycosylation?
membrane proteins
Which of the following processes require a transport protein?
active transport and facilitated diffusion
Which type of transport requires a source of energy and a transport protein?
active
To move a substance through a membrane against a concentration gradient, which of the following are necessary?
a source of energy and a transport protein
Small, uncharged molecules pass through the membrane via ___ ___
passive diffusion
In a solution, the ions that are dissolved are called the ___ molecules, and the liquid in which they are dissolved is called the ___
solute, solvent
When the concentration of a solute is higher on one side of membrane than the other, a transmembrane ___ is established
gradient
A term that describes a situation in which the concentration of a solute is higher on one side of a membrane than the other is ___
transmembrane gradient
A cell contains less sodium than the surrounding environment. What type of transport is required to import sodium ions into the cell?
facilitated
When the concentration of solutes on both sides of the plasma membrane are equal, the two solutions are said to be ___
isotonic
A cell contains a higher concentration of glucose than the surrounding environment. What type of transport is required to import glucose into the cell?
active
A solution whose solute concentration is higher than the concentration of solutes inside a cell is ___
hypertonic
A solution with a concentration of solutes lower than that in a cell is said to be ___ relative to the cell
hypotonic
Osmosis is the flow of ___ across a membrane
water
Osmosis describes the movement of water from areas where the solute concentration is ___ to areas in which the solute concentration is ___
lower, higher
Animal cells will take up water if present in
___ solutions. In extreme cases, the cells can rupture in a process called osmotic lysis.
hypotonic
A sample of cells is placed in a salt solution. The cells subsequently shrink, and the membrane deforms. Relative to the cells, the salt solution is ___
hypertonic
What is the result of placing a plant cell into a hypertonic solution?
plasmolysis
If the medium surrounding a plant cell is ___ water exits the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall in a process known as plasmolysis
hypertonic
What component of plant cells prevents changes in cell volume that result in osmotic lysis?
the cell wall
What is one way that solutes that cannot diffuse across the membrane can still gain access to the interior of the cell?
transport proteins
What is the function of channel proteins?
facilitated diffusion
A contractile vacuole is an important feature of microorganisms living in a(n) ___ environment
hypotonic
If the medium surrounding a plant cell is ___ , water exits the cell and the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall in a process known as plasmolysis.
hypertonic
Ions and hydrophilic molecules are able to cross the phospholipid bilayer via transmembrane proteins called ___ proteins
channel
When channel proteins are ___ , it means they can open and close to regulate the movement of ions and molecules across the cell membrane.
gated
What are the categories of proteins that assist in the movement of molecules and ions across membranes?
channels, transporters
What type of proteins forms an open passageway for facilitated diffusion of ions or molecules across the membrane?
channels
Some freshwater microorganisms that live in hypotonic environments use a contractile vacuole to help prevent ___ ___
osmotic lysis
What is the function of channel proteins?
facilitated diffusion
Unlike channel proteins which provide an open passageway all the way across the plasma membrane, proteins known as ___ bind solutes and then undergo a conformational change
transporters
Which type of protein is the principal pathway for the uptake of sugars, amino acids, and nucleotides?
transporter proteins
Some proteins act as channels to allow the facilitated diffusion of water across a membrane. These proteins are called ___
aquaporins
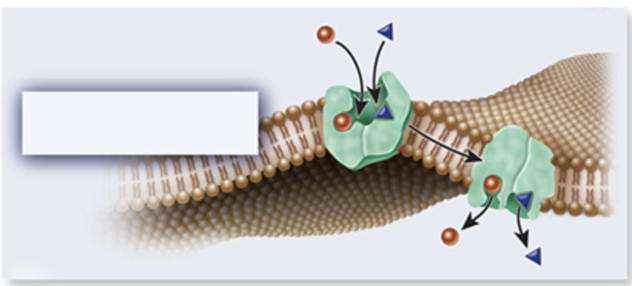
This figure depicts a transporter known as a…
symporter
An integral membrane protein that transports two different molecules across the plasma membrane in the same direction is called a(n) ___
symporter
Which type of protein is the principal pathway for the uptake of sugars, amino acids, and nucleotides?
transporter proteins
an ___ is a channel for water
aquaporin
Which of the following move solutes in only one direction?
uniporter and symporter
Active transport is the movement of a solute across the membrane ___ its concentration gradient
against
In order to move a solute from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration ___ is required
an input of energy
Moving a solute against its chemical or electrochemical gradient requires a source of ___
energy
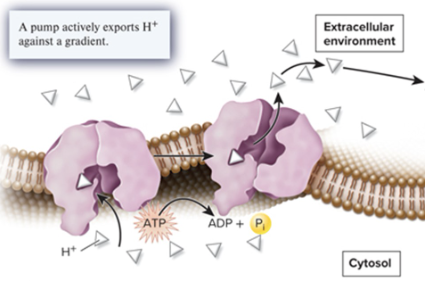
what form of membrane transport is this?
primary active transport
Which of the following types of transport involves pumping ions against a gradient using ATP as a source of energy?
primary active transport
What type of transport uses a pre-existing gradient to drive the transport of another molecule?
secondary active transport
The use of a pre-existing gradient to drive the active transport of another solute is termed ___ active transport
secondary
The Na+/K+-ATPase actively transports Na+ and K+ ions ___ their gradients by using the energy from ATP hydrolysis
against
Due to the Na+/K+-ATPase, cells are able to maintain concentration gradients so that the concentration of ___ ions is greater outside the cell than inside, and the concentration of ___ ions is greater inside the cell than outside
Na, K
The Na+/K+-ATPase pump is considered a(n) ______ because it binds both Na+ and K+ and transports them in opposite directions.
antiporter
A pump that creates an electrical gradient is called a(n) ___
electrogenic pump
Eukaryotic cells can transport large molecules such as proteins and polysaccharides via ___ and ___. Both of these mechanisms involve membrane vesicles or vauoles
endocytosis, exocytosis
Bacterial swimming, nerve signaling, and osmotic regulation depend on the maintenance of ___ gradients
ionic/electrochemical
What processes are used by eukaryotic cells to transport large molecules such as proteins and polysaccharides?
exycytosis, endocytosis