Chapter 8 - SPH 3U1
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Vibration
A cyclical motion of an object about an equilibrium position
Ex:
The pendulum going back and forth
Equilibrium Point
The position in which the object is in the same position as rest
Mechanical Waves
The transfer of energy through a material due to vibration.
Medium
The material that permits the transmission of energy through vibrations
Net Motion
The displacement of a particle over a certain time interval; the difference between particle’s initial and final positions
Elastic
Property of a medium that returns to its original shape after being disturbed
Translational Molecular Motion
Straight-line motion of a molecule; this motion is typical of gases because the particles in liquids and solids are not free to move in this manner
Waves in Solid Mediums
Transfers waves efficiently —> Waves go far and fast
Waves in liquids and gases
Less efficient compared to solids
Liquids > Gasses —> Waves transfer better in the water
Gasses usually only use translational movement —> Net Motion ≠ 0
Transverse Wave
A wave in which particles vibrate perpendicular to the direction of the flow of energy
Ex: A string moving up and down
Longitudinal Wave
A wave in which particles vibrate parallel to the direction of the flow of energy
Ex: A slinky
Compression
The region in a longitudinal wave in which the medium’s particles are closer together
Rarefractions
Region in a longitudinal wave in which the medium’s particles are farther apart
Sound
A form of energy produced by rapidly vibrating objects detectable by the ear
Amplitude
Maximum displacement of a wave from its equilibrium point
Waveform
Shape of a wave when graphed
Crest
Maximum point of a transverse wave
Trough
Minimum point of a transverse wave
Wavelength
Distance between 2 similar points in successive identical cycles in a wave.
Crest to Crest
Trough to Trough
Phase
A continuous transverse or longitudinal wave, the x-coordinate of a unique point of the wave
Phase shift
A shift of an entire wave along the x-axis with respect to an otherwise identical wave
In-Phase
The state of 2 identical waves that have the same shift
Out of Phase
State of 2 identical waves that have different phase shifts
Frequency (Hz)
Number of complete cycles that occur in unit time
Period
Time for a vibrating particle to complete one cycle
Formula for Frequency
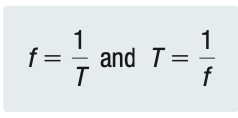
Wave Speed
Rate at which a wave is travelling through a medium
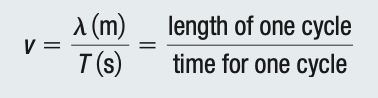
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
Any motion that repeats itself at regular intervals
Universal Wave Equation
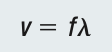
A trumpet produces a sound wave that is observed travelling at 350 m/s with a frequency of 1046.50 Hz. Calculate the wavelength of the sound wave.

Factors that Affect Wave Speed
Temperature:
Colder temperatures result in slower-moving molecules
Hotter temperatures result in faster-moving molecules
Linear Density and Tension
Linear Density is how much force is needed to make the string vibrate (kg/m)
µ = Linear Density
m = Mass
L = length
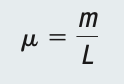
Wave Speed with Tension
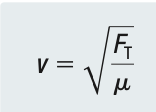
On your class wave machine, you have a string of mass 350 g and length 2.3 m. You would like to send a wave along this string at a speed of 50.0 m/s. What must the tension of the string be?

Audible Sound Waves
Sound waves within the range of human hearing: 20 Hz to 20 kHz
Infrasonic Waves
Sound waves with frequency below 20 Hz
Ultrasonic Waves
Sound waves with a frequency above 20 kHz
Speed of Sound

Mach Number

Sound Intensity
Amount of sound energy being transferred per unit of area; measured in W/m2
Decibel
The unit of sound level used to describe the sound intensity level
The difference between sound intensities of 10-12 W/m2 and 10-8 W/m2 is 10,000 units. This is equivalent to 40 dB or 4 B