OCR GATEWAY GCSE CHEMISTRY C3
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
C3
Write down the formulae of elements(M + NM) and simple covalent compounds
M= empirical forumlar bc exist as giant metallic latties
NM= same as their chemical symbol bc exist as individual atoms attracted by weka IMF
SC= symbol for each element it contains and no of atoms in each element
Table of formuale of common ions
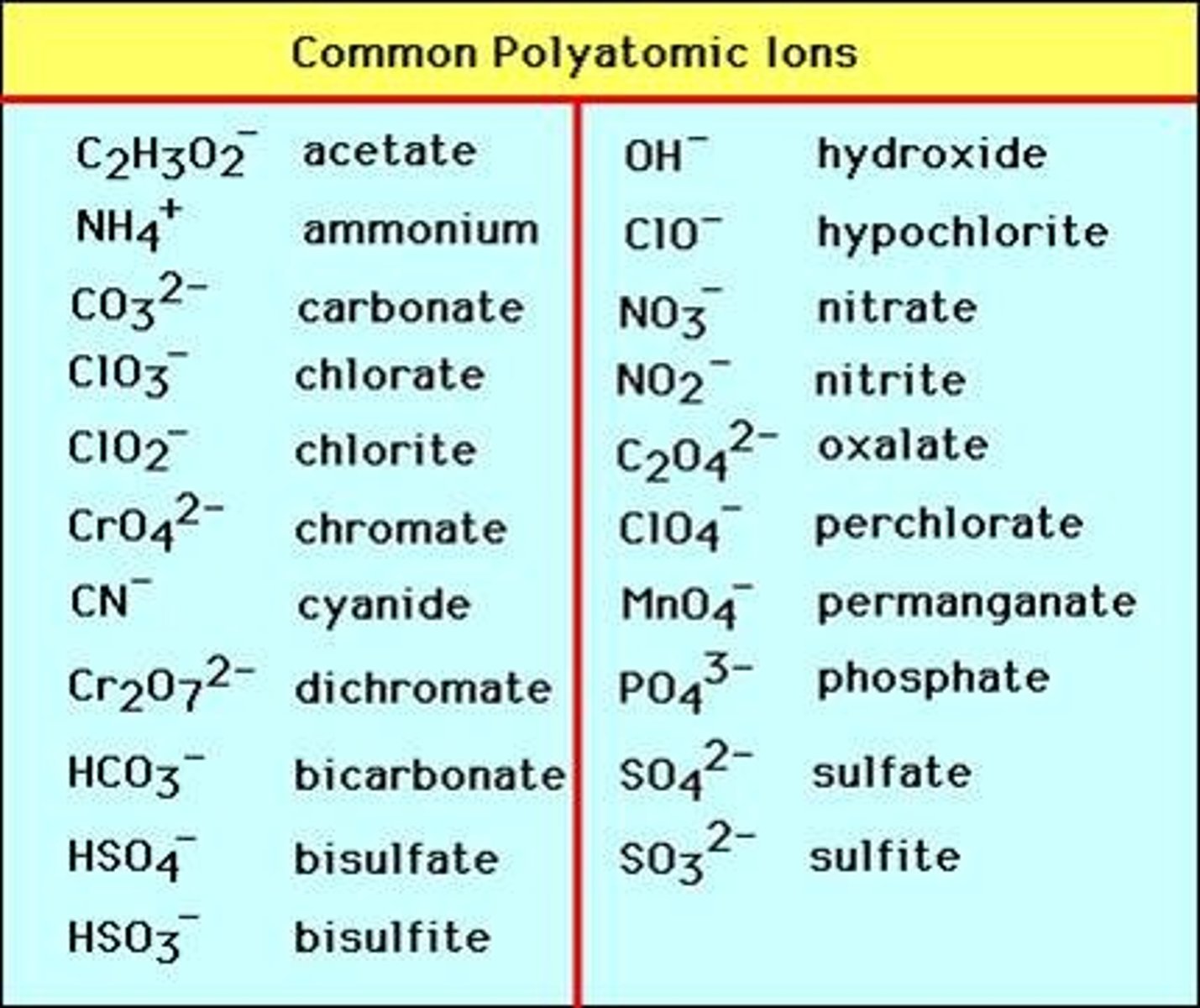
What are the formulae of common ions?
1. HYDROGEN ions have +1
2.METALS IN G.1,2,3 produce +ions where the no of charge is the same as their group no.
e.g Na+ bc its in G1
Al3+ bc its in G3
3.TRANSITION METALS(G3-12) produce 2+
except: Ag+
Fe(III)3+
4. NONMETALS IN G5,6,7 produce -ions where is no of charge is 8 - the no of group column.
e.g Cl- bc its in G7 - 8 = -1
State and use the law of conservation of mass
-atoms cannot be created or destroyed by chemical reactions
-same atoms at start and end of reaction
-only rearranged so total mass is the same
Explain mass changes in reactions using the particle model
GASES= can escape if non-enclosed system
Common compound ions
NH4+ = ammonium
OH- = hydroxide
NO3- = nitrate
CO3 2- = carbonate
SO4 2- = sulfate
Explain how to calculate masses
You know that the mass before the reaction should equal the mass after.
You may need to rearrange the equation to find what they are asking for
How to do half equations
ALL ABOUT THE CHARGES
1. Look at your given elements and work out which one becomes an ion when they LOSE electrons and when they GAIN electrons
2. To work it out look at the periodic table and notice what group they are in OR look at the product and if it has a charge then like yk
3. for gain: X+ = X + e-
for loss Y -e-= Y-
4. Loss= add on right
Gain = add on left
What are ionic equations?
1. write down the word equation for the reaction
2. write down the balance symbol equation with state symbols
3. ONLY SPLIT THE AQUEOUS COMPOUNDS INTO into their indiviual ions
4. Highlight the species which are UNCHANGED in going from reactants to products. These species are not involved in the reaction. They are called SPECTATOR IONS. A change can be a change in state.
5. The remaining species (the ones that have changed) are the ones involved in the ionic equation. Rewrite the equation showing ONLY the species involved in the reaction.
P.S if the element has a number in front to balance it, add that number infront of the split ions that make up that compound
What is a mole?
-the unit for the amount of substance
-1 mole of substance(element)= the Mr(relative formula mass)
e.g 1 mole of Co2 = 12 bc 1 carbon + 32 bc 2 oxygen
What is the Avogadro constant?
6.02 x 10 23
It is the number of entities in 1 mol
Used bc atoms are minuscule and impossible to count individually
What is the equation to work out the moles?
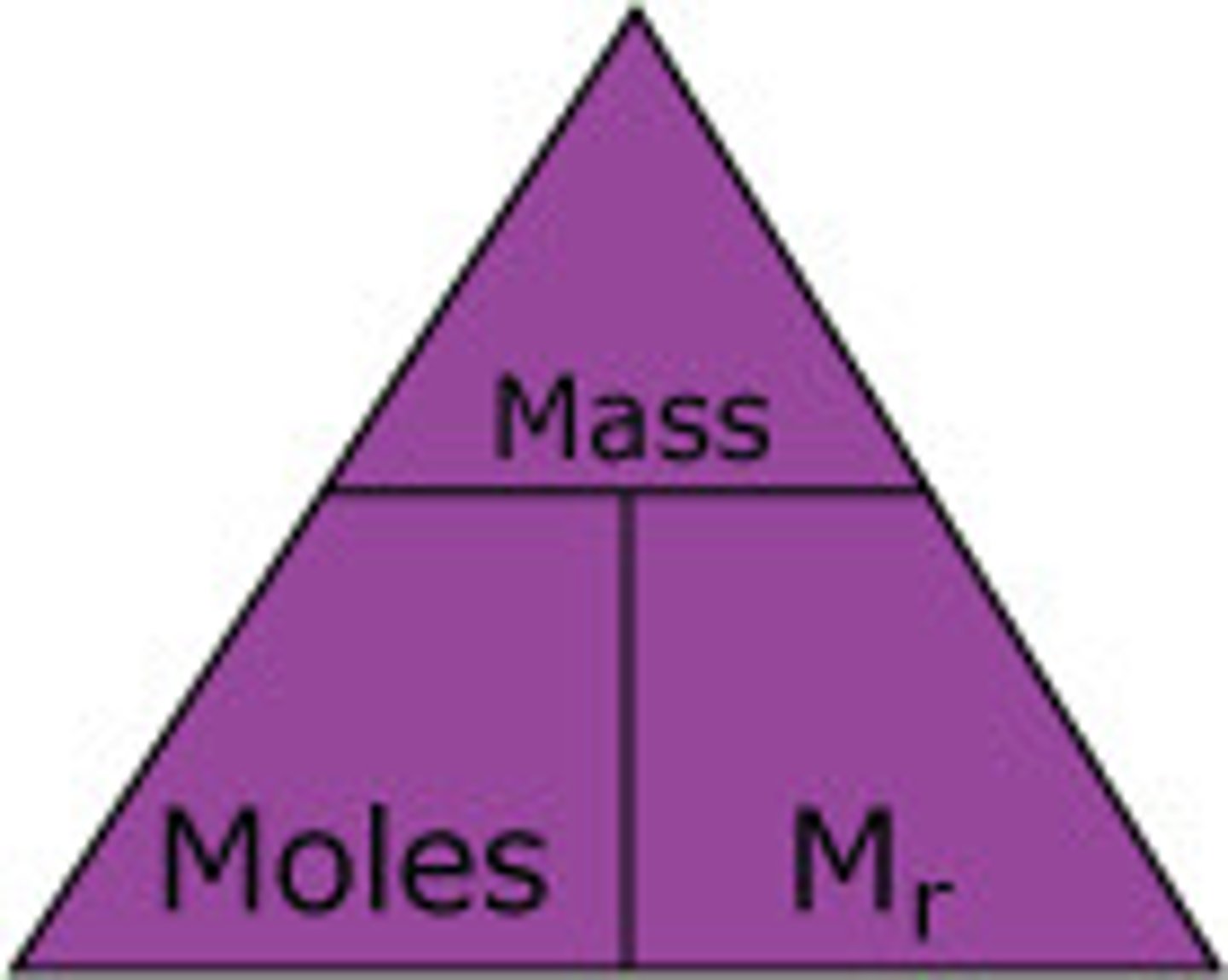
Rules for working out masses and moles?
- grams to mole=
add Mr s and divide by however many moles are asked
- moles to grams =
grams divided by Mr
-how many atoms or molecules USE=
Avogadro constant multipled by number of moles
-the element they give is irrelevant
Explain the effect of a limiting reactant
-one reactant is usually in excess in a reaction mixture
-the other reactant is in a limiting amount
-amount of product produced is determined by the amount of limiting reactant
Explain how to use moles in calculations (well not really but thats what its called)
E.G nitrogen + hydrogen = ammnonia
Calculate the mass of ammonia made from 84g of nitrogen.
NEEDED WHEN: they give u a random equation and a random mass of one of the reactants
1. X is the mass given of element cat
2. Calculate the Mr of both reactants (in the equation that contain/is element cat. the one with is cat and the other is called dog)
3. then do X/cat x dog
What is stoichiometry?
E.G copper is heated w hydrogen forming 6.4g of Cu and 0.9g of H20. calculate the balanced equation
BASICALLY ITS ANOTHER WAY OF ACCURATELY BALANCING AN EQUATION; when u calculate the amounts of each substance involved in a chemical reaction
1. Using the mole equation work out the moles of each substance
2. Place the reactant and product in a ratio
3. Apply ratio to equation
What is an exothermic reaction?
It is when energy taken in to break bonds is LESS than the energy given out when new bonds are made which is often released as heat energy. Reactants have MORE ENERGY. Temperatureof the reaction mixture INCREASES. Symbol is - ∆T since energy is transferred FROM chemicals. FOr example combustion or neutralisation
What is an endothermic reaction?
It is when energy taken in to break bonds is MORE than the energy given outwhen new bonds are made. Reactants have LESS ENERGY. Temperature of the reaction mixture DECREASES. Symbol is + ∆T since energy is transferred TO chemicals. FOr example photosynthesis.
How can you make the experiment accurate and fair?
Use the same amount and concentration. Same starting temperature and weigh the amount. Also add lid prevent heat escaping quicker.
What is a reaction profile?
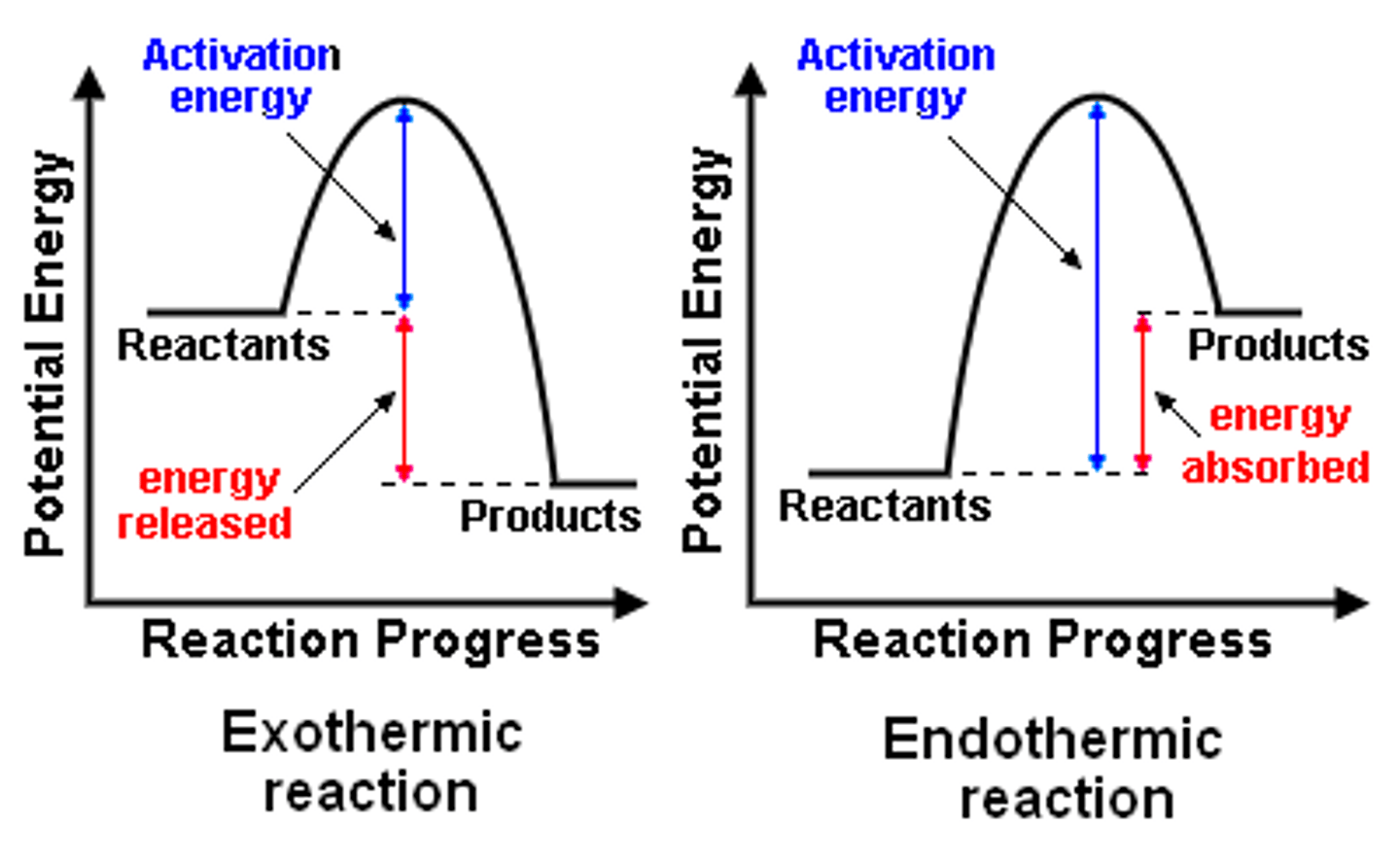
What is activation energy?
The amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction. A catalyst can lower it.
What is the equation used to work out energy change?
Q=MC∆T. energy(j) = mass of substance x specific heat capacity x change in temp('C) should always be positive
What is bond energy?
energy required to break a bond between two atoms. It is also the energy given out when a bond is made
How to Work out Bond Energies.
1. Write the balanced equation
2. Count all the bonds on both sides and assign the values.
3. Subtract left to right
4. If the result is positive + ∆T the reaction is ENDOTHERMIC
If the result is negative - ∆T the reaction is EXOTHERMIC
What is a redox reaction?
The transfer of one or more electrons from one reactant to another. A reaction in which both reduction and oxidation are taking place.
What is reduction?
Gain of electrons/ loss of oxygen
What is oxidation?
Loss of electrons. The gain of oxygen
How to do Redox equations
If it's oxidation, electrons are added on the right hand side. If it's reduction, electrons are added on the left hand side
How to tell which one is the oxidating and reduction agent?
ITS ACC STUPIDLY SIMPLE
u literally just look at the equation and see which one gained oxygen and which one lost
What are acids and alkali?
Acids always release H+ ions and are below pH 7. Red on the scale. Alkali always release OH- ions and are above pH 7. Purple on the scale. Alkali are a soluble base meaning they accept protons. Ions are always (aq).
Describe how to measure pH
universal indicator
pH meter:
1. Wash prode w water then put in calibration buffer
2. Adjust rewading to match pH of buffer solution
How do you predict the salt made during neutralisation and what happens
1. First part comes from metal in the base/alkali
2. The 2nd part of the name comes from the acid
What happens during neutralisation with aqueous solutions?
H+ (aq) + OH- = H2O (l)
- produced salt depends on other ions
What are the 4 rules for acid reactions?
ACID + ALKALI = SALT + H2O
ACID +METAL = SALT + H2
ACID + METAL OXIDE =SALT + H2O
ACID +CARBONATE (CO3) = SALT + CO2 + H2O
What are dilute and concentrated acids?
D: Contain a low ratio of acid to volume of solution
C:Contain a high ratio of acid to volume of solution. A acid is more acidic when concentrated.
What are weak acids?
Partially dissociated/ionised. Meaning reaction is not complete. (like only a lil bit of the reactant actually reacts)
Only a small fraction of the molecules release H+ ions
What are strong acids?
100% dissociation/fully ionised
Reaction is complete.
All of their molecules release H+ ions
How is pH linked to hydrogen ion concentration?
-acid has lower pH when its con than dilute
-strong acid has lower pH than weak acid at same con
What is electrolysis?
The breaking down of a substance into its ions using electricity.
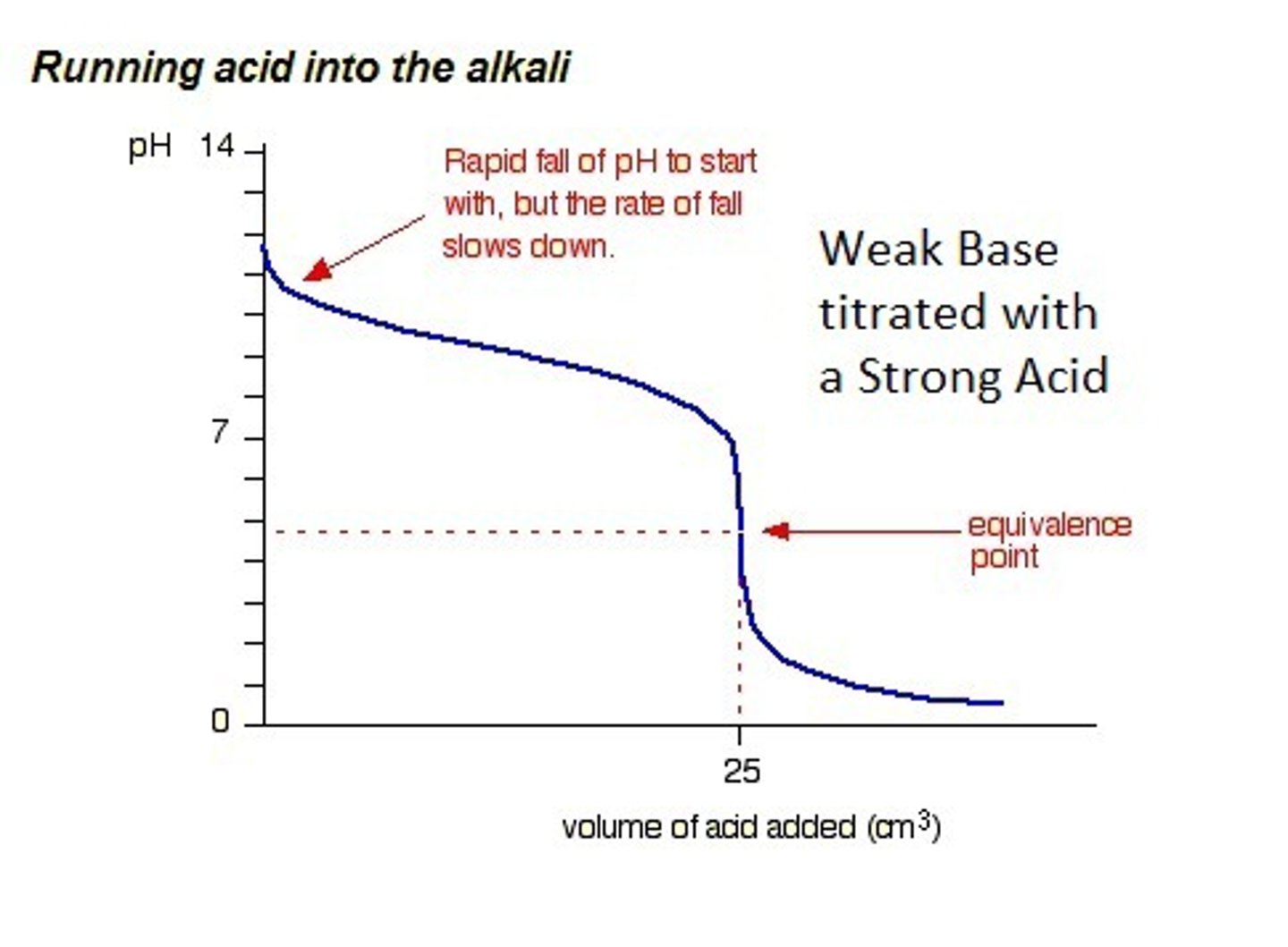
What is a titration curve?
The straight line is how much acid is needed to neutralise and the middle of that line is the neutralisation point
effect on pH of changing the H+ concentration
What is needed for electrolysis?
A electrolyte = compound in liquid state/in solution containing mobile ions and conducts electricity
2 electrodes = made from metal/graphite and can conduct electricity to the electrolyte
Electrical supply =power pack/battery
What are the electrodes?
1 negative (cathode)
1 positive (anode)
What happens at the electrodes during electrolysis?
Cations (positive ions) gain electrons at the cathode and become atoms
Anions (negative ions) lose electrons at the anode and become atoms. The ions are now discharged. If atoms formed are nonmetal covalent bonds may form.
ONCE EITHER OF THESE PROCESSES FINISH, THE IONS HAVE BEEN DISCHARGED
Why can't ionic compounds conduct electricity when in the solid state?
Compounds need heat/water to break fixed bonds and create delocalised electrons
What will happen at the anode (+)
NONMETALS ARE FORMED
If the anion is a halogen, you will see the halogen.
If the anion is SO4, NO3, PO4, CO3 you will see O2
What will happen at the cathode (-)
METALS/HYDROGEN
If the cation is Cu, Ag, Au, Pt you will see the metal
If the cation is any other metal you will see the metal
How do you predict the products of electrolysis of binary ionic compound in the molten state?
BIC means it contains just 2 elements
You can model what happens at the electrodes using half equations