resting membrane potential google form
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
the movement of materials from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration as a result of their kinetic energy.
diffusion
an atom or small molecule with a positive or negative electric charge.
ion
the difference in the concentration of a particular substance between two adjacent areas.
concentration gradient
uneven distribution of electrical charge, especially across a membrane.
electrical gradient
a transmembrane protein that forms an aqueous pore, allowing substances to move from one side of the membrane to the other.
channels
a primary active transporter that simultaneously drives Na+ out of the cell against a steep gradient and pumps K+ back in, also against a steep gradient; also called the Na+-K+ ATPase.
sodium-potassium pump
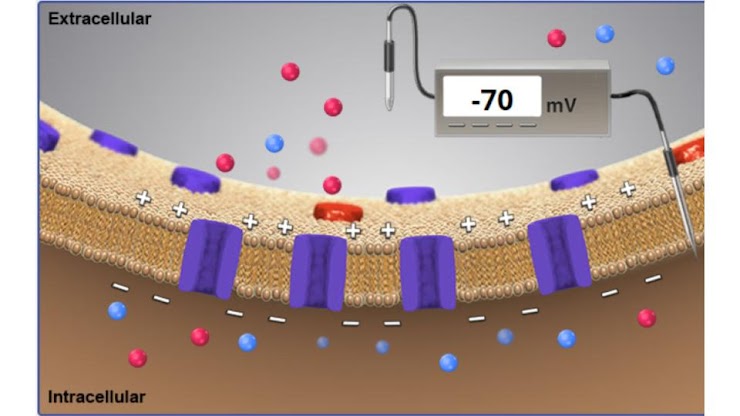
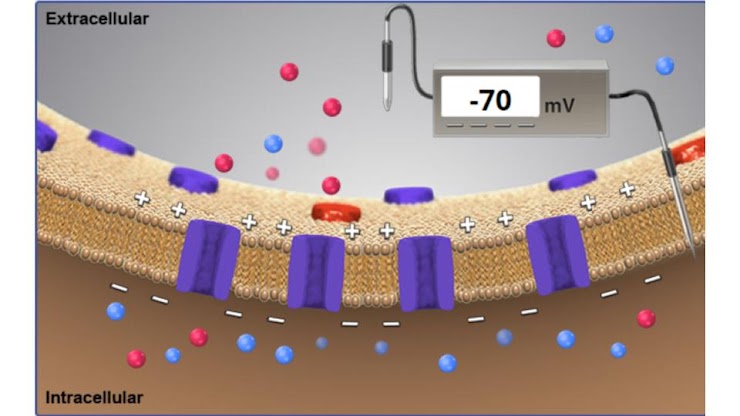
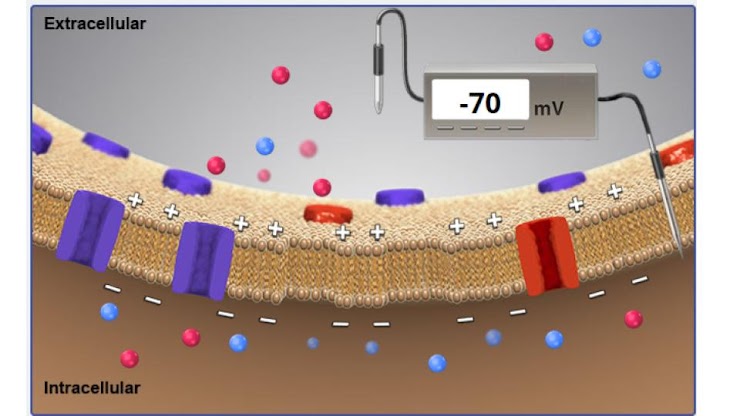
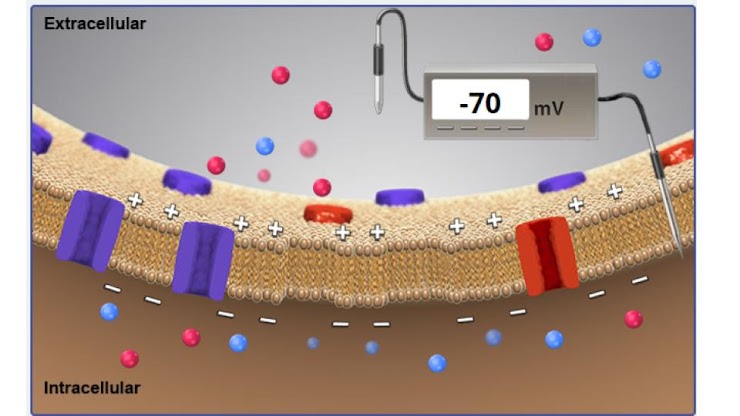
the voltmeter is recording a membrane potential of -70 mV. is this neuron at rest?
yes!
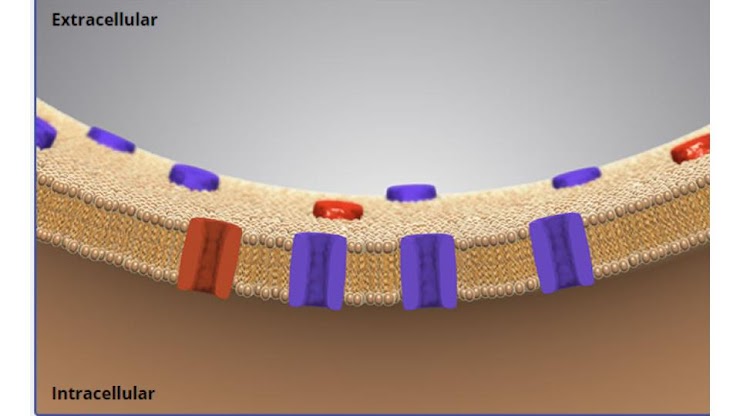
what area has a higher concentration of sodium ions?
extracellular
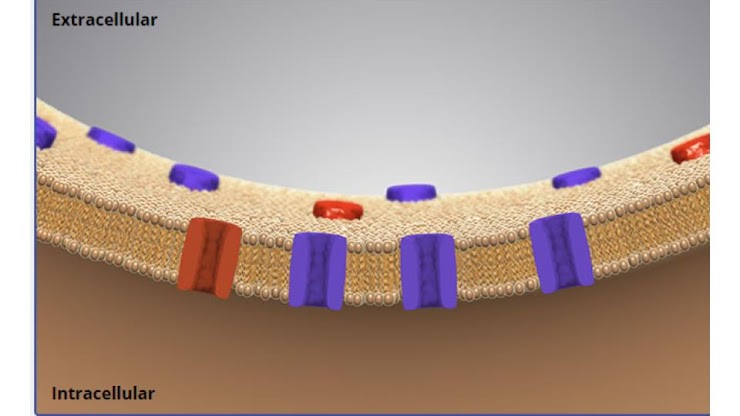
which area has a higher concentration of potassium ions?
intracellular
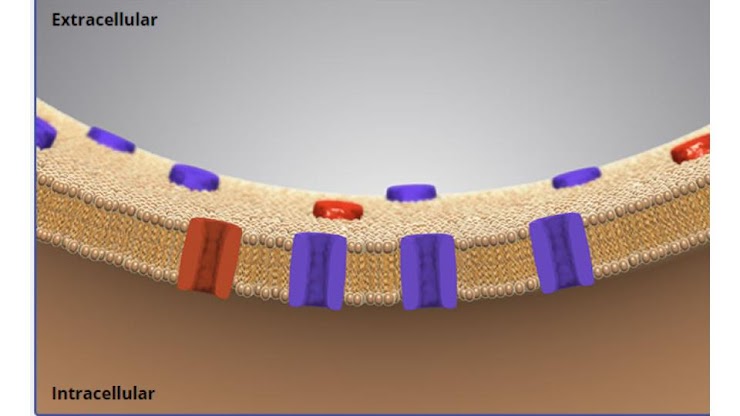
which area has a higher concentration of Chloride ions?
extracellular
which area has a higher concentration of protein ions?
intracellular
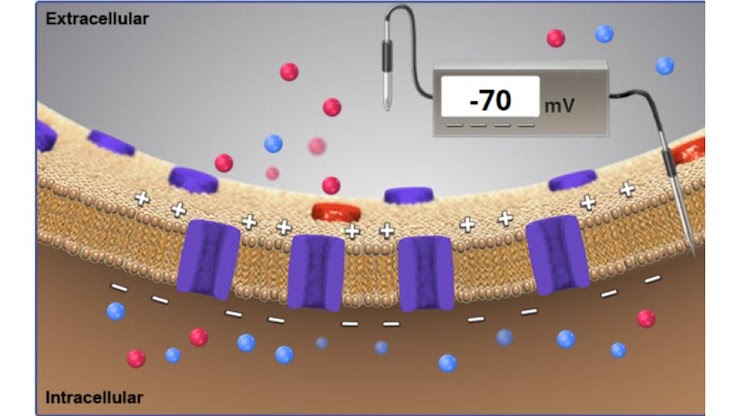
if the concentration of K+ in the extracellular fluid were increased
K+ diffusion out of the cell would decrease
The membrane potential would become less negative
if the concentration of K+ in the extracellular fluid were decreased
the membrane potential would become more negative
K+ diffusion out of the cell would increase
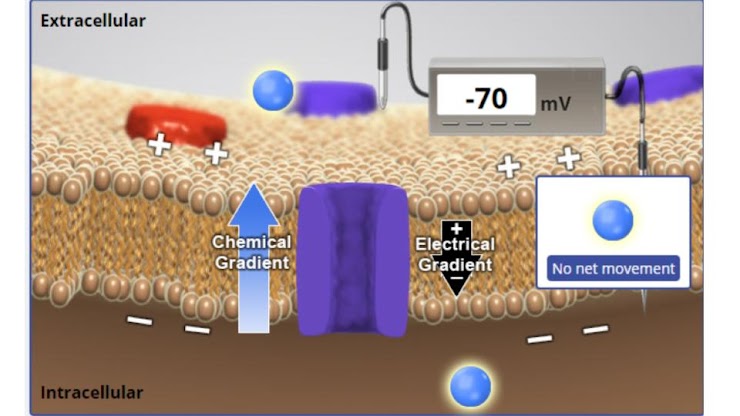
at –70 mV consider the net effect of the chemical and electrical gradients. will more K+ flow into or out of the cell or will there be no net movement?
K will flow out of the cell
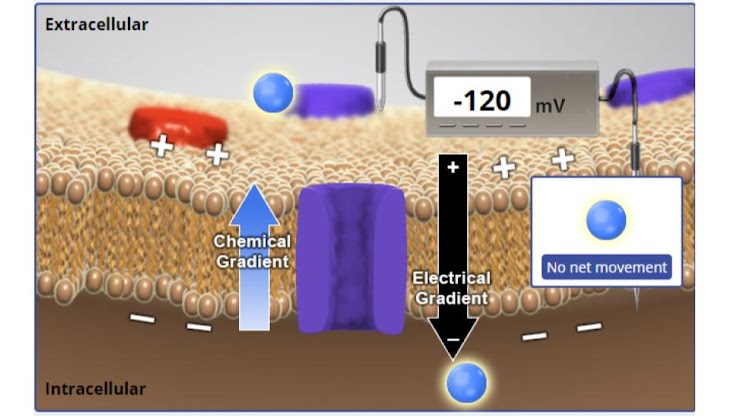
at –120 mV consider the net effect of the chemical and electrical gradients. will more K+ flow into or out of the cell or will there be no net movement?
K will flow into the cell
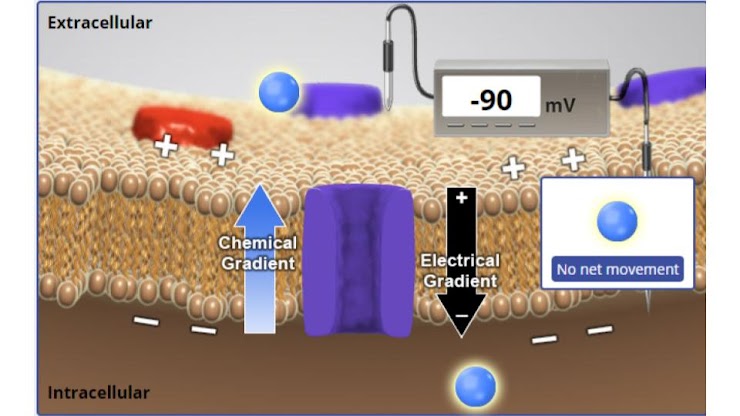
at –90 mV consider the net effect of the chemical and electrical gradients. will more K+ flow into or out of the cell or will there be no net movement?
there will be no net movement
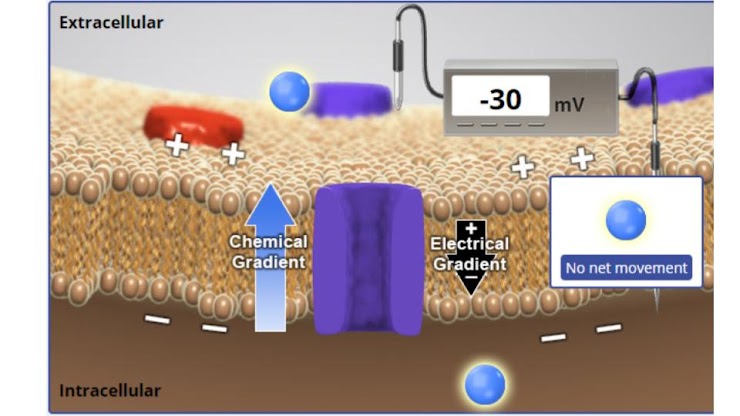
at –30 mV consider the net effect of the chemical and electrical gradients. will more K+ flow into or out of the cell or will there be no net movement?
K will flow out of the cell
what would happen if the membrane became more permeable to K+?
net movement of K+ would be out of the cell
The membrane potential would become more negative
what would happen if the membrane became more permeable to Na+?
net movement of Na+ would be into the cell
the membrane potential would become less negative.
at rest, a neuron’s plasma membrane is most permeable to which of the following ions?
potassium (K+)
which cation is most concentrated inside the cell?
potassium (K+)
how is the membrane potential of a neuron is measured.
use a voltmeter with two electrodes, one placed in the extracellular fluid and the other placed in the intracellular fluid.
what would increase a neuron’s membrane permeability to (K+)?
increasing the number of K+ leak channels
a K+ deficiency reduces extracellular K+ concentration from 4 mM to 2 mM. as a result, a neuron’s resting membrane potential will __________.
become more negative
which of the following factors is important in creating a resting membrane potential of –70 mV?
different permeabilities of the membrane to Na+ and K+ ions
in order to ensure that Na+ concentration remains high outside a neuron, and that K+ concentration remains high inside, the neuron depends on the activity of the _______________.
Na+/K+ pump
when the electrical charge of an ion as well as its concentration gradient favor movement of that ion into the cell, the ion is said to move down its ________ gradient.
electrochemical