Biology Unit 7- Mitosis and Meiosis
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
cells grow, develop, and divide
mitosis
cells reproduce
meiosis
MITOSIS:
3 phases of interphase
G1, S, G2
What type of cells never grow and divide?
nerve cells
term meaning when cells come into contact they stop diving
density-dependent inhibition
term meaning that cells must be in contact with a solid surface to divide
anchorage dependence
90% of the cell cycle is in what phase of mitosis?
interphase
MITOSIS OR MEIOSIS:
genetic goal is cloning
mitosis
MITOSIS OR MEIOSIS:
genetic goal is variation among species
meiosis
WHICH CHECKPOINT IN THE CELL CYCLE?
DNA has been completely replicated and checked for errors
G2
WHICH CHECKPOINT IN THE CELL CYCLE?
There is enough cellular material to accommodate two cells.
G2
WHICH CHECKPOINT IN THE CELL CYCLE?
All chromosomes are attached to the spindles.
M
WHICH CHECKPOINT IN THE CELL CYCLE?
There is adequate room in the environment for more cells
G1
WHICH CHECKPOINT IN THE CELL CYCLE?
There are enough resources in the environment for more cells.
G1
Which checkpoint appears to regulate whether a cell is in G0 or not?
G1
MEIOSIS: IN WHICH PHASE…..
does crossing over occur
prophase I
MEIOSIS: IN WHICH PHASE…..
are chromosomes visible under a microscope
prophase
What is the midway location called?
metaphase plate
What do spindle microtubules attach to on the chromosomes?
kinetochore
As homologous chromosomes begin to move are sister chromatids still attached in meiosis I?
yes
MEIOSIS: IN WHICH PHASE…..
does the cell go from being diploid to haploid
telophase I
The end result of a single diploid cell going through meiosis (meiosis I and II) is ___(#) ______(word) daughter cells.
4 haploid
In which stage of meiosis does independent arrangement occur?
metaphase I
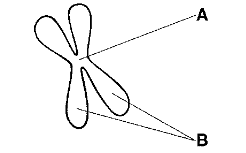
The structure labeled A in the figure above is called the
centromere
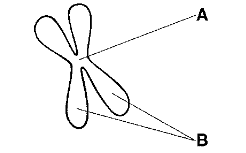
The structures labeled B in the figure above is called the
sister chromatids
During which phase(s) of mitosis is the “X-like” structure above visible under a light microscope?
A. Prophase and metaphase
B. Anaphase and prophase
C. Anaphase and interphase
D. Interphase
A
Which option correctly pairs the stage with what happens during that stage?
A. G1, DNA replication
B. G2, preparation for mitosis
C. S phase, cell separation
D. M phase, massive cell growth
B
Eukaryotic chromosomes differ from prokaryotic chromosomes in that they
A. Are housed in a membrane-enclosed nucleus
B. Are simpler
C. Are circular in structure
D. Do not condense during cell division
A
A bacteria cell is derived from another bacteria cell by which process?
A. meiosis
B. replication
C. cytokinesis alone
D. binary fission
D
Mitosis
A. Can increase the number of body cells without changing the genetic information
B. Is a means of reproducing cells sexually
C. Results in new daughter cells that are genetically different from each other.
D. Never occurs after a cell goes through meiosis and fertilization
A
DNA replication occurs
A. during the S phase of the cell cycle
B. as the nuclear envelope breaks down in early mitosis
C. during mitosis but not during meiosis
D. in animal cells but not in plant cells
A
Why do chromosomes coil during mitosis?
A. to increase their potential energy
B. to allow the chromosomes to move without becoming entangled and breaking
C. to allow the sister chromatids to remain attached
D. to provide for the structure of the centromere
B
Which of the following features likely accounts for the difference between plant and animal cell cytokinesis?
A. Animal cells lack the microfilaments required for forming a cleavage furrow.
B. Animal cells lack chloroplasts.
C. Plant cell division must maintain the integrity of the cell wall.
D.The difference between plant and animal cell cytokinesis are too trivial to distinguish between.
C
If mammalian cells receive a go-ahead signal at the G1 checkpoint, they will
A. move directly into telophase.
B. complete the cycle and divide or die trying.
C. exit the cycle and switch to a nondividing state.
D. complete cytokinesis and form new cell walls.
B
Which of the following must occur for a plant or animal to grow and develop normally?
A.The organism must receive a supply of the appropriate hormones from its parents.
B. The organism must be able to control the timing and rate of cell division.
C. Dividing cells must be freed from all attachment sites.
D. All cells in the organism must be able to divide.
B
You are asked to grow an unidentified sample of animal tissue. You notice that the cells do not follow the rules of density-dependent inhibition. The source of this tissue sample is most likely
A. A scar
B. A cancer
C. The sperm-producing tissue of the testis.
D. A plant
B
Microtubules are the target of many chemotherapy agents because they _____.
A. Fail to function in cancer cells
B. Are required for DNA replication to occur
C. Are specific to cancer cells, leading to limited side effects
D. Allow a cell's chromosomes to divide during cell division
D
All of the following are current treatments for cancer except?
A. radiation
B. chemotherapy
C. antibiotics
D. surgery
C
How do the daughter cells at the end of mitosis and cytokinesis compare with the parent cell when it was in G1 of the cell cycle?
A. The daughter cells have half the number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA.
B. The daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA.
C. The daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes and the same amount of DNA.
D. The daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes and twice the amount of DNA.
C
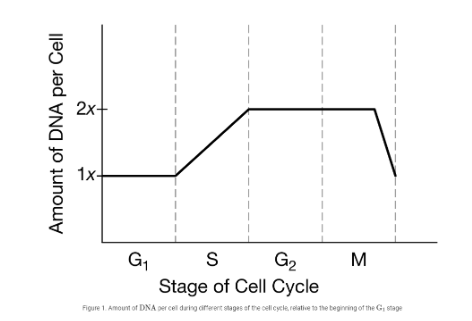
Referring to the graph above, which of the following best describes how the amount of DNA in the cell changes during M phase?
A. The amount of DNA does not change while the cell grows.
B. The amount of DNA is halved as the cell divides into two daughter cells.
C. The amount of DNA doubles as the DNA is replicated.
D. The amount of DNA slightly increases as a result of new organelle synthesis.
B
Two chromosomes in a nucleus that carry loci for the same traits in the same positions on the chromosome but specify different versions (or alleles) of some traits constitute a pair of
A. Homologous chromosomes
B. Heterologous chromosomes
C. Sister chromosomes
D. Sister chromatids
A
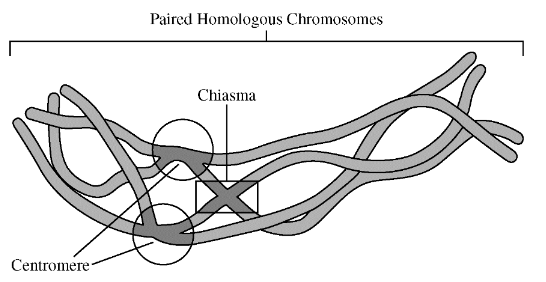
The process depicted in the image above is best summarized by which of the following descriptions?
A. During the synthesis phase of the cell cycle, DNA molecules replicate to generate identical daughter cells.
B. Centromeres align specific gene sequences of homologous chromosomes during mitotic divisions.
C. The spindle apparatus attaches at chiasma during metaphase of mitosis.
D. During meiosis, crossing over leads to recombination of alleles between homologous chromosomes.
D
Which of the following statements regarding mitosis and meiosis is false?
A. Mitosis provides for growth and tissue repair.
B. Meiosis provides for asexual reproduction.
C. In mitosis, the chromosomes replicate only once in the preceding interphase.
D. In meiosis, the chromosomes replicate only once in the preceding interphase.
B
Which of the statements below correctly describes the relationship between the cells at the end of meiosis I and the original cell in G1?
A. The new cells have one copy of all of the genetic information in the original cell.
B. The new cells have two copies of all of the genetic information in the original cell.
C. The new cells have one copy of half of the genetic information in the original cell.
D. The new cells have two copies of half of the genetic information in the original cell.
D
Which of the statements below correctly describes the relationship between the cells at the end of meiosis II and the original cell in G1?
A. The new cells have one copy of all of the genetic information in the original cell.
B. The new cells have two copies of all of the genetic information in the original cell.
C. The new cells have one copy of half of the genetic information in the original cell.
D. The new cells have two copies of half of the genetic information in the original cell.
C
The diploid number of an earthworm is 36. What is the haploid number?
18
When a chromosome is broken in two places and reconnected so that a region is flipped from the normal order, it’s called
A. Inversion
B. Duplication
C. Deletion
D. Translocation
A
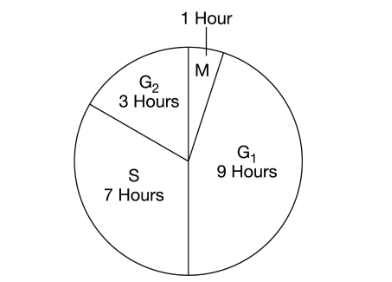
Based on the figure above, what percent of the time required to complete a full cycle do the cells typically spend in interphase?
A. 5%
B. 35%
C. 50%
D. 95%
D
Which cell cycle checkpoint would be involved with making sure that the chromosomes properly line up prior to being pulled apart?
M checkpoint
Which cell cycle checkpoint would be involved with contact inhibition?
G1
Which cell cycle checkpoint would be involved with responding to a growth factor in the cell’s environment?
G0
Microtubules begin to emerge from centrosomes, forming the spindle; chromosomes coil and become compact; nucleoli disappear.
A) Metaphase
B) Interphase
C) Anaphase
D) Telophase
E) Prophase
AB) Cytokinesis
E
Sister chromatids split and kinetochore spindle fibers shorten causing chromatids to move to opposite poles of the cell.
A) Metaphase
B) Interphase
C) Anaphase
D) Telophase
E) Prophase
AB) Cytokinesis
C
Cytoplasmic content doubles; two centrosomes form; chromosomes duplicate.
A) Metaphase
B) Interphase
C) Anaphase
D) Telophase
E) Prophase
AB) Cytokinesis
B
Nuclear envelope reforms; chromosomes begin to uncoil; nucleoli reappear; the spindle disappears.
A) Metaphase
B) Interphase
C) Anaphase
D) Telophase
E) Prophase
AB) Cytokinesis
D
Homologous chromosomes move to opposite sides of the cell.
A) Metaphase I
B) Prophase I
C) Anaphase I
D) Metaphase II
E) Anaphase II
AB) Prophase II
C
Sister chromatids line up at the center of the cell.
A) Metaphase I
B) Prophase I
C) Anaphase I
D) Metaphase II
E) Anaphase II
AB) Prophase II
D
PROKARYOTE, EUKARYOTE, OR BOTH:
located in nucleus
eukaryote
PROKARYOTE, EUKARYOTE, OR BOTH:
single chromosome
prokaryote
PROKARYOTE, EUKARYOTE, OR BOTH:
multiple chromosomes
eukaryote
PROKARYOTE, EUKARYOTE, OR BOTH:
circular chromosomes
prokaryote
PROKARYOTE, EUKARYOTE, OR BOTH:
linear chromosomes
eukaryote
PROKARYOTE, EUKARYOTE, OR BOTH:
has genes that code for proteins
both
PROKARYOTE, EUKARYOTE, OR BOTH:
double stranded alpha helix structure
both
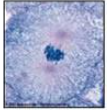
Which phase of mitosis is depicted?
prometaphase
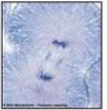
Which phase of mitosis is depicted?
telophase

Which phase of mitosis is depicted?
metaphase
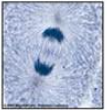
Which phase of mitosis is depicted?
anaphase
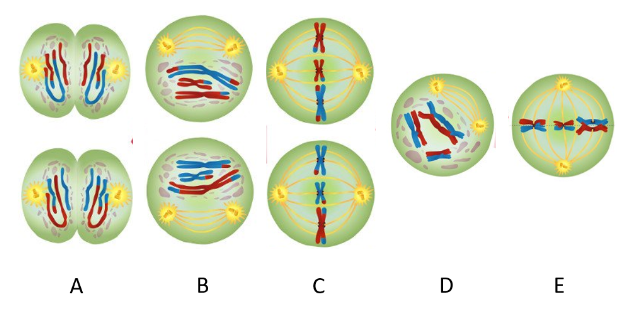
Which phase represents Prophase I?
D
In Prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair up, forming structures called _______
tetrads
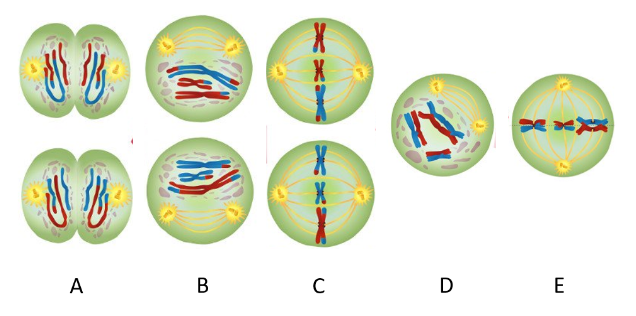
What is the haploid number (n) for this species? n=?
n=3
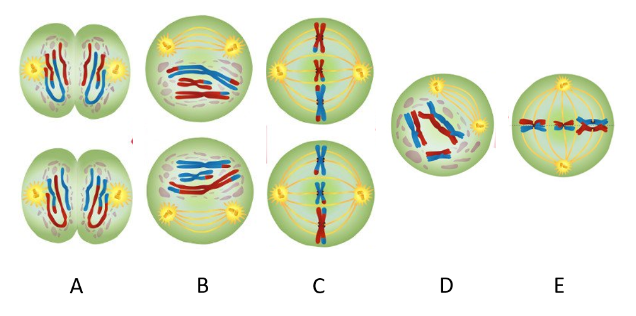
Which picture represents metaphase I?
E
In metaphase I, _______ align on the metaphase plate.
tetrads
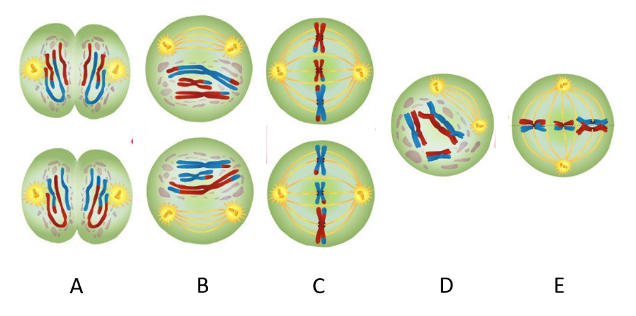
Which picture represents end of Meiosis I?
B
______(#) ____________(referring to chromosome number) daughter cells have been produced
3, 1n
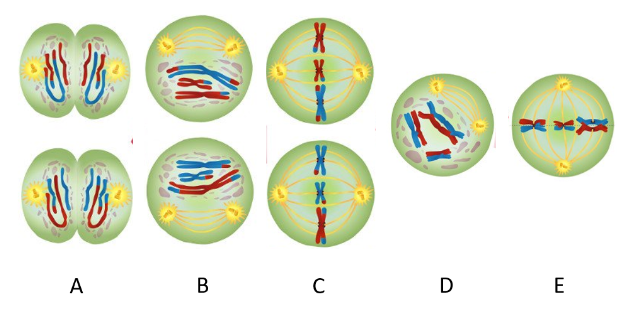
Which picture depicts metaphse II?
C
In metaphase II, ______________ align on the metaphase plate.
sister chromatids
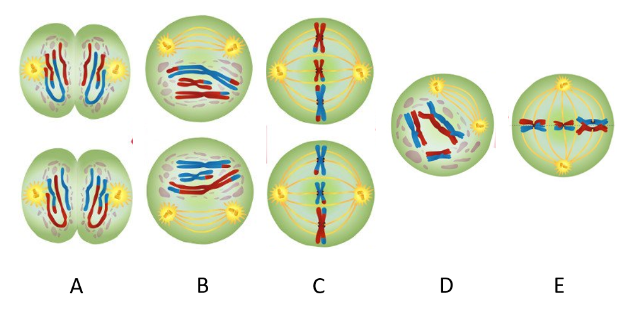
Which picture depicts end of meiosis II?
A
Most sexual reproducing organisms live in a 2n state. How do these 1n cells go back to being 2n?
random fertilization