*MCAT Concept 7A: Individual Influences on Behavior
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
6 Theories of Personality (describe each in 2 words)
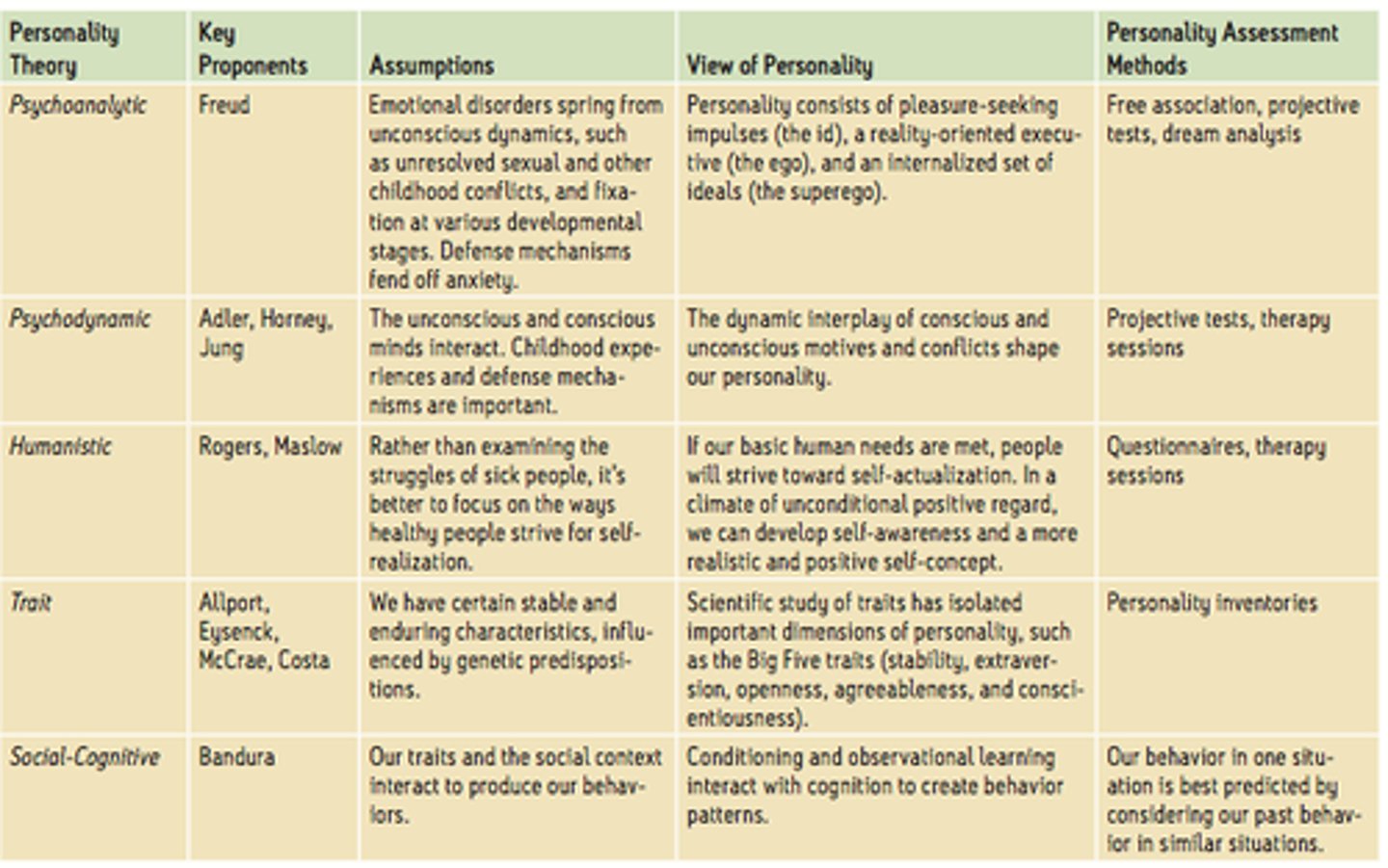
1. Psychoanalytic perspective: unconscious thoughts
2. Humanistic perspective: free will
3. Trait perspective: trait mixture
4. Social cognitive perspective: reciprocal interactions
5. Biological perspective: genes & neurotransmitters
6. Behaviorist perspective: environmental learning
6 Types of Personality Disorders
1. Anxiety disorders
2. Mood disorders
3. Somatoform disorders
4. Schizophrenia
5. Dissociative disorder
6. Personality disorders

"Personality"
a person's individual way of thinking, feeling, and behaviors
Psychoanalytic Theory
personality is shaped by unconscious thoughts, feelings, and memories
conscious thought is quite limited - unconscious is inferred from behaviors like dreams & slips of the tongue
associated with Sigmund Freud
[Freud] Libido & Death instinct
(2 instincts described by Freud - psychoanalytic theory)
Libido =life instinct - drives behavior based on survival, growth, pain avoidance & pleasure
Death instinct drives aggressive behavior fueled by unconscious wish to die or to hurt onself or others
Freud's 3 Personality Components: Id, Ego, Superego
source of energy & instincts (unconscious)
- ruled by "pleasure principle"
- seeks pleasure, avoids pain & reduces tension
- doesn't use logical/moral reasoning
- doesn't distinguish mental images from external objects
(1 of 3 personality components functioning together that compose psychic energy - Freud's psychoanalytic theory)

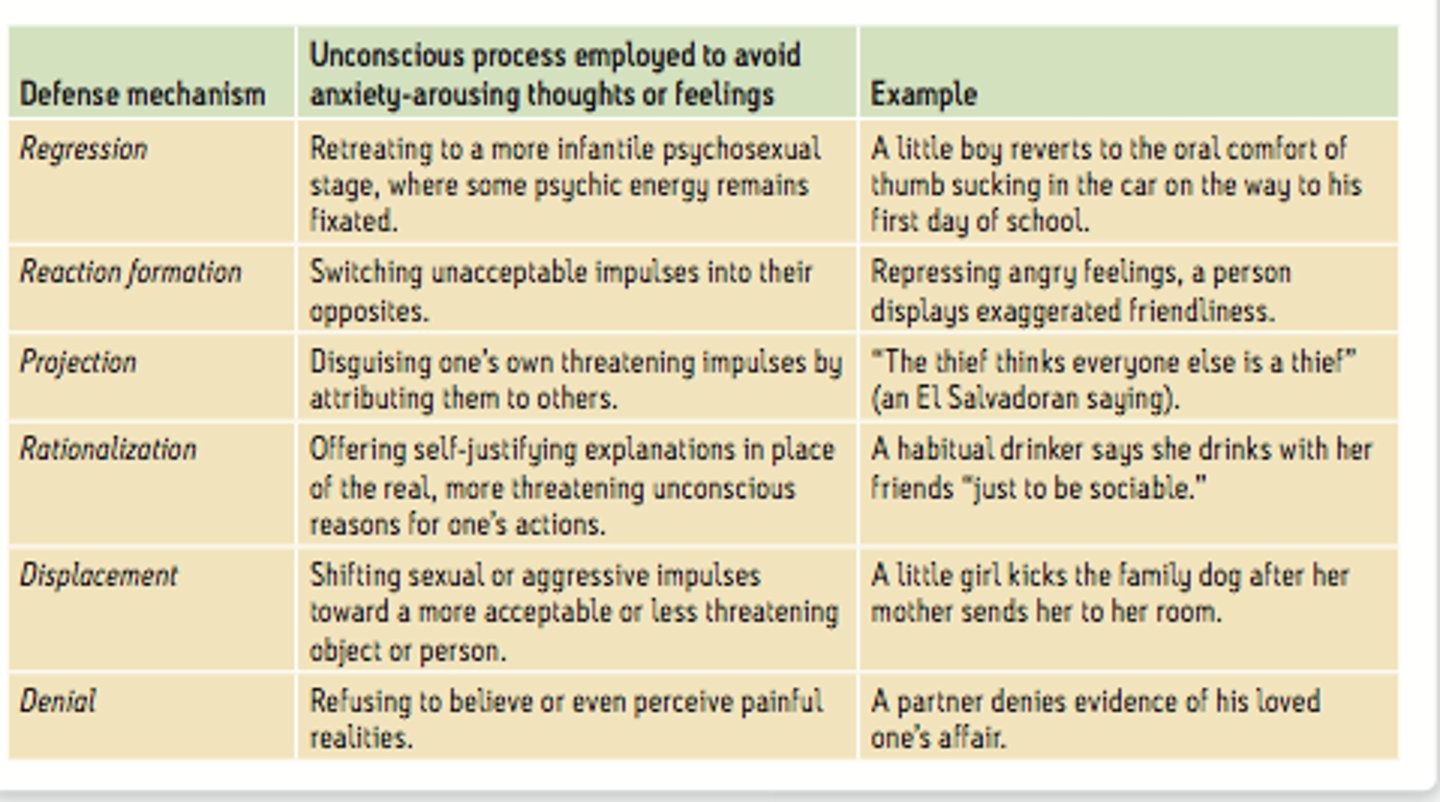
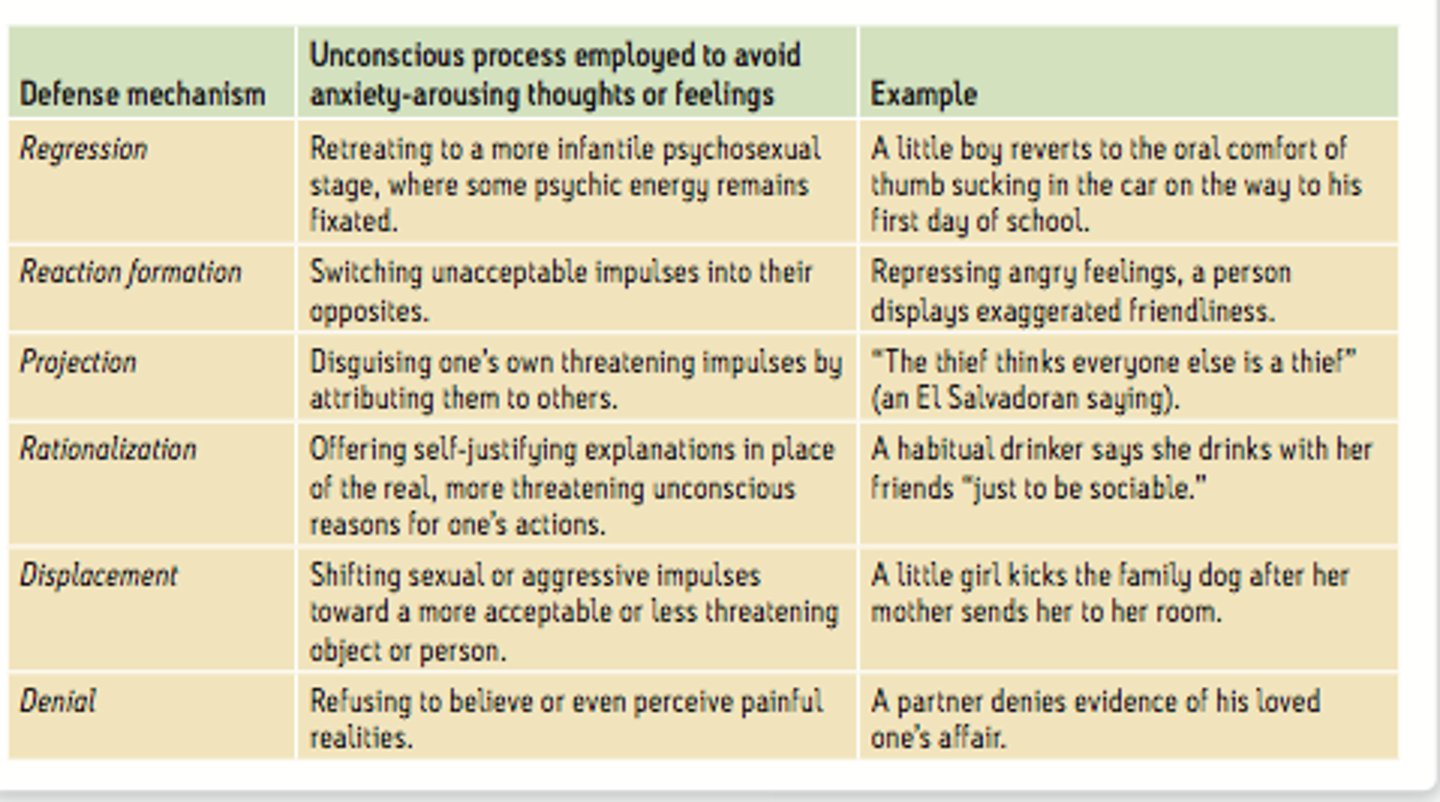
Ego defense mechanisms
anxiety coping mechanisms that protect the ego by unconsciously denying/distorting reality
(i.e. repression, denial, projection, rationalization)
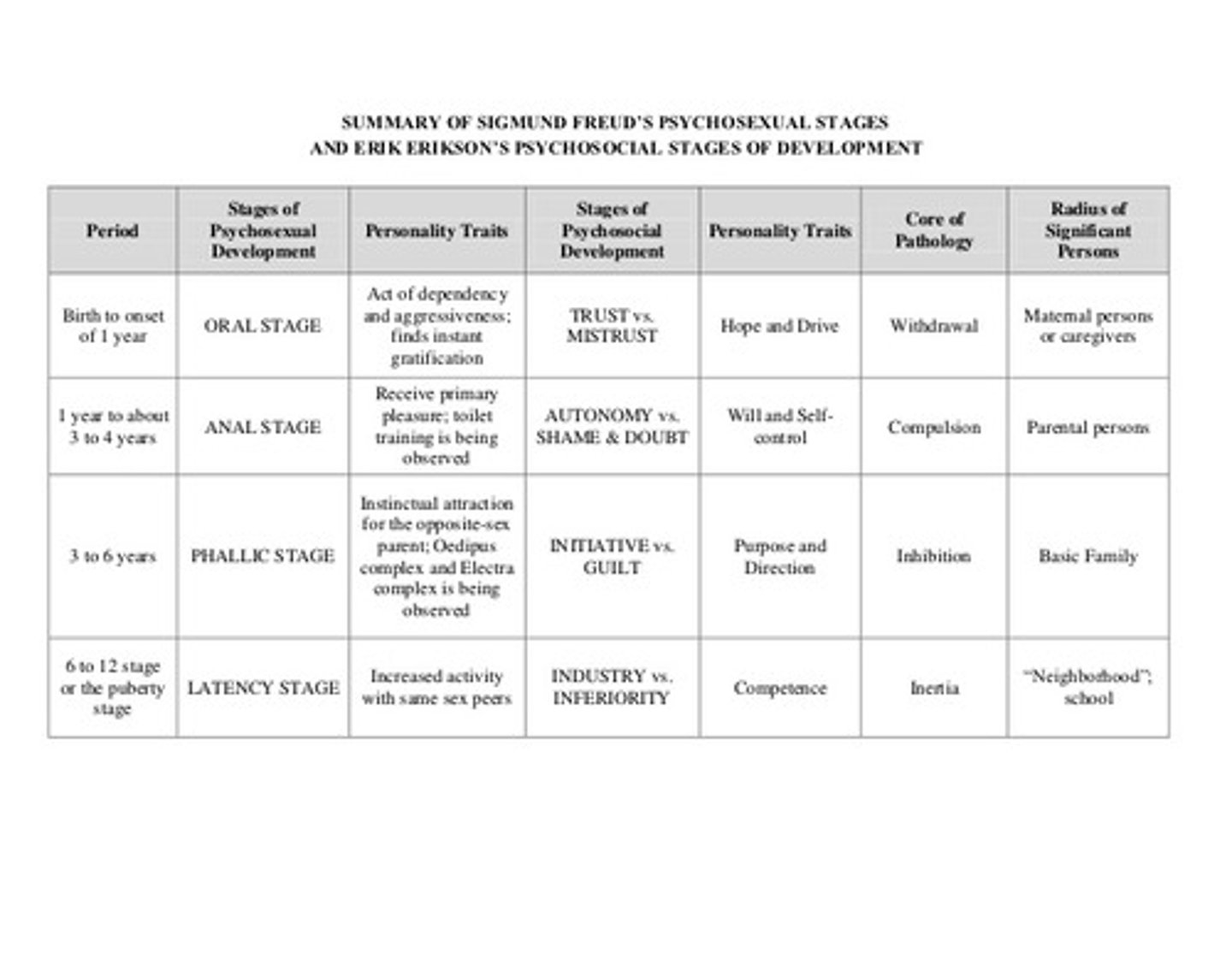
Freud's 5 Psychosexual Stages
Child seeks sensual pleasure
1. Oral stage - sucking/chewing
2. Anal stage - control of elimination
3. Phallic stage - genitals
4. Latent stage - sexual interests subside
5. Genital stage - sexual themes resurface/fuel activities

Psychological fixation (Freud)
sensual pleasure at certain psychosexual stage of development causes adult personality to exhibit behaviors related to that stage of developmental conflict
Freud vs. His Followers: Developmental Stages
Jung/Horney/Adler/Erikson
- had more optimistic views of humanity
- personality more changeable over lifespan (less dependent on early childhood)
- people motivated/influenced by growth instinct, striving for superiority, or social factors (as opposed to sensual urges)
Erikson vs. Freud - Developmental Stages
Erikson extended Freud's developmental stages
1. Added social/interpersonal factors
2. Delineated 8 developmental stages/conflicts in adolescence & adulthood
Psychoanalytic Therapy
focuses on making patient aware of unconscious motives & gaining insight into emotional issues/conflicts that are presenting difficulties
- help choose conscious behaviors
- strengthen ego
Humanistic Theory
humans are inherently good & have free will
focuses on healthy personality development
associated with Carl Rogers
Behaviorist Theory
personality is learned behavior patterns based on person's environment (deterministic)
(people begin as blank slates and are punished/reinforced into behaviors/personalities)
Humanistic therapy
provides environment that helps clients trust/accept themselves and their emotional reactions so that they can learn and grow from experiences
[Humanistic perspective]
Behavioral therapy
uses conditioning to shape clients behaviors in desired direction using ABC model (antecedents and consequences of behavior) - therapy changes antecedents and consequences using least aversive means possible
common applications: densensitization
[Behaviorist perspective]
Social Cognitive Perspective
personality formed by reciprocal interaction among behavioral, cognitive, and environmental factors
- learned behavior via classical/operant conditioning
- observational learning
- conscious cognitive processes
- situational influences/opportunities/rewards/punishments
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
Behavioral therapy + cognitive approach
helps client become more aware of irrational/dysfunctional thoughts & beliefs and substitute rational/accurate beliefs and thoughts, hopefully leading to more functional feelings and behaviors
[Social cognitive perspective]
Personality trait
predisposition toward a certain behavior
(Trait theory)
Trait Theory
focus on identifying, describing, measuring, and comparing individual differences and similarities with respect to traits
associated with Raymond Cattell
Raymond Cattell
identified 16 surface traits using factor analysis (Trait Theory)
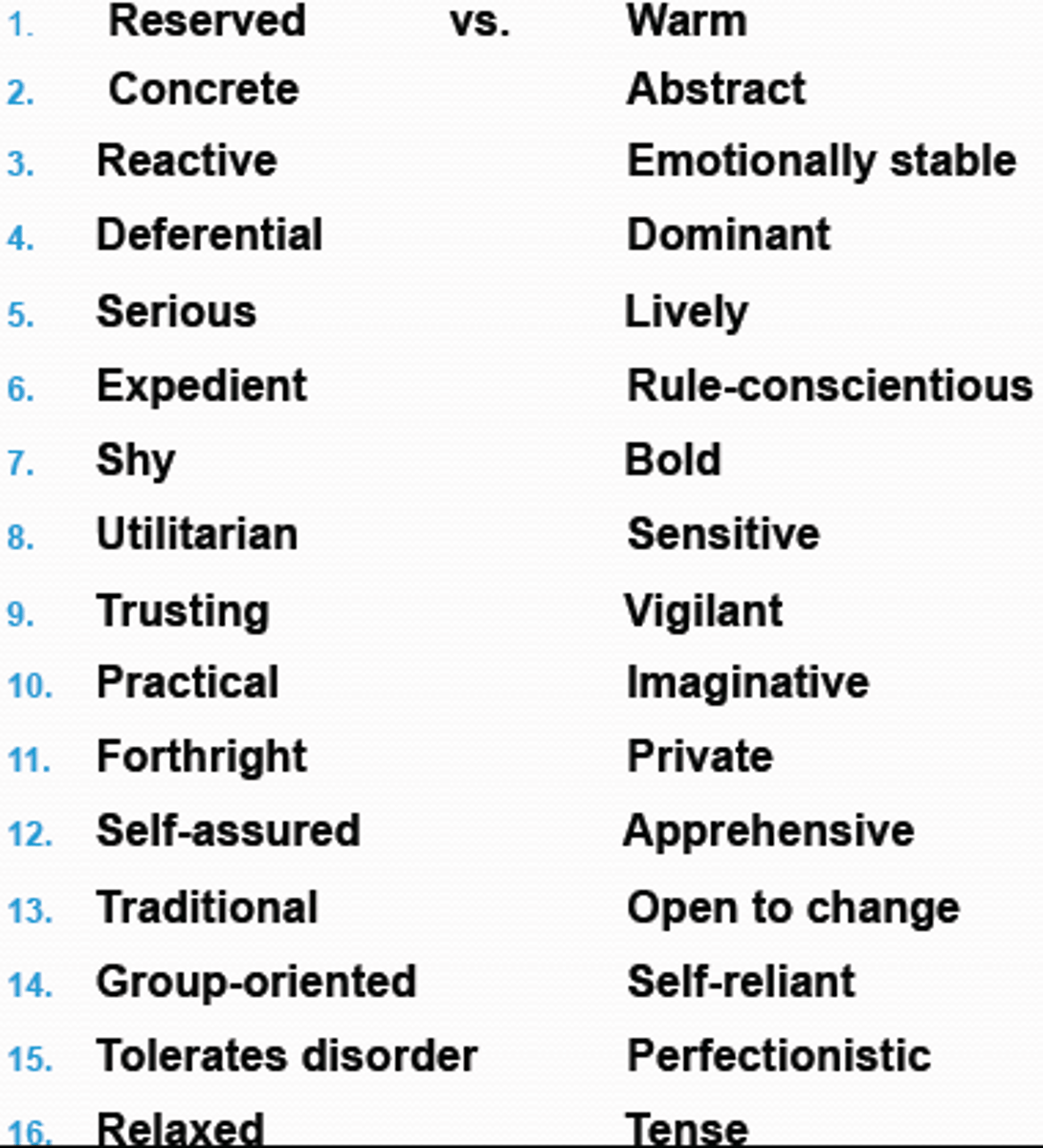
Surface traits & Source Traits
Surface traits evident from a person's behavior
i.e. "talkative"
Source Traits factors underlying human personality/behavior
i.e. "extrovert"
(Trait theory)
"Global factors" initially created to characterize personality traits
source traits
1. Extroversion
2. Anxiety
3. Receptivity
4. Accommodation
5. Self-control
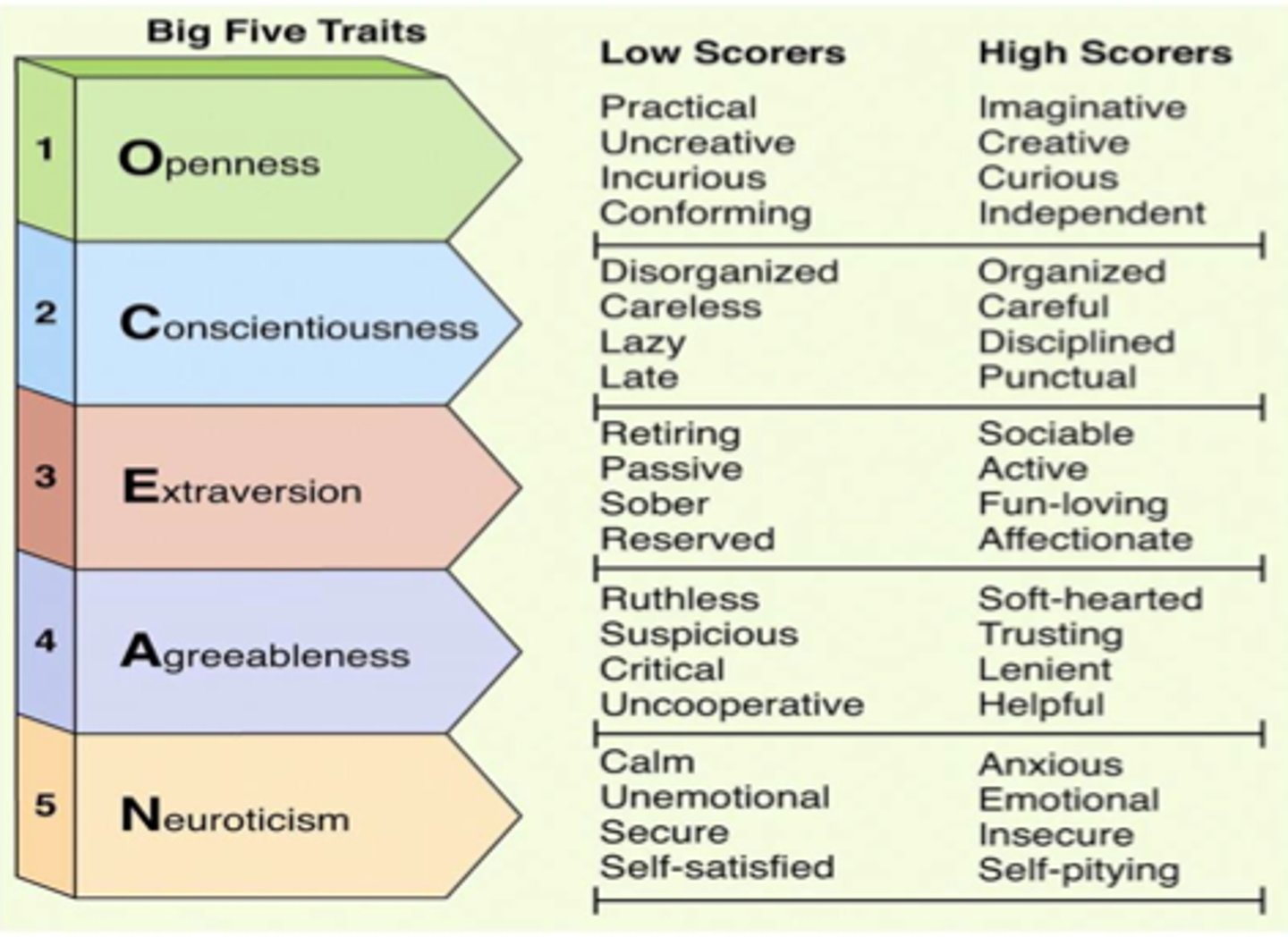
Five-Factor Model
(McCrae & Costa)
widely accepted model of global factors attributed to Trait theory
Biological perspective
much of personality is at least partly due to innate biological differences among people
supported by heritability of basic personality traits & correlations in brain structure
associated with Hans Eysenck, Jeffrey Alan Gray, and C. Robert Cloninger
Hans Eysenck
1. Extroversion based on individual differences in reticular formation (introverts more easily aroused & handle less stimulation)
2. Neuroticism based on individual differences in limbic system
(Biological perspective)
Jeffrey Alan Gray
personality governed by interactions among 3 brain systems responding to reward/punishment stimuli
1. Fear/avoidance linked to sympathetic nervous system
2. Worry/anxiety linked to behavioral inhibition system
3. Optimism/impulsivity linked to behavioral approach system
(Biological perspective)
C. Robert Cloninger
personality linked to level of brain neurotransmitter in 3 interacting systems
- low dopamine = higher impulsivity/novelty seeking
- low norepinephrine = higher approval seeking/reward dependence
(Biological perspective)
Person-situation controversy (trait vs. state controversy)
considers degree to which a person's reaction to situation is due to personality (trait) vs. situation (state)
[Situational Approach]
Traits vs. States
Trait: internal, stable, enduring personality aspects
State: situational (unstable, temporary) variable aspects of personality influenced by external environment
[Situational Approach]
Social cues
People modify behavior in uncomfortable situations based on nonverbal/verbal hints - specific traits may stay hidden
[Situational Approach]
Actualizing tendency
most basic motive of all people - innate drive to maintain & enhance the organism
[Humanistic perspective]
Self-actualization
realizing his or her human potential (as long as no obstacle intervenes)
[Humanistic perspective]
Carl Rogers
developed humanistic theory
- proposed that child introjects value of caregiver into his or her own self-concept to still see both self and caregiver as good
Self-Concept
conscious, subjective perceptions and believes about an individuals self
[Humanistic perspective]
Incongruence
Feeling experienced by people when they encounter experiences that are contradict their self-concepts
[Humanistic perspective]
Comparing the Roots of Psychopathology
Humanistic: discrepancy between conscious introjected values and unconscious true values
Social Cognitive: irrational/dysfunctional thoughts and beliefs
Trait: N/A - each personality type has strengths/weaknesses
Psychoanalytic: needs/tasks not met during psychosexual stages of development - also childhood events, unconscious feelings, thoughts, and motivations
Anxiety disorders (general definition)
characterized by excessive worry, uneasiness, apprehension and fear with both physical and psychological symptoms
Mood disorders (general definition)
characterized by a disturbance in mood or affect; 2 broad categories distinguished by the presence/absence of a manic or hypomanic episode
Prevalence of Psychological Disorders - (most to least)
(18%) Anxiety
(10%) Mood/dissociative
(6-10%) Personality
(1-6%) Eating
(.2-2%) Somatoform
(1%) Psychotic
Somatoform disorders (general definition)
symptoms not explained by medical conditions or substance abuse - not attributable to another mental disorder
Conversion disorder (general definition)
Emotional conflict/stressor causes physical symptoms severe enough to warrant medical attention
Dopamine hypothesis (Schizophrenia)
[Schizophrenia]
hyperactive dopaminergic pathway
- overabundance of dopamine
- hypersensitive dopamine receptors
Biological Basis of Schizophrenia (including positive/negative signs)
Genetic Predisposition + Environmental Trigger
Positive Signs:
1) Dopamine hypothesis
2) Hyperactivation of temporal lobes
Negative Signs:
1) Hypofunctioning frontal lobes
2) Smaller brains due to atrophy: increaseed ventricles, enalrged sulci and fissures
Biological Basis of Depression
Genetic Basis (increased risk)
1) Hypofunctioning of dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine pathways
2) Damage to areas of brain can be accompanied by neurological diseases
Alzheimer's Disease (general definition)
most prevalent form of dementia
- retrograde amnesia
- impaired visual memory (lost/confused)
cortical disease (affects cortex)
Biological Basis of Alzheimer's Disease
caused by formation of neuritic plaques (hard formations of beta-amyloid protein and neurofibrillary tangles)
Unclear why plaques form - thought to accumulate and reach "Critical mass" and cause neuronal connection death
some evidence of abnormalities in activity of acetylcholine in hippocampus
Biological Basis of Parkinson's Disease
movement disorder caused by death of dopamine-generating cells in basal ganglia and substantia nigra
Positive Symptoms of Psychosis
(something has been added)
- delusions
- hallucinations
- disorganized speech
- disorganized/catatonic behavior
Negative Symptoms of Psychosis
(something has been taken away)
- reduced/absent emotional expression (flat affect)
- reduced quantity/fluency of speech
- reduced initiative/willpower (avolition)
Schizophrenia (general definition)
chronic, incapacitating disorder in which a person is out of touch with reality (psychotic) and suffers occupational, social, or personal functioning
5 Types of Schizophrenia
1. Paranoid-type (hallucinations/delusions)
2. Catatonic-type (catatonic/strange behavior)
3. Disorganized-type (negative symptoms)
4. Undifferentiated-type (doesn't fit other subtype)
5. Residual-type (previously met criteria, now milder)
Schizoaffective disorder (general definition)
combo of mood/psychotic symptoms (i.e. schizophrenia + major depressive/manic/mixed episodes)
Schizophreniform disorder (general definition)
AKA pre-schizophrenia
displayed schizophrenia symptoms for 1-6 months, may or may not have interfered with person's functioning
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
individuals will seek to fulfill physiological needs before looking to fill higher-level needs
[Motivation]
![<p>individuals will seek to fulfill physiological needs before looking to fill higher-level needs</p><p>[Motivation]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a923a122-1b8a-4e43-9787-0e6f2161105a.jpg)
Principle of Aggregation
attitudes predict general overall behavior well, but don't always predict specific behaviors
Philip Zimbardo
discovered that role-playing has a powerful influence on attitudes & behaviors
Cognitive Dissonance Theory
suggests that individuals will attempt to reduce tension (dissonance) between beliefs that are incompatible
Drive-Reduction Theory
suggests that individuals engage in certain behavior in an attempt to alleviate physiological states of discomfort
[Motivation]
![<p>suggests that individuals engage in certain behavior in an attempt to alleviate physiological states of discomfort</p><p>[Motivation]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/46f7e7bb-fd8c-4e17-a622-d4302f363356.jpg)
3 Main Components of Attitude
ABC's
1) Affect (emotion)
2) Behavior tendencies
3) Cognition (thought)
3 Situations in which Behaviors are Likely to Influence Attitudes
1) Role-playing
2) Public declarations
3) Justification of Effort
Justification of effort
modification of attitude to match their behaviors
foot-in-the-door phenomenon
enticing people to take small actions (i.e. join mailing list) at first, then later further encourage raised stakes (i.e. attaining bumper stickers)
Instincts
behaviors that are unlearned and present in fixed patterns throughout a species
[Motivation]
Drive
urge originating from physiological discomfort (i.e. hunger, sleepiness, thirst)
[Motivation]
Incentive Theory
[Motivation]
external stimuli, objects, and events in the environment that help induce/discourage certain behaviors
- can be positive or negative
- behaviors most strongly motivated when there are physiological needs, strong positive incentives, and a lack of negative incentives
Attitude
person's feelings and beliefs about other people or events around them and their tendency to react behaviorally based on those underlying evaluations
Medulla
Involuntary functions
(BP, HR, RR, reflexes)
Brainstem Components
Medulla
Pons
Midbrain
Hindbrain Components
Medulla
Pons
Cerebellum
Pons (function)
Relay station & balance/posture
Cerebellum (function)
movement coordination/spatial equilibrium
Midbrain (function)
eye movement
Thalamus (function)
Integrating center/relay station for somatic (conscious) sensation
Hypothalamus (function)
homeostatic functions/regulation
primitive emotions/behavior
Basal nuclei (function)
movement/coordination of learned patterns
Limbic system (function)
Emotion, memory, & learning
*memory storage/retrieval
*conscious/unconscious linkage
Cerebral Cortex (4 lobes) (function)
Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, Occipital
Frontal Lobe (function)
voluntary movement
complex reasoning/thinking
Parietal Lobes (function)
general sensations & gustation (taste)
Temporal Lobes (function)
Auditory/olfactory sensation
Short-term memory/language/emotion
Occipital Lobe (function)
Vision
Corpus callous (function)
connects L/R cerebral hemispheres
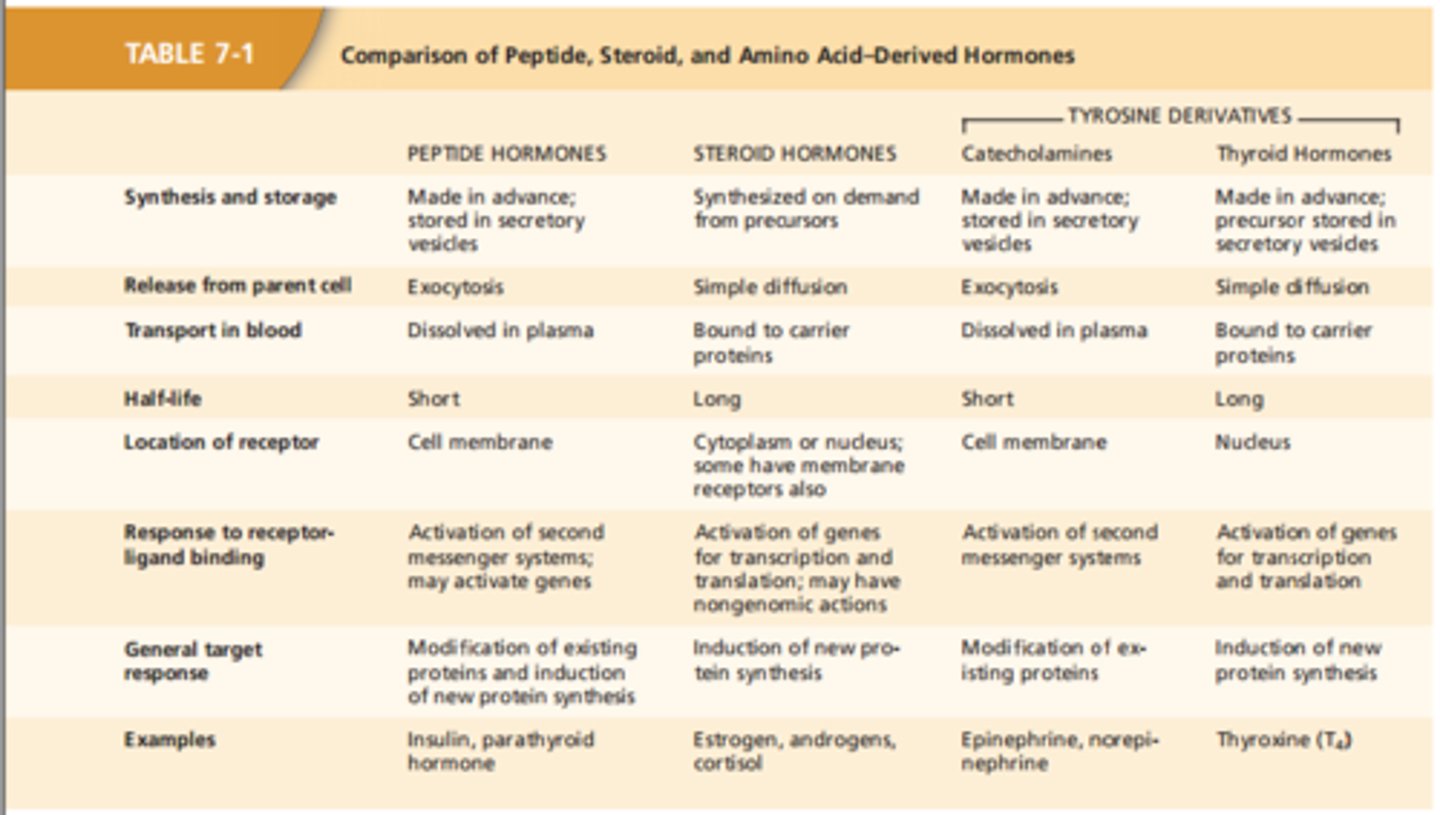
Peptide vs. Steroid Hormones
Diencephalon
(component of forebrain) - includes thalamus + hypothalamus
Forebrain components (2)
diancephalon
telencephalon
3 Major Changes to the Brain during Adolescence
1. Cell Proliferation (prefrontal lobes/limbic system)
2. Synaptic Pruning (unused/unneeded connections)
3. Myelination (strengthens connections)
*Limbic system develops very rapidly - explains emotional tendencies
Motor Development

Proponents of the Biological Perspective of Personality
Hans Eysenck
Raymond Catell
Biological Perspective of Personality: Strengths/Weaknesses
Strengths uses quantifiable scientific data and methodology; deterministic in its ability to establish causal relationships (used to treat disorders)
Limitations disregards social/environmental influences
Proponents of the Trait Perspective of Personality
Gordon Allport
Raymond Cattell
Hans Eysenck
5-Factor Model of Personality (5 Factors)
(OCEAN)
Openness to experience
Conscientousness
Extraversion
Agreeableness
Neuroticism
Criticisms of the 5 Factor Model of Personality
Biomedical vs Biopsychosocial Approach to Understanding Psychological Disorders
Biopsychosocial approach attempts to find underlying psychological/social conditions that may be contributing to the manifestation of disease
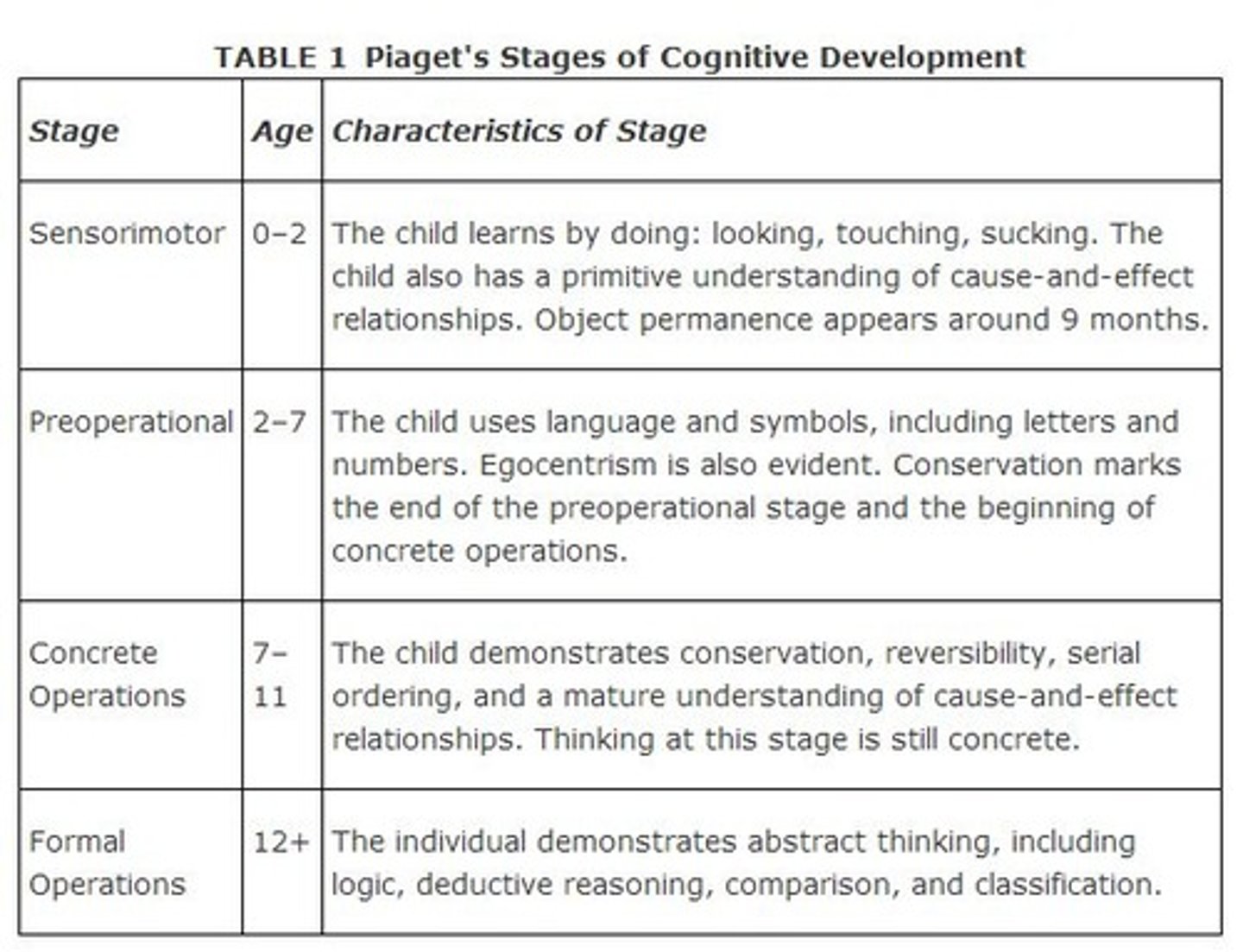
Piaget's Stages of Cognitive Development
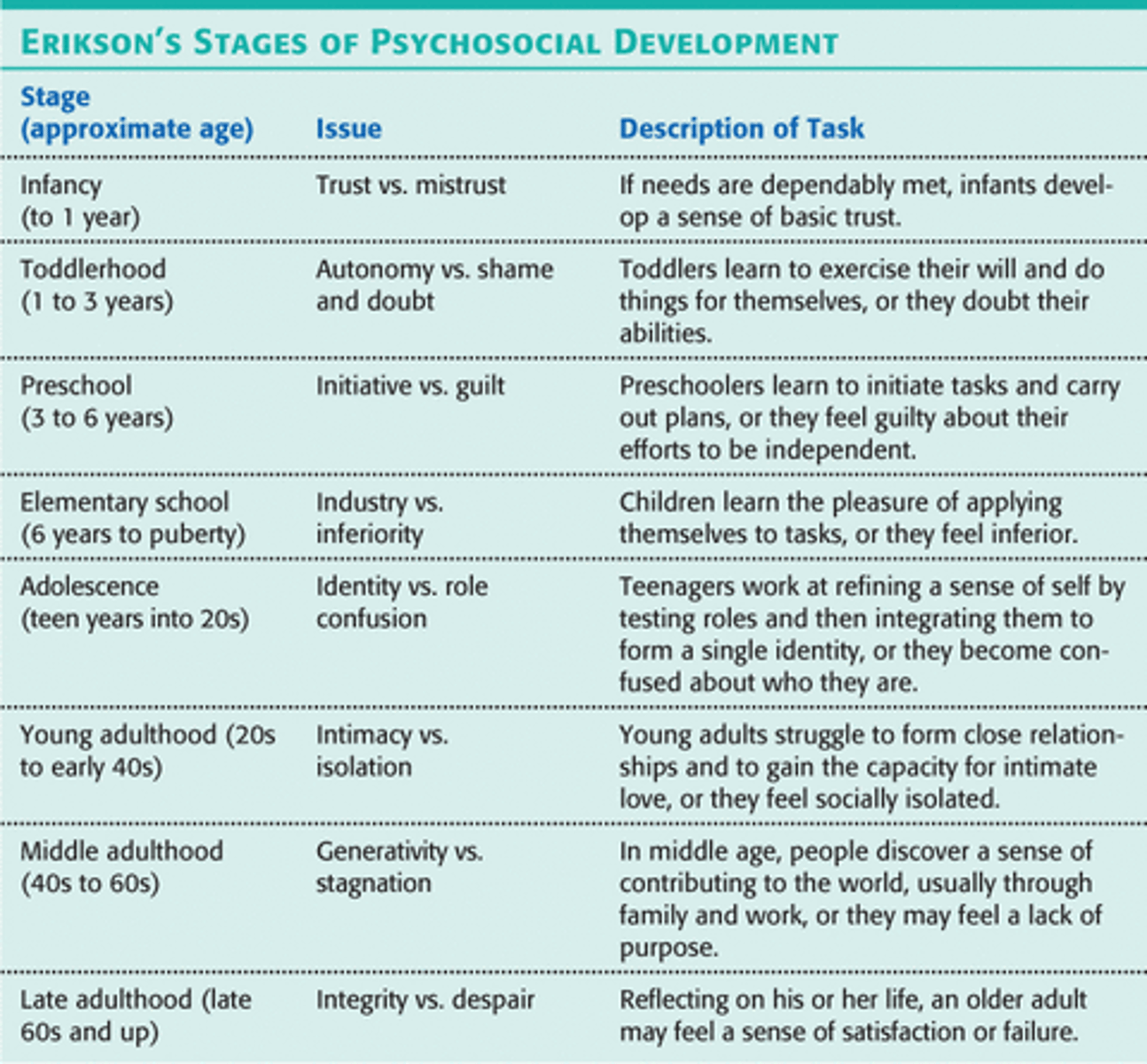
Erikson's Stages of Psychosocial Development
modification of Freud's psychosexual theory that revolves around the resolution of 2 conflicting ideas at each of the 8 stages
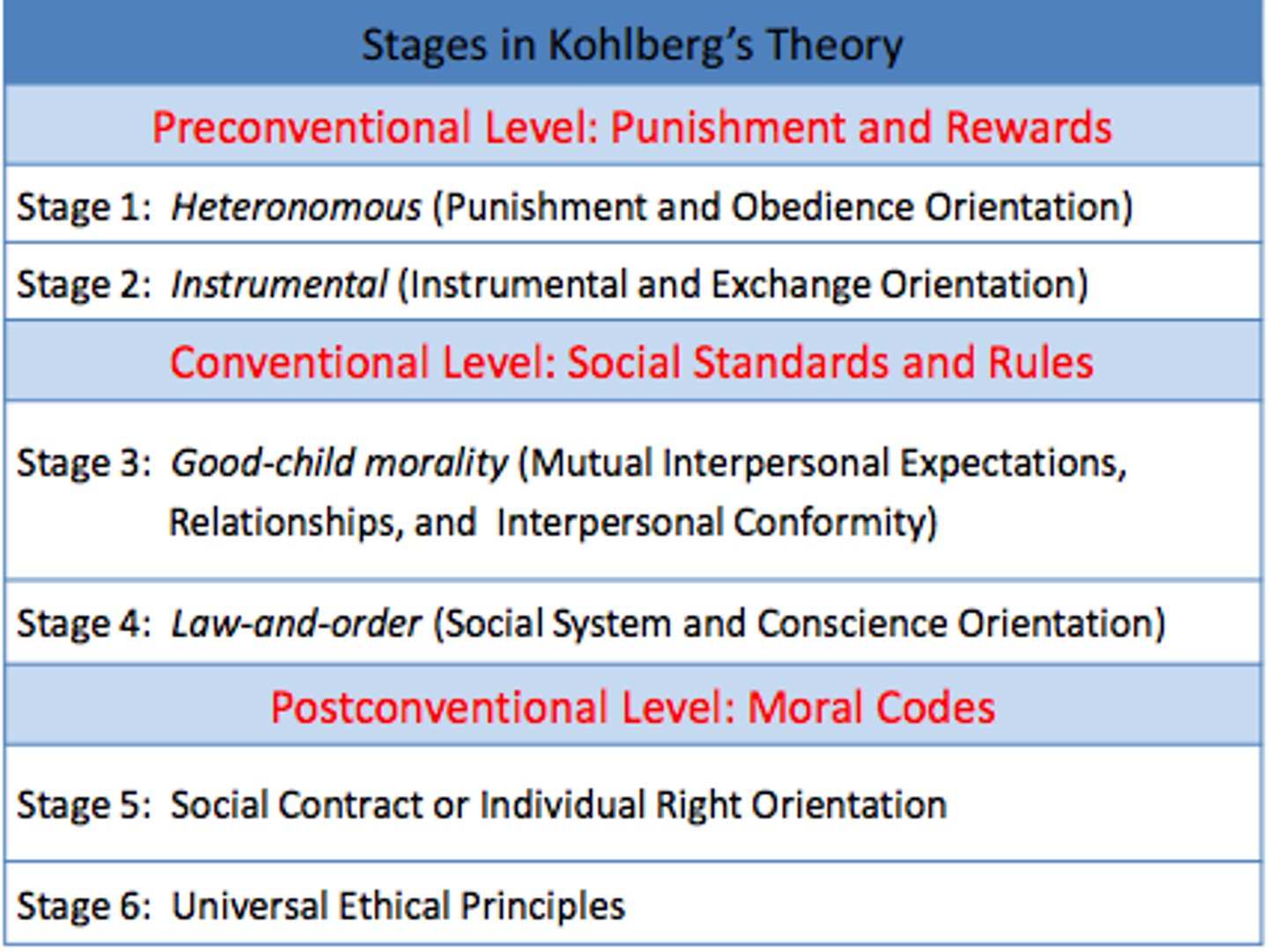
Kohlberg's Theory of Moral Development
Behavioral Genetics: Heritability Estimates
in specific subgroups of individuals in a population, heritability estimates try to identify the amount of variance that can be attributed to genes
(population-specific)
highest in uniform environments, where genes play a larger role
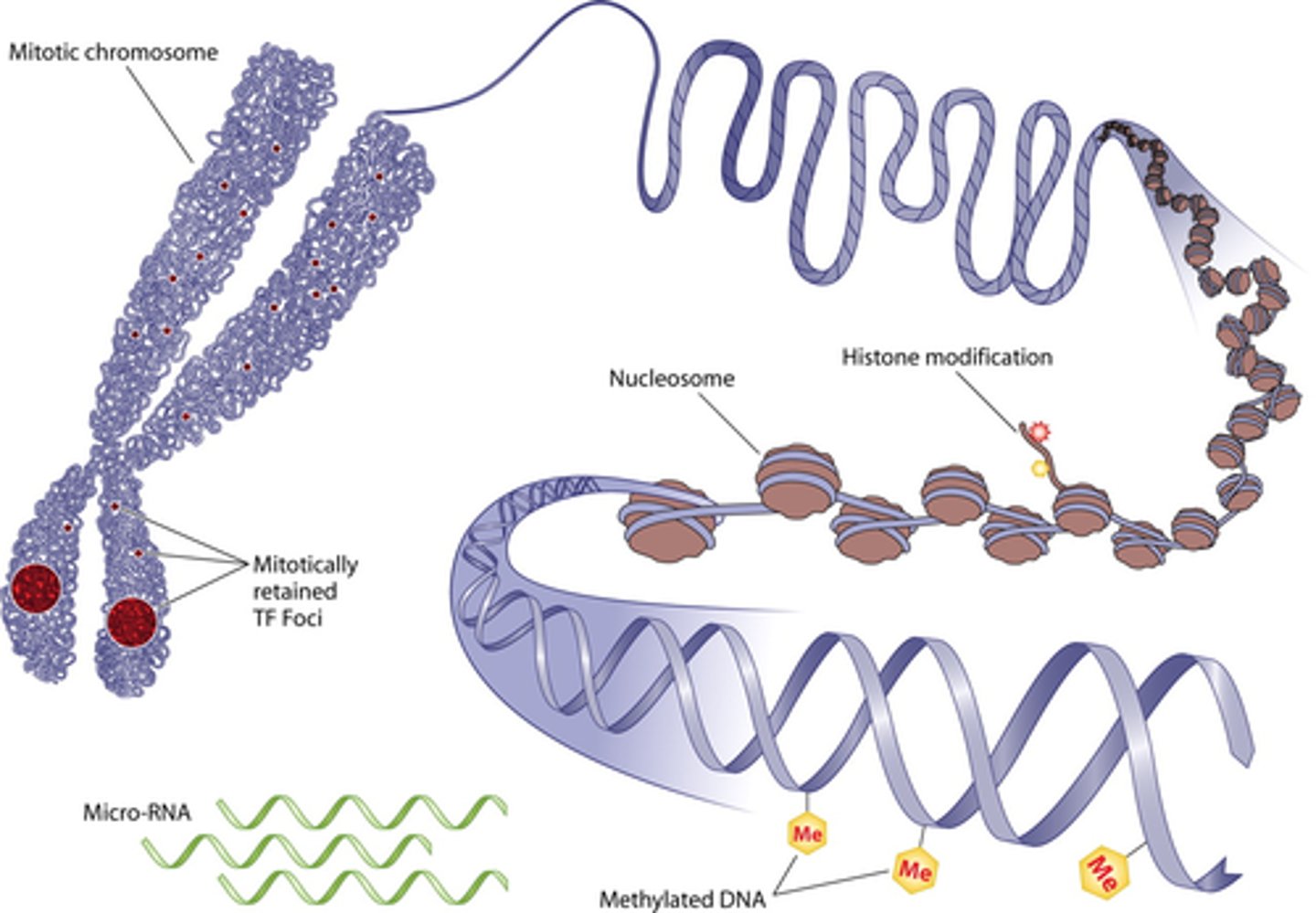
Epigenetics
the study of gene expression that deals with manipulations in components OTHER THAN DNA
i.e. methylation
Covert Behavior
behavior that is not observed